Getting Started Guide: Cisco Aironet 1550 Series Outdoor Mesh Access Points
Available Languages
Table of Contents
Cisco Aironet 1550 Series Outdoor Mesh Access Points
FCC Safety Compliance Statement
Declaration of Conformity for RF Exposure
Declaration of Conformity with Regard to the EU Directive 1999/5/EC (R&TTE Directive)
Introduction to the Access Point Mono Band Antennas (used on AIR-CAP1552EU/CU APs)
Becoming Familiar With the Access Point Antenna Mounting Configurations
Point-to-Multipoint Mesh Network
Avoiding Damage to Radios in a Testing Environment
Verifying the Wireless LAN Controller Mode
Verifying the Wireless LAN Controller Software Version
Recording the Access Point MAC Address
Adding the Access Point MAC Address to the Wireless LAN Controller Filter List
Verifying Controller Association
Using a DHCP Server in a Layer 3 Mesh Network
Declarations of Conformity and Regulatory Information Manufacturers Federal Communication Commission Declaration of Conformity Statement
Guidelines for Operating Cisco Aironet Access Points in Japan
Statement 371—Power Cable and AC Adapter
European Community, Switzerland, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein
Declaration of Conformity with regard to the R&TTE Directive 1999/5/EC & Medical Directive 93/42/EEC
Declaration of Conformity for RF Exposure
Administrative Rules for Cisco Aironet Access Points in Taiwan
Operation of Cisco Aironet Access Points in Brazil
Declaration of Conformity Statements
Guidelines for Using the Access Point
Misconfigured Access Point IP address
Verifying the Controller MAC Filter List
Cisco 1-Year Limited Hardware Warranty Terms Cisco Aironet 1550 Series Outdoor Mesh Access Points
About this Guide
This guide is designed to familiarize yourself with your Cisco Aironet 1550 Series Outdoor Mesh Access Point and prepare it for use in your wireless network. Due to the complexity and number of product options available, this guide does not provide detailed mounting and configuration instructions. Those instructions can be found in the following documents:
- Cisco Mesh Networking Solution Deployment Guide
- Cisco Aironet 1550 Series Outdoor Mesh Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
- Cisco Aironet 1520 Series Access Point Power Injector Installation Instructions
Detailed configuration information can also be found in the Cisco wireless LAN controller documentation for the controller and software release you are using. These and other documents, such as the Cisco Aironet 1550 Data Sheet, are available on Cisco.com. Follow these steps to access these documents:
Step 1
Browse to http://www.cisco.com .
Step 2
Click Support. A pop-up window appears.
Step 3
Click Wireless under Select a Product Name. The Select Your Product or Technology page appears.
Step 4
Click Wireless > Outdoor Wireless.
Step 5
Click Cisco Aironet 1550 Series in the Search for a Specific Product field. The Cisco Aironet 1550 Series Introduction page appears.
Step 6
Choose the appropriate link for the documentation you want to view or download.
FCC Safety Compliance Statement
The FCC with its action in ET Docket 96-8 has adopted a safety standard for human exposure to radio frequency (RF) electromagnetic energy emitted by FCC certified equipment. When used with approved Cisco Aironet antennas, Cisco Aironet products meet the uncontrolled environmental limits found in OET-65 and ANSI C95.1, 1991. Proper installation of this radio according to the instructions found in this manual will result in user exposure that is substantially below the FCC recommended limits.
Declaration of Conformity for RF Exposure
This access point product has been found to be compliant to the requirements set forth in CFR 47 Section 1.1307 addressing RF Exposure from radio frequency devices as defined in Evaluating Compliance with FCC Guidelines for Human Exposure to Radio Frequency Electromagnetic Fields.
Use is permitted with antenna gain not exceeding 8 dBi in both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz band, as described in filing, with a minimum separation distance of 20 cm (8") between the antenna and all persons during normal operation.
Use is permitted with antenna gain not exceeding 13 dBi in the 2.4 GHz and 14 dBi in the 5 GHz band, as described in filing, with a minimum separation distance of 50 cm (20") between the antenna and all persons during normal operation.
Only antennas provided by Cisco for use with the product should be installed. The use of any other antennas may cause damage to the access points or violate regulatory emission limits and will not be supported by Cisco.
Declaration of Conformity with Regard to the EU Directive 1999/5/EC (R&TTE Directive)
This declaration is only valid for configurations (combinations of software, firmware and hardware) provided and/or supported by Cisco Systems. The use software or firmware not supported/provided by Cisco Systems may result that the equipment is no longer compliant with the regulatory requirements.
Warnings
Safety warnings appear throughout this guide in procedures that may harm you if performed incorrectly. A warning symbol precedes each warning statement. The warnings below are general warnings that are applicable to the entire guide. Specific warnings are included in the sections to which they apply.
Translated versions of the safety warnings in this guide are provided in the Safety Warnings for Cisco Aironet 1550 Series Outdoor Mesh Access Points document that accompanies this guide. The translated warnings are also in Appendix A of the Cisco Aironet 1550 Series Outdoor Mesh Access Point Hardware Installation Guide, which is available at cisco.com.

Warning This warning symbol means danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury. Before you work on any equipment, be aware of the hazards involved with electrical circuitry and be familiar with standard practices for preventing accidents. Use the statement number provided at the end of each warning to locate its translation in the translated safety warnings that accompanied this device.
Statement 1071
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS
Warning There is the danger of explosion if the battery is replaced incorrectly. Replace the battery only with the same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Statement 1015

Warning Do not operate the unit near unshielded blasting caps or in an explosive environment unless the device has been modified to be especially qualified for such use.
Statement 364
Warning This equipment must be externally grounded using a customer-supplied ground wire before power is applied. Contact the appropriate electrical inspection authority or an electrician if you are uncertain that suitable grounding is available.
Statement 366
Warning Read the installation instructions before connecting the system to the power source. Statement 1004

