排除HSRP常见问题
下载选项
非歧视性语言
此产品的文档集力求使用非歧视性语言。在本文档集中,非歧视性语言是指不隐含针对年龄、残障、性别、种族身份、族群身份、性取向、社会经济地位和交叉性的歧视的语言。由于产品软件的用户界面中使用的硬编码语言、基于 RFP 文档使用的语言或引用的第三方产品使用的语言,文档中可能无法确保完全使用非歧视性语言。 深入了解思科如何使用包容性语言。
关于此翻译
思科采用人工翻译与机器翻译相结合的方式将此文档翻译成不同语言,希望全球的用户都能通过各自的语言得到支持性的内容。 请注意:即使是最好的机器翻译,其准确度也不及专业翻译人员的水平。 Cisco Systems, Inc. 对于翻译的准确性不承担任何责任,并建议您总是参考英文原始文档(已提供链接)。
目录
简介
本文档介绍常见问题和排除热备份路由器协议(HSRP)故障的方法。
先决条件
要求
本文档没有任何特定的要求。
使用的组件
本文档不限于特定的软件和硬件版本。
本文档中的信息都是基于特定实验室环境中的设备编写的。本文档中使用的所有设备最初均采用原始(默认)配置。如果您的网络处于活动状态,请确保您了解所有命令的潜在影响。
了解 HSRP
背景信息
本文档介绍了这些与 HSRP 相关的最常见问题:
-
路由器报告 HSRP 备用 IP 地址重复
-
HSRP 状态持续更改(活动、备用、对话)
-
HSRP对等体不存在
-
与 HSRP 相关的交换机错误消息
-
与 HSRP 配置相关的过度网络单播泛洪
注意:本文档详细描述了如何排除 Catalyst 交换机环境中的 HSRP 故障。本文档包含很多有关软件版本和网络拓扑设计的参考。然而,本文档唯一目的是帮助和引导工程师排除 HSRP 故障。本文档并非设计指南、软件推荐文档或者最佳实践文档。
依靠 Intranet 和 Internet 业务实现重要任务通信的企业和消费者需要并盼望他们的网络和应用程序是持续可用的。如果客户有效利用 Cisco IOS® 软件中的 HSRP,则能满足他们近 100% 的网络正常运行时间的需求。Cisco 平台独特的 HSRP 通过某种方式为 IP 网络提供网络冗余,以确保用户流量可以立即、透明地从网络边缘设备或接入电路的首跳故障中恢复。
如果共享 IP 地址和 MAC(第二层 [L2])地址,则两个或多个路由器可以充当单个虚拟路由器。对于主机工作站默认网关冗余,该地址是必要的。大多数主机工作站不包含路由表,并且仅使用单个下一跳 IP 和 MAC 地址。此地址称为默认网关。使用 HSRP,虚拟路由器组的成员可连续交换状态消息。如果某个路由器由于计划内或计划外的原因而停止工作,则另一个路由器可以接管该路由器的工作。主机配置有单个默认网关,并继续向一致的 IP 和 MAC 地址转发 IP 数据包。执行路由的设备转换对终端工作站是透明的。
注意:您可以为多个默认网关配置运行 Microsoft 操作系统的主机工作站。但是多个默认网关不是动态的。操作系统每次只使用一个默认网关。如果互联网控制管理协议 (ICMP) 确定第一个配置的默认网关不可到达时,系统只是在引导时选择另外的已配置默认网关。
基本操作
运行 HSRP 的一组路由器协作运行,使得从 LAN 上的主机来看,好像只有单个默认网关路由器。此组路由器称为 HSRP 组或备用组。从组中选出的单个路由器负责转发主机发送到虚拟路由器的数据包。此路由器称为活动路由器。另一台路由器则被选为备用路由器。如果活动路由器发生故障,则备用路由器承担转发数据包的职责。尽管任意数量的路由器可以运行HSRP,但只有活动路由器会转发发送到虚拟路由器IP地址的数据包。
为了使网络流量减到最小,协议完成选举过程之后,只有活动路由器和备用路由器定期发送 HSRP 消息。HSRP 组中的其他路由器保持在 Listen 状态。如果活动路由器发生故障,则备用路由器接管活动路由器。如果备用路由器发生故障或变成活动路由器,另一台路由器则被选为备用路由器。
每个备用组模拟一个虚拟路由器(默认网关)。 对于每个组,会为该组分配单个已知的 MAC 和 IP 地址。多个备用组可在 LAN 上同时存在和重叠,单个路由器可参与多个组。在这种情况下,路由器为每个组维护独立的状态和计时器。
