Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Ethernet VPN (EVPN) Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN) is a campus and data center network solution
for Cisco devices running Cisco IOS XE software. It is designed to provide a unified overlay network solution.
VXLAN is a MAC in IP/UDP overlay that allows Layer 2 segments to be stretched across an IP core. All the benefits of Layer
3 topologies are thereby available with VXLAN. The encapsulation and decapsulation of VXLAN headers is handled by a functionality
embedded in VXLAN Tunnel End Points (VTEPs). VTEPs themselves can be implemented in a software or a hardware form factor.
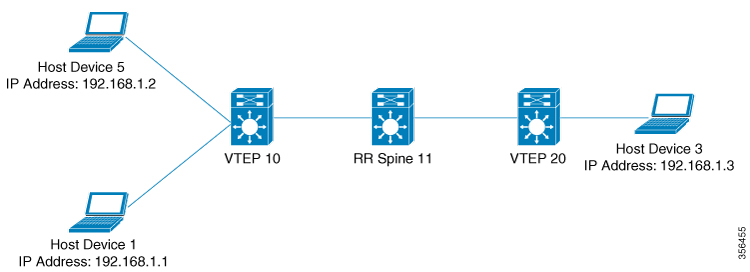
VXLAN natively operates on a flood and learn mechanism where Broadcast, unknown-unicast and multicast (BU) traffic and Layer
2 Multicast traffic in a given VXLAN network is sent over the IP core to every VTEP that has membership in that network. IP
multicast is used to send traffic over the network. The receiving VTEPs decapsulate the packet, and based on the inner frame,
perform Layer 2 MAC learning. The inner Source MAC is learnt against the outer Source IP Address (SIP) corresponding to the
