Add Cloud OnRamp Colocation Devices Using Cisco vManage
Before you begin
-
Cisco SD-WAN setup details such as, Cisco vManage IP address and credentials, Cisco vBond IP address and credentials
-
NFVIS setup details such as, Cisco CSP device CIMC IP address and credentials or UCSC CIMC IP address and credentials
-
Able to access both the switch consoles
Procedure
| Step 1 |
From the Cisco vManage menu, choose to start an SSH session with Cisco vManage. |
||
| Step 2 |
Choose a CSP device or a switch device. |
||
| Step 3 |
Enter the username and password for the CSP device or switch device, and click Enter. |
||
| Step 4 |
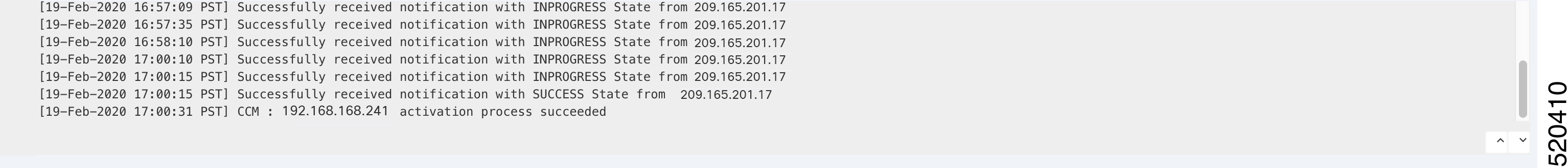
Get the PID and serial number (SN) of a CSP device. The following sample output shows the PID for one of the CSP devices. The output shows both the CSP device PID and serial number. |
||
| Step 5 |
Get the serial number of both the Catalyst 9500 switch devices. The following sample shows the serial