Overview of the Digital I/O, Ignition, and CAN Bus Connectivity
The connector has four GPIO connections, one Return connection, and one Ignition connection. The Digital I/O supports both Dry and Wet contacts up to 60 V.
-
Dry contact is isolated from a voltage source (or no volt), with an embedded relay function (NPN transistor), usually used to indicate an event, for example, open/close, alarm.
-
Wet contact is a contact with external power (+3.3V to +60V, and a maximum 150mA of current allowed at high voltage) applied, and is usually used to energize something, for example, solenoid, light.
-
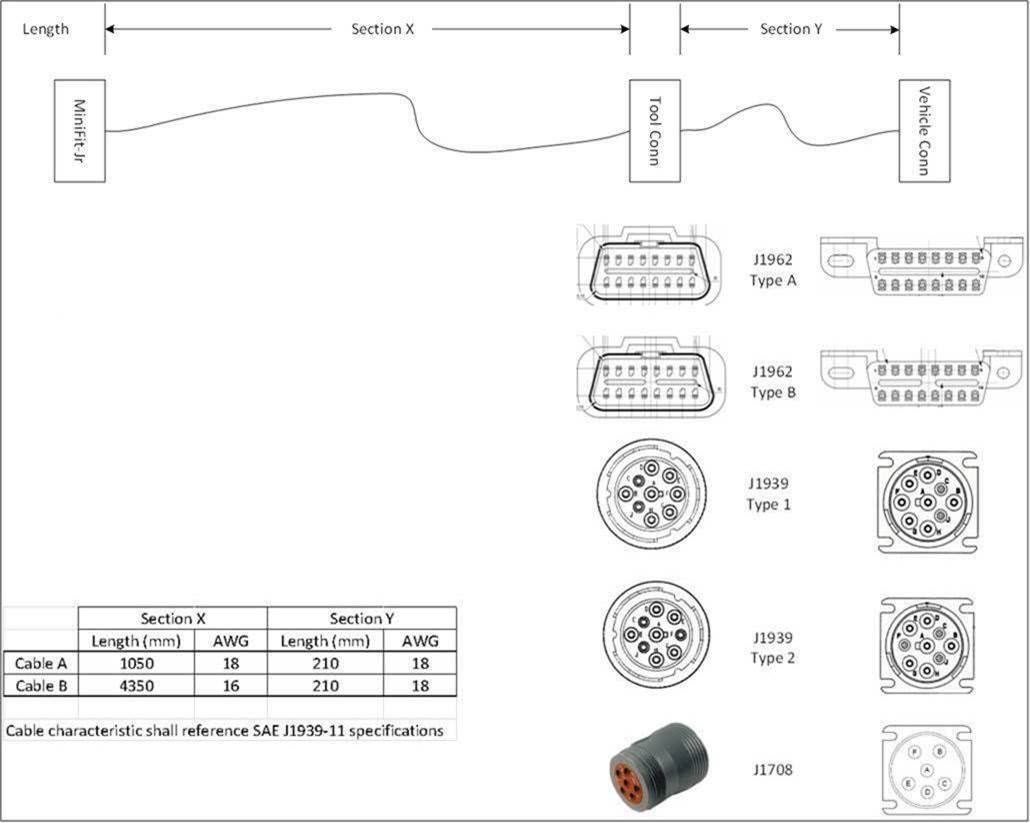
Connectivity for the CAN Bus is through two wires on the power connector that connects to the OBD-II connector of the vehicle.


 Feedback
Feedback