source VTEP. In this way, reverse traffic can be unicasted toward the previously learnt end host.
One of the biggest limitations of VXLAN flood and learn is the inherent flooding that is required to ensure that learning
happens at the VTEPs. In a traditional deployment, a Layer 2 segment is represented with a VLAN that comprises a broadcast
domain, which also scopes BU traffic. With VXLAN, the Layer 2 segment spans a much larger boundary across an IP core where
floods are translated to IP multicast. Consequently, the flood and learn based scheme presents serious scale challenges, especially
as the number of end hosts go up. This is addressed through learning using a control plane for distribution of end-host addresses.
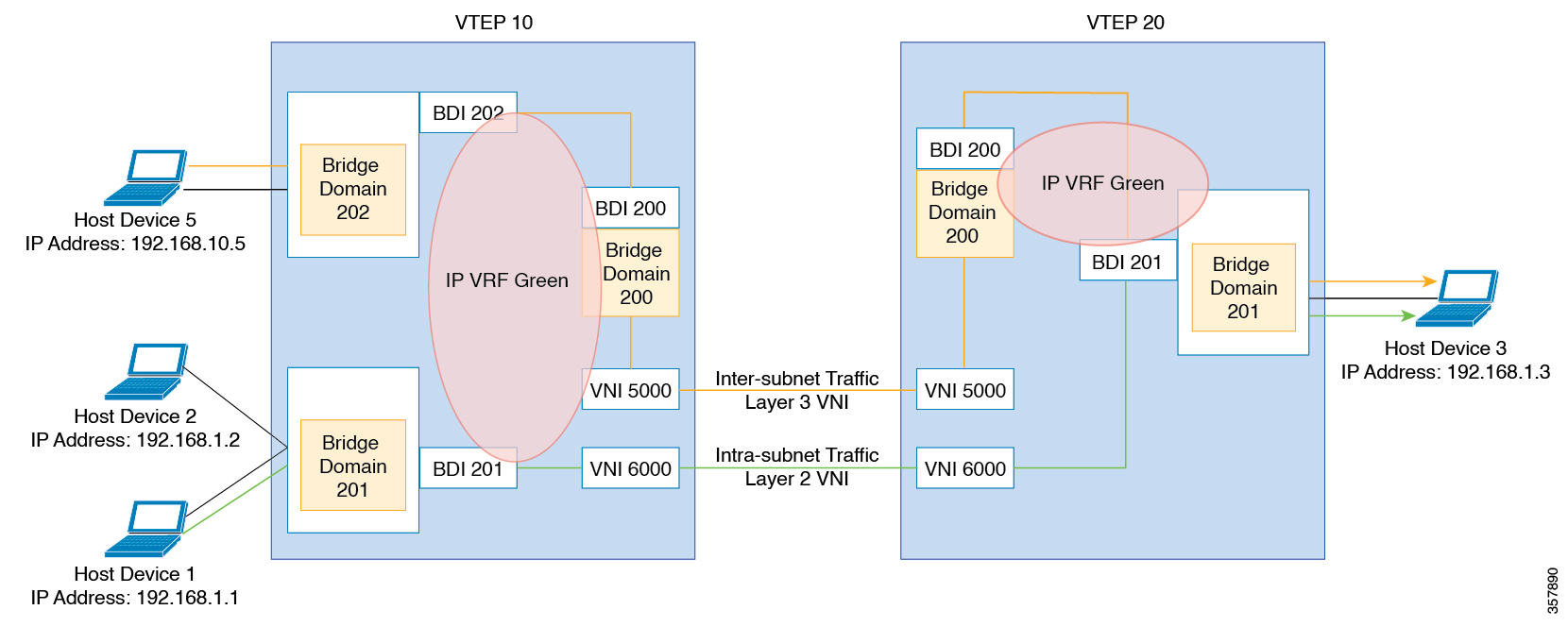
The control plane of choice is BGP EVPN. BGP EVPN VXLAN modes come with integrated routing and bridging (IRB) capabilities.
Depending on the subnets in which the hosts are configured, EVPN over VXLAN operates in two modes:
-
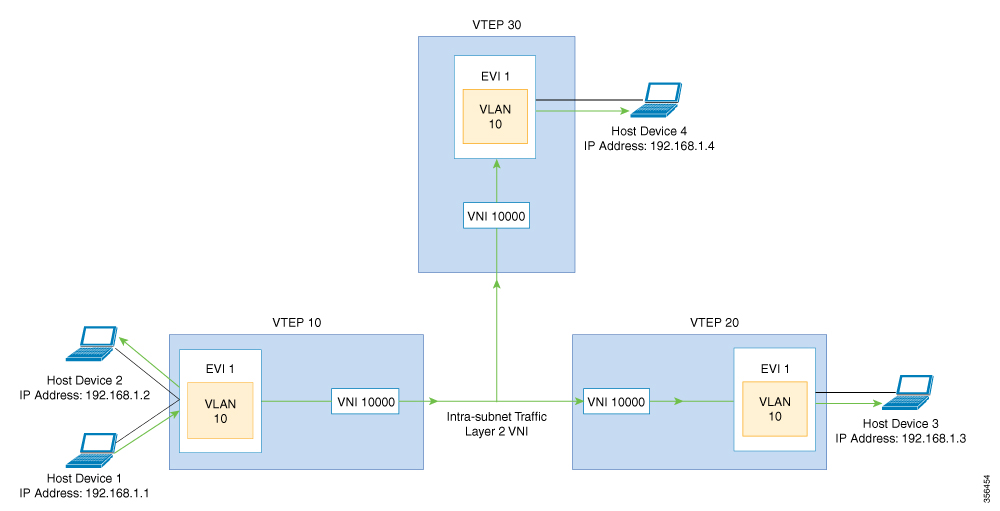
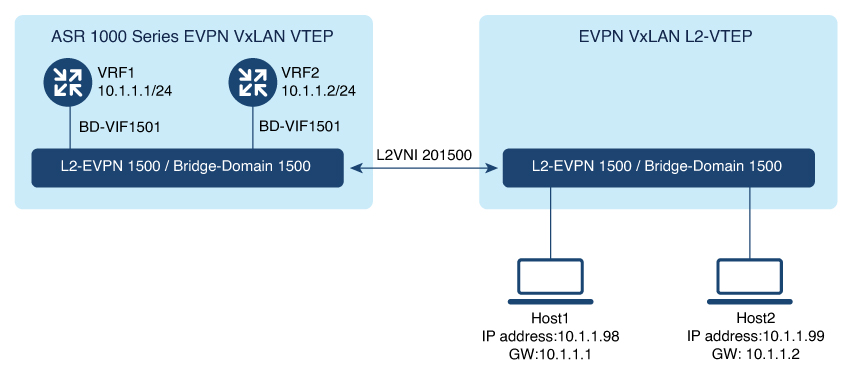
Bridged Mode:EVPN over VXLAN operates in Bridged mode when the hosts are in the same subnet. Intra-subnet trafffic moves seamlessly
as it involves only a Layer 2 MAC lookup.