number of the first switch. From this output, you can know the Catalyst 9500 switch series and the serial number. |
||
| Step 6 |
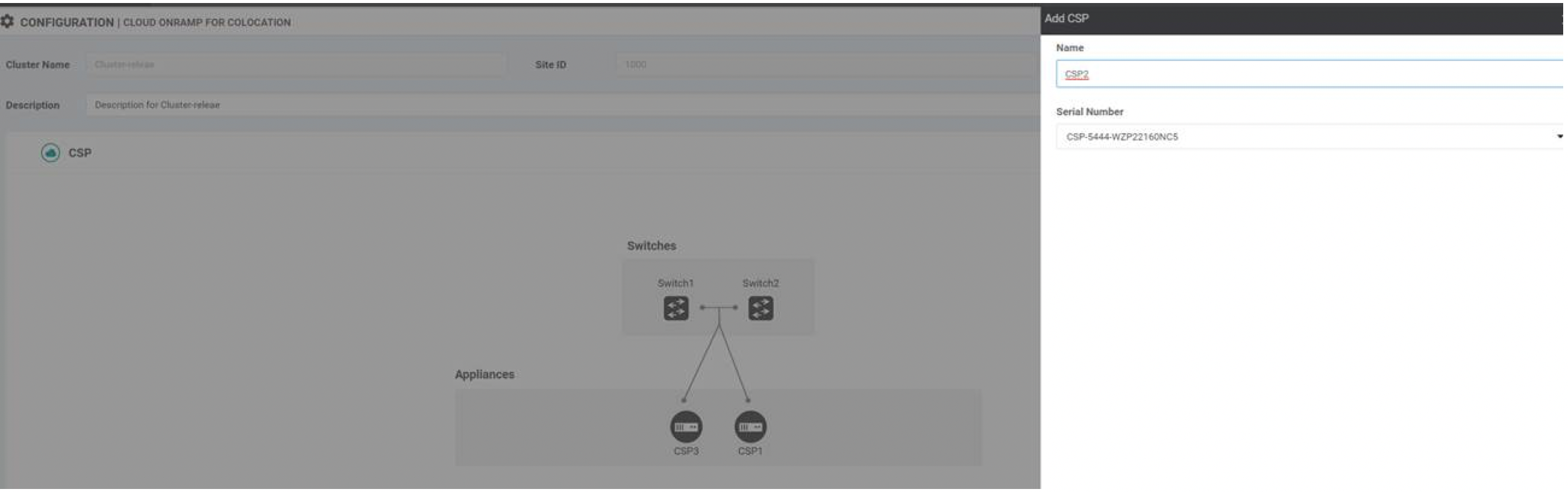
Create a .CSV file with the PID and serial number records for all the CSP devices and Catalyst 9500 switches in a colocation cluster. For example, from