Overview
Cisco Nexus Dashboard Fabric Controller is the comprehensive management solution for all NX-OS deployments spanning LAN Fabric, SAN, and IP Fabric for Media (IPFM) networks in data centers powered by Cisco. Cisco Nexus Dashboard Fabric Controller also supports other devices, such as IOS-XE switches, IOS-XR routers, and non-Cisco devices. Being a multi-fabric controller, Cisco Nexus Dashboard Fabric Controller manages multiple deployment models like VXLAN EVPN, Classic 3-Tier, FabricPath, and Routed based fabrics for LAN while providing ready-to-use control, management, monitoring, and automation capabilities for all these environments. In addition, Cisco NDFC when enabled as a SAN Controller automates Cisco MDS Switches and Cisco Nexus Family infrastructure in NX-OS mode with a focus on storage-specific features and analytics capabilities.
Nexus Dashboard Fabric Controller primarily focuses on Control and Management for three primary market segments:
-
LAN networking including VXLAN, Multi-Site, Classic Ethernet, and External Fabrics supporting Cisco Nexus switches running standalone NX-OS, with additional support for IOS-XR, IOS-XE, and adjacent Host, Compute, Virtual Machine, and Container Management systems.
-
SAN networking for Cisco MDS and Cisco Nexus switches running standalone NX-OS, including support for integration with storage arrays and additionally Host, Compute, Virtual Machine, and Container Orchestration systems.
-
Media Control for Multicast Video production networks running Cisco Nexus switches operated as standalone NX-OS, with additional integrations for 3rd party media control systems.
Previously, DCNM was an application server running on a VM deployed via OVA or ISO, a physical appliance deployed via ISO, or software installed on a qualified Windows or Linux machine. Cisco Nexus Dashboard Fabric Controller, Release 12 is available as an application running exclusively on top of the Cisco Nexus Dashboard Virtual or Physical Appliance.
Virtual Nexus Dashboard deployment with OVA is also referred to as virtual Nexus Dashboard (vND) deployment, while the deployment of Nexus Dashboard on physical appliance (Service Engine) is known as physical Nexus Dashboard (pND) deployment. To deploy Nexus Dashboard based on your requirement, refer to Cisco Nexus Dashboard Deployment Guide.
Beginning with Release 12, Cisco Nexus Dashboard Fabric Controller has a single installation mode. Post installation, it supports selection from multiple personas at run-time. After the Nexus Dashboard Fabric Controller Release 12.1.3 is installed, you can choose from one of the following personas:
-
Fabric Discovery—Discover, Monitor, and Visualize LAN Deployments.
-
Fabric Controller—LAN Controller for Classic Ethernet (vPC), Routed, VXLAN, and IP Fabric for Media Deployments.
-
SAN Controller—SAN Controller for MDS and Nexus switches. Enhanced SAN Analytics with streaming telemetry.
 Note |
For any given instance of Nexus Dashboard, only one version of NDFC service will be active. On the active NDFC service, you can configure only one persona at any given instance. |
All features/services are modularized, broken into smaller microservices, and the required microservices are orchestrated based on the feature set or feature selections. Therefore, if any feature or microservice is down, only that microservice is restarted and recovered, resulting in minimal disruption.
In contrast to the previous DCNM Active-Standby HA model, Cisco NDFC introduces Active-Active HA deployment model utilizing all three nodes in a cluster for deploying microservices. This has significant improvement in both latency and effective resource utilization.