Warning Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment. Statement 1030

Warning Ultimate disposal of this product should be handled according to all national laws and regulations. Statement 1040
Introduction to the Access Point
The Cisco Aironet 1550 Series Outdoor Mesh Access Point (hereafter called the access point or AP) is a ruggedized outdoor access point designed for service in mesh networks. The 1550 series leverages 802.11n technology with integrated radio and internal/external antennas. The 1550 outdoor platform consists of Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) WLAN radios and integrated spectrum intelligence (Clean Air).
CleanAir provides full 802.11n data rates while detecting, locating, classifying and mitigating radio frequency (RF) interference to provide the best client experience possible. CleanAir technology on the outdoor 11n platform mitigates WiFi and non-WiFi interference on both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz radios.
The 1550 AP series contains a 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz radio with an option to configure in centralized, Flexconnect, or mesh mode. The 2.4 GHz radios are used primarily for local access, and the 5 GHz radios can be configured for both local access and/or wireless backhaul in the Mesh mode.
The 1550 series supports the modularity of the 1520 series and allows flexibility in radio configuration. In addition to full interoperability with 802.11n clients, the 1550 series interoperates with legacy clients and offers enhanced backhaul performance. The 1552C access point is configured with an integrated DOCSIS 3.0 cable modem.
The access point is a standalone unit that can be cable strand or tower mounted. The access point can also operate as a relay node for other access points not directly connected to a wired network. Intelligent wireless routing is provided by the Adaptive Wireless Path Protocol (AWPP). This enables each access point to identify its neighbors and intelligently choose the optimal path to the wired network by calculating the cost of each path in terms of signal strength and the number of hops required to get to a controller. The access point is configured, monitored, and operated through a Cisco wireless LAN controller (WLC), referred to as a controller in this document. The WLC is described in the appropriate Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide. The Cisco Mesh Networking Solution Deployment Guide describes how to plan and initially configure the Cisco mesh network, which supports wireless point-to-multipoint mesh deployments. The controllers use a browser-based management system, a command-line interface (CLI), or the Cisco Prime Infrastructure network management system to manage the controller and the associated access points. The access point is compliant with Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2) and employs hardware-based Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption between wireless nodes to provide end-to-end security.
Unpacking the Access Point
Follow these steps to unpack the access point:
Step 1
Open the shipping container and carefully remove the contents.
Step 2
Return all packing materials to the shipping container and save it.
Step 3
Ensure that all items listed in the “Package Contents” section are included in the shipment. Check each item for damage. If any item is damaged or missing, notify your authorized Cisco sales representative.
Package Contents
Each access point package contains the following items:
- One 1550 series access point
- Two-pin DC power connector
- Ground lug (Panduit PLCD6-10A-L) and screws with lock washers
- Watertight cable glands for Power-over-Ethernet (PoE) ports (depending on the 1552 access point model, 2 or 3 cable glands are provided)
- Cisco product documentation and translated safety warnings
Optional Equipment
Depending on what you ordered, the following optional equipment may be part of your shipment:
- External antennas, depending on which ones you purchased
- Strand mount kit (AIR-ACCSMK1550=)
- Pole mount kit (AIR-ACCPMK1550=)
- Band installation tool for pole mount kit (AIR-BAND-INS-TL=)
- AC power cord, 40 ft. (12.2 m) with North American plug (AIR-CORD-R3P-40NA=)
- AC power cord, 40 ft (12.2 m) with European unterminated end (AIR-CORD-R3P-40UE=)
- Street light power tap (AIR-PWR-ST-LT-R3P=)
- Power injector (AIR-PWRINJ1500-2=)
- 1000BASELX single-mode Rugged SFP (GLC-LX-SM-RGD=)
- 1000BASESX multimode Rugged SFP (GLC-SX-MM-RGD=)
- EPON ONU Rugged SFP module
- Battery, 6 amp hour (AIR-1520-BATT-6AH=)
- FIPS kit (AIRLAP-FIPSKIT=)
- Optional directional-antenna mounting kit (AIR-ACCAMK-1)
- Lightning arrestor (AIR-ACC245LA-N)
Configurations
There are two radio configurations for the 1552 AP radio, the 2 GHz MIMO radio and the 5 GHz MIMO radio. The 2GHz MIMO radio operates in 2.4 GHz ISM band. It supports channels 1-11 in US, 1-13 in Europe, and 1-13 in Japan.The 5GHz MIMO radio operates in the UNII-2 band (5.25 – 5.35 GHz), the UNII-2 Extended/ETSI band (5.47 – 5.725 GHz), and the upper ISM band (5.725 – 5.850 GHz).
The configurations for the two 1552 radios are:
- AIR-CAP1552E-x-K9 2.4GHz b/g/n, 5GHz a/n MIMO, Outdoor Mesh AP with external antennas
- AIR-CAP1552H-x-K9 2.4GHz b/g/n, 5GHz a/n MIMO, Outdoor Mesh AP for hazardous locations
- AIR-CAP1552C-x-K9 2.4GHz b/g/n, 5GHz a/n MIMO, Outdoor Mesh AP with integrated antennas and DOCSIS 3.0 and Euro DOCSIS 3.0 Cable Modem
- AIR-CAP1552I-x-K9 2.4GHz b/g/n, 5GHz a/g/n MIMO, Outdoor Mesh AP with integrated antennas
- AIR-CAP1552EU-x-K9 Band Separated Outdoor Mesh AP with External Antennas
- AIR-CAP1552CU-x-K9 Band Separated Outdoor Mesh Cable AP with External Antenna and DOCSIS 3.0 and EURO DOCSIS 3.0 Cable Modem
For information on the regulatory domains (shown above as “x”) see “Regulatory Domains” section .
Regulatory Domains
For the latest details and accurate listing of country homologation, refer to “Table 3. 802.11abgn Mesh Access Points” on the Wireless-LAN-Compliance-Status page at:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/wireless/aironet-1300-series/product_data_sheet0900aecd80537b6a.html#wp9005628Becoming Familiar With the Access Point
The following illustrations show identify the access point connections. Before you begin the installation process, use these illustrations to familiarize yourself with the access point.
Note The illustrations show all available connections for the configuration ordered. Unused connections are capped to ensure the watertight integrity of the access point. Liquid tight connectors are provided for all ports, which can be installed prior to or after deploying the access point.
Figure 1 and Figure 3 shows the access point bottom and side connectors for models AIR-CAP1552E-x-K9, AIR-CAP1552EU-x-K9, and AIR-CAP1552H-x-K9.
Figure 2 and Figure 6 show the access point top connectors for AIR-CAP1552EU-x-K9 and AIR-CAP1552CU-x-K9.
Figure 4 and Figure 5 show the access point bottom and side connectors for models AIR-CAP1552I-x-K9, AIR-CAP1552C-x-K9, and AIR-CAP1552CU-x-K9.
Figure 7 shows the RF splitter components for models AIR-CAP1552C-x-K9 and AIR-CAP1552CU-x-K9.
Figure 8 shows the access point right side connectors for all models.
Figure 1 Access Point Bottom Connectors - Models AIR-CAP1552E-x-K9, AIR-CAP1552EU-x-K9, and AIR-CAP1552H-x-K9

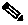
Note Antenna ports 1, 2 and 3 are not shown in Figure 1. These ports are reserved for future use and will be located on the top of the access point.
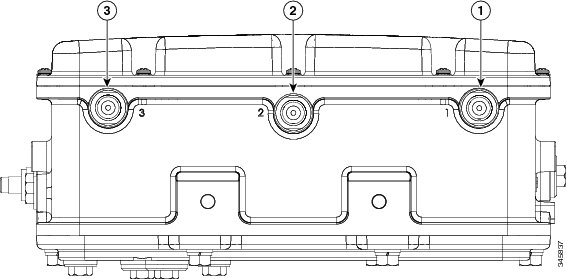
Figure 2 Access Point Top Connectors - Model AIR-CAP1552EU-x-K9
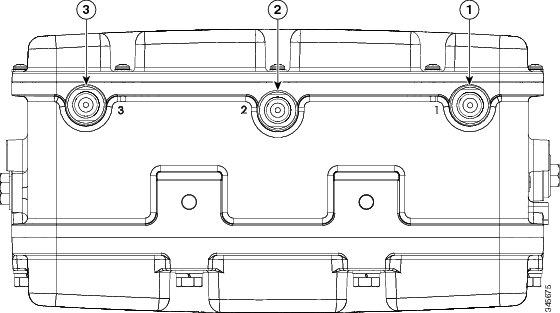
Figure 3 Access Point Left Side Connectors - Models AIR-CAP1552E-x-K9, AIR-CAP1552EU-x-K9, and AIR-CAP1552H-x-K9

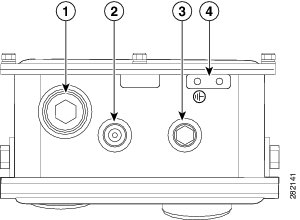
Figure 4 Access Point Bottom Connectors - Model AIR-CAP1552I-x-K9