the information available from Steps 4,5, the CSV-formatted file can be as follows: C9500-40,FCW2229A0RK CSP-5444,SN WZP224208MB
|
||
| Step 7 |
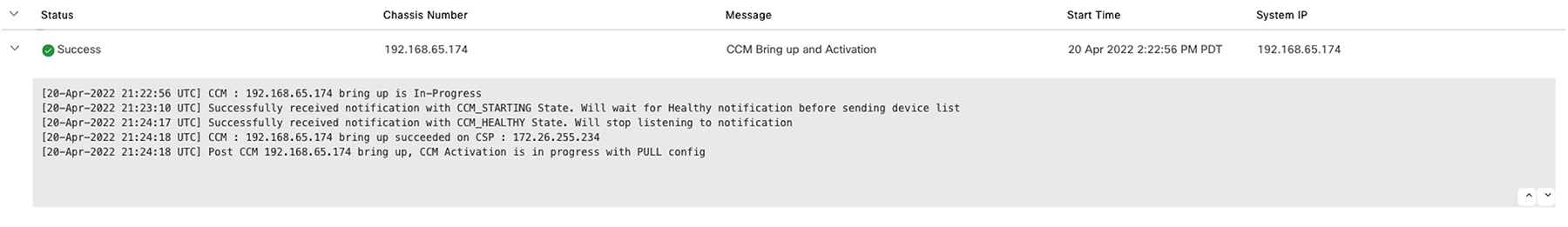
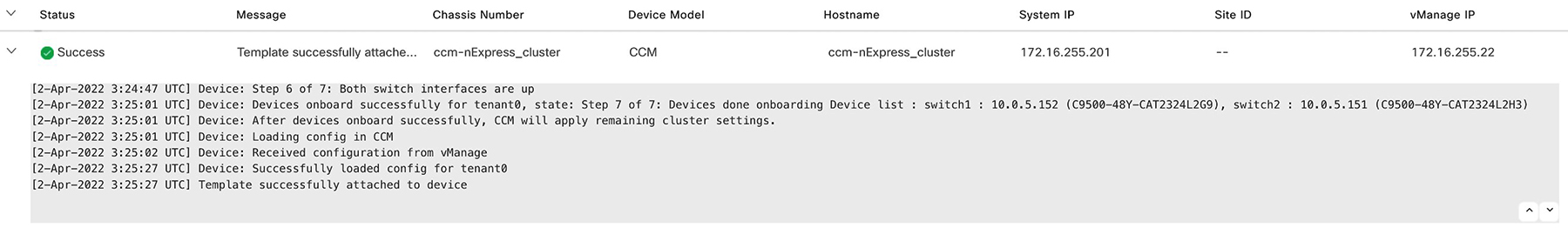
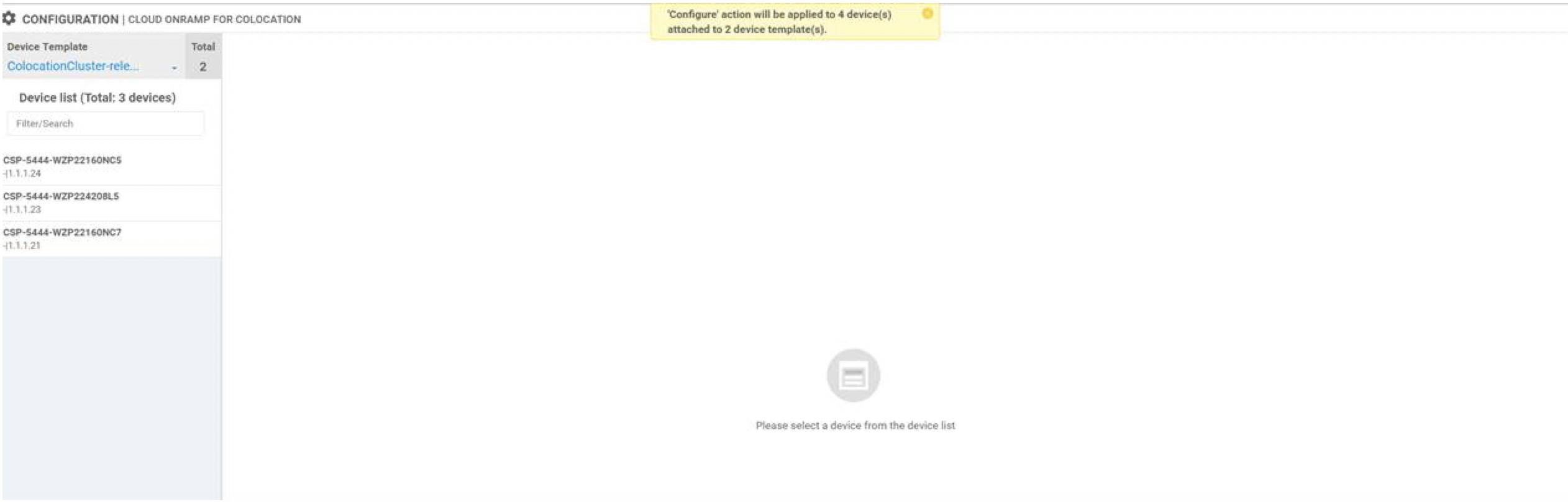
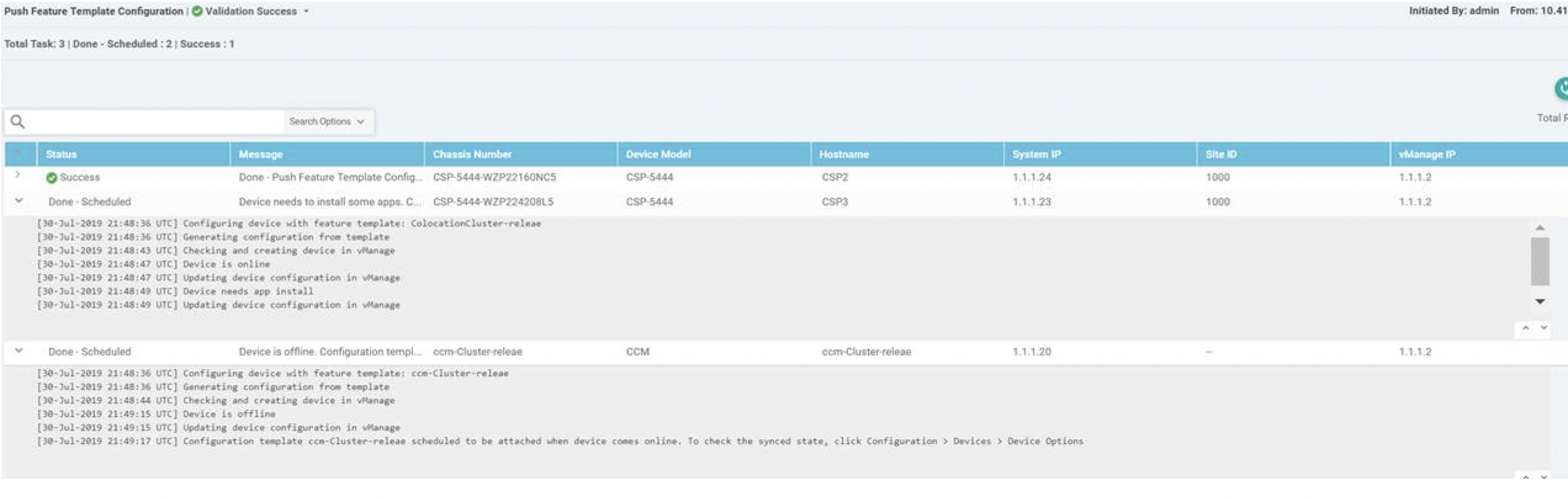
