Overview
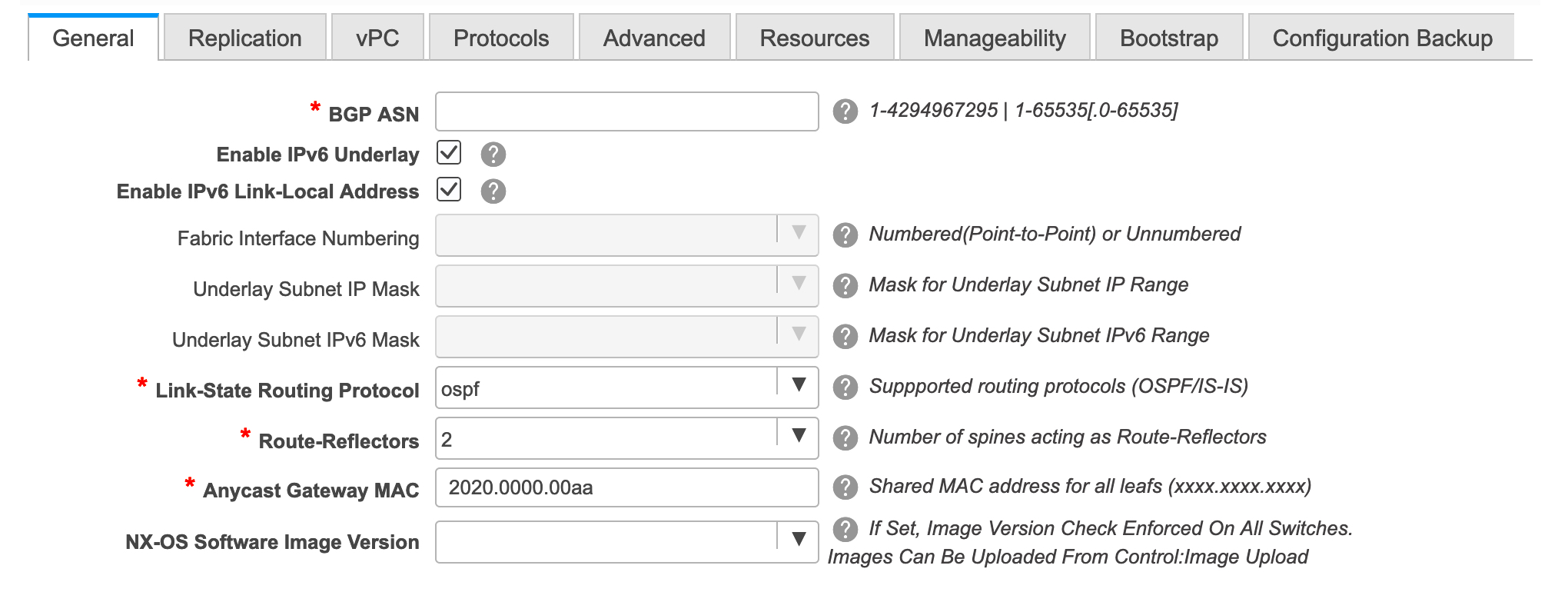
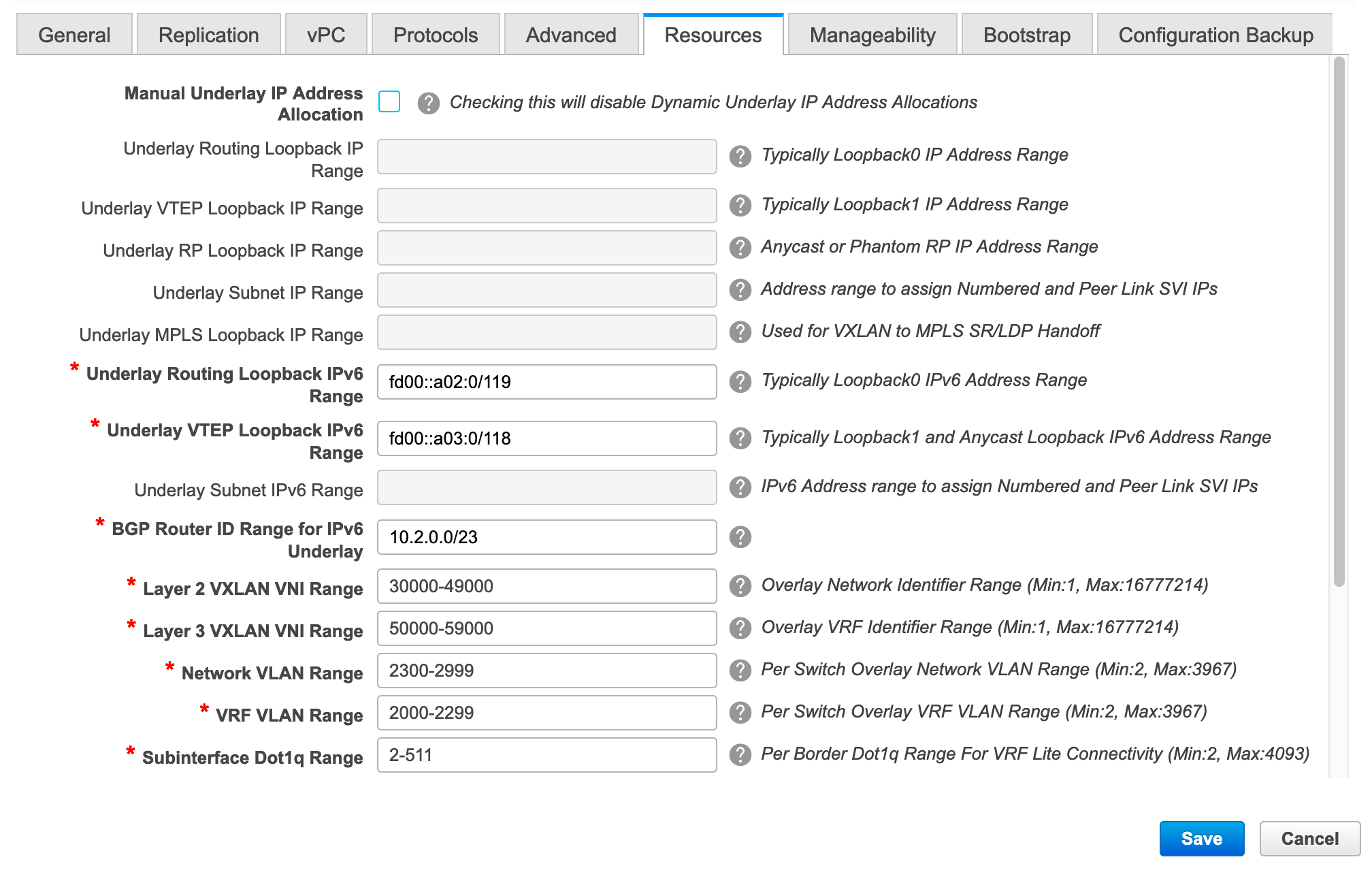
From Cisco DCNM Release 11.3(1), you can create an Easy fabric with IPv6 only underlay. The IPv6 underlay is supported only for the Easy_Fabric_11_1 template. In the IPv6 underlay fabric, intra-fabric links, routing loopback, vPC peer link SVI, and NVE loopback interface for VTEP are configured with IPv6 addresses. EVPN BGP neighbor peering is also established using IPv6 addressing.
The following guidelines are applicable for IPv6 underlay:
-
IPv6 underlay is supported for the Cisco Nexus 9000 Series switches with Cisco NX-OS Release 9.3(1) or higher.
-
VXLANv6 is only supported Cisco Nexus 9332C, Cisco Nexus C9364C, and Cisco Nexus modules that end with EX, FX, FX2, FX3, or FXP.

Note
VXLANv6 is defined as a VXLAN fabric with IPv6 underlay.
