Information About Deploying Cisco SD-WAN Controllers in AWS
Minimum supported controller images: Cisco vManage Release 20.6.1, Cisco vSmart controller Release 20.6.1, and Cisco vBond orchestrator Release 20.6.1.
You can deploy the following Cisco SD-WAN Controllers in an Amazon Web Services (AWS) environment using Amazon Machine Images (AMI): Cisco SD-WAN Manager, Cisco SD-WAN Controller, and Cisco SD-WAN Validator.
The AMI images that Cisco provides to you are for your use only. Do not share them with others. You can do the following:
-
You can deploy the number of controllers as per your order quantity. For example, if you have ordered 50 Cisco SD-WAN Manager controller PIDs, then you can deploy only 50 Cisco SD-WAN Manager controllers within your AWS account.
-
You can copy the AMI between regions and your own separate AWS accounts, if you do not exceed the quantity of PIDs ordered.
-
After the initial deployment of the controllers, you are responsible for any upgrades or downgrades.
The following illustration shows the architecture of the AWS region, virtual private cloud (VPC), security group, and so on, and it shows where the Cisco SD-WAN Controllers function within the architecture.
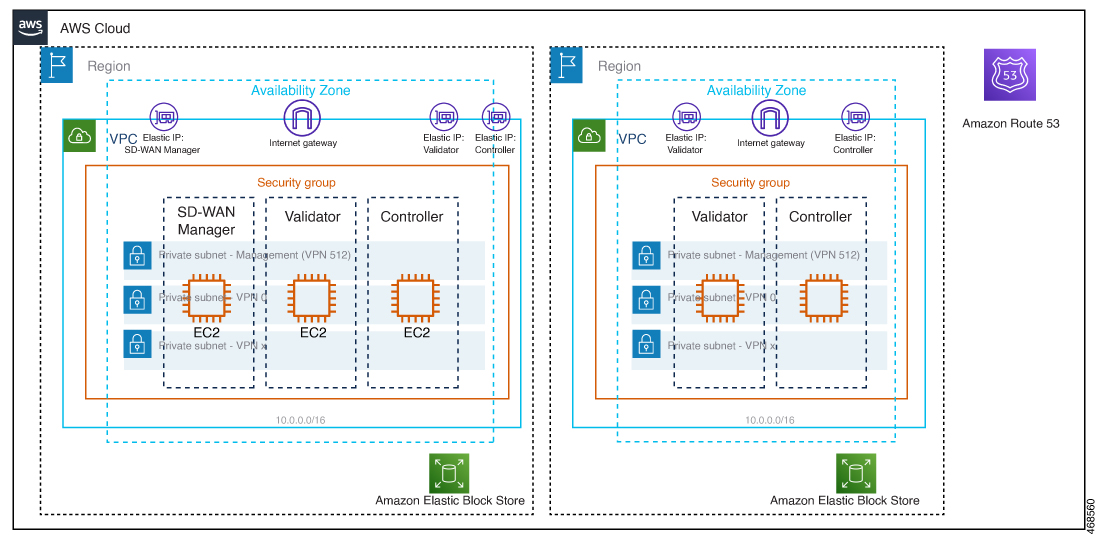
Considerations Before Installing Cisco SD-WAN Controllers in AWS
-
Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN controller AMIs are not available on the Cisco software download site or AWS marketplace. They are provided only when you request them with a valid business case to set up Cisco SD-WAN Controllers in your AWS cloud account.
-
For information about ordering Cisco SD-WAN Controllers to use with AWS, contact your Cisco account team or Cisco partner.
-
Cisco does not provide support for any issues that arise with the cloud infrastructure during the provisioning or installation of the controllers.
-
Troubleshooting:
-
Functionality issues: Please open a Cisco TAC case for functionality issues.
-
Infrastructure issues: You are responsible for infrastructure management, monitoring, and troubleshooting. After the controllers are provisioned and running in your cloud account, Cisco does not provide support for cloud infrastructure-related issues.
-
-
Software upgrade: Controller software upgrade doesn't require AMI images. You can download the controller images from the Cisco software download site and upgrade the controller software as described in the Manage Software Upgrade and Repository chapter of the Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Monitor and Maintain Configuration Guide.
Benefits of Deploying Cisco SD-WAN Controllers in AWS
-
Set-up cost: Low initial set-up cost, as compared with on-premises hosting, as there is no requirement to purchase additional data center infrastructure.
-
Deployment: Ease of cloud-based deployment.
-
Management: Ability to manage devices worldwide.
-
Stability: Because of its reliability, AWS hosting provides a stable environment for Cisco SD-WAN Controllers.
-
Security: AWS provides a secure hosting environment.
-
Scaling: AWS provides an easy path to increase the scale of your Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN network.

 Feedback
Feedback