Rate-based attacks are attacks that depend on frequency of
connection or repeated attempts to perpetrate the attack. You can use
rate-based detection criteria to detect a rate-based attack as it occurs and
respond to it when it happens, then return to normal detection settings after
it stops.
You can configure your network analysis policy to include
rate-based filters that detect excessive activity directed at hosts on your
network. You can use this feature on managed devices deployed in inline mode to
block rate-based attacks for a specified time, then revert to only generating
events and not drop traffic.
The SYN attack prevention option helps you protect your network
hosts against SYN floods. You can protect individual hosts or whole networks
based on the number of packets seen over a period of time. If your device is
deployed passively, you can generate events. If your device is placed inline,
you can also drop the malicious packets. After the timeout period elapses, if
the rate condition has stopped, the event generation and packet dropping stops.
For example, you could configure a setting to allow a maximum number of SYN packets from any one IP address, and block further
connections from that IP address for 60 seconds.
You can also limit TCP/IP connections to or from hosts on your
network to prevent denial of service (DoS) attacks or excessive activity by
users. When the system detects the configured number of successful connections
to or from a specified IP address or range of addresses, it generates events on
additional connections. The rate-based event generation continues until the
timeout period elapses without the rate condition occurring. In an inline
deployment you can choose to drop packets until the rate condition times out.
For example, you could configure a setting to allow a maximum of
10 successful simultaneous connections from any one IP address, and block
further connections from that IP address for 60 seconds.

Note
|
Devices load-balance inspection across internal resources. When you configure rate-based attack prevention, you configure
the triggering rate per resource, not per device. If rate-based attack prevention is not working as expected, you may need
to lower the triggering rate. It triggers alert, if users send too many connection attempts within prescribed time intervals.
Hence it is recommended to rate limit the rule. For help determining the correct rate, contact Support.
|
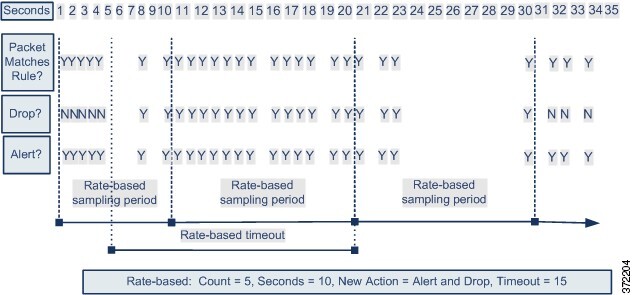
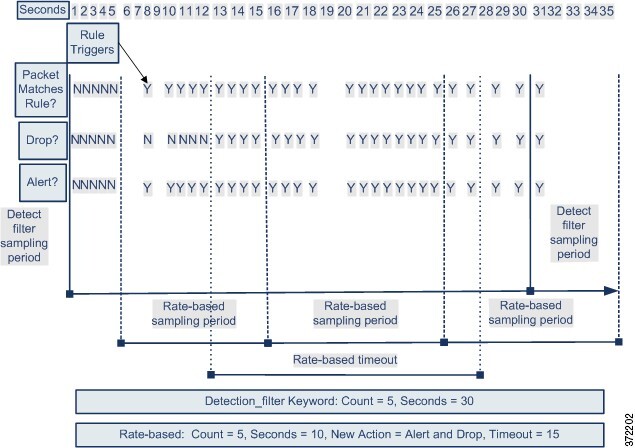
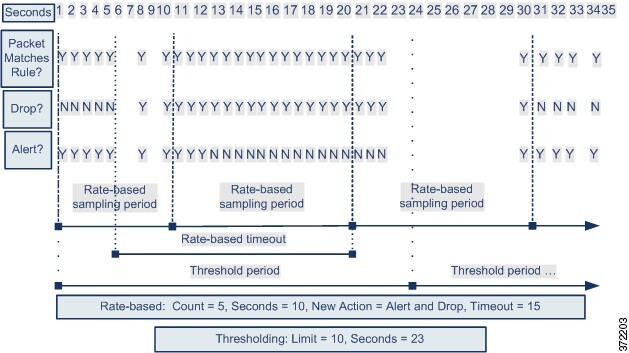
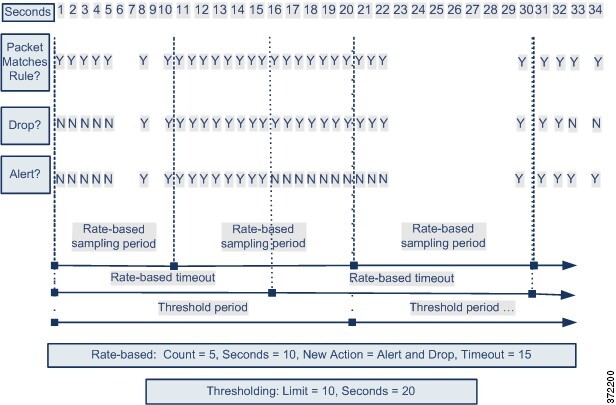
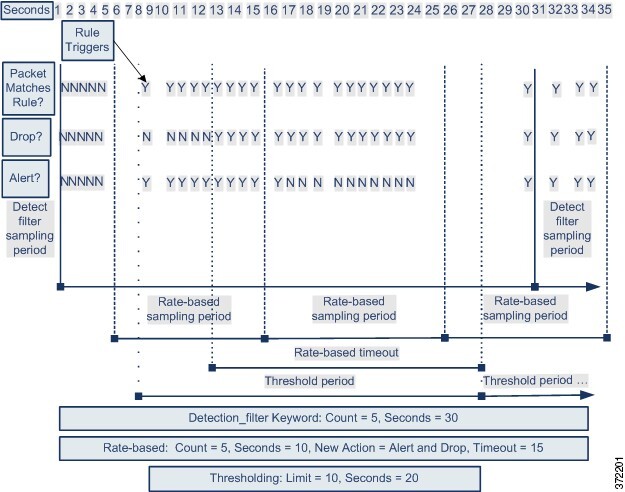
The following diagram shows an example where an attacker is
attempting to access a host. Repeated attempts to find a password trigger a
rule which has rate-based attack prevention configured. The rate-based settings
change the rule attribute to Drop and Generate Events after rule matches occur
five times in a 10-second span. The new rule attribute times out after 15
seconds.
After the timeout, note that packets are still dropped in the
rate-based sampling period that follows. If the sampled rate is above the
threshold in the current or previous sampling period, the new action continues.
The new action reverts to generating events only after a sampling period
completes where the sampled rate is below the threshold rate.


 )
)
 Feedback
Feedback