Guidelines
-
Auto IFC is supported on Cisco Nexus devices only.
-
You can configure Cisco ASR 1000 Series routers and Cisco Catalyst 9000 Series switches as edge routers. To configure, set
up a VRF Lite IFC, and connect it as a border device with easy fabric.
-
You can configure Cisco ASR 9000 Series routers as edge routers in managed mode.
-
If the device in the External fabric is non-Nexus, you must create IFC manually.
-
Ensure that no user policy is enabled on the interface that connects to the edge router. If a policy exists, then the interface
will not be configured.
-
Autoconfiguration is supported for the following cases:
-
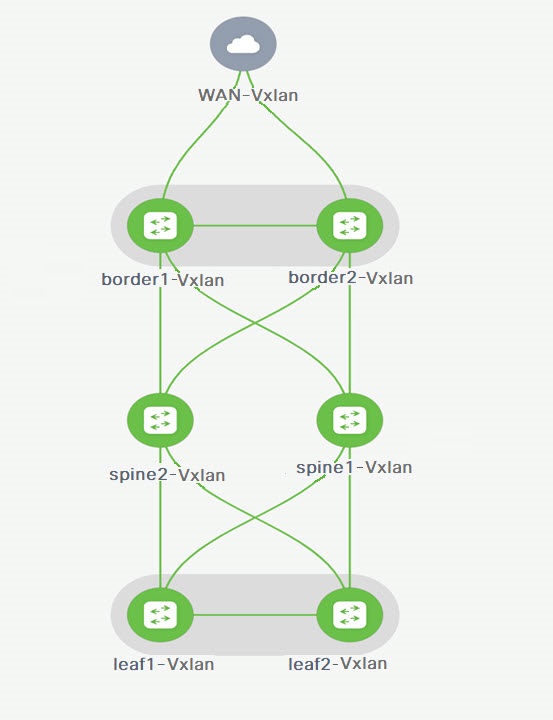
Border role in the VXLAN fabric and Edge Router role in the connected external fabric device
-
Border Gateway role in the VXLAN fabric and Edge Router role in the connected external fabric device
-
Border role to another Border role directly

Note
|
Autoconfiguration is not provided between two Border Gateways (BGWs).
|
If VRF Lite is required between other roles, you must deploy it manually on the NDFC Web UI.
-
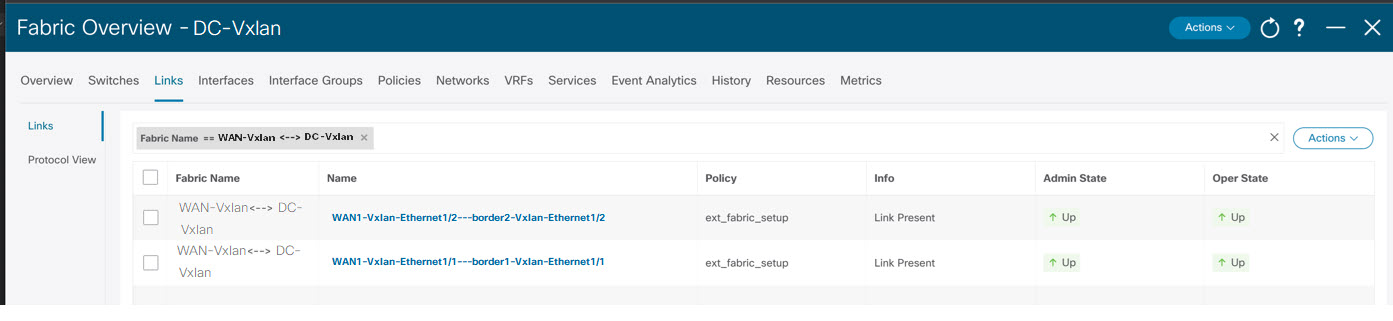
To deploy configurations in the external fabric, you must uncheck the Fabric Monitor Mode check box in the external fabric settings. When an external fabric is set to Fabric Monitor Mode Only, you cannot deploy configurations on the switches.
Easy Fabric Settings
The following are the 2 modes in which you can deploy VRF Lite. By default, VRF Lite deployment is set to Manual. You can change the settings based
on your requirement.
-
Manual - Use this option to deploy the VRF Lite IFCs manually between the source and the destination devices.
-
Back2Back&ToExternal - Use this option to automatically configure VRF Lite IFCs between a border switch and the edge or core switches in external
fabric or between back-to-back border switches in VXLAN EVPN fabric.

Note
|
Though VRF Lite mode is set to Manual for NDFC resource handling, Data Center Interconnectivity (DCI) subnet is required.
|
The Manual mode is the default mode in fabric settings. To change the default mode to other mode, click Edit fabric settings. On Resource tab, modify VRF Lite Deployment field to the above mentioned auto configuration modes.
