Understanding Components of Hybrid Cloud Connectivity
This document describes deployment steps for the Cisco Hybrid Cloud Networking Solution powered by Cisco Nexus Dashboard Orchestrator (NDO) with a Cisco Nexus 9000 NX-OS based fabric managed by Nexus Dashboard Fabric Controller (NDFC) and public cloud sites managed by Cisco Cloud Network Controller (CNC).
The Cisco Nexus Dashboard Orchestrator (NDO) based Hybrid Cloud solution offers seamless connectivity between on-premises and cloud networks. This solution uses NDFC to manage on-premises VXLAN-based fabric and on-premises Cisco Catalyst 8000Vs, while cloud sites (AWS or Microsoft Azure) are managed by the Cisco Cloud Network Controller (CNC). NDO is used to orchestrate connectivity between on-premises and cloud sites, and between two or more cloud sites. VXLAN is used to build overlay tunnels between the sites.
The following figure shows an example topology for hybrid cloud connectivity using these components. See Supported Topologies for more information.
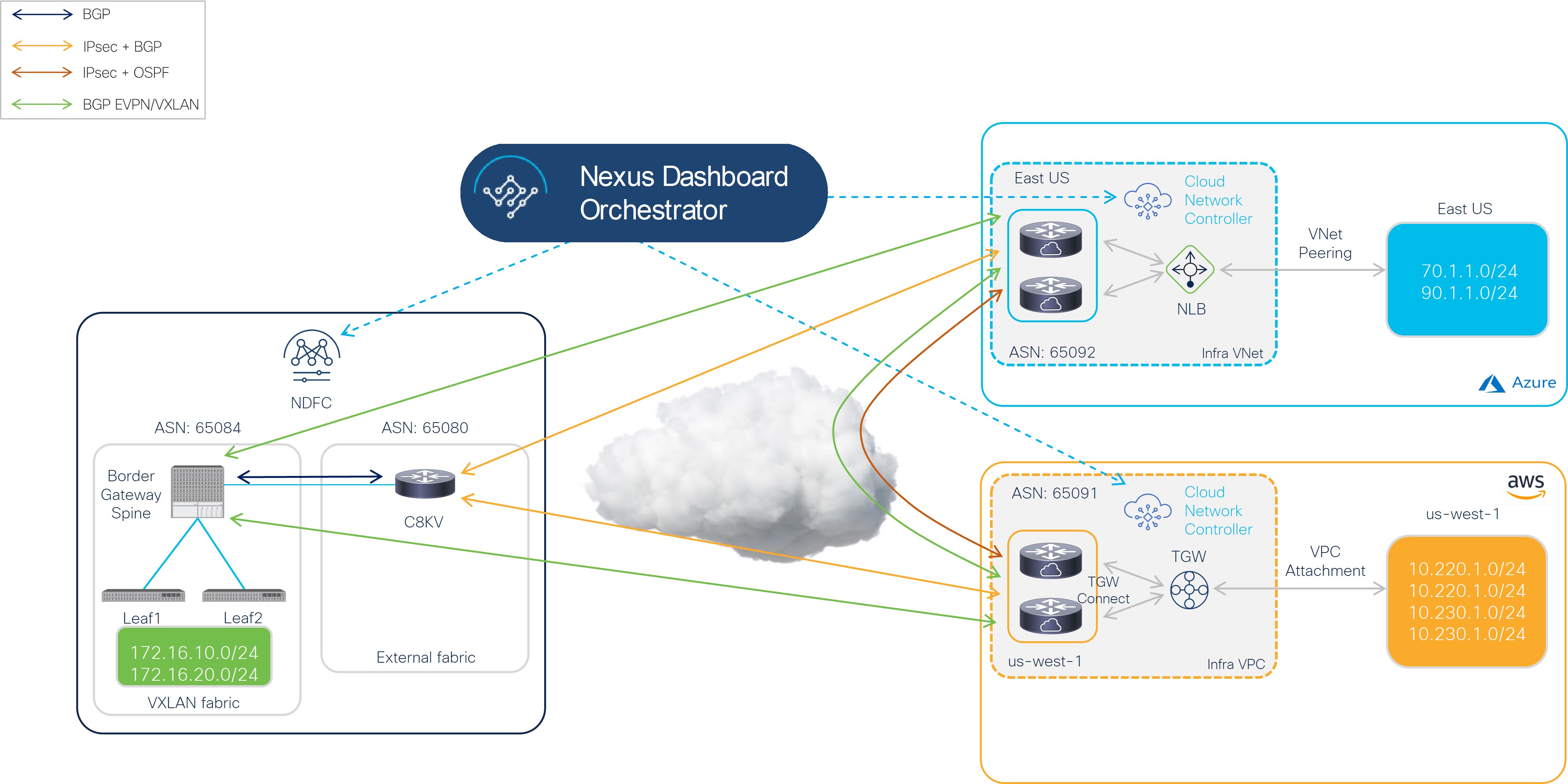
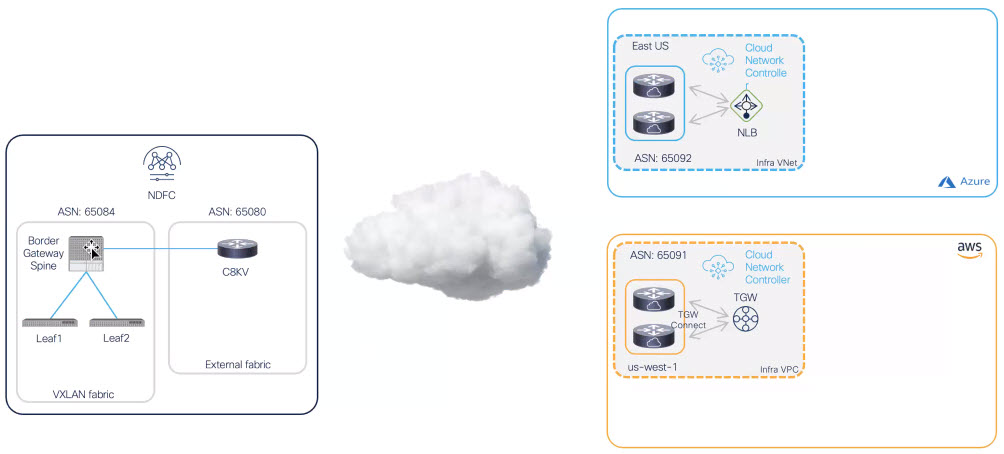
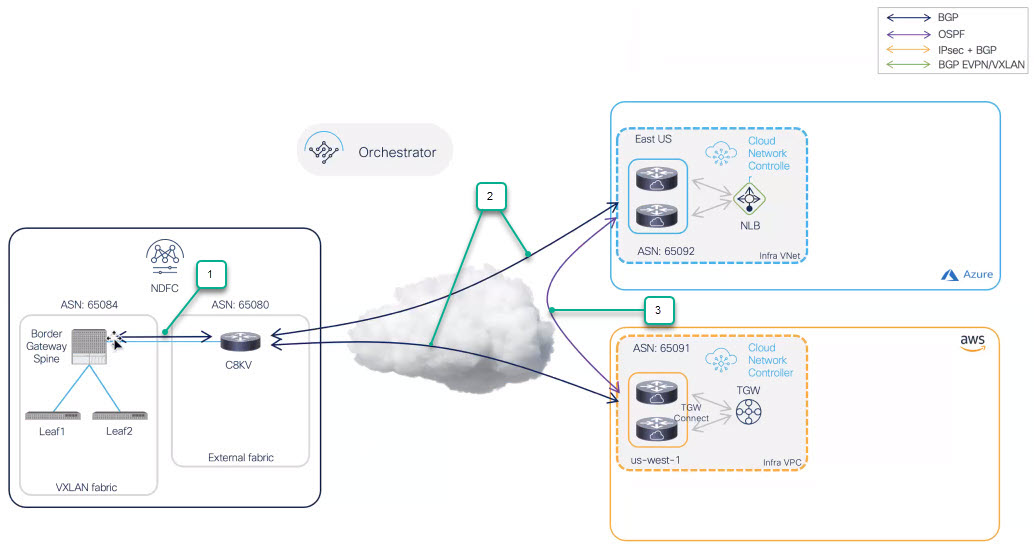
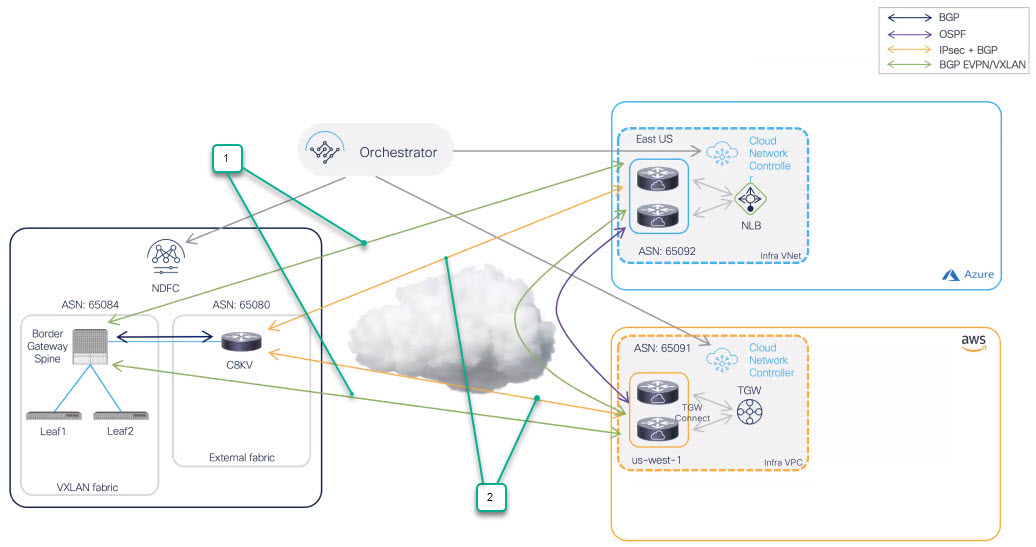
In this example topology, the on-premises site managed by NDFC has a secure connection setup to AWS and Azure cloud sites, where Cisco Catalyst 8000Vs sitting on the infra VPC/VNet serve as the cloud gateway for all traffic to and from the on-premises data centers.
On the on-premises site, Border Gateways (BGWs), which support seamless Layer-2/Layer-3 DCI extensions between different on-premises VXLAN EVPN sites, also support Layer-3 extension to the public cloud.
BGP-EVPN is used for the control plane between the BGWs and the Cisco Catalyst 8000Vs in the cloud, and VXLAN is used for the data plane.
As shown in the previous figure, the Cisco Hybrid Cloud Networking Solution consists of the following components:
-
Cisco Nexus Dashboard Orchestrator (NDO): NDO acts as a central policy controller, managing policies across multiple on-premises fabrics managed by different NDFC instances, with each cloud site being abstracted by its own Cisco Cloud Network Controller. NDO runs as a service on top of Nexus Dashboard, where Nexus Dashboard can be deployed as a cluster of physical appliances or virtual machines running on VMware ESXi, Linux KVM, Amazon Web Services or Microsoft Azure. Inter-version support was introduced previously, so NDO can manage Cisco Cloud Network Controller running different software versions.
-
Cisco Nexus Dashboard Fabric Controller (NDFC): NDFC is a network automation and orchestration tool for building LAN, VXLAN, SAN and Cisco IP Fabric for Media (IPFM) fabrics. NDFC runs as a service on top of Nexus Dashboard cluster that can be either a physical or a virtual cluster. For the Hybrid Cloud Networking Solution, NDFC manages the on-premises VXLAN fabric and on-premises Cisco Cloud Routers (Catalyst 8000V).
-
On-premises VXLAN fabric: The on-premises VXLAN fabric is built with Nexus 90000/3000 switches managed by NDFC. The fabric should have one or more Border Gateway (BGW) devices that are responsible for originating and terminating VXLAN Multisite Overlay tunnels between on-premises and cloud sites. NDFC has pre-built templates for creating a VXLAN fabric; this document uses the
External_Fabrictemplate for the VXLAN fabric. -
On-premises Cisco Cloud Router (CCR): The CCR is used to provide reachability between the on-premises VXLAN fabric and the cloud sites. The CCR provides connectivity to the cloud sites using either public internet or private connections (such as AWS Direct Connect or Azure ExpressRoute). The on-premises CCRs are managed by NDFC using a pre-built
External_Fabrictemplate and need to be assigned theCore Routerrole.The Cisco Catalyst 8000V is used as the on-premises CCR for the Cisco Hybrid Cloud Networking Solution.
-
Cisco Cloud Network Controller (CNC): Cisco Cloud Network Controller runs as a virtual instance on a supported public cloud to provide automated connectivity, policy translation, and enhanced visibility of workloads in the public cloud. The Cisco Cloud Network Controller translates all the policies received from NDO and programs them into cloud-native constructs, such as VPCs and security groups on AWS, and VNets on Microsoft Azure. Cisco Cloud Network Controller is deployed through the public cloud Marketplace, such as AWS Marketplace and Azure Marketplace.
-
Cisco Catalyst 8000V: The Cisco Catalyst 8000V is an important component in the public cloud platforms. Cisco Catalyst 8000Vs are used for inter-site communication to on-premises sites and the public cloud platforms. In addition, Cisco Catalyst 8000Vs are used for on-premises cloud connectivity and for connectivity between different cloud providers (for example, Azure to AWS).
 Feedback
Feedback