-
In VXLANv6, the platforms supported on spine are all Nexus 9000 Series and Nexus 3000 Series platforms.
-
The overlay routing protocol supported for the IPv6 fabric is BGP EVPN.
-
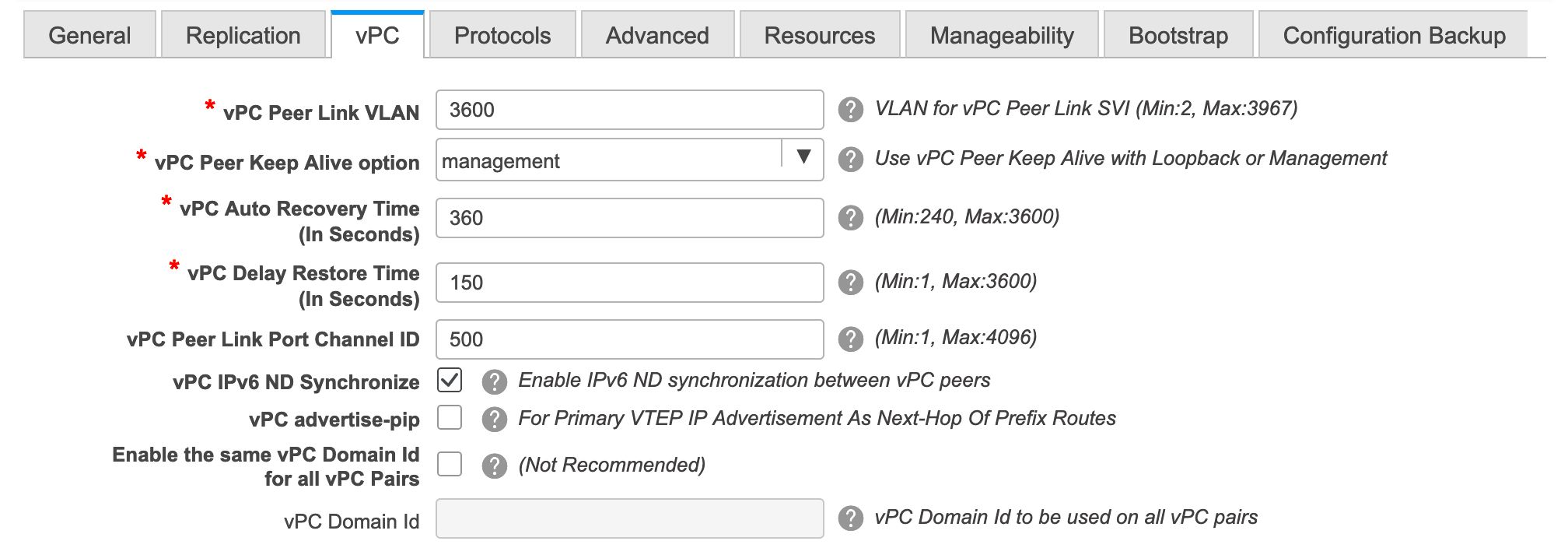
vPC with physical multichassis EtherChannel trunk (MCT) feature is supported for the IPv6 underlay network in DCNM. The vPC peer keep-alive can be loopback or management with IPv4 or IPv6 address.
-
Brownfield migration is supported for the VXLANv6 fabrics. Note that L3 vPC keep-alive using IPv6 address is not supported for brownfield migration. This vPC configuration is deleted after the migration. However, L3 vPC keep-alive using IPv4 address is supported.