HSRP 术语
| 期限 | 定义 |
|---|---|
| 活动路由器 | 目前为虚拟路由器转发数据包的路由器 |
| 备用路由器 | 主备份路由器 |
| 备用组 | 参加 HSRP 并共同模拟虚拟路由器的一组路由器 |
| Hello 时间 | 来自给定路由器的连续 HSRP hello 消息之间的时间间隔 |
| 保持时间 | 接收 hello 信息和假定发送路由器发生故障之间的时间间隔 |
HSRP 编址
HSRP 路由器通信
运行 HSRP 的路由器通过 HSRP hello 数据包在彼此之间传达 HSRP 信息。这些数据包基于用户数据报协议 (UDP) 端口 1985 被发送到目标 IP 多播地址 224.0.0.2。IP 多播地址 224.0.0.2 是保留用于与所有路由器通信的多播地址。活动路由器从其配置的 IP 地址和 HSRP 虚拟 MAC 地址发送 hello 数据包。备用路由器从其配置的 IP 地址和固化 MAC 地址 (BIA) 发送 hello 数据包。 使用源寻址是必要的,以便 HSRP 路由器能正确地互相识别。
在多数情况下,当您将路由器配置为 HSRP 组的组成部分时,这些路由器将监听该组的 HSRP MAC 地址,以及它们自己的 BIA。此行为不适用于 Cisco 2500、4000 及 4500 路由器。这些路由器具有只识别单个 MAC 地址的以太网硬件。所以,当这些路由器作为活动路由器时,它们将使用 HSRP MAC 地址。当这些路由器作为备用路由器时,它们将使用其 BIA。
除令牌环以外的所有介质上的 HSRP 备用 IP 地址通信
由于主机工作站将其默认网关配置为 HSRP 备用 IP 地址,因此主机必须与 HSRP 备用 IP 地址关联的 MAC 地址进行通信。此 MAC 地址是由 0000.0c07.ac** 组成的虚拟 MAC 地址。** 是基于各自接口的十六进制 HSRP 组号码。例如,HSRP组1使用HSRP虚拟MAC地址0000.0c07.ac01。邻接LAN网段上的主机使用正常的地址解析协议(ARP)过程来解析关联的MAC地址。
ICMP 重定向
保护子网的 HSRP 对等路由器能提供访问网络中所有其他子网的权限。这是 HSRP 的基础。所以,哪个路由器成为活动 HSRP 路由器并没有关系。在早于 Cisco IOS 软件版本 12.1(3)T 的 Cisco IOS 软件版本中,当 HSRP 用于某一接口时,将在该接口上自动禁用 ICMP 重定向。没有此配置,主机可从 HSRP 虚拟 IP 地址重定向到单个路由器的接口 IP 和 MAC 地址。于是失去冗余。
Cisco IOS软件引入了通过HSRP允许ICMP重定向的方法。此方法通过 HSRP 过滤出站 ICMP 重定向消息。下一跳 IP 地址更改为 HSRP 虚拟地址。将出站 ICMP 重定向消息中的网关 IP 地址与存在于该网络上的 HSRP 活动路由器列表进行比较。如果对应于网关 IP 地址的路由器是 HSRP 组的活动路由器,则用该组虚拟 IP 地址替换网关 IP 地址。此解决方案使主机能够获知到达远程网络的最佳路由,同时维持 HSRP 提供的灵活性。
HSRP 功能一览表
要了解支持HSRP的功能和Cisco IOS软件版本,请参阅了解热备份路由器协议特性和功能中的Cisco IOS®版本和HSRP功能表部分。
HSRP 功能
本文档提供有关这些 HSRP 功能的信息:
-
优先占用
-
接口跟踪
-
使用 BIA
-
多个 HSRP 组
-
可配置的 MAC 地址
-
Syslog 支持
-
HSRP 调试
-
增强的 HSRP 调试
-
身份验证
-
IP 冗余
-
简单网络管理协议 (SNMP) MIB
-
针对多协议标签交换 (MPLS) 的 HSRP
注意:您可以使用浏览器的“查找”功能,找出本文档中的这些部分。
数据包格式
此表显示 UDP HSRP 帧的数据部分的格式:
| version | 操作码 | 状态 | Hello 时间 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 保持时间 | 优先级 | 组 | 预留 |