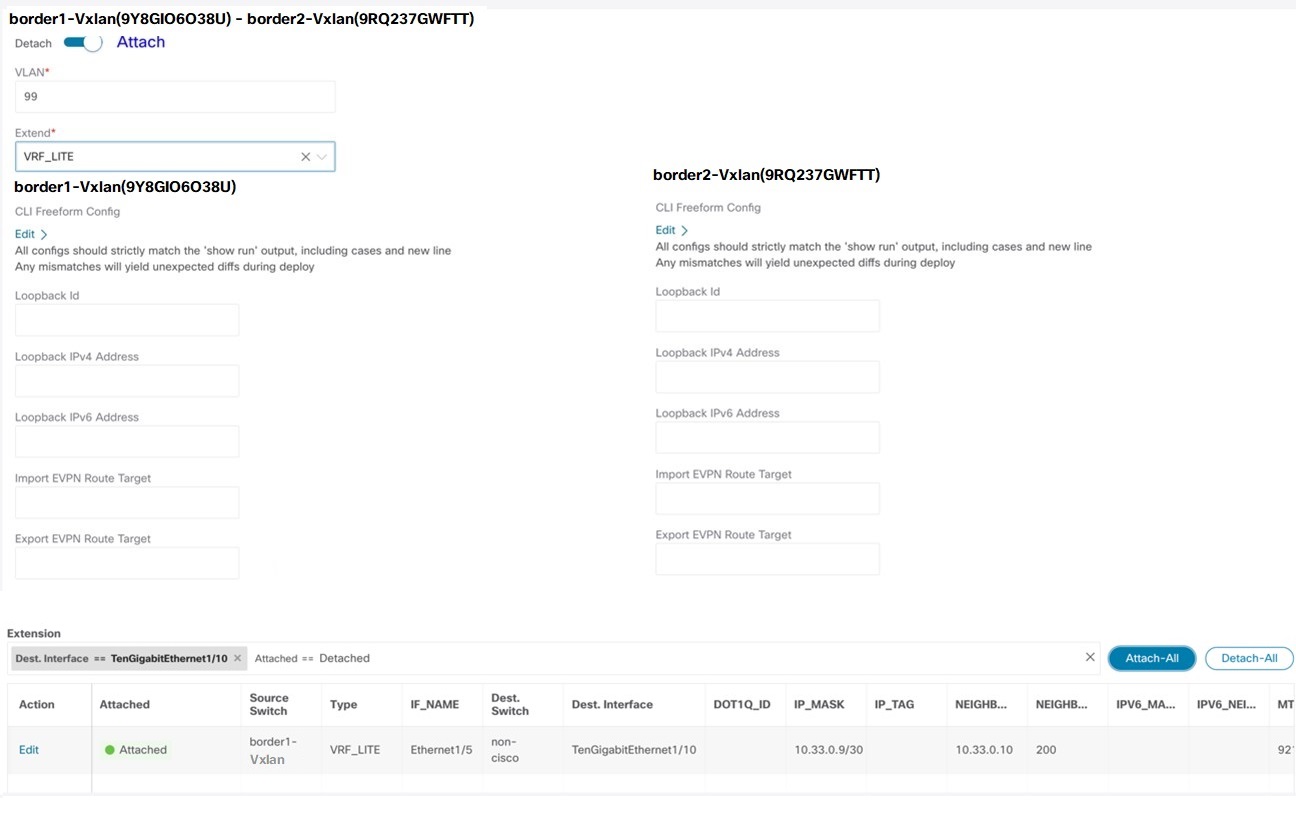
Auto Deploy Peer - This check box is applicable for VRF Lite deployment. When you check this check box, IFCs are automatically created for
peer devices. You can check or uncheck this check box when the VRF Lite Deployment field is not set to Manual. The value you choose takes priority. This configuration only affects the new auto-created IFCs and does not affect the existing
IFCs.
Auto Deploy Default VRF – When you select this check box, the Auto Generate Configuration on default VRF field is automatically enabled for auto-created VRF Lite IFCs. You can check or uncheck this checkbox when the VRF Lite Deployment
field is not set to Manual. The Auto Generate Configuration on default VRF field when set, automatically configures the physical interface for the border device in the default VRF, and establishes
an EBGP connection between the border device and the edge device or another border device in a different VXLAN EVPN fabric.