Figure 5 Access Point Bottom and Left Side Connectors - Model AIR-CAP1552C-x-K9 and AIR-CAP1552CU-x-K9 (1552C shown)
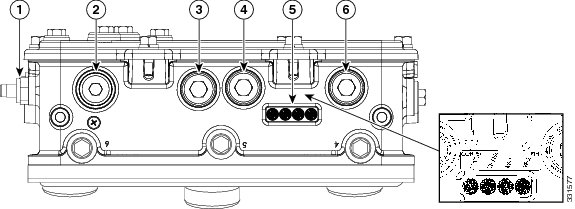
Figure 6 Access Point Top Connectors - Model AIR-CAP1552CU-x-K9
The RF splitter components are shown in Figure 7 .
Figure 7 RF Splitter Components
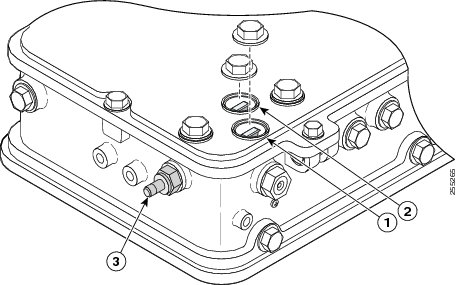
Figure 8 shows the access point DC power connector and ground lug.
Figure 8 Access Point DC Power Connector and Ground Lug (All Models)
Radio Operation
The 1552 access point 802.11b/g/n radio is used primarily for local access and its 802.11a/n radio for wireless backhaul in the Mesh.
The 2 GHz b/g/n radio operates in 2.4 GHz ISM band. It supports channels 1-11 in US, 1-13 in Europe, and 1-13 in Japan. It has two transmitters with a maximum total output power of 25dBm for 802.11b/g/n operation. Output power is configurable to 5 levels. It has three receivers that enables maximum-ratio combining (MRC).
The 5GHz a/n radio operates in the UNII-2 band (5.25 - 5.35 GHz), UNII-2 Extended/ETSI band (5.47 - 5.725 GHz), and the upper ISM band (5.725 - 5.850 GHz). It has two transmitters with a maximum total output power of 26 dBm for UNII-2 and Extended/ETSI bands for the A-domain. The total maximum output power for the upper ISM band is 28 dBm for A-domain. Tx power settings will change depending on the regulatory domain. Output power is configurable for 5 power levels in 3 dB steps. Its three receivers enables maximum-ratio combining (MRC).
The 1552 models C and I access points are equipped with three integrated dual-band antennas, with 2 dBi gain at 2.4 GHz and 4 dBi gain at 5 GHz. The antenna works in cable strand mount and low profile applications.
External Antenna Option

Warning In order to comply with radio frequency (RF) exposure limits, the antennas up to 8 dBi gain for this product should be placed no less than 20 cm (8") from your body or nearby persons. This distance shall be increased to 50 cm (20 ") with antennas that have gain between 8 and 14 dBi. Statement 339

Warning Do not locate the antenna near overhead power lines or other electric light or power circuits, or where it can come into contact with such circuits. When installing the antenna, take extreme care not to come into contact with such circuits, because they may cause serious injury or death. For proper installation and grounding of the antenna, please refer to national and local codes (for example, U.S.:NFPA 70, National Electrical Code, Article 810, Canada: Canadian Electrical Code, Section 54). Statement 1052

Warning Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment.
Statement 1030The 1552E and 1552H access points are equipped with three N-type radio frequency (RF) connectors (antenna ports 4, 5, and 6) on the bottom of the unit for external antennas to support multiple input multiple output (MIMO) operation as shown in Figure 9 . The 1552E and 1552H models must always be operated with the three external antennas attached. When using the Cisco Aironet AIR-ANT2547V-N Dual-Band Omnidirectional Antenna, the 2.4- and 5-GHz antennas connect directly to the access point, as shown in Figure 10 . If the antennas are remotely located, an appropriate low loss RF coax cable should be used.
The 1552EU and 1552CU access points are equipped with six N-type radio frequency (RF) connectors (antenna ports 1-3 on the top of the unit for 5 GHz and antenna ports 4-6 on the bottom of the unit for 2.4 GHz) for external antennas to support multiple input multiple output (MIMO) operation. The antenna ports located of top of the 1552EU and 1552CU models are shown in Figure 11 . The 1552EU and 1552CU models must always be operated with the appropriate external antennas attached.
Figure 9 Access Point External Antenna Connectors - Models AP-CAP1552E-x-K9, and AP-CAP1552H-x-K9
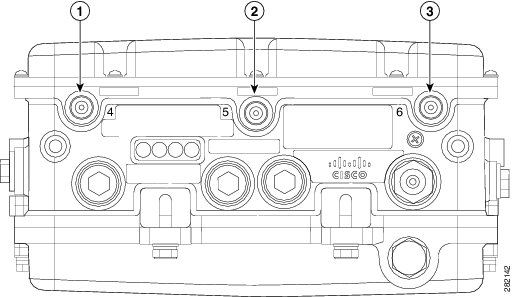
Figure 10 Access Point Dual-Band Omnidirectional Antennas - Installed Only on Models AIR-CAP1552E-x-K9 and AIR-CAP1552H-x-K9

Antenna connected to antenna port 4 (Type-N connector) (TX/RX)
Antenna connected to antenna port 6 (Type-N connector) (TX/RX)
Antenna connected to antenna port 5 (Type-N connector) (RX only)
Figure 11 Access Point External Antenna Connectors - Models AP-CAP1552EU-x-K9 and AP-CAP1552CU-x-K9 only

Note The FCC limits the amount of power this device can transmit. Power transmitted is a combination of the amplification of the signal and the antenna gain. The access point has been designed to operate with the Cisco provided antennas.
Integrated Antenna Option
The 1552C and 1552I models use the Integrated Low Profile Dual-Band 2.4/5 GHz Dipole Antenna Array. The antenna contains an array of three dual-band dipole antennas. The three dipole antennas are contained within this single radome, thereby greatly reducing the antennas visual footprint, and greatly reducing the possibility of snagging the antenna on the cable bundle, the RF cable, or test cables. The antennas operate over both 2.4 GHz and 5.25 – 5.85 GHz bands. Each of the three dipole antennas is a dual-band antenna, covering both the 2.4 – 2.483 GHz band, and the 5.25 – 5.85 GHz bands. The antenna have a peak gain of about 2 dBi at 2.4 GHz and 4 dBi at 5 GHz. The antenna unit is gray weatherproof radome for outdoor operation.
The low profile integrated antennas are attached to the bottom of a Cisco access point. The 1552C comes with the option of a C-bracket for strand mounting. The 1552C mesh access point chassis mounting brackets and low profile antenna all fit within the 30 cm vertical right-of-way for cable strand-mounted equipment. The antennas are internally connected to the diplexer ports of the outdoor mesh access point 2.4/5 GHz 2x3 MIMO radios.
Figure 12 shows an installed integrated low-profile dual-band (2.4 GHz and 5.25 GHz) 3-element array antenna. It is available on models AIR-CAP1552I-x-K9 and AIR-CAP1552C-x-K9.
Figure 12 Access Point Cisco Integrated Low-Profile Dual-Band 2.4/5 GHz Omni Antenna Array – Built-In on Models AIR-CAP1552C-x-K9 and AIR-CAP1552I-x-K9
Antenna Mounting Configurations
The selection of the antenna is determined in the configuration of the product. Depending on the 1552 models selected, the antennas can be mounted on a pole and/or cable strand mounted. Refer to the Cisco Aironet 1550 Outdoor Mesh Access Point Hardware Installation Guide for detailed information on mounting the antennas.
Power

Warning Installation of the equipment must comply with local and national electrical codes. Statement 1074

Warning This equipment must be externally grounded using a customer-supplied ground wire before power is applied. Contact the appropriate electrical inspection authority or an electrician if you are uncertain that suitable grounding is available. Statement 366