| 身份验证数据 | |||
| 身份验证数据 | |||
| 虚拟 IP 地址 | |||
下表说明了 HSRP 数据包中的每一个字段:
| 数据包字段 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 操作码(1 个八位组) | 操作码说明数据包包含的消息类型。可能的值包括:0- hello、1 - coup 和 2 - resign。发送 hello 消息可表明路由器运行 HSRP,并且能够成为活动路由器。当路由器希望成为活动路由器时,发送 coup 消息。当路由器不再希望作为活动路由器时,发送 resign 消息。 |
| 状态(1 个八位组) | 备用组中的每个路由器架设一台状态机。状态字段描述传送消息的路由器的当前状态。以下是有关各个状态的详细信息:0 - 初始、1 - 学习、2 - 监听、4 - 对话、8 - 备用以及 16 - 活动。 |
| Hellotime(1 个八位组) | 此字段仅在 hello 消息中才有意义。它包含路由器发送的 hello 消息之间的大致周期。时间以秒为单位提供。 |
| Holdtime(1 个八位组) | 此字段仅在 hello 消息中才有意义。它包含在路由器启动状态更改之前,路由器等待 hello 消息的时间。 |
| 优先级(1 个八位组) | 此字段用于选择活动和备用路由器。当比较两台路由器的优先级时,值最高的路由器将成为活动路由器。取 IP 地址较高的路由器。 |
| 组(1 个八位组) | 此字段标识备用组。 |
| 身份验证数据(8 个八位组) | 此字段包含一个明文的 8 字符口令。 |
| 虚拟 IP 地址(4 个八位组) | 如果路由器上没有配置虚拟 IP 地址,则可以从来自活动路由器的 hello 消息获知该地址。只有在未配置 HSRP 备用 IP 地址,并且 hello 消息经过身份验证(如果配置了验证)的情况下,才能获知地址。 |
HSRP 状态
| 状态 | 定义 |
|---|---|
| 初始 | 这是起始状态。此状态表明 HSRP 没有运行。配置发生更改或接口首次变得可用时,进入此状态。 |
| 学习 | 路由器没有确定虚拟 IP 地址,也没有看到活动路由器发出的经过身份验证的 hello 消息。在此状态下,路由器仍然等待来自活动路由器的消息。 |
| 侦听 | 路由器知道虚拟 IP 地址,但该路由器既不是活动路由器,也不是备用路由器。它侦听来自那些路由器的 hello 消息。 |
| 发言 | 路由器定期发送 hello 消息,并积极参与活动路由器和/或备用路由器的竞选。除非路由器有虚拟 IP 地址,否则该路由器不能进入 speak 状态。 |
| 备用 | 该路由器适合作为下一个活动路由器的候选者,并定期发送 hello 消息。除临时情况以外,组中至多有一个路由器处于 standby state。 |
| 主用 | 当前转发被发送到组虚拟 MAC 地址的数据包的路由器。该路由器定期发送 hello 消息。除临时情况以外,组中至多有一个路由器处于 active state。 |
HSRP 计时器
在 HSRP 中每个路由器仅使用三个计时器。计时器计算 hello 消息的时间。当故障发生时 HSRP 的收敛时间取决于 HSRP hello 计时器和 hold 计时器的配置。默认情况下,这两个计时器分别设置为 3 和 10 秒,这意味着每 3 秒在 HSRP 备用组设备之间发送一次 hello 数据包,并且如果 10 秒钟内未收到 hello 数据包,则备用设备将成为活动设备。您可以降低这些计时器设置以加快故障切换或抢占,但是,要避免CPU使用率增加和备用状态出现不必要的抖动,请不要将hello计时器设置为低于一(1)秒或保持计时器设置为低于4秒。

注意:如果使用HSRP跟踪机制且跟踪的链路发生故障,则无论呼叫计时器和保持计时器如何,都会立即发生故障转移或抢占。当计时器到期时,路由器转换为新的 HSRP 状态。可以使用此命令更改计时器:standby [group-number] timers hellotime holdtime。例如,standby 1 timers 5 15。
