Recover Router From Boot Failure
If the command line interface is not accessible, you can recover the router from a boot failure using one of these recovery methods.
Boot the Router Using USB Drive
Problem:
After installing the hardware, you boot the router after connecting to the console port and powering ON the router. The router initiates the boot process using the pre-installed operating system (OS) image. But the router fails to boot, times out or stops responding after the boot process initializes.
Cause:
The router does not boot if an install image is not present on the router or the image is corrupt.
Solution:
Boot the router using a bootable USB flash drive.
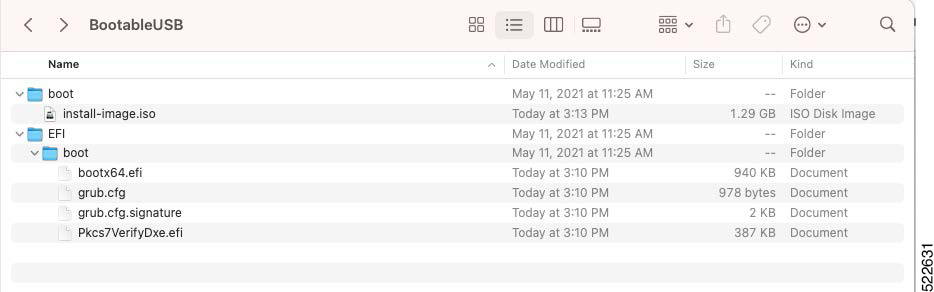
The bootable USB flash drive is used to reimage the router during system upgrade or boot the router in case of boot failure. During the USB boot process, the router is re-imaged with the version available on the USB flash drive.
To boot the router using a USB flash drive, you need the following devices:
-
A local machine (Windows, Linux, or MAC) with USB Type-A.
-
USB flash drive with a storage capacity that is between 8GB (min) and 32 GB (max). USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 are supported.

Note
USB Type-C is not supported.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Create a bootable USB flash drive from your local machine (Windows or MAC): |
|
Step 2 |
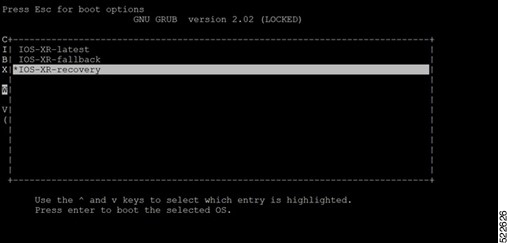
Boot the router using the bootable USB flash drive. |
Boot the Router Using iPXE
Problem:
You connect to the console port and power ON the router. The router initiates the boot process using the pre-installed operating system (OS) image. But the router fails to boot, times out or stops responding after the boot process initializes.
Cause:
The router does not boot if an install image is not present on the router or the image is corrupt.
Solution:
Boot the router using the image from an iPXE server.
iPXE is a pre-boot execution environment that is included in the network card of the management interfaces. It works at the system firmware (UEFI) level of the router. iPXE enables network boot for a router that is offline. The bootloader downloads and installs the ISO image located on an HTTP, FTP, or TFTP server. iPXE boot re-images the router. iPXE acts as a boot loader and provides the flexibility to choose the image that the system will boot based on the Platform Identifier (PID), the serial number, or the management MAC address. iPXE must be defined in the DHCP server configuration file.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Configure the DHCP server for IPv4, IPv6, or both communication protocols before you use the iPXE boot.
|
||
|
Step 2 |
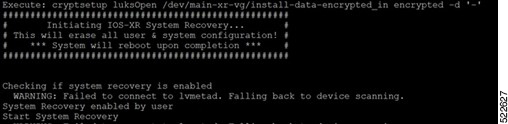
Recover the router using iPXE boot. You must keep the standby RP in the BIOS while installing the image on the active RP. The BIOS GRUB automatically detects the image from the iPXE server, starts the installation, and displays the progress of the installation operation. After the installation is complete, the router reboots and enters the prompt to configure the root username and password. You can also boot the router from the iPXE server by using the hw-module location all bootmedia network reload command. This command configures the router to perform a network-based boot across all modules in the router before a restart. Upon reload, the router attempts to load the operating system image from the specified iPXE server. |
 Feedback
Feedback