Warning Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during periods of lightning activity. Statement 1001
The 1550 series access point supports these power sources:
- AC power—100 to 480 VAC, models 1552E and 1552EU access points, pole-mount configuration
- AC power—100 to 277 VAC, model 1552I access point
- Power-over-Cable (POC)—40 to 90 VAC, quasi-square wave AC, models 1552C and 1552CU (standard power source for the cable modem configuration)
- External 12 VDC
- Power-over-Ethernet (PoE)—56 VDC power injector (AIR-PWRINJ1500-2=), only on models 1552E and 1552EU access points
- Internal 6 ampere-hour battery backup—only for the 1552E and 1552EUaccess point
Caution Do not place the power injector in an unprotected outdoor environment because water could get into the power injector and cause a short circuit and possible fire.
Warning Connect the unit only to DC power source that complies with the Safety Extra-Low Voltage (SELV) requirements in IEC 60950 based safety standards Statement 1033
The 1550 series access point can be connected to more than one power source. The access point detects available input sources and switches to the preferred power source using the following prioritization:

Warning This unit might have more than one power supply connection. All connections must be removed to de-energize the unit. Statement 1028

Warning To reduce the risk of fire, use only No. 26 AWG or larger telecommunication line cord. Statement 1023

Caution To provide inline PoE, you must use the 1500 power injector (AIR-PWRINJ1500-2=). Other power injectors, PoE switches, and 802.3af power sources cannot provide adequate power, which may cause the access point to malfunction and cause over-current conditions at the power source. You must ensure that the switch port connected to the access point has PoE turned off.

Caution When the access point is installed outdoors or in a wet or damp location, the AC branch circuit that is powering the access point should be provided with ground fault protection (GFCI), as required by Article 210 of the National Electrical Code (NEC).
Note In the cable configuration, the cable modem is activated only when the access point is powered by POC or external 12 VDC power. When using only PoE power, the cable modem is deactivated.
Three AC power cord options are available:
- 40-ft (12.2-m) power cord for installations in the US and Canada. One end of the power cord is terminated with an access point AC power connector and the other end is terminated with an AC plug (AIR-CORD-R3P-40NA=).
- 40-ft (12.2-m) power cord for use outside the US and Canada. One end of the power cord is terminated with an access point AC power connector and the other end is unterminated. (AIR-CORD-R3P-40UE=).
- 4-ft (1.2-m) streetlight power tap adapter for light pole installations in the US and Canada (AIR-PWR-ST-LT-R3P=).
Ethernet (PoE) Ports
The access point supports an Ethernet uplink port (PoE-In) and a PoE out port (PoE-Out). The access point Ethernet uplink port uses an RJ-45 connector (with weatherproofing) to link the access point to the 10BASE-T, 100BASE-T, or 1000BASE-T network. The Ethernet cable is used to send and receive Ethernet data and to optionally supply inline 56-VDC power from the power injector.
Note When a 1552E or 1552EU access point is powered by PoE, the PoE-Out port is not active.
The access point PoE-Out Ethernet port uses an RJ-45 connector (with weatherproofing) to provide LAN connectivity and IEEE 802.3af power to a peripheral customer device, such as a camera or sensor gateway. The PoE-out port should not be connected to a switch or hub. The Ethernet MAC addresses are printed on a label on the bottom of the access point under the LEDs.
Note The PoE-out port is disabled when the access point is powered by the power injector.

Tip The access point senses the Ethernet and power signals and automatically switches internal circuitry to match the cable connections.

Warning To reduce the risk of fire, use only No. 26 AWG or larger telecommunication line cord. Statement 1023
The Ethernet cable must be a shielded outdoor rated Category 5e (CAT5e) or better cable. The access point senses the Ethernet and power signals and automatically switches internal circuitry to match the cable connections.

Cable Option
The access point POC cable modem configuration contains an internal cable modem for connection to the cable network from the pole-mounted cable lines. The access point can be powered using the 40-to 90-VAC (quasi-square wave AC) power provided by the cable network.
Fiber Option