此表提供有关这些计时器的详细信息:
| 计时器 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 活动计时器 | 此计时器用于监控活动路由器。只要活动路由器收到 hello 数据包,此计时器就会启动。此计时器到期与否将根据设置在 HSRP hello 消息的相关字段中的保持时间值而定。 |
| 备用计时器 | 此计时器用于监控备用路由器。只要备用路由器收到 hello 数据包,此计时器就会启动。此计时器到期与否将根据设置在各自 hello 数据包中的保持时间值而定。 |
| Hello 计时器 | 此计时器用于对 hello 数据包计时。当此 hello 计时器到期时,任何 HSRP 状态下的所有 HSRP 路由器都将生成 hello 数据包。 |
HSRP 事件
此表提供 HSRP 有限状态机中的事件:
| 密钥 | 事件 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 在已启用的接口上配置了 HSRP。 |
| 2 | HSRP 在某接口上被禁用或该接口被禁用。 |
| 3 | 主用计时器到期。主用计时器设置为在主用路由器上收到最后一条 Hello 消息时的保持时间。 |
| 4 | 备用计时器到期。备用计时器设置为在备用路由器上收到最后一条 Hello 消息时的保持时间。 |
| 5 | Hello 计时器到期。用于发送 Hello 消息的周期性计时器到期。 |
| 6 | 从 speak 状态的路由器收到较高优先级的 hello 消息 |
| 7 | 从活动路由器收到较高优先级的 hello 消息 |
| 8 | 从活动路由器收到较低优先级的 hello 消息 |
| 9 | 从活动路由器收到 resign 消息 |
| 10 | 从较高优先级的路由器收到 coup 消息 |
| 11 | 从备用路由器收到较高优先级的 hello 消息 |
| 12 | 从备用路由器收到较低优先级的 hello 消息 |
HSRP 操作
此表指定作为状态机一部分所采取的操作:
| 字母 | 操作 |
|---|---|
| A | Start active timer — 如果由于从活动路由器收到经过身份验证的hello消息而产生此操作,则活动计时器将设置为hello消息中的保持时间字段。否则,活动计时器设置为由此路由器使用的当前保持时间值。然后活动计时器启动。 |
| B | Start standby timer — 如果由于从备用路由器接收到经过身份验证的hello消息而产生此操作,则备用计时器将设置为hello消息中的保持时间字段。否则,备用计时器将设置为此路由器使用的当前保持时间值。然后备用计时器启动。 |
| C | 终止活动计时器 - 活动计时器终止。 |
| D | 终止备用计时器 - 备用计时器终止。 |
| E | 学习参数 - 当从活动路由器收到经过身份验证的消息时,采取此操作。如果没有手工配置此组的虚拟 IP 地址,可以从此消息中获知虚拟 IP 地址。路由器可以从该消息获知 hello 时间和保持时间的值。 |
| F | 发送 hello 消息 - 路由器根据其当前状态、hello 时间和保持时间发送一个 hello 消息。 |
| G | 发送 coup 消息 - 路由器发送一条 coup 消息,以通知活动路由器有一个更高的优先级的路由器可用。 |
| H | 发送 resign 消息 - 路由器发送 resign 消息,以允许其他路由器成为活动路由器。 |
| I | 发送无故 ARP 消息 - 路由器广播一个通告组虚拟 IP 和 MAC 地址的 ARP 响应数据包。发送该数据包时,使用虚拟 MAC 地址作为链路层报头中以及 ARP 数据包中的源 MAC 地址。 |
HSRP 状态表
在此部分的图表显示 HSRP 状态机的状态转换。每次事件发生时产生,将产生相关联的操作,并且路由器转换到下一个 HSRP 状态。在图表中,编号指示事件,字母指示相关联的操作。HSRP 事件部分中的表定义了编号,HSRP 操作部分中的表定义了字母。此图表仅供参考。该图很详细,不是用于常规故障排除所必需的。
