Routed Optical Networking Overview
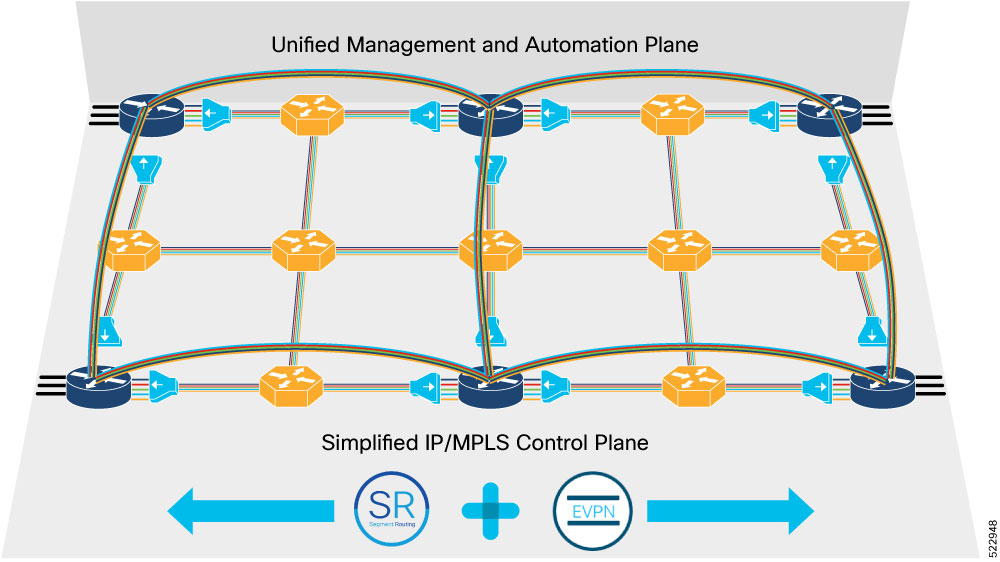
Routed Optical Networking simplifies complex multilayer networks by collapsing network layers and minimizing the functional overlap. Routed Optical Networking also improves the overall network efficiency by optimizing each layer of the network. The architecture also integrates open data models and standard APIs, enriching powerful automation making Routed Optical Networking easier to operate than legacy networks.
Routed Optical Networking is able to provide improvements and simplification because it:
-
Leverages state of the art optical and routing technologies to converge services over an IP infrastructure connected by a simplified DWDM layer
-
Merges IP and private line services onto a single unified IP layer
-
Simplifies end-to-end network architecture
-
Utilizes a modern software stack that spans across network management and control planes
-
Improves the capacity and cost efficiency of networks
-
Has a smaller carbon footprint
-
Offers unified capacity planning, unified EMS, unified path optimization, orchestration, and assurance
-
Provides an automation ecosystem with open, programmable, and modular components
-
Total Cost of Ownership savings across CapEx and OpEx
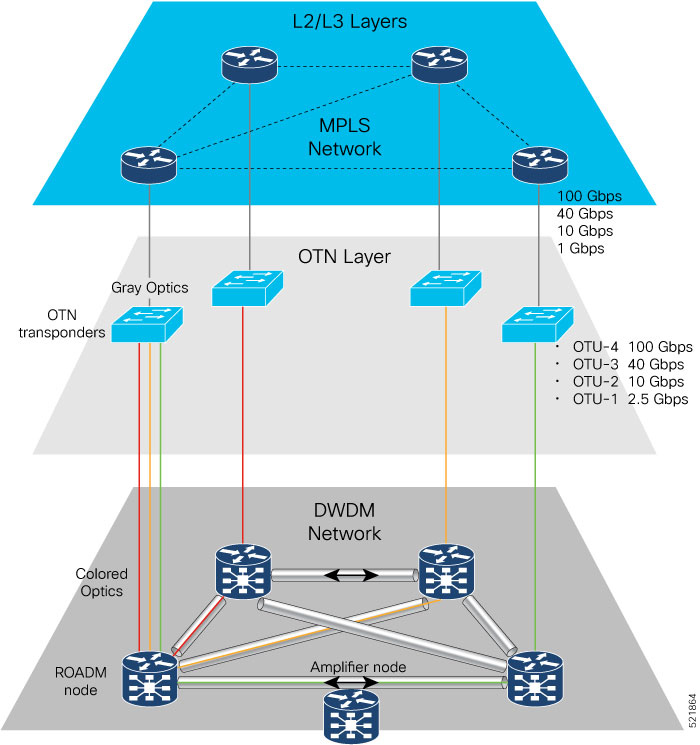
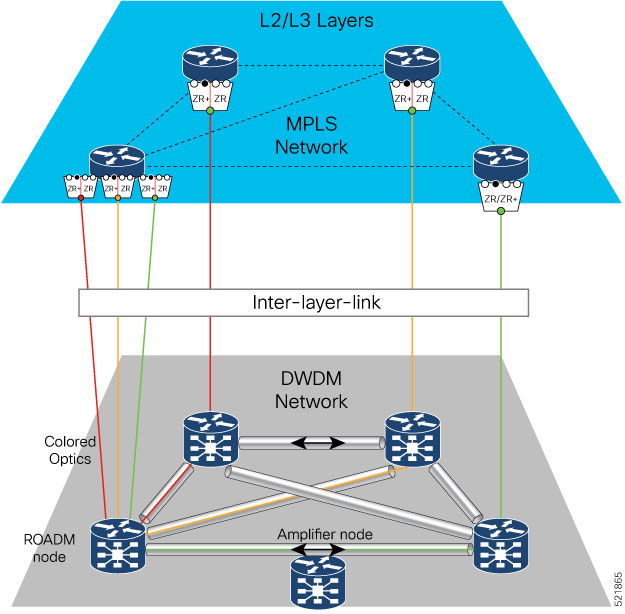
Routed Optical Networking utilizes high-density routers, high-capacity ZR or ZR+ pluggable digital coherent optics, simplified DWDM line systems, and end-to-end multi-layer automation to create next generation networks.
 Feedback
Feedback