Warning Class 1 laser product. Statement 1008
The factory-orderable fiber option provides a fiber input and output capability. Fiber data is transmitted and received over a single-strand fiber cable, which is connected to the access point using these small-factor pluggable (SFP) modules:
- 100BASE-BX10-U fiber Rugged SFP module
- 1000BASELX single-mode Rugged SFP module
- 1000BASESX multimode Rugged SFP module
Note SFP modules are not hot-swappable.
One fiber connection is available on both the 1552E and 1552H access points. The fiber connection is on the bottom of both the 1552E and 1552H access points (shown on Figure 1). Client data is passed to the network controller through the fiber connection via a fiber capable switch. For detailed installation information about the fiber option, see the Cisco Aironet 1550 Series Outdoor Mesh Access Point Hardware Installation Guide. Configuration information can be found in the controller configuration guide of the controller you are using.
Network Deployment Examples
The access point is a wireless device designed for wireless client access and point-to-point bridging, point-to-multipoint bridging, and point-to-multipoint mesh wireless connectivity. The access point provides 5-GHz backhaul capability to link with another access point to reach a wired network connection or to provide repeater operations for other access points.
The access point plays two primary radio roles: a root access point (hereafter called a RAP) or a mesh (non-root) access point (hereafter called a MAP), which is the default role of all access points. When the access point has a fiber or wired Ethernet or cable connector connection to the controller (through a switch), the radio role is called a RAP. In order to be considered a RAP, the access point must be configured as a RAP. A RAP is a parent node to any bridging or mesh network. A controller can support one or more RAPs, each one parenting the same or different wireless networks. There can be more than one RAP for the same mesh network for redundancy. RAPs and MAPs can support wireless clients on the 2.4-GHz and 5-GHz band. Client access on 5-GHz is called universal client access.
When the access point does not have a wired Ethernet connection to the controller (through a switch), the radio role is called a MAP. The MAPs have a wireless connection (through the backhaul interface) to other MAPs and finally to a RAP which has an Ethernet connection through a switch to the controller. MAPs may also have a wired Ethernet connection to a local LAN and serve as a bridge endpoint for that LAN (using a point-to-point or point-to-multipoint bridge connection).
Wireless Backhaul
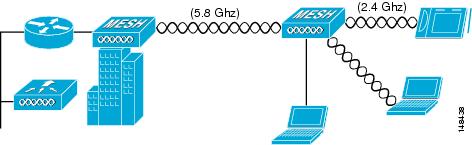
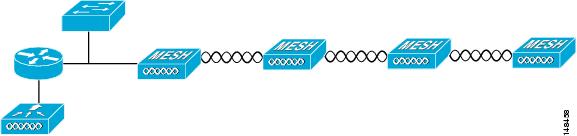
The access point supports wireless backhaul capability using the 5-GHz radio to bridge to another access point to reach a wired network connection to a controller as shown in Figure 13 . The access point connected to the wired network is considered a RAP in this configuration. The remote access point is considered a MAP and transfers wireless client traffic to the RAP for transfer to the wired network. Control And Provisioning of Wireless Access Points (CAPWAP) control traffic is also transferred over this bridged link.
Figure 13 Access Point Backhaul Example
Point-to-Point Bridging
The access points can be used to extend a remote network by using the 5-GHz backhaul radio to bridge the two network segments as shown in Figure 14 . To support Ethernet bridging, you must enable bridging on the controller for each access point. By default this capability is turned-off for all access points.
Wireless client access is supported; however, if bridging between tall buildings, the 2.4-GHz wireless coverage area may be limited and possibly not suitable for direct wireless client access.
Figure 14 Access Point Point-to-Point Bridging Example
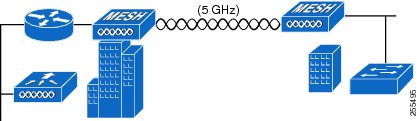
Point-to-Multipoint Bridging
The access points can be used as a RAP to connect multiple remote MAPs with their associated wired networks. By default this capability is turned-off for all access points. To support Ethernet bridging, you must enable bridging on the controller for each access point. Wireless client access can be provided over the bridging link; however, if bridging between tall buildings, the 2.4-GHz wireless coverage area may be limited and possibly not suitable for direct wireless client access.
Figure 15 illustrates an example of access point-to-multipoint bridging.
Figure 15 Access Point Point-to-Multipoint Bridging Example
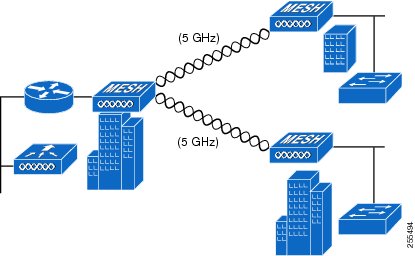
Point-to-Multipoint Mesh Network
The access point is typically deployed in a mesh network configuration. In a typical mesh deployment, one or more RAPs have a wired network connection through a switch to a controller. Other remote MAPs without wired network connections use the backhaul feature to optimally link to a RAP that is connected to the wired network. In the mesh network, the links between the access points are referred to as the backhaul links.
Intelligent wireless routing is provided by the Adaptive Wireless Path protocol (AWPP). This enables each MAP to identify its neighbors and intelligently choose the optimal path to the RAP with the wired network connection by calculating the cost of each path in terms of signal strength and the number of hops required to get to a controller with signal strength given priority since signal strength determines the data rate available for backhaul.
Figure 16 illustrates a typical mesh configuration using access points.
Figure 16 Typical Mesh Configuration Using Access Points
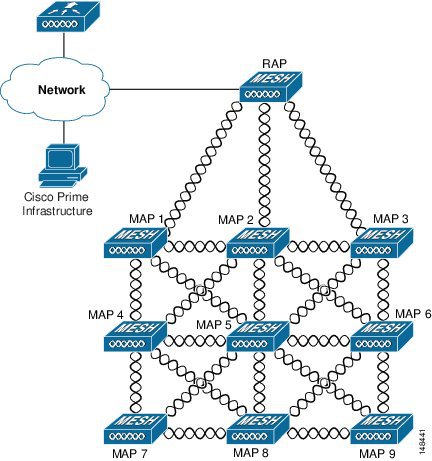
Layer 3 Network Operation
The access points support Layer 3 network operation. Access points and controllers in Layer 3 configurations use IP addresses and UDP packets, which can be routed through large networks.
Layer 3 operation is scalable and is the recommended operation. Figure 17 illustrates a typical Layer-3 wireless network configuration containing access points and a controller.Figure 17 Typical Layer 3 Access Point Network Configuration Example
Preparing the Access Point
The access point is a radio device which is susceptible to common causes of interference that can reduce throughput and range. Follow these basic guidelines to ensure the best possible performance:
- For information on planning and initially configuring your Cisco mesh network, refer to the Cisco Wireless Mesh Access Points, Design and Deployment Guide, Release 7.0. These documents are available on cisco.com.
- Do not install the access point in an area where structures, trees, or hills obstruct radio signals to and from the access point.
- You can install the access point at any height, but best throughput is achieved when the access points are mounted at the same height.
Note To perform path loss calculation and to determine how far apart to install access points, consult an RF planning expert.
Site Surveys
Cisco recommends that you perform a site survey before installing the equipment. A site survey reveals problems that can be resolved before the network is operational. Because 802.11a/b/g/n operates in an unlicensed spectrum, there may be sources of interference from other 802.11a wireless devices (especially in multi-tenant buildings) that could degrade your 802.11 signals. A site survey can determine if such interference exists at the time of deployment.
A proper site survey involves temporarily setting up mesh links and taking measurements to determine whether your antenna calculations are accurate. Determine the correct locations and antenna types before you drill holes and route cables and mounting equipment.

Tip When power is not readily available during a site survey, use an unrestricted power supply (UPS) to temporarily power the mesh link.
Consider the following operating and environmental conditions when performing a site survey:
- How far is your wireless link?
- Has a previous site survey been conducted?
- Do you have a clear Fresnel zone between the access points or radio line of sight?
- What is the minimum acceptable data rate within the link?
- Do you have the correct antenna (if more than one antenna is being offered)?
- Do you have access to both of the mesh site locations?
- Do you have the proper permits, if required?
- Are you following the proper safety procedures and practices?
- Have you configured the access points before you go onsite? It is always easier to resolve configurations or device problems first.
- Do you have the proper tools and equipment to complete your survey?
Avoiding Damage to Radios in a Testing Environment
The radios on outdoor units (bridges) have higher transmit power levels than radios on indoor units (access points). When you test radios in a link, you must avoid exceeding the maximum receive input level of the receiver. At levels higher than the normal the operating range and packet error rate (PER) performance of the receiver is degraded. At even higher levels, the receiver can be permanently damaged.
To avoid receiver damage and PER degradation, you can use one of the following techniques:
- Separate the omnidirectional antennas by at least 2 ft (0.6 m) to avoid receiver damage or by at least 25 ft (7.6 m) to avoid PER degradation.
- Reduce the configured transmit power to the minimum level.
- Cable the radios together using a combination of attenuators, combiners, or splitters to achieve a total attenuation of at least 60 dB.
For a radiated test bed, the following equation describes the relationships among transmit power, antenna gain, attenuation, and receiver sensitivity:
For a conducted test bed, the following equation describes the relationships among transmit power, antenna gain, and receiver sensitivity:

Caution Under no circumstances should you connect the antenna port from one access point to the antenna port of another access point without using an RF attenuator. If you connect antenna ports you must not exceed the maximum survivable receive level of 0 dBm. Never exceed 0 dBm or damage to the access point can occur. Using attenuators, combiners, and splitters having a total of at least 60 dB of attenuation ensures that the receiver is not damaged and PER performance is not degraded.Before You Begin

Warning Read the installation instructions before connecting the system to the power source. Statement 1004
Before you begin the installation process:
- Become familiar with the procedures for mounting the access point.
- Become familiar with the access point connections ( Figure 1 , Figure 3 , and Figure 8 ).
- Verify that the switch you are using to connect the controller is configured properly.
Note For additional installation, mounting and safety information for the outdoor mesh access point, see the Cisco Aironet 1550 Series Outdoor Mesh Access Point Hardware Installation Guide, which is available on Cisco.com, and Safety Warnings for Cisco Aironet 1520 Series Outdoor Mesh Access Points, which accompanies this guide.
Deploying the Access Point