-
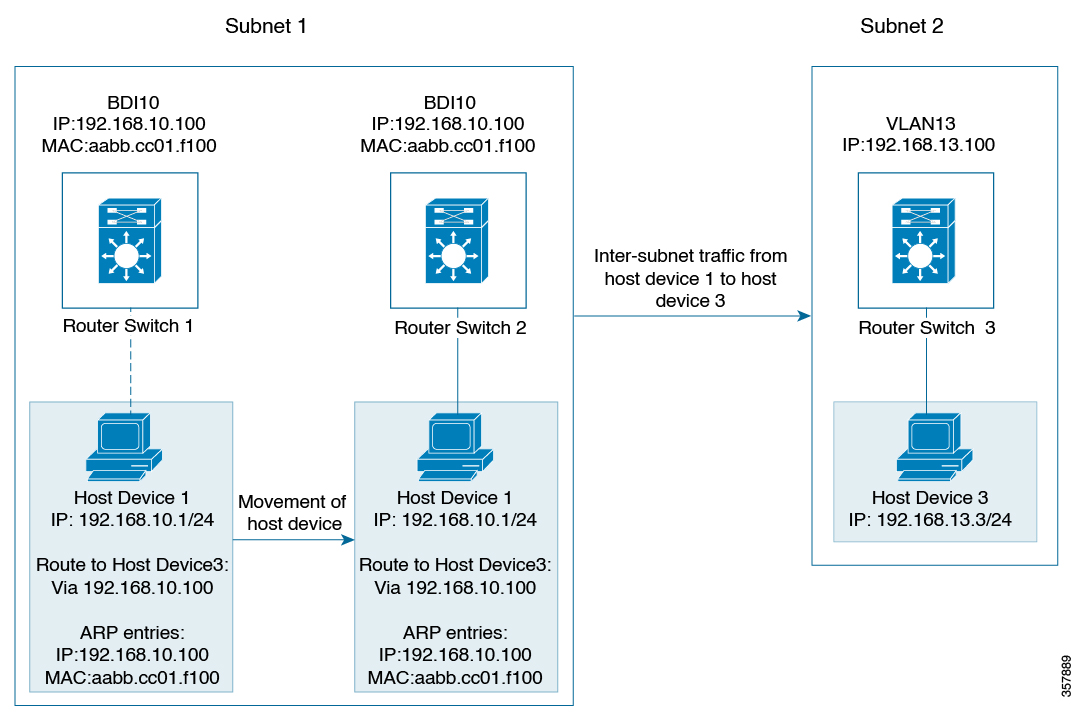
Routed Mode: EVPN over VXLAN operates in Routed mode when the hosts are in different subnets. Inter-subnet traffic involves
Layer 2 MAC lookups and Layer 3 IP lookups.
This chapter provides a background for the evolution of the solution and covers conceptual information and basic terminology
that is required to understand BGP EVPN VXLAN. Later chapters of this configuration guide include information about configuration,
implementation, functionalities, and troubleshooting BGP EVPN VXLAN.

Note
|
This feature is supported only on Cisco ASR 1000 Series, Cisco Catalyst 8500 Edge Series platforms, and Cisco Catalyst 8000V
Edge platform.
|



 Feedback
Feedback