About Clustering on the Firepower 9300 Chassis
The cluster consists of multiple devices acting as a single logical unit. When you deploy a cluster on the Firepower 9300 chassis, it does the following:
-
Creates a cluster-control link (by default, port-channel 48) for unit-to-unit communication.
For intra-chassis clustering, this link utilizes the Firepower 9300 backplane for cluster communications.
-
Creates the cluster bootstrap configuration within the application.
When you deploy the cluster, the chassis supervisor pushes a minimal bootstrap configuration to each unit that includes the cluster name, cluster control link interface, and other cluster settings. Some parts of the bootstrap configuration may be user-configurable within the application if you want to customize your clustering environment.
-
Assigns data interfaces to the cluster as Spanned interfaces.
For intra-chassis clustering, spanned interfaces are not limited to EtherChannels, like it is for inter-chassis clustering.The Firepower 9300 supervisor uses EtherChannel technology internally to load-balance traffic to multiple modules on a shared interface, so any data interface type works for Spanned mode.

Note
Individual interfaces are not supported, with the exception of a management interface.
-
Assigns a management interface to all units in the cluster.
The following sections provide more detail about clustering concepts and implementation. See also Reference for Clustering.
Bootstrap Configuration
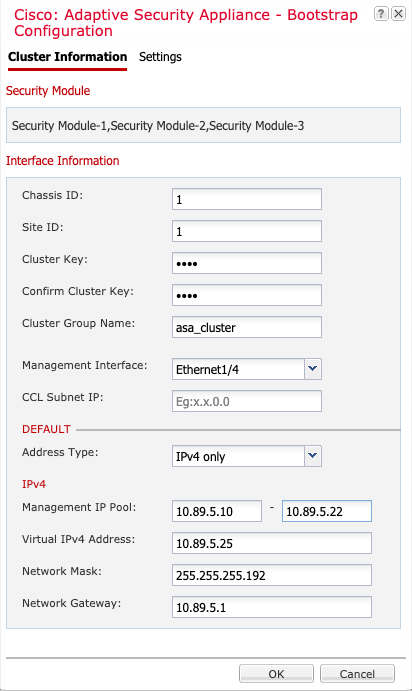
When you deploy the cluster, the Firepower 9300 chassis supervisor pushes a minimal bootstrap configuration to each unit that includes the cluster name, cluster control link interface, and other cluster settings. Some parts of the bootstrap configuration are user-configurable if you want to customize your clustering environment.
Cluster Members
Cluster members work together to accomplish the sharing of the security policy and traffic flows.
One member of the cluster is the control unit. The control unit is determined automatically. All other members are data units.
You must perform all configuration on the control unit only; the configuration is then replicated to the data units.
Some features do not scale in a cluster, and the control unit handles all traffic for those features. See Centralized Features for Clustering.
Master and Slave Unit Roles
One member of the cluster is the master unit. The master unit is determined automatically. All other members are slave units.
You must perform all configuration on the master unit only; the configuration is then replicated to the slave units.
Some features do not scale in a cluster, and the master unit handles all traffic for those features. See Centralized Features for Clustering.
Cluster Control Link
The cluster-control link is an EtherChannel (port-channel 48) for unit-to-unit communication. For intra-chassis clustering, this link utilizes the Firepower 9300 backplane for cluster communications.
Cluster control link traffic includes both control and data traffic.
Control traffic includes:
-
Control unit election.
-
Configuration replication.
-
Health monitoring.
Data traffic includes:
-
State replication.
-
Connection ownership queries and data packet forwarding.
Cluster Control Link Network
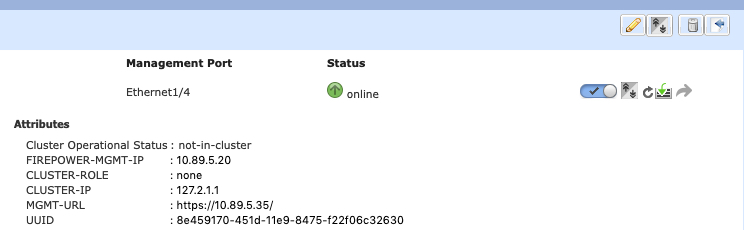
The Firepower 9300 chassis auto-generates the cluster control link interface IP address for each unit based on the chassis ID and slot ID: 127.2.chassis_id.slot_id. You cannot set this IP address manually, either in FXOS or within the application. The cluster control link network cannot include any routers between units; only Layer 2 switching is allowed.
Cluster Interfaces
For intra-chassis clustering, you can assign both physical interfaces or EtherChannels (also known as port channels) to the cluster. Interfaces assigned to the cluster are Spanned interfaces that load-balance traffic across all members of the cluster.
Individual interfaces are not supported, with the exception of a management interface.
Connecting to a VSS or vPC
We recommend connecting EtherChannels to a VSS or vPC to provide redundancy for your interfaces.
Configuration Replication
All units in the cluster share a single configuration. You can only make configuration changes on the control unit, and changes are automatically synced to all other units in the cluster.
ASA Cluster Management
One of the benefits of using ASA clustering is the ease of management. This section describes how to manage the cluster.
Management Interface
You must assign a Management type interface to the cluster. This interface is a special individual interface as opposed to a Spanned interface. The management interface lets you connect directly to each unit.
The Main cluster IP address is a fixed address for the cluster that always belongs to the current control unit. You also configure a range of addresses so that each unit, including the current control unit, can use a Local address from the range. The Main cluster IP address provides consistent management access to an address; when a control unit changes, the Main cluster IP address moves to the new control unit, so management of the cluster continues seamlessly.
For example, you can manage the cluster by connecting to the Main cluster IP address, which is always attached to the current control unit. To manage an individual member, you can connect to the Local IP address.
For outbound management traffic such as TFTP or syslog, each unit, including the control unit, uses the Local IP address to connect to the server.
Control Unit Management Vs. Data Unit Management
All management and monitoring can take place on the control unit. From the control unit, you can check runtime statistics, resource usage, or other monitoring information of all units. You can also issue a command to all units in the cluster, and replicate the console messages from data units to the control unit.
You can monitor data units directly if desired. Although also available from the control unit, you can perform file management on data units (including backing up the configuration and updating images). The following functions are not available from the control unit:
-
Monitoring per-unit cluster-specific statistics.
-
Syslog monitoring per unit (except for syslogs sent to the console when console replication is enabled).
-
SNMP
-
NetFlow
RSA Key Replication
When you create an RSA key on the control unit, the key is replicated to all data units. If you have an SSH session to the Main cluster IP address, you will be disconnected if the control unit fails. The new control unit uses the same key for SSH connections, so that you do not need to update the cached SSH host key when you reconnect to the new control unit.
ASDM Connection Certificate IP Address Mismatch
By default, a self-signed certificate is used for the ASDM connection based on the Local IP address. If you connect to the Main cluster IP address using ASDM, then a warning message about a mismatched IP address might appear because the certificate uses the Local IP address, and not the Main cluster IP address. You can ignore the message and establish the ASDM connection. However, to avoid this type of warning, you can enroll a certificate that contains the Main cluster IP address and all the Local IP addresses from the IP address pool. You can then use this certificate for each cluster member. See https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/security/asdm/identity-cert/cert-install.html for more information.
 )
) )
) )
)


 Feedback
Feedback