Warning Do not operate the unit near unshielded blasting caps or in an explosive environment unless the device has been modified to be especially qualified for such use. Statement 364
The access point is deployed on Layer 3 networks. Layer 3 is the default mode for a newly configured wireless LAN controller. This guide assumes that you will be deploying your access point on a Layer 3 network and a DHCP server is available.
Before deploying the access point, make sure the controller to which the access point will associate is properly configured by performing the following operations:
- Make sure that the wireless LAN controller is set to Layer 3 mode
- Verify the wireless LAN controller software version
- Record the access point BVI MAC address
- Enter the access point BVI MAC address to the wireless LAN controller filter list
Verifying the Wireless LAN Controller Mode
Follow these steps to verify that the wireless LAN controller mode is set to Layer 3:
Step 1
Open your web-browser and enter the IP address of your wireless LAN controller. Be sure to precede the IP address with https://. A login screen appears.
Step 2
Enter your username and password. The default case-sensitive username and password are admin and admin. The Summary page appears.
Step 3
From the top menu bar, click CONTROLLER. The Controller General page appears.
Step 4
Verify that the CAPWAP Transport Mode is set to Layer 3. If it is not, change it to Layer 3 and click Apply.
Step 5
Save any changes you made.
Step 6
From the menu bar, click MONITOR to return to the Monitor Summary page.
Verifying the Wireless LAN Controller Software Version
On the Summary page, you can verify the software version that the wireless LAN controller is running. If a version update is necessary, refer to the appropriate controller configuration documentation.
Recording the Access Point MAC Address
Use a text file to record the MAC address of all the access points you intend to deploy in your network. Having a file of access point MAC addresses will be of considerable value for future testing. While you are compiling the list, you might want to change the name of the access point to something you can easily remember. The name can contain up to 32 characters. The following example, fisher_street:ea:co contains the last four HEX characters of the access point MAC address.
Adding the Access Point MAC Address to the Wireless LAN Controller
Filter ListThe wireless LAN controller maintains an access point authorization MAC address list and responds to discovery requests from access points on that list. To add the access point MAC address (or MAC addresses) to the Wireless LAN controller filter list, follow these steps:
Step 1
If you are not logged onto the wireless LAN controller, log on now. The Summary page appears.
Step 2
On the menu bar, click SECURITY . The Security RADIUS Authentication Server page appears.
Step 3
Under AAA in the left frame, click MAC Filtering. The Security MAC Filtering page appears.
Step 4
Click New. The MAC Filters New page appears.
Step 5
Enter the MAC address of the access point in the MAC Address field. You can also use the config macfilter add command to add a MAC filter entry to the controller.
Step 6
Select a WLAN ID or Any WLAN from the WLAN ID pop-up menu.
Step 7
Enter a description (32 characters maximum) of the access point in the Description field.
Step 8
Choose an interface from the Interface Name pop-up menu.
Step 10
Repeat this process to add other access points to the list.
Note You can also use the controller CLI command config macfilter add to add a MAC filter entry on the controller.
Step 11
On the menu bar, click Monitor to return to the Monitor Summary page.
Verifying Controller Association
To verify that your access point is associated to the wireless LAN controller, perform these steps:
Step 1
Log into your controller web interface (https) using a web browser.
Step 2
Click Wireless and verify that your access point MAC address is listed under Ethernet MAC.
Step 3
Log out of the controller and close your web browser.
Using a DHCP Server in a Layer 3 Mesh Network
To use a DHCP server in a Layer 3 mesh network, make sure the wireless LAN controller is in Layer 3 mode. You must also configure DHCP option 43 on the DHCP server. After the controller is restarted, the access point receives IP addresses from the DHCP server.
Configuring DHCP Option 43
You can use DHCP Option 43 to provide a list of controller IP addresses to the access points, enabling each access point to find and join a controller. This section contains a DHCP Option 43 configuration example on a Microsoft Windows 2003 Enterprise DHCP server for use with Cisco Aironet lightweight access points.
Additional information about Microsoft DHCP Option 43 is available on Cisco.com at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk722/tk809/technologies_configuration_example09186a00808714fe.shtml
DHCP Option 43 server implementation information for Cisco IOS is available at cisco.com at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/wireless/technology/controller/deployment/guide/dep.html#wp1068287
Note In DHCP Option 43, you should use the IP address of the controller management interface.
Note DHCP Option 43 is limited to one access point type per DHCP pool. You must configure a separate DHCP pool for each access point type.
Cisco Aironet 1000 and 1500 (1505 and 1510) series access points use a comma-separated string format for DHCP Option 43. Other Cisco Aironet access points use the type-length-value (TLV) format for DHCP Option 43. DHCP servers must be programmed to return the option based on the DHCP Vendor Class Identifier (VCI) string (DHCP Option 60) of the access point. The VCI strings for Cisco access points capable of operating in lightweight mode are listed in Table 1 :
Table 1 Lightweight Access Point VCI Strings
The format of the TLV block for 1100, 1130, 1200, 1240, 1250, 1300, 1520, and 1552 access points are listed below:
Configuring Option 43 for Cisco 1000, 1500, and 1550 Series Access Points
To configure DHCP Option 43 for Cisco 1000, 1500, and 1550 series access points in the embedded Cisco IOS DHCP server, follow these steps:
Step 1
Enter configuration mode at the Cisco IOS CLI.
Step 2
Create the DHCP pool, including the necessary parameters such as default router and name server. The commands used to create a DHCP pool are as follows:
Step 3
Add the Option 60 line using the following syntax:
For the VCI string, use the value from Table 1 . The quotation marks must be included.
Step 4
Add the option 43 line using the following syntax:
For example, if you are configuring Option 43 for Cisco 1000, 1500, or 1550 series access points using the controller IP addresses 10.126.126.2 and 10.127.127.2, add the following line to the DHCP pool in the Cisco IOS CLI:
option 43 ascii “10.126.126.2,10.127.127.2”
The quotation marks must be included.
Configuring Option 43 for Cisco 1100, 1130, 1200, 1240, 1250, 1300, 1520, and 1550 Series Access Points
To configure DHCP Option 43 for Cisco 1100, 1130, 1200, 1240, 1250, 1300, 1520, and 1550 series access points in the embedded Cisco IOS DHCP server, follow these steps:
Step 1
Enter configuration mode at the Cisco IOS CLI.
Step 2
Create the DHCP pool, including the necessary parameters such as default router and name server. The commands used to create a DHCP pool are as follows:
Step 3
Add the Option 60 line using the following syntax:
For the VCI string, use the value from Table 1 . The quotation marks must be included.
Step 4
Add the option 43 line using the following syntax:
The hex string is assembled by concatenating the TLV values shown below:
Type is always f1(hex) . Length is the number of controller management IP addresses times 4 in hex. Value is the IP address of the controller listed sequentially in hex.
For example, suppose that there are two controllers with management interface IP addresses, 10.126.126.2 and 10.127.127.2. The type is f1(hex). The length is 2 * 4 = 8 = 08 (hex) . The IP addresses translate to 0a7e7e02 and 0a7f7f02 . Assembling the string then yields f1080a7e7e020a7f7f02. The resulting Cisco IOS command added to the DHCP scope is listed below:
Declarations of Conformity and Regulatory Information
This section provides declarations of conformity and regulatory information for the Cisco Aironet 1550 Series Access Point.
Manufacturers Federal Communication Commission Declaration of Conformity Statement

Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USAThis device complies with Part 15 rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
1.
This device may not cause harmful interference, and
2.
This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits of a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a residential environment. This equipment generates, uses, and radiates radio frequency energy, and if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur. If this equipment does cause interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to correct the interference by one of the following measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from which the receiver is connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician.