Auto Deploy Default VRF for Peer – When you select this checkbox, the Auto Generate Configuration for NX-OS Peer on default VRF field is automatically enabled for auto-created VRF Lite IFCs. You can check or uncheck this checkbox when the VRF Lite Deployment field is not set to Manual. The Auto Generate Configuration for NX-OS Peer on default VRF field when set, automatically configures the physical interface and the EBGP commands for the peer NX-OS switch.

Note
|
You can access the Auto Generate Configuration on default VRF and Auto Generate Configuration for NX-OS Peer on default VRF fields for an IFC link by navigating to .
|
Redistribute BGP Route-map Name – Defines the route map for redistributing the BGP routes in default VRF.
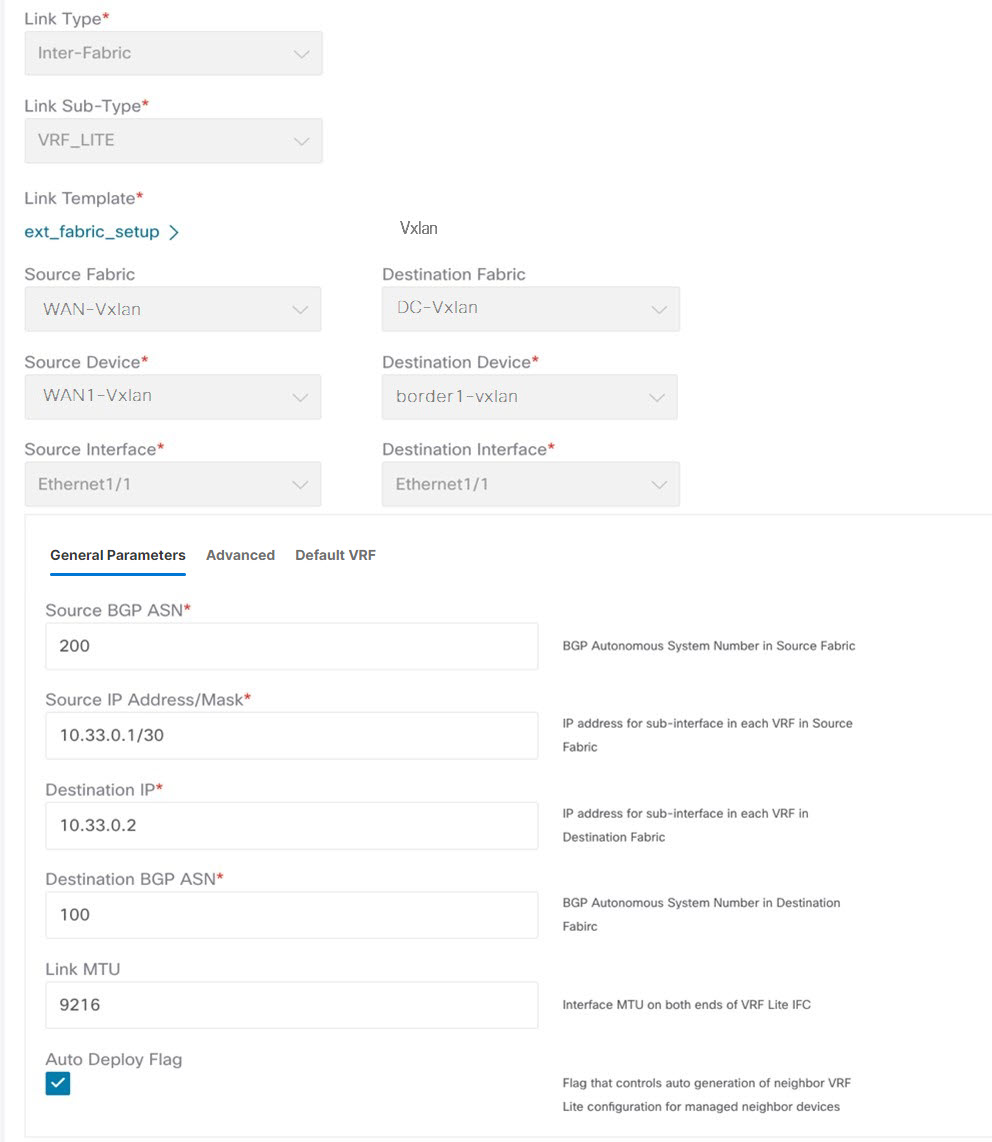
VRF Lite Subnet IP Range: The IP address for VRF Lite IFC deployment is chosen from this range. The default value is 10.33.0.0/16. Ensure that each
fabric has its own unique range and is distinct from any underlay range to avoid possible duplication. These addresses are
reserved with the Resource Manager.
VRF Lite Subnet Mask: By default, it is set to /30, which is a best practice for point-to-point (P2P) links.



 Feedback
Feedback