Configure NAT
Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN includes the following types of Network Address Translation (NAT) configuration:
-
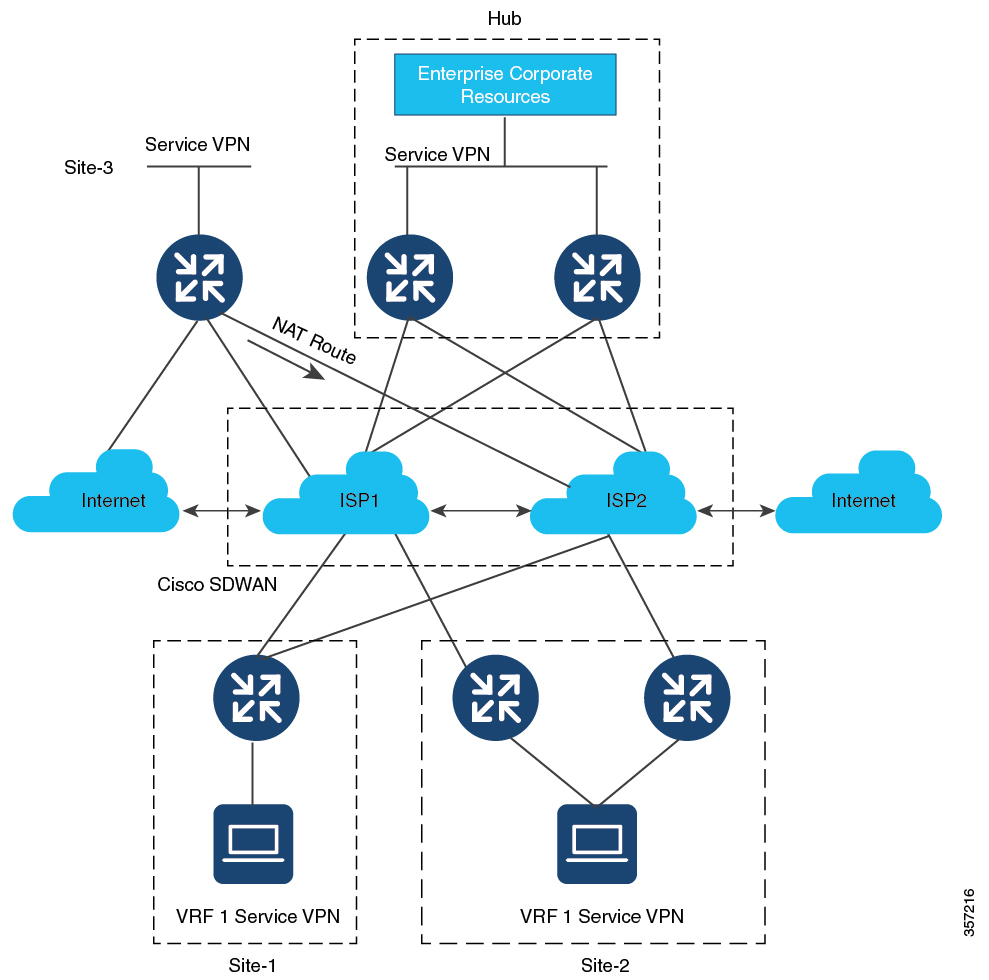
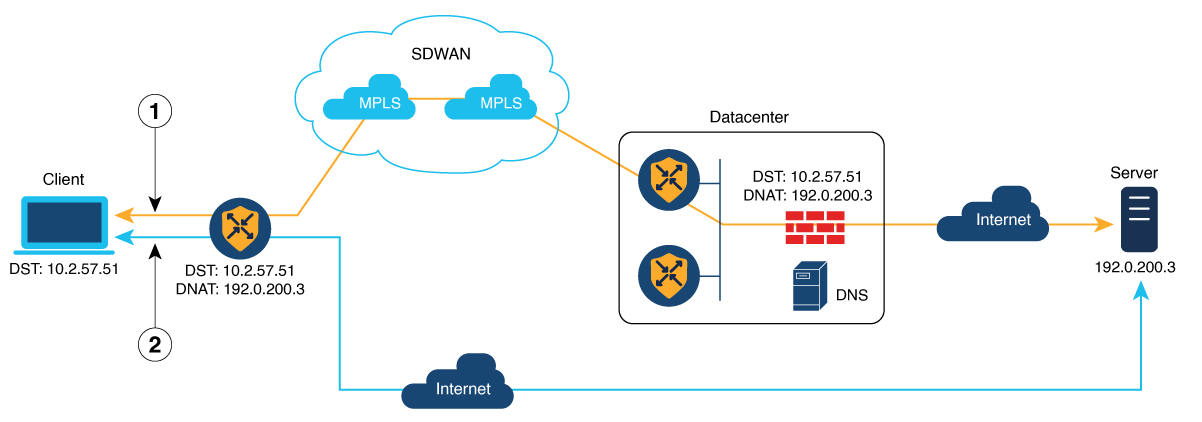
NAT Direct Internet Access (DIA): Allows remote sites to route traffic directly to the internet rather than routing the traffic to a central site or data center.