Caution The Part 15 radio device operates on a non-interference basis with other devices operating at this frequency when using the integrated antennas. Any changes or modification to the product (including the use of non-Cisco antennas specified for this model) provided not expressly approved by Cisco could void the user’s authority to operate this device.VCCI Statement for Japan


Guidelines for Operating Cisco Aironet Access Points in Japan
This section provides guidelines for avoiding interference when operating Cisco Aironet access points in Japan. These guidelines are provided in both Japanese and English.
English Translation
This equipment operates in the same frequency bandwidth as industrial, scientific, and medical devices such as microwave ovens and mobile object identification (RF-ID) systems (licensed premises radio stations and unlicensed specified low-power radio stations) used in factory production lines.
1.
Before using this equipment, make sure that no premises radio stations or specified low-power radio stations of RF-ID are used in the vicinity.
2.
If this equipment causes RF interference to a premises radio station of RF-ID, promptly change the frequency or stop using the device; contact the number below and ask for recommendations on avoiding radio interference, such as setting partitions.
3.
If this equipment causes RF interference to a specified low-power radio station of RF-ID, contact the number below.
English Translation
When installing the product, please use the provided or designated connection cables/power cables/AC adaptors. Using any other cables/adaptors could cause a malfunction or a fire. Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law prohibits the use of UL-certified cables (that have the “UL” shown on the code) for any other electrical devices than products designated by CISCO. The use of cables that are certified by Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law (that have “PSE” shown on the code) is not limited to CISCO-designated products.
Canadian Compliance Statement
This Class B Digital apparatus meets all the requirements of the Canadian Interference-Causing Equipment Regulations.
Cet appareil numerique de la classe B respecte les exigences du Reglement sur le material broilleur du Canada.
This device complies with Class B Limits of Industry Canada. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
1.
This device may not cause harmful interference, and
2.
This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Cisco Aironet Access Points are certified to the requirements of RSS-210. The use of this device in a system operating either partially or completely outdoors may require the user to obtain a license for the system according to the Canadian regulations. For further information, contact your local Industry Canada office.
This device has been designed to operate with antennas having a maximum gain of 13 dBi for 2.4 GHz and 14 dBi for 5 GHz. Antennas having a gain greater than 6 dB are strictly prohibited for use with this device. The required antenna impedance is 50 ohms.
To reduce potential radio interference to other users, the antenna type and its gain should be so chosen that the equivalent isotropically radiated power (EIRP) is not more than that permitted for successful communication.
European Community, Switzerland, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein
AIR-CAP1552E-E-K9
AIR-CAP1552H-E-K9Declaration of Conformity with regard to the R&TTE Directive 1999/5/EC & Medical Directive 93/42/EEC
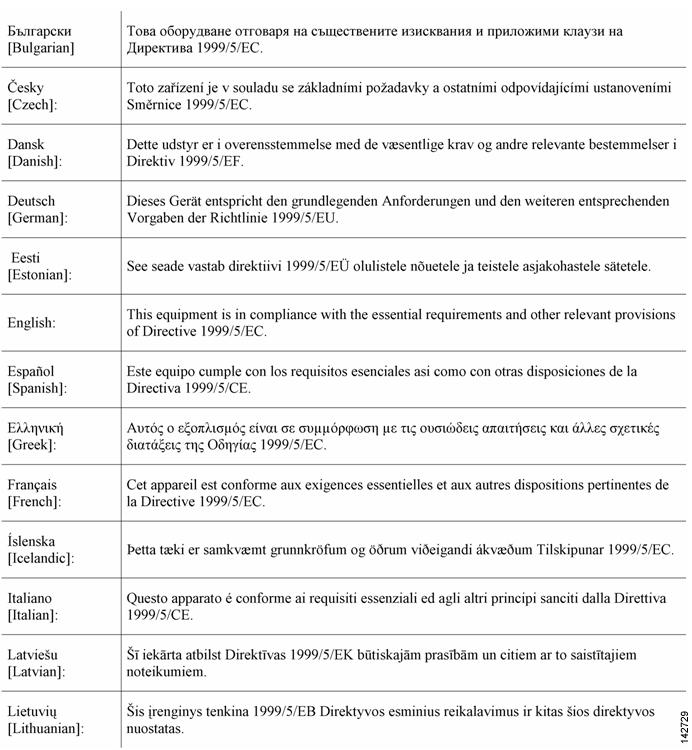
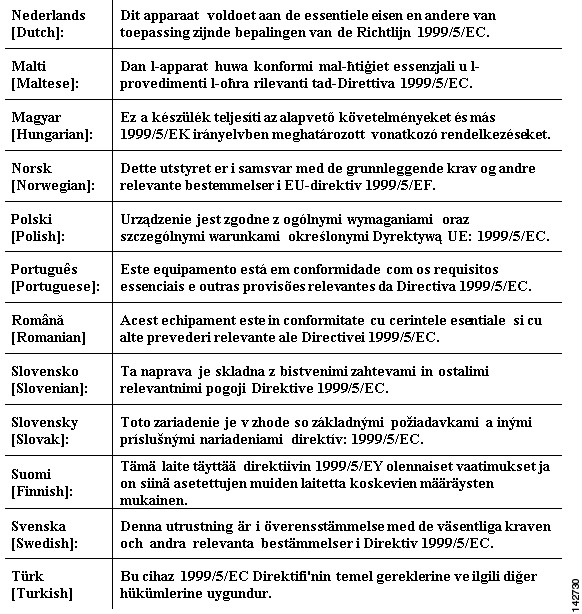
The following standards were applied:
EMC—EMC-EN 301.489-1 v1.8.1; EN 301.489-17 v2.1.1
Health & Safety—EN60950-1: 2005; EN 50385: 2002
Radio—EN 300 328 v 1.7.1; EN 301.893 v 1.5.1
The conformity assessment procedure referred to in Article 10.4 and Annex III of Directive 1999/5/EC has been followed.
This device also conforms to the EMC requirements of the Medical Devices Directive 93/42/EEC.
Note This equipment is intended to be used in all EU and EFTA countries. Outdoor use may be restricted to certain frequencies and/or may require a license for operation. For more details, contact Cisco Corporate Compliance.
The product carries the CE Mark:

United States
This system has been evaluated for RF exposure for Humans in reference to ANSI C 95.1 (American National Standards Institute) limits. The evaluation was based on ANSI C 95.1 and FCC OET Bulletin 65C rev 01.01. The minimum separation distance from the antenna to general bystander is 8" (20 cm) for antenna gains up to 8 dBi and 20" (50 cm) for antenna gains from 8.1 to 14 dbi to maintain compliance.
Canada
This system has been evaluated for RF exposure for Humans in reference to ANSI C 95.1 (American National Standards Institute) limits. The evaluation was based on RSS-102 Rev 2. The minimum separation distance from the antenna to general bystander is 8" (20 cm) for antenna gains up to 8 dBi and 20" (50 cm) for antenna gains from 8.1 to 14 dbi to maintain compliance.
European Union
This system has been evaluated for RF exposure for Humans in reference to the ICNIRP (International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection) limits. The evaluation was based on the EN 50385 Product Standard to Demonstrate Compliance of Radio Base stations and Fixed Terminals for Wireless Telecommunications Systems with basic restrictions or reference levels related to Human Exposure to Radio Frequency Electromagnetic Fields from 300 MHz to 40 GHz. The minimum separation distance from the antenna to general bystander is 8" (20 cm) for antenna gains up to 8 dBi and 20" (50 cm) for antenna gains from 8.1 to 14 dbi.
Australia
This system has been evaluated for RF exposure for Humans as referenced in the Australian Radiation Protection standard and has been evaluated to the ICNIRP (International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection) limits. The minimum separation distance from the antenna to general bystander is 8" (20 cm) for antenna gains up to 8 dBi and 20" (50 cm) for antenna gains from 8.1 to 14 dbi.
Administrative Rules for Cisco Aironet Access Points in Taiwan
This section provides administrative rules for operating Cisco Aironet access points in Taiwan. The rules for all access points are provided in both Chinese and English.
English Translation
Administrative Rules for Low-power Radio-Frequency Devices
For those low-power radio-frequency devices that have already received a type-approval, companies, business units or users should not change its frequencies, increase its power or change its original features and functions.
The operation of the low-power radio-frequency devices is subject to the conditions that no harmful interference is caused to aviation safety and authorized radio station; and if interference is caused, the user must stop operating the device immediately and can't re-operate it until the harmful interference is clear.
The authorized radio station means a radio-communication service operating in accordance with the Communication Act.
The operation of the low-power radio-frequency devices is subject to the interference caused by the operation of an authorized radio station, by another intentional or unintentional radiator, by industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) equipment, or by an incidental radiator.
English Translation
Low-power Radio-frequency Devices Technical Specifications
Operation of Cisco Aironet Access Points in Brazil
This section contains special information for operation of Cisco Aironet access points in Brazil.
Regulatory Information
Figure 18 contains Brazil regulatory information for the access point models identified in the previous section.
Figure 18 Reglatory Information for Brazil

