Prerequisites and Guidelines
Prerequisites
-
The VRF Lite feature requires Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS Release 7.0(3)I6(2) or later.
-
Familiarity with VXLAN BGP EVPN data center fabric architecture and top-down based LAN fabric provisioning through the DCNM.
-
Fully configured VXLAN BGP EVPN fabrics including underlay and overlay configurations on the various leaf and spine devices, external fabric configuration through DCNM, and relevant external fabric device configuration (edge routers, for example).
-
A VXLAN BGP EVPN fabric (and its connectivity to an external Layer 3 domain for north-south traffic flow) can be configured manually or using DCNM. This document explains the process to connect the fabric to an edge router (outside the fabric, towards the external fabric) through DCNM. So, you should know how to configure and deploy VXLAN BGP EVPN and external fabrics through DCNM. For more details, see the Control chapter in the Cisco DCNM LAN Fabric Configuration Guide, Release 11.2(1).
-
-
Ensure that the role of the designated border device is Border, Border Spine, Border Gateway, or Border Gateway Spine (a switch on which Multi-Site and VRF Lite functions co-exist). To verify, right-click the switch and click Set role. You can see that (current) is added to the current role of the switch. If the role is inappropriate for a border device, set the appropriate role.
-
Create an external fabric. If you connect the VLXAN fabric border device to a Nexus 7000 Series switch (or other Nexus device) for external connectivity, add the Nexus 7000 series switch to the external fabric and set its role to Edge Router. In DCNM, you can import switches to an external fabric, and update selected configurations. For details, refer the Creating an External Fabric section in the Control chapter.
-
To allow inter-subnet communication between end hosts in different VXLAN fabrics, where the subnets are present in both fabrics, you must disable the Advertise Default Route feature for the associated VRF. This will result in /32 routes for hosts being seen in both fabrics. For example, Host1 (VNI 30000, VRF 50001) in Fabric1 can send traffic to Host2 (VNI 30001, VRF 50001) in Fabric2 only if the host route is present in both fabrics. When a subnet is present in only one fabric, then default route is sufficient for inter-subnet communication. Steps:
-
Go to the fabric’s VRFs screen and select the VRF.
-
Click the Edit option at the top left part of the screen.
-
In the Edit VRF screen, click Advanced in the VRF Profile section.
-
Clear the Advertise Default Route checkbox and click Save.
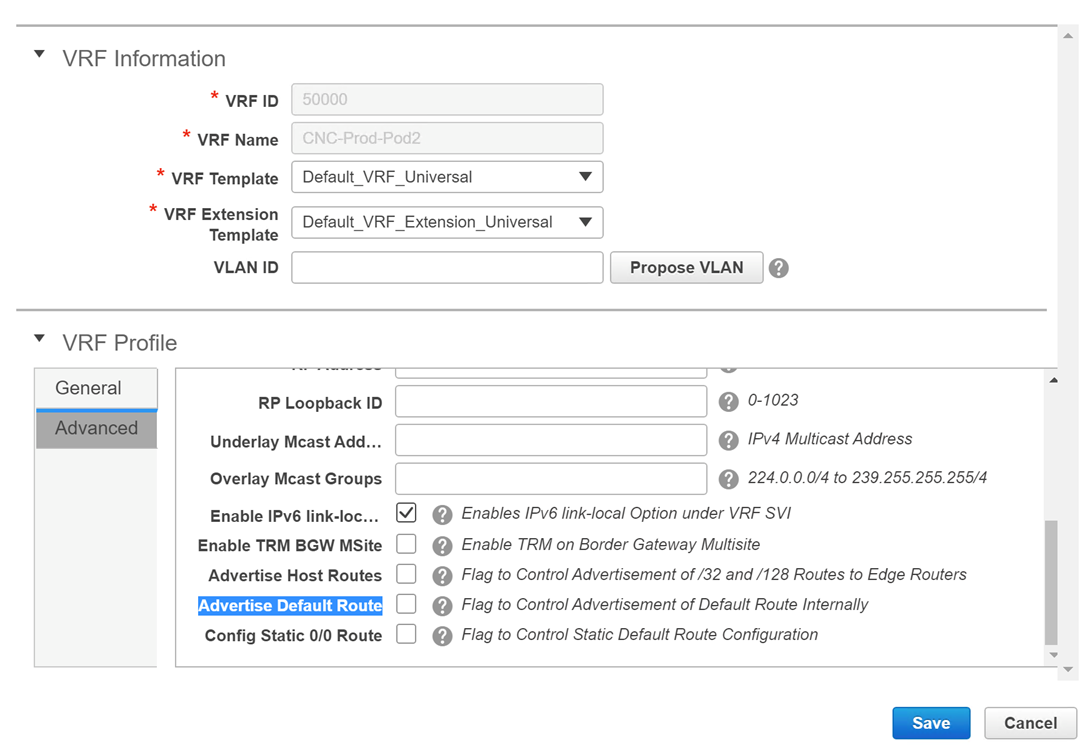
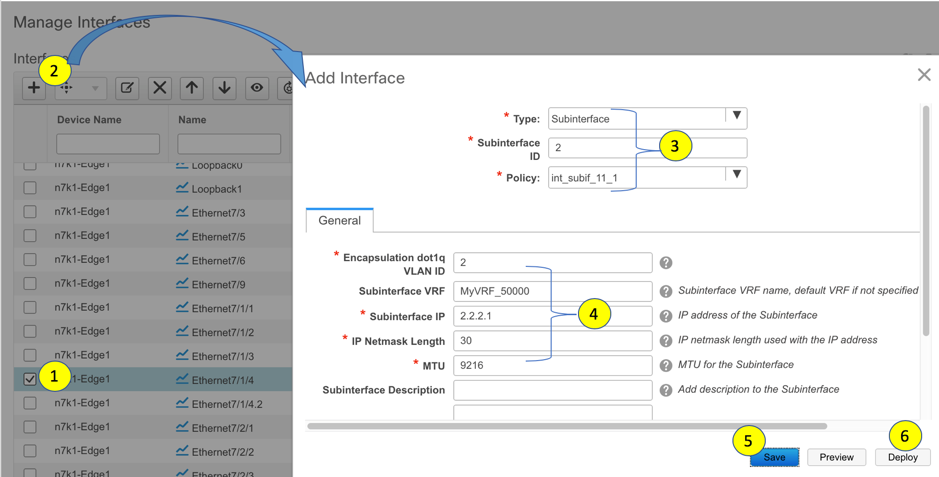
The following options apply only when VRF Lite connectivity is enabled on the border devices. By default, following Cisco best practices, DCNM uses eBGP over sub-interfaces for VRF Lite, Option-A peering. In other words, for each VRF Lite Inter-fabric connection (IFC), there is a per VRF per peer eBGP peering session established over IPv4/IPv6 respectively from the border device to the edge/WAN router. As applicable to this VRF Lite peering, there are 3 fields:
-
Advertise Host Routes – By default, over the VRF Lite peering session, only non-host (/32 or /128) prefixes are advertised. But if host routes (/32 or /128) need to be enabled and advertised from the border device to the edge/WAN router, then the “Advertise Host Routes” check box can be enabled. Route-map does outbound filtering. By default, this check box is disabled.
-
Advertise Default Route – This field controls whether a network statement 0/0 will be enabled under the vrf. This in turn will advertise a 0/0 route in BGP. By default, this field is enabled. When the check box is enabled, this will ensure that a 0/0 route is advertised inside the fabric over EVPN Route-type 5 to the leafs thereby providing a default route out of the leafs toward the border devices.
-
Config Static 0/0 Route –The field controls whether a static 0/0 route to the edge/WAN router, should be configured under the VRF, on the border device. By default, this field is enabled. If WAN/edge routers are advertising a default route over the VRF Lite peering, to the border device in the fabric, then this field should be disabled. In addition, the “Advertise Default Route” field should also be disabled. This is because the 0/0 route advertised over eBGP will be sent over EVPN to the leafs without the need for any additional configuration. The clean iBGP EVPN separation inside the fabric with eBGP for external out-of-fabric peering, provides for this desired behavior.
Note that all of the options listed are per fabric fields. Hence, in Multi-Site deployments with MSD, these fields can be controlled at a per member fabric level.
-
-
Follow this procedure for all VRFs deployed on the VXLAN fabrics’ border devices connected through VRF Lite.

Note
If you create a new VRF, ensure that you clear the Advertise Default Route checkbox.
-
 Note |
For an explanation on the VRF Lite feature, see the Cisco Programmable Fabric with VXLAN BGP EVPN Configuration Guide document. |
Guideline
In a DCNM Release 10.4(2) setup where VRF-Lite IFCs are created, the required default prefix-lists or route-maps configs are added on the switch. When this DCNM Release 10.4(2) setup is upgraded to any of the DCNM 11.x releases, VRF-Lite related RPM configs might be saved as part of the switch_freeform policy.
The following route-map config is part of this switch_freeform:
route-map EXTCON-RMAP-FILTER-V6 deny 20
match ip address prefix-list host-route-v6When this setup is upgraded from DCNM Release 11.x to 11.3(1), the route-map config is corrected with the following config:
route-map EXTCON-RMAP-FILTER-V6 deny 20
match ipv6 address prefix-list host-route-v6Since RPM configs are saved in DCNM 11.x as switch_freeform, you need to manually delete the ip prefix-list match config in the switch_freeformpolicy so that ipv6 match config is successful on the switch.

























 Feedback
Feedback