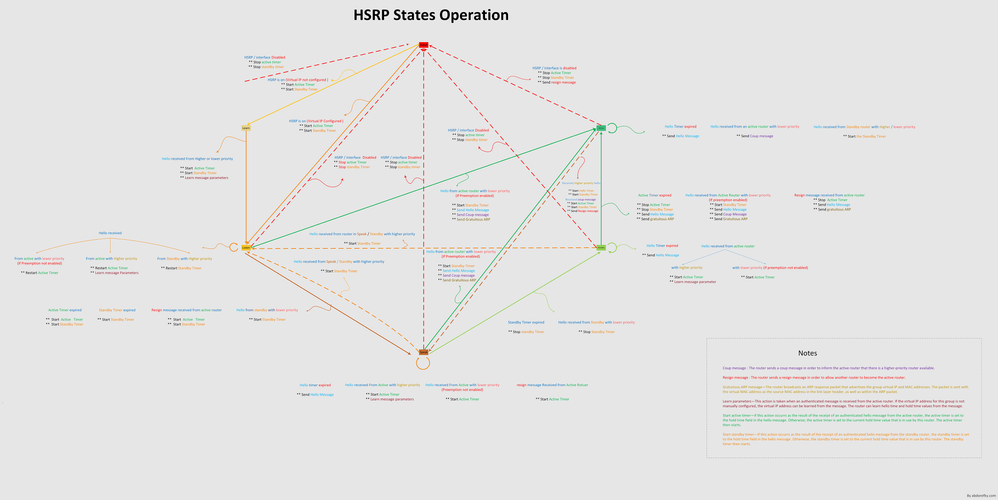 HSRP状态操作
HSRP状态操作
数据包流
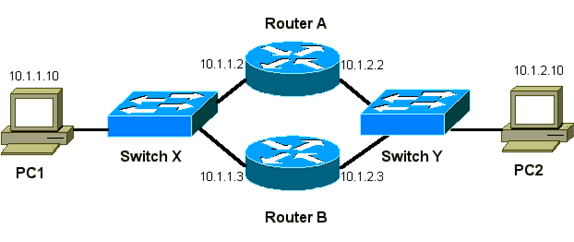
| 设备 | Mac 地址 | IP Address | 子网掩码 | 默认网关 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | 0000.0c00.0001 | 10.1.1.10 | 255.255.255.0 | 10.1.1.1 |
| PC2 | 0000.0c00.1110 | 10.1.2.10 | 255.255.255.0 | 10.1.2.1 |
路由器 A 的配置(活动路由器)
interface GigabitEthernet 0/0 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mac-address 4000.0000.0010 standby 1 ip 10.1.1.1 standby 1 priority 200
interface GigabitEthernet 0/1 ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0 mac-address 4000.0000.0011 standby 1 ip 10.1.2.1 standby 1 priority 200
路由器 B 的配置(备用路由器)
interface GigabitEthernet 0/0
ip address 10.1.1.3 255.255.225.0
mac-address 4000.0000.0020
standby 1 ip 10.1.1.1
interface GigabitEthernet 0/1
ip address 10.1.2.3 255.255.255.0
mac-address 4000.0000.0021
standby 1 ip 10.1.2.1
注意:这些示例仅出于示例目的而配置静态 MAC 地址。除非要求如此,请勿配置静态 MAC 地址。
获取嗅探器踪迹以排除HSRP故障时,您必须了解数据包流背后的概念。路由器 A 使用优先级 200,并在两个接口上都成为活动路由器。在本部分的示例中,从路由器发送到某主机工作站的数据包的源 MAC 地址为路由器的物理 MAC 地址 (BIA)。 由主机发出、发往 HSRP IP 地址的数据包的目标 MAC 地址为 HSRP 虚拟 MAC 地址。请注意,在路由器和主机之间,每个数据流的 MAC 地址并不相同。
下表显示的是每个数据流各自的 MAC 和 IP 地址信息,它基于从交换机 X 取得的嗅探器踪迹。
| 数据包流 | 源 MAC | 目的 MAC | 源 IP | 目的 IP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 从 PC1 到 PC2 的数据包 | PC1 (0000.0c00.0001) | 路由器 A 接口 Ethernet 0 的 HSRP 虚拟 MAC 地址 (0000.0c07.ac01) | 10.1.1.10 | 10.1.2.10 |
| 通过路由器 A 从 PC2 返回且目标为 PC1 的数据包 | 路由器 A Ethernet 0 BIA (4000.0000.0010) | PC1 (0000.0c00.0001) | 10.1.2.10 | 10.1.1.10 |
| 来自 PC1 发往 HSRP 备用 IP 地址的数据包 (ICMP,Telnet) | PC1 (0000.0c00.0001) | 路由器 A 接口 Ethernet 0 的 HSRP 虚拟 MAC 地址 (0000.0c07.ac01) | 10.1.1.10 | 10.1.1.1 |
| 发往活动路由器的实际 IP 地址的数据包 (ICMP, Telnet) | PC1 (0000.0c00.0001) | 路由器 A Ethernet 0 BIA (4000.0000.0010) | 10.1.1.10 | 