Section is a logical grouping of report contents. It’s up to the user to create these sections and add information to be displayed.
Section can be added as shown:
section = report.add_section (“Section title”,_id)
Adding Content to a Section
Key and values
You can add simple key and value pair to section as shown below:
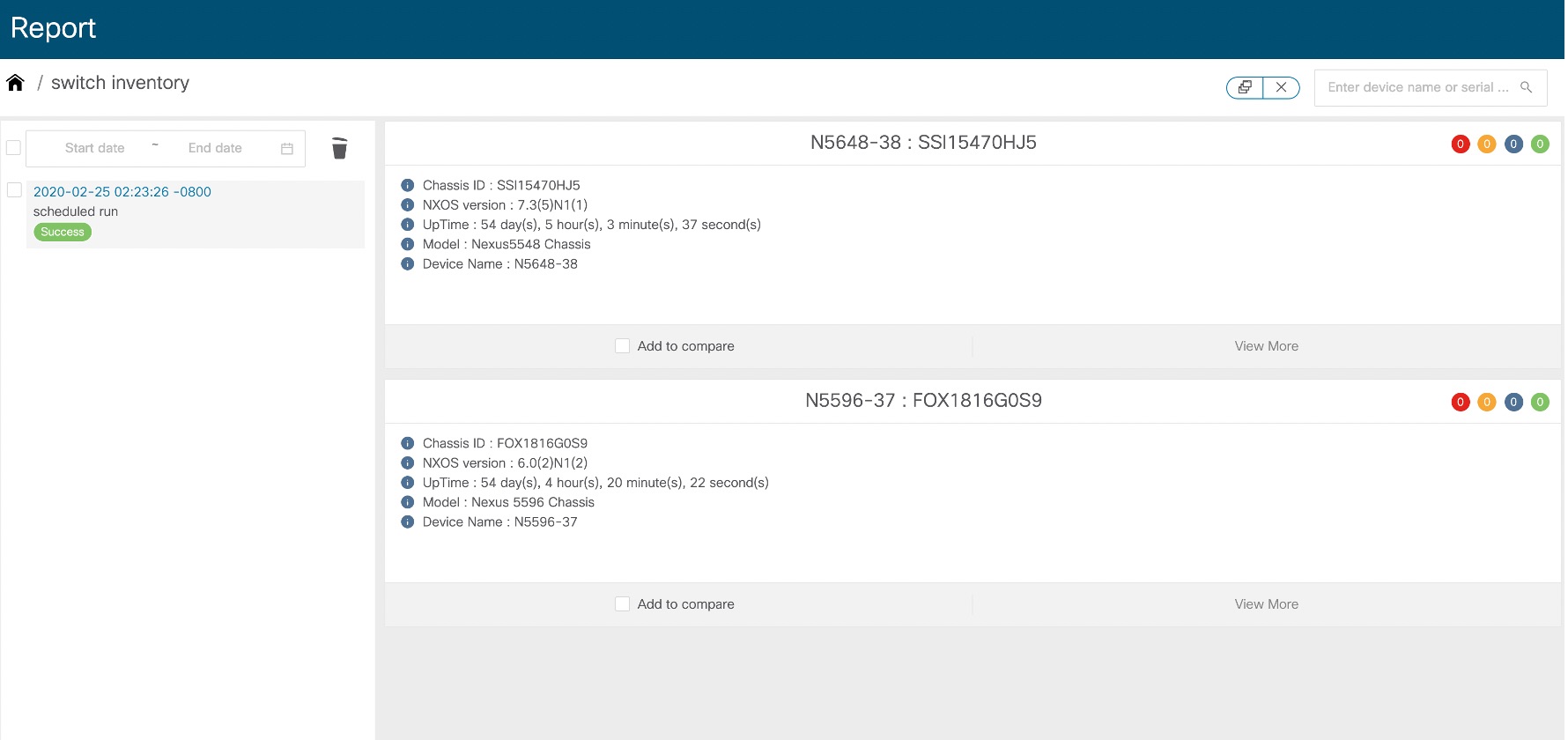
A JSON document – Cards
A single JSON document can be added as same as any key value pair. Nested JSON is not supported in 11.4(1)
section[‘key’] = {‘key’:’value’,’key-2’:’value’}
The JSON document is displayed in a card widget as shown:

Array of JSON Documents – Tables
The section.append API allows user to create a table and add rows to it with following restriction:
-
All JSON document should have same set of keys
-
Nested JSON is not supported
section.append(key, dictionary, _id)
_id: Unique identifier which uniquely identifies a row in a table. Duplicate _id resultx in Unique id violation error.
For example:
section.append('Switch Details', {'name': 'N5K'},'DSDAS244455')
section.append('Switch Details', {'name': 'N6K'}, 'CSDAS244456')
section.append('Switch Details', {'name': 'N7K'}, 'ASDAS244457')






 Feedback
Feedback