About Installing Cards and Associated Components
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage, which can occur when electronic cards or components are improperly handled, results in complete or intermittent failures. We recommend use of an ESD-preventive wrist strap whenever you handle network equipment or one of its components.
- Always use an ESD-preventive wrist or ankle strap, and ensure that it makes good skin contact. Connect the equipment end of the connection cord to an ESD jack or a bare metal surface on the chassis (ensure that the chassis is grounded).
- Handle a card by its ejector levers, when applicable, or its metal carrier only; avoid touching the board or connector pins (see the Guidelines for Installing and Removing a Card).
- Place a removed card board-side-up on an antistatic surface or in a static-shielding bag. If you plan to return the component to the factory, immediately place it in a static-shielding bag.
- Avoid contact between a card and clothing. The wrist strap protects the board from only ESD voltage on the body; ESD voltage on clothing can still cause damage.
- Be careful not to lay any tools on the aluminum honeycomb panel, or insert your fingers into the panel.
Guidelines for Installing and Removing a Card
- Online (in-service) insertion and removal (OIR) is supported, enabling you to remove and install cards while the chassis is operating. OIR is seamless to users on the network, maintains all routing information, and ensures session preservation. You do not need to notify the software or reset the power. You have the option of using the Cisco IOS XR shutdown command before removing a card.
 Note |
OIR removes power to a specific slot before the card is replaced. The power remains on for all other card slots. |
- The different cards in the Cisco NCS 4016 chassis are all attached to the chassis itself using a pair of ejector levers and captive screws. The two ejector levers release the card from its backplane connector. The exact locations of the ejector levers and captive screws can vary slightly from card to card, but they are generally in the same locations: on the upper and bottom ends of the faceplate.
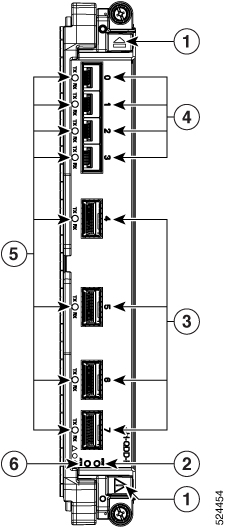
- When you remove a card, press the OIR buttons before using the ejector levers to ensure that the connector pins disconnect from the backplane in the sequence expected by the chassis.
- The correct card orientation is shown by the eject symbol on the OIR buttons. The symbol must be oriented upward for cards in the top row, and downward for cards in the bottom row.
- Every FC, LC, and RP card has a key mounted on the board that matches a corresponding slot on the chassis side (top of each card slot). This key-slot mechanism prevents a card from being inserted into the wrong, non-matching card slot. It also prevents a card from being inserted upside down. When a card is inserted into the wrong card slot or upside down, the key will get blocked against the chassis card guide and not slide though the slot. When the key gets blocked, remove the card and find the correct card slot.
 Note |
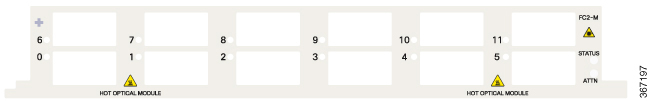
RP card faceplates are labeled with the square symbol. Card slots on the chassis for RP cards are also labeled with the square symbol. FC faceplates are labeled with the plus symbol. Card slots on the chassis for FCs are also labeled with the plus symbol. |
- The chassis is shipped with all card slots containing filler cards to help maintain chassis stiffness and prevent any damage to the chassis during shipment.
- Any unused card slots that are uncovered would allow air used for chassis cooling to escape. Therefore, to ensure proper air flow and maintain system EMC and safety compliance, any unused LC slots must contain filler cards, and all FC and RP cards must remain installed in their card slots.
- Fully insert all FC and RP cards into the chassis before tightening their captive screws.
- For information about the slot numbers, see the “Chassis Slot Numbers” section on page -7 .
 Caution |
The chassis may indicate a hardware failure if you do not follow proper procedures. Remove or install only one card at a time. Allow at least 30 seconds for the chassis to complete its tasks before removing or installing another card. |



















 Feedback
Feedback