Portuguese Translation
Este equipamento opera em caráter secundário, isto é, não tem direito a proteção contra interferência prejudicial, mesmo de estações do mesmo tipo, e não pode causar interferência a sistemas operando em caráter primário.
English Translation
This equipment operates on a secondary basis and consequently must accept harmful interference, including interference from stations of the same kind. This equipment may not cause harmful interference to systems operating on a primary basis.
Declaration of Conformity Statements
All the Declaration of Conformity statements related to this product can be found at the following location: http://www.ciscofax.com.
In Case of Difficulty
Help is available from Cisco should you experience difficulties; however, before contacting Cisco, look for a solution to your problem in the following places:
- The Troubleshooting section of this guide
- The troubleshooting section of the Cisco Aironet 1550 Series Outdoor Mesh Access Point Hardware Installation Guide
- The Troubleshooting a Mesh Network troubleshooting guide found on cisco.com at
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps8368/prod_troubleshooting_guides_list.html- The Tools and Resources section on the Technical Support and Documentation page at cisco.com
Follow these steps to contact the Technical Assistance Center on cisco.com:
Step 1
Open your browser and go to http://www.cisco.com/ .
Step 2
Click Support. The Support page appears.
Step 3
Choose the link that best serves your support requirements.

Note Click My Tech Support if you are a registered user.
Step 4
Follow the instructions on the page.
Troubleshooting

This section provides troubleshooting procedures for basic problems with the access point. For the most up-to-date, detailed troubleshooting information, refer to the Cisco Support website at cisco.com.
Guidelines for Using the Access Point
You should keep these guidelines in mind when you use the access point:
- The access points can only communicate with controllers and cannot operate independently in standalone mode.
- The access point communicates only with controllers and does not support Wireless Domain Services (WDS). The access points cannot communicate with WDS devices. However, the controller provides functionality equivalent to WDS when an access point associates to it.
- The access point supports Layer 3 CAPWAP communications with the controllers. In Layer 3 operation, the access point and the controller can be on the same or different subnets. The access point communicates with the controller using standard IP packets. Layer 3 operation is scalable and is recommended by Cisco. Unless it has a static IP address, a Layer 3 access point on a different subnet than the controller requires a DHCP server on the access point subnet and a route to the controller. The route to the controller must have destination UDP ports 12222 and 12223 open for CAPWAP communications. The routes to the primary, secondary, and tertiary controllers must allow IP packet fragments.
- Before deploying your mesh access points ensure that the following has been done:
–
Your controllers are connected to switch ports that are configured as trunk ports.
–
Your mesh access points are connected to switch ports that are configured as untagged access ports.
–
A DHCP server is reachable by your mesh access points and has been configured with Option 43. Option 43 is used to provide the IP addresses of the Management Interfaces of your controllers. Typically, a DHCP server can be configured on a Cisco Layer 3 switch or router.
–
Optionally a DNS server can be configured to enable a local domain Cisco CAPWAP controller (CISCO-CAPWAP-CONTROLLER.<local domain>) to resolve to the IP address of the Management Interface of your controller.
–
Your controllers are configured and reachable by the mesh access points.
–
Your controllers are configured with the MAC addresses of the mesh access points.
Checking the LEDs
Four LEDs, located between the PoE-In and PoE-Out connectors, monitor the status of the access point power, uplinks, and radios. Figure 19 identifies and describes the LED functions. Table 2 provides additional LED signal information.
Figure 19 Access Point LEDs –Shown on the Bottom of Model AIR-CAP1552E-x-K9

Table 2 Access Point LED Signals
nullnull 
Note Regarding LED status colors, it is expected that there will be small variations in color intensity and hue from unit to unit. This is within the normal range of the LED manufacturer’s specifications and is not a defect.
See the Cisco Aironet 1550 Series Outdoor Mesh Access Point Hardware Installation Guide for a detailed description of the LEDs and additional troubleshooting tips.
Misconfigured Access Point IP address
IP address misconfiguration can occur when you are re-addressing a segment of your mesh network and you start at the mesh access point connected to the wired network (RAP). To avoid this problem, always start the IP addressing changes from the farthest access point and work your way back to the root access point. This problem might also happen if you move equipment such as uninstalling an mesh access point and then redeploying with a different IP subnet in another physical location on the mesh network.
Another option to fix this misconfigured IP address is to physically take a controller in Layer 3 mode with a root access point to the location of the misconfigured mesh access point. Set the bridge group name for the root access point to match the misconfigured access point. Add the access point MAC address to the filter list of the controller. When the misconfigured access point appears in the Summary page of the controller, configure the access point with an IP address.
If you are using a static IP address on the access point and plan on redeploying the access point on another subnet, perform a clear config command from the controller for that access point while it is joined before you remove it from the network.
Verifying the Controller MAC Filter List
Prior to activating your access point, you must ensure that the access point MAC address has been added to the controller MAC Filter list and that Mac Filter List is enabled. To view the MAC addresses added to the controller MAC filter list and ensure the MAC filter list is enabled, you can use the controller CLI or the controller GUI.
Cisco 1-Year Limited Hardware Warranty Terms
There are special terms applicable to your hardware warranty and various services that you can use during the warranty period. Your formal Warranty Statement, including the warranties and license agreements applicable to Cisco software, is available on Cisco.com. Follow these steps to access and download the Cisco Information Packet and your warranty and license agreements from Cisco.com.
1.
Launch your browser, and go to this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/prod_warranties_listing.html
The Warranties and License Agreements page appears.
2.
To read the Cisco Information Packet , follow these steps:
a.
Click the Information Packet Number field, and make sure that the part number 78-5235-03D0 is highlighted.
b.
Select the language in which you would like to read the document.
The Cisco Limited Warranty and Software License page from the Information Packet appears.
d.
Read the document online, or click the PDF icon to download and print the document in Adobe Portable Document Format (PDF).

Note You must have Adobe Acrobat Reader to view and print PDF files. You can download the reader from the Adobe website: http://www.adobe.com
3.
To read translated and localized warranty information about your product, follow these steps:
a.
Enter this part number in the Warranty Document Number field:
b.
Select the language in which you would like to view the document.
The Cisco warranty page appears.
d.
Read the document online, or click the PDF icon to download and print the document in Adobe Portable Document Format (PDF).
You can also contact the Cisco service and support website for assistance:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/support/
The following are special terms applicable to your hardware warranty.
Replacement, Repair, or Refund Policy for Hardware
Cisco or its service center will use commercially reasonable efforts to ship a replacement part within ten (10) working days after receipt of a Return Materials Authorization (RMA) request. Actual delivery times can vary, depending on the customer location.
Cisco reserves the right to refund the purchase price as its exclusive warranty remedy.
To Receive a Return Materials Authorization (RMA) Number
Contact the company from whom you purchased the product. If you purchased the product directly from Cisco, contact your Cisco Sales and Service Representative.
Complete the information below, and keep it for your reference.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)




 Feedback
Feedback