-
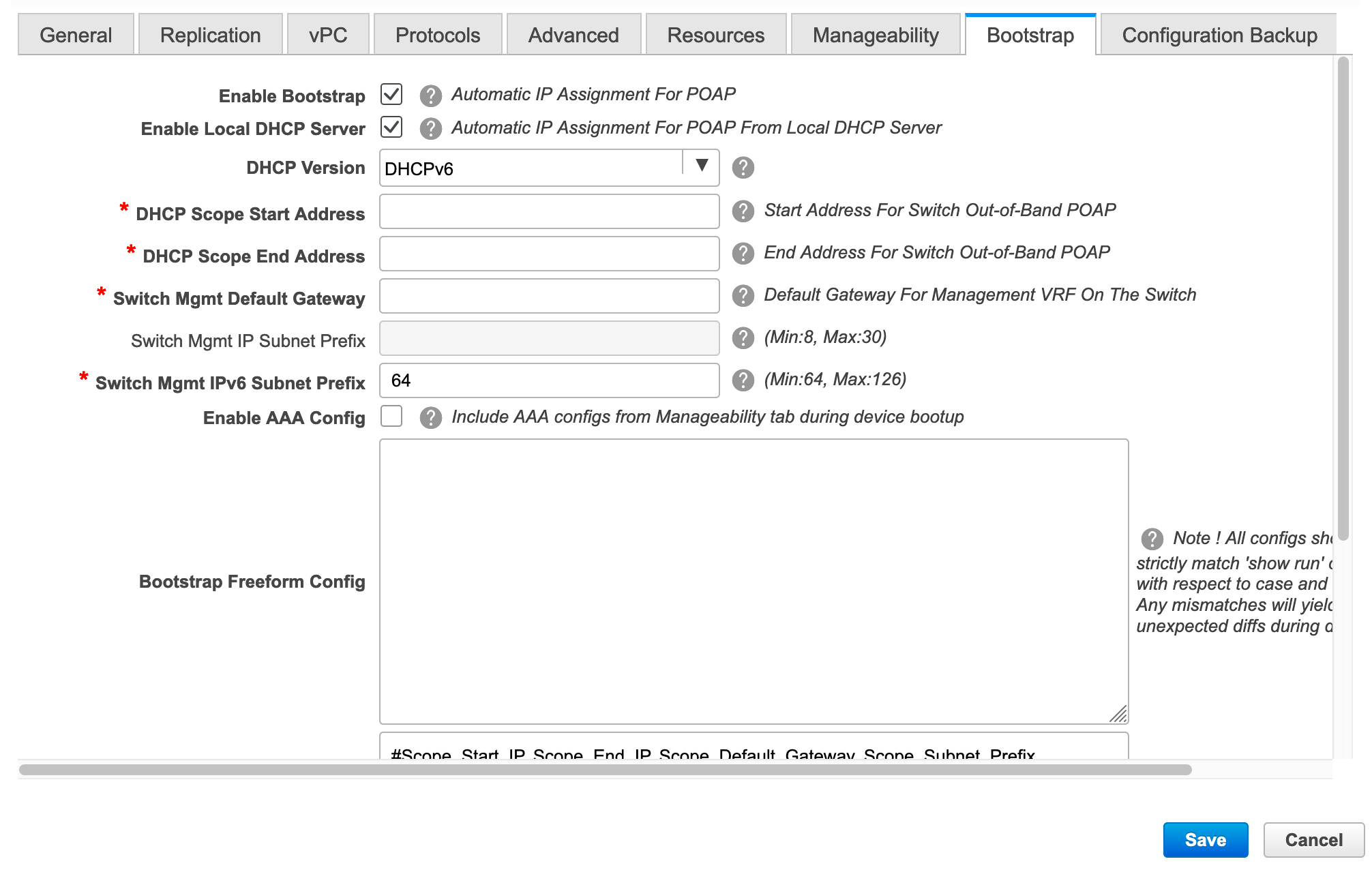
DHCPv6 is supported for the IPv6 underlay network.
-
The following features are not supported for VXLAN IPv6 underlay:
-
Multicast underlay
-
Tenant Routed Multicast (TRM)
-
ISIS, OSPF, and BGP authentication
-
VXLAN Multi-Site
-
Dual stack underlay
-
vPC Fabric Peering
-
DCI SR-MPLS or MPLS-LDP handoff
-
BFD
-
Super Spine switch roles
-
NGOAM
-

 Feedback
Feedback