Upload all the CSP and switch devices using Cisco vManage. For more information, see Uploading a device authorized serial number file. |





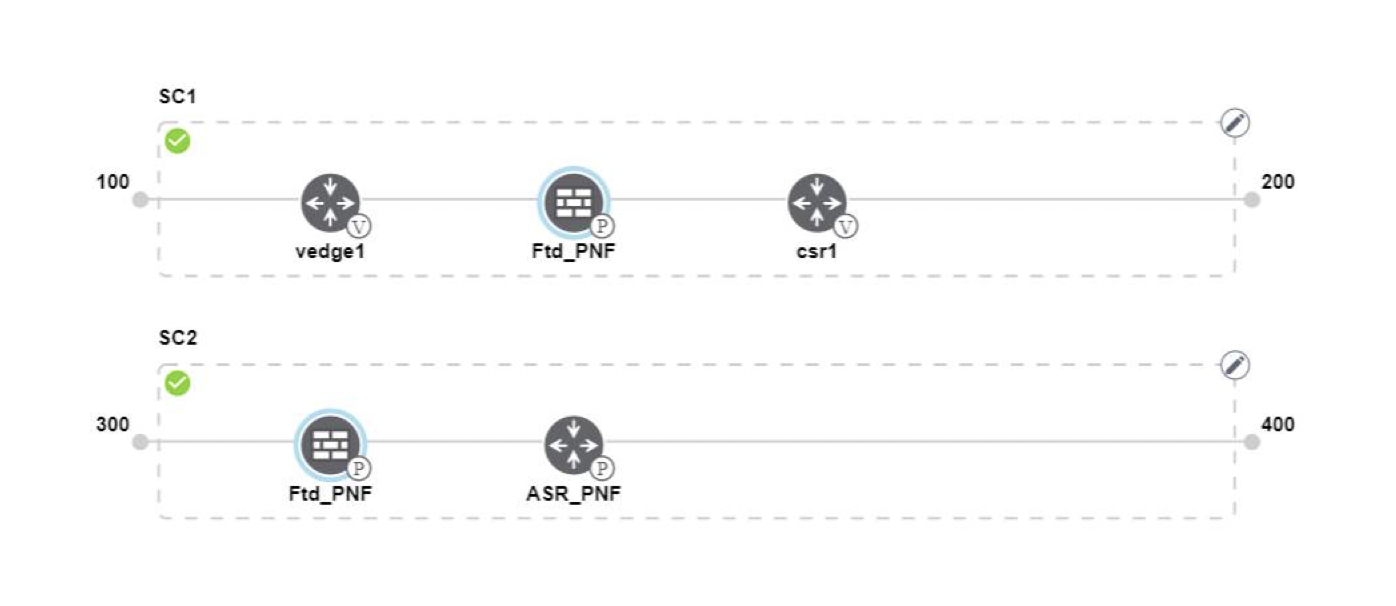



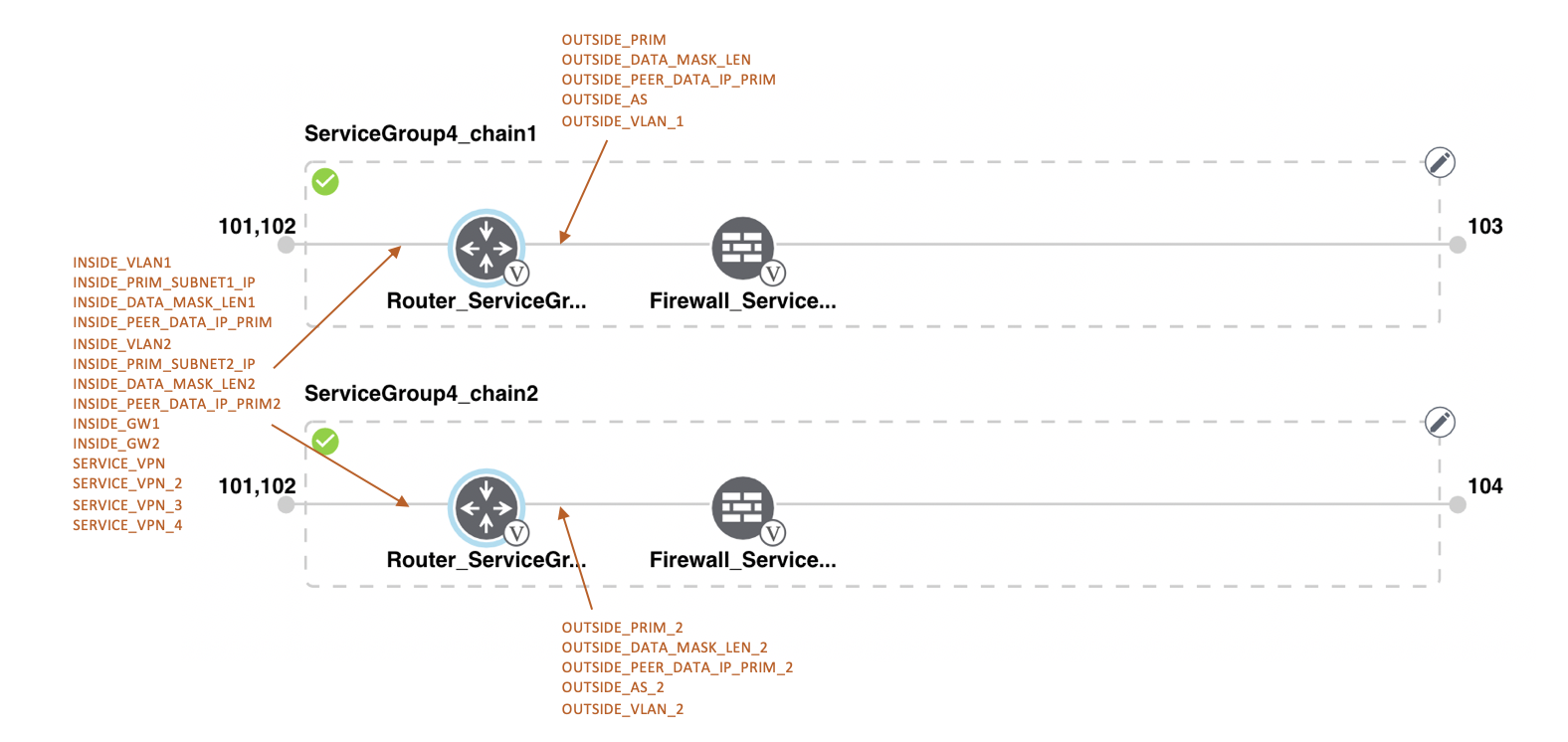


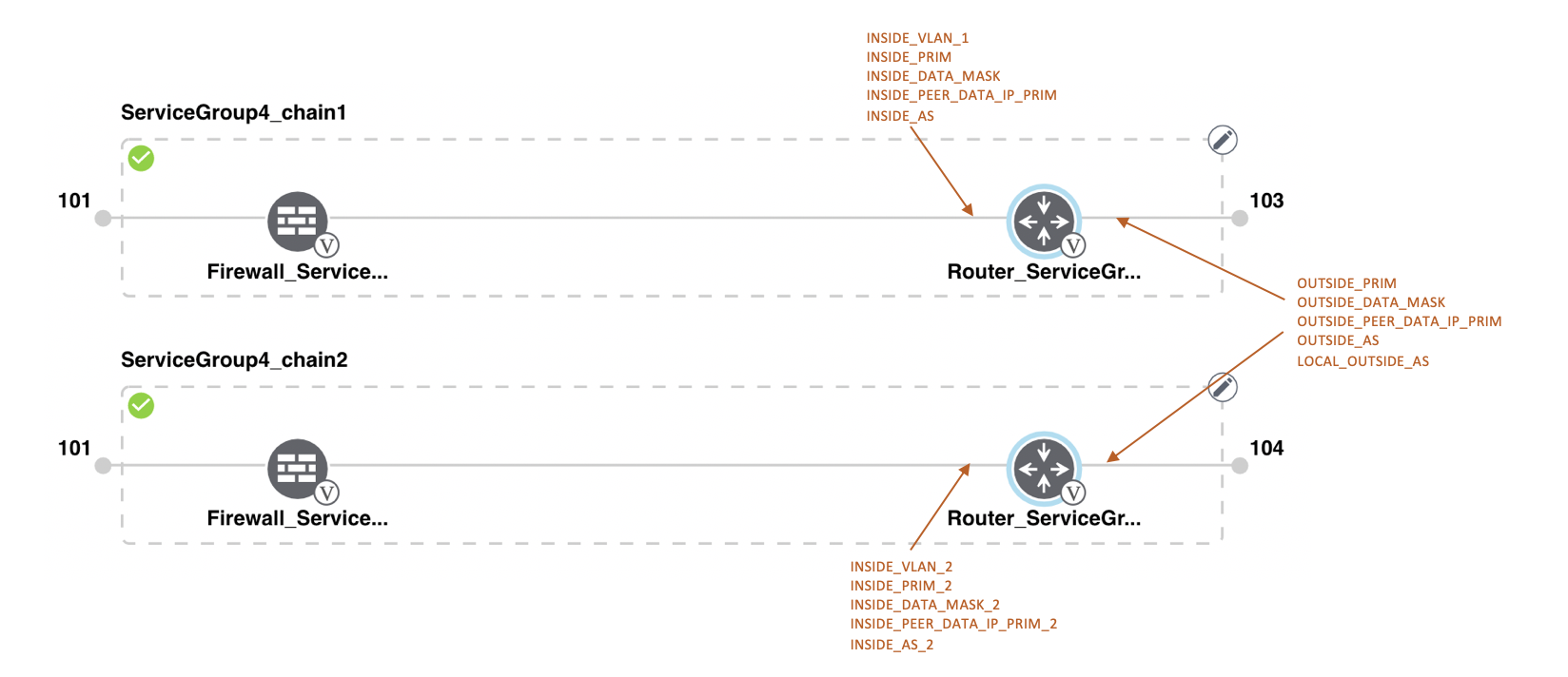

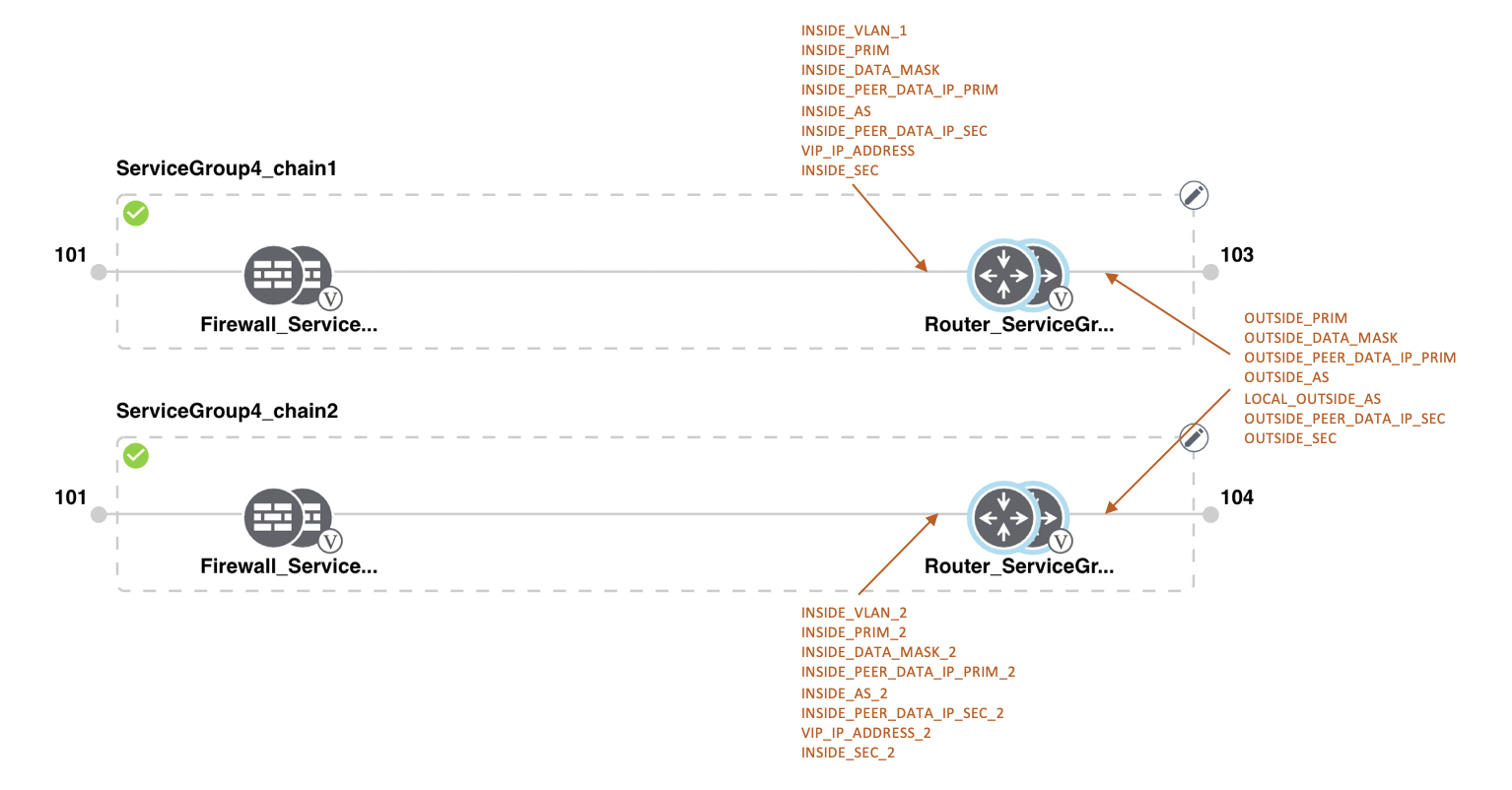


 Feedback
Feedback