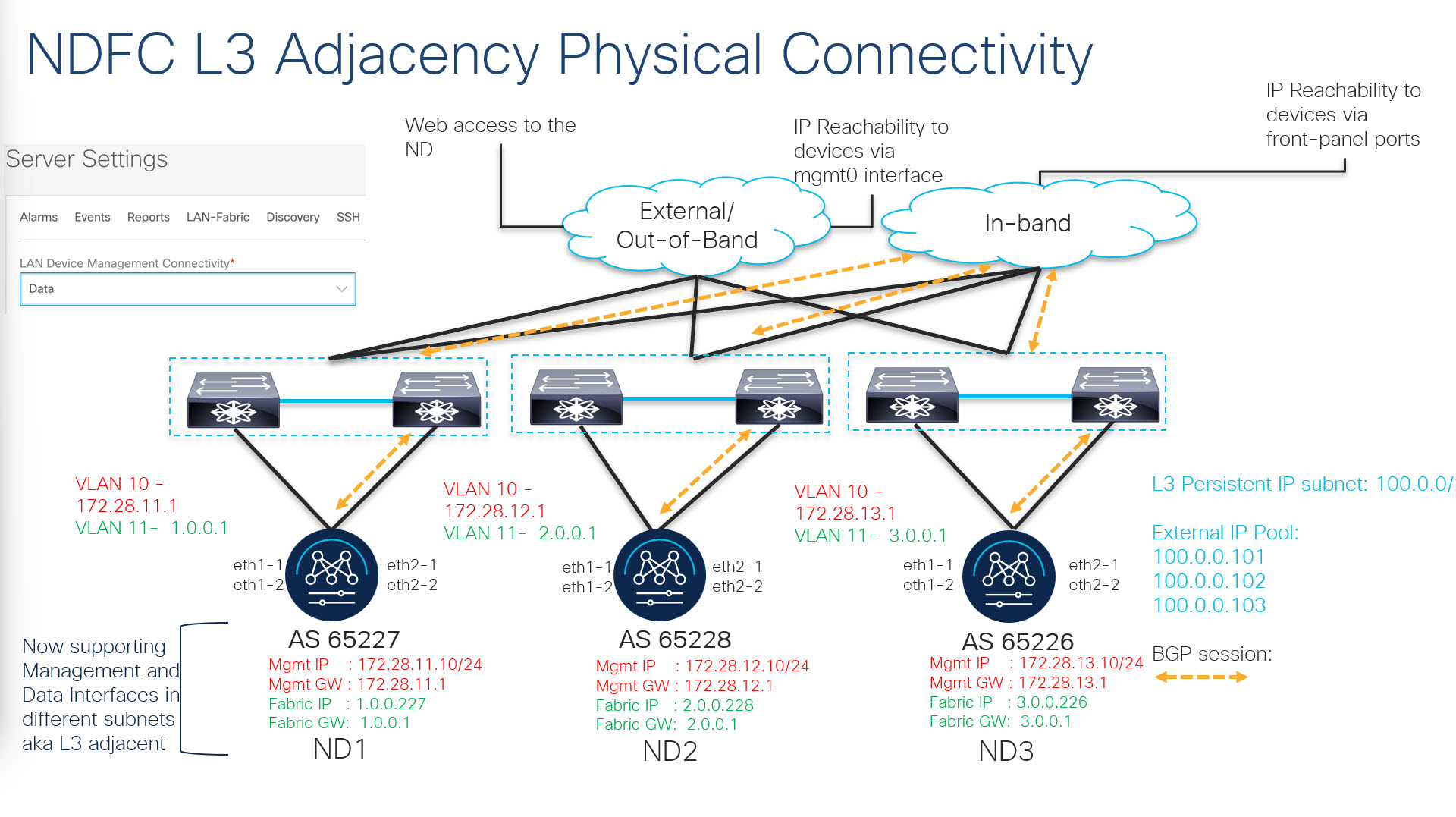
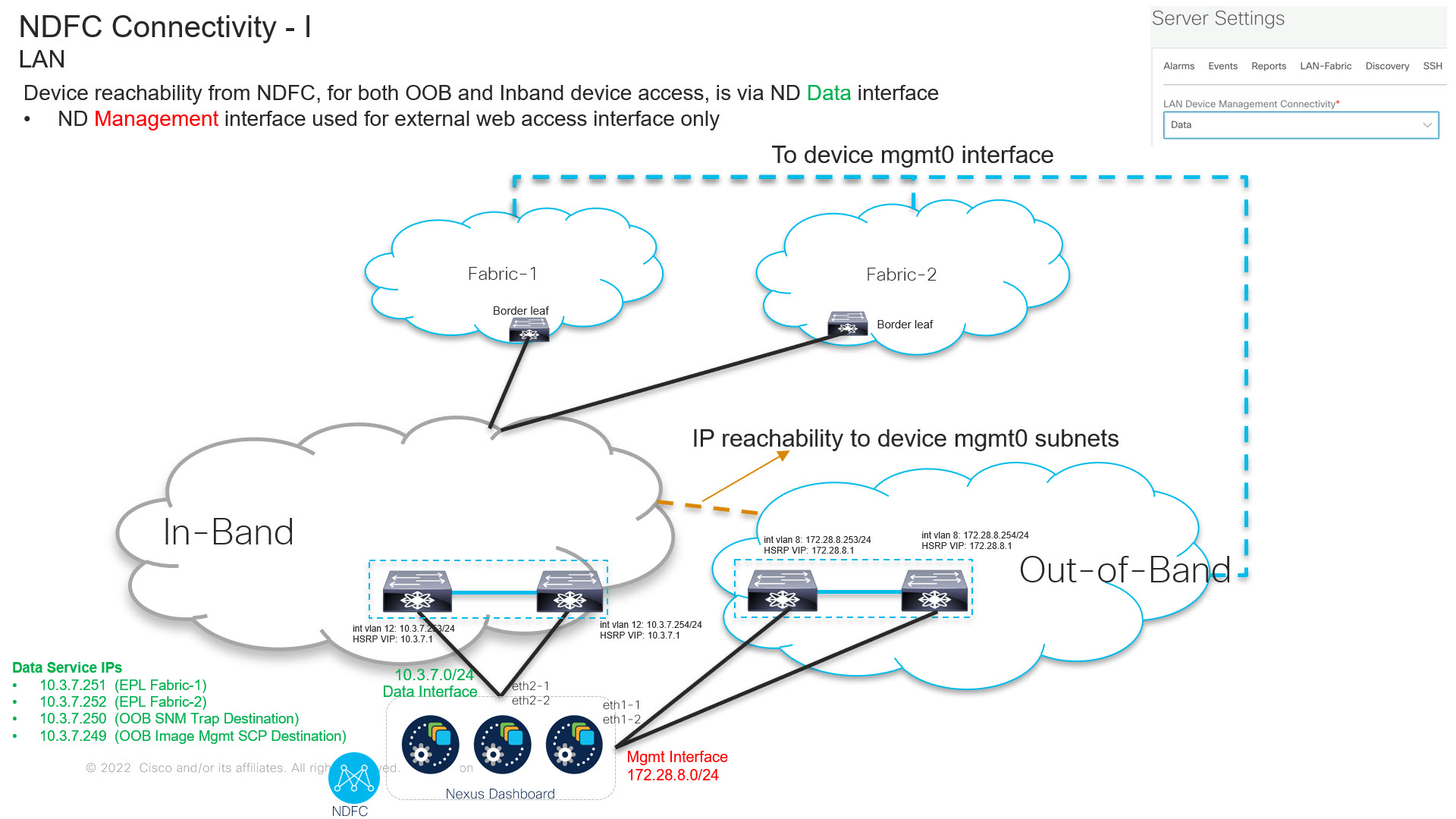
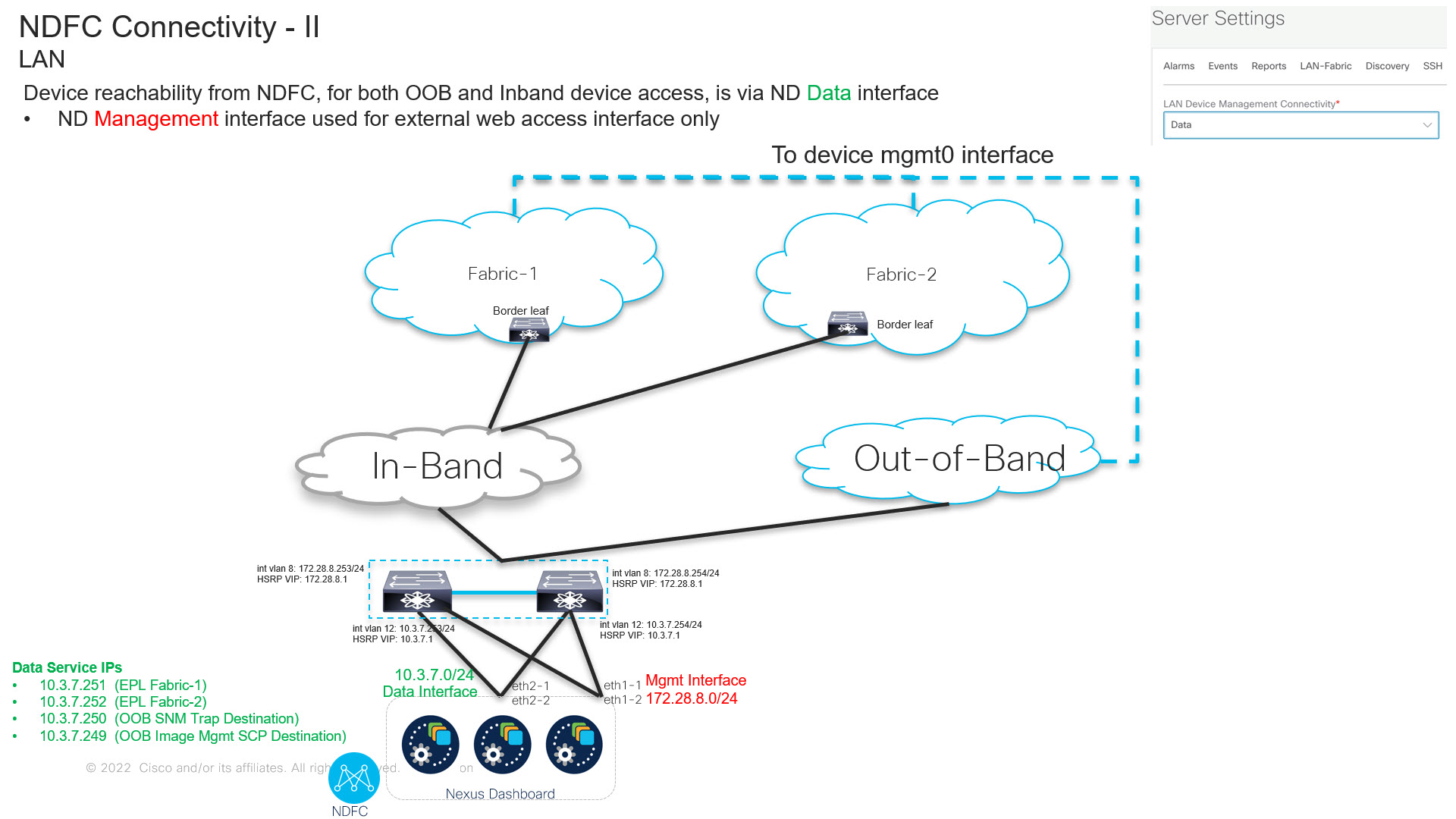
From Cisco NDFC Release 12.1.2, you can run NDFC on top of virtual Nexus Dashboard (vND) instance with promiscuous mode disabled on port groups that are associated with Nexus Dashboard interfaces where External Service IP addresses are specified. Recall that vND comprises a management interface and a data interface. By default, for LAN deployments, two external service IP addresses are required for the Nexus Dashboard management interface subnet. Similarly, by default, for SAN deployments, two external service IP addresses are required for the Nexus Dashboard data interface subnet.
Before the NDFC Release 12.1.2, if in-band management or Endpoint Locator or POAP feature was enabled on NDFC, you were required to enable promiscuous mode for the Nexus Dashboard data or fabric interface port-groups. This setting was mandatory for these features to work correctly. Again, as mentioned earlier, enabling promiscuous mode is no longer required for any port-groups associated with the vND. In fact, it is recommended to disable promiscuous mode for the port-groups post upgrade to ND 2.3.1/NDFC 12.1.2, in case customers are coming from previous versions.
 Note |
|
 Note |
Default option for promiscuous mode on VMware ESXi environments is Reject, meaning promiscuous mode is disabled. |
This release of NDFC supports hybrid cloud connectivity between on-prem and public cloud networks. Using Cisco Nexus Dashboard Orchestrator, connectivity is orchestrated between NDFC managed VXLAN fabric and Cloud Application Policy Infrastructure Controller (cAPIC) deployed on public cloud.
For more information, see Cisco Nexus Dashboard Fabric Controller (Formerly DCNM).
 Feedback
Feedback