-
NAT service-side: Allows you to configure inside and outside NAT on data traffic traveling to and from the service hosts of the network overlay. Service-side NAT translates data traffic, of inside and outside host addresses, that match a configured centralized data policy.
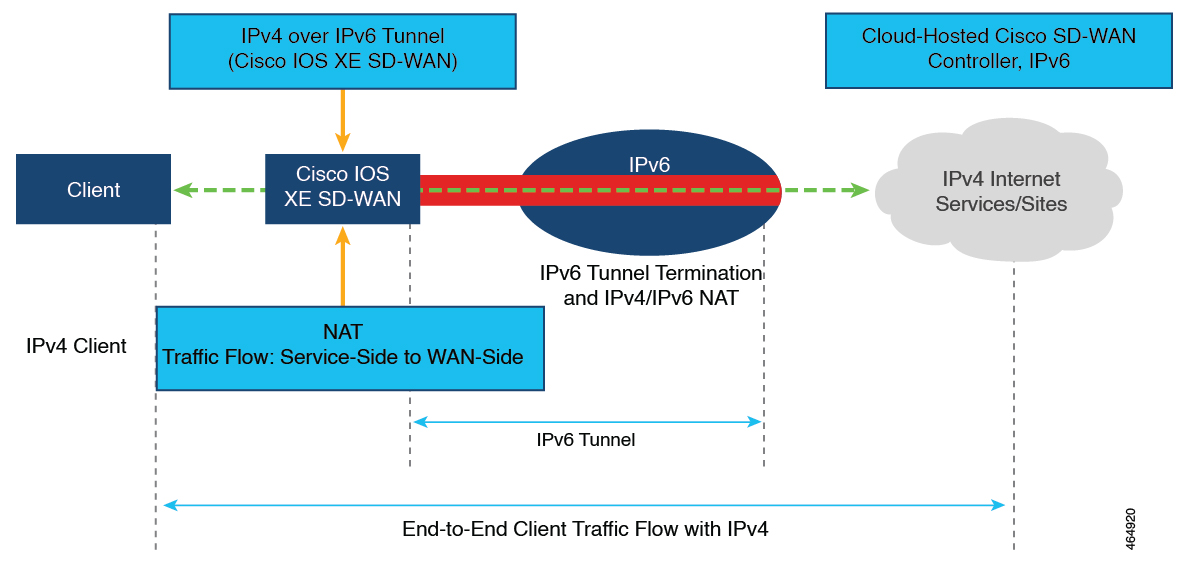
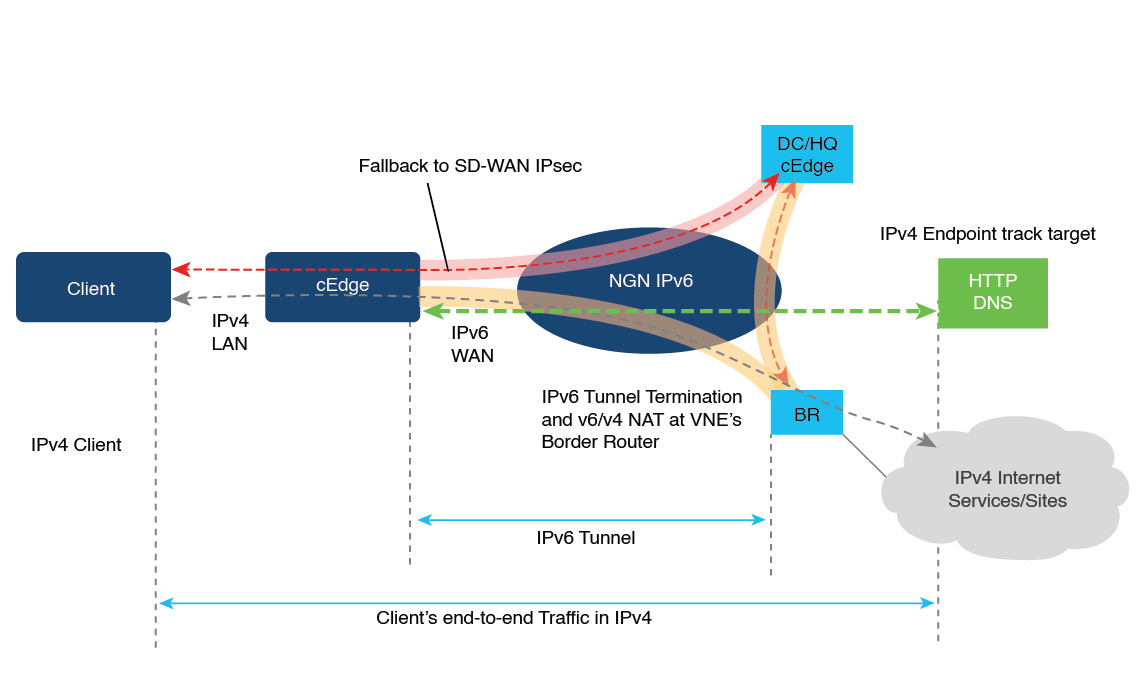
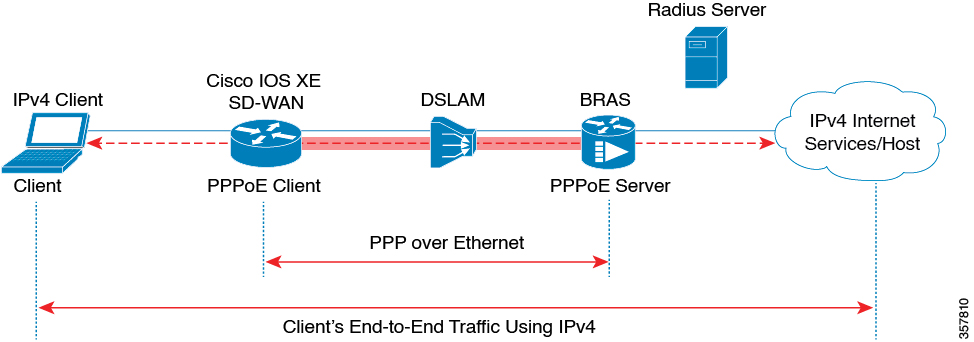
NAT is designed for IP address conservation. NAT enables private IP networks that use nonregistered IP addresses to connect to the internet. NAT operates on a device, usually connecting two networks. Before packets are forwarded onto another network, NAT translates the private (not globally unique) addresses in the internal network into legal addresses.
NAT allows a single device to act as an agent between the internet (or public network) and a local network (or private network), which means that only a single unique IP address is required to represent an entire group of computers to anything outside their network.
 Note |
When NAT performs maintenance operations, it needs to lock the NAT database. When the NAT database is locked, NAT does not process any packets for translations. Typically, NAT maintenance operations are less than a second to a few seconds. Usually, NAT sending out untranslated packets is not an issue because these packets are dropped by an ISP. Configure the following command to ensure that NAT drops packets when performing NAT database updates: |
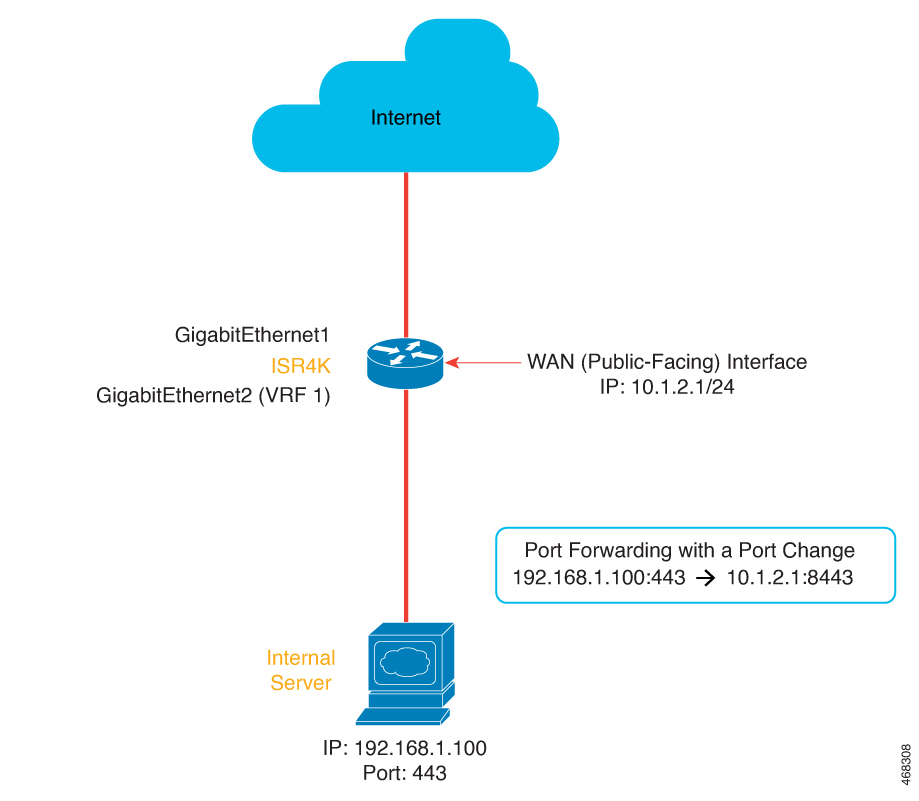
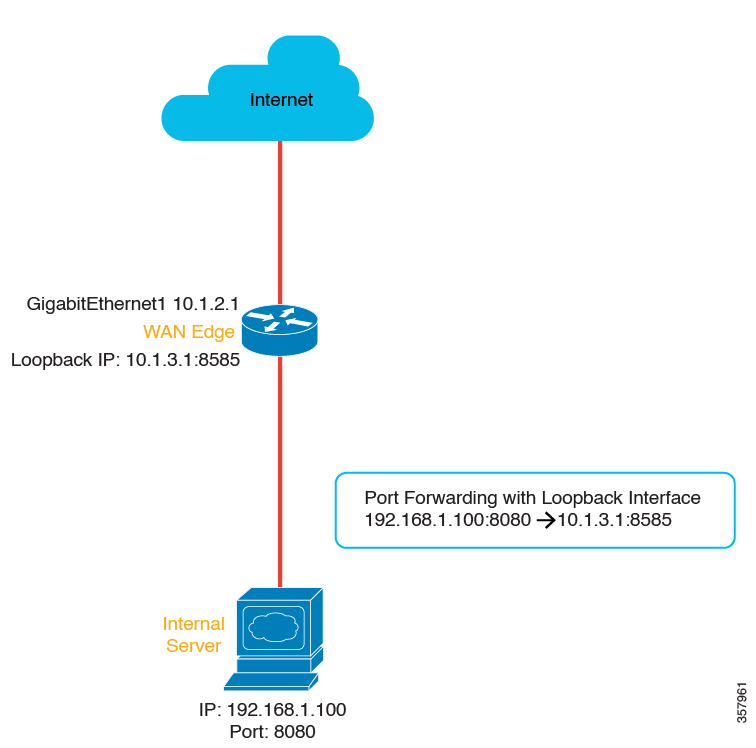
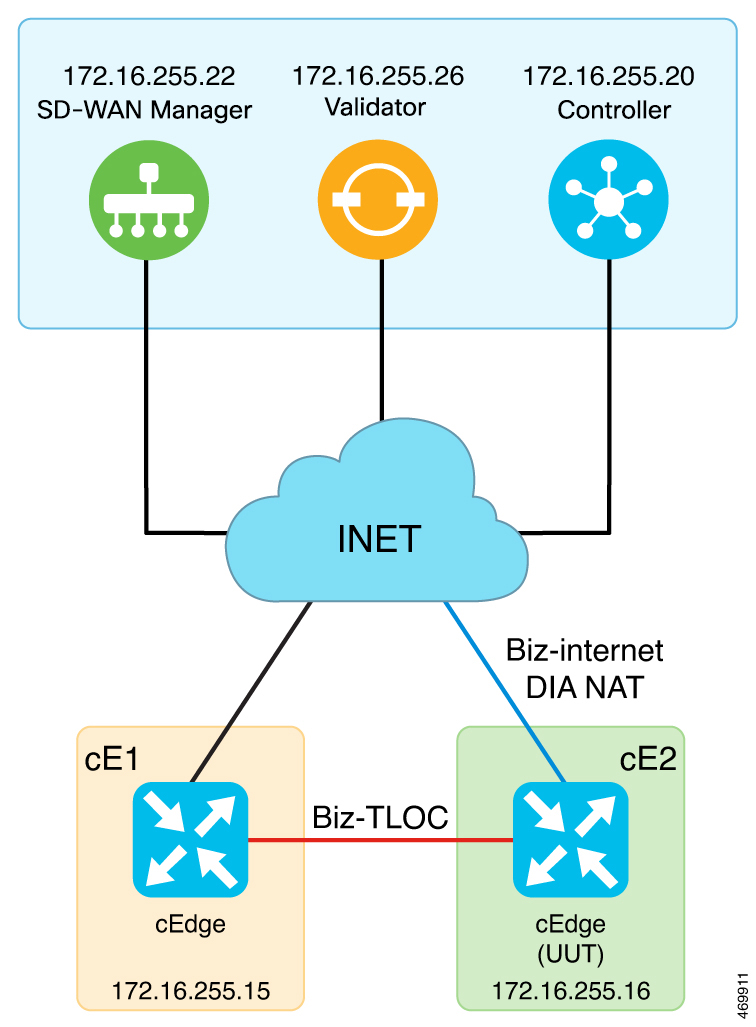
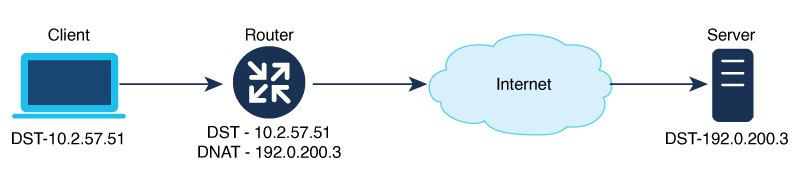

 Feedback
Feedback