Overview
This section provides an overview of the Cisco Wi-Fi Interface Module (WIM). The PID is WP-WIFI6-x where x signifies the regulatory domain.
Highlights of the WIM are:
-
Pluggable 802.11ax module for Cisco Catalyst IR1800 series
-
WiFi-6 (802.11ax), 2x2 MIMO with 2 spatial streams
-
Extended Temperature Range
-
Field Replaceable Unit (FRU), however does not support OIR (Online Insertion and Removal)
-
Versatile RF coverage with external RP-SMA antenna connectors
-
Flexible Antenna Port feature support
-
Based on the Cisco AP 9105AXI
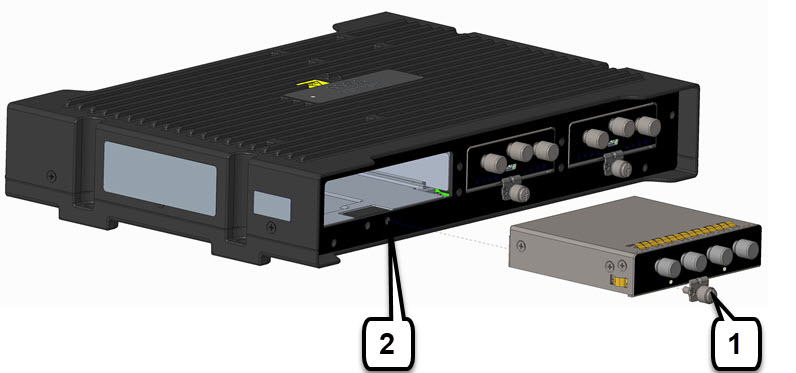
The following graphic shows the front panel of the WIM.

|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Disabled when the flexible antenna ports are set to dual-band mode (Default). 2.4 GHz when the flexible antenna ports are set to single-band mode. |
|
2 |
Disabled when the flexible antenna ports are set to dual-band mode (Default). 2.4 GHz when the flexible antenna ports are set to single-band mode. |
|
3 |
2.4/5 GHz when the flexible antenna ports are set to dual-band mode (Default). 5 GHz only when the flexible antenna ports are set to single-band mode. |
|
4 |
2.4/5 GHz when the flexible antenna ports are set to dual-band mode (Default). 5 GHz only when the flexible antenna ports are set to single-band mode. |
|
5 |
Enable LED |
|
6 |
Wi-Fi LED |
The following table describes the Enable LED:
|
LED Status |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Off |
No Power |
|
Yellow |
Power is on, module is not yet functional |
|
Green |
Module is fully functional |
The following table describes the Wi-Fi LED:
 Note |
LED status information is not applicable to concurrent radio mode. Concurrent radio Root AP + wireless client displays the default LED behavior — Alternate blinking red/green. |
|
LED Status |
Status Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Solid Green |
Association Status |
Normal operating condition, but no wireless client associated. |
|
Solid Blue |
Association Status |
|
|
Solid Green |
Boot Loader Status |
Executing Boot Loader |
|
Flashing Green |
Boot Loader Status |
Boot Loader Error, signing verification error. |
|
Flashing Blue |
Operating Status |
Software upgrade in progress. |
|
Alternate between Green and Red |
Operating Status |
Discovery/Join process is in progress. |
|
Cycle through Red-Off-Green-Off-Blue-Off |
Access Point operating system error |
General warning; insufficient inline power. |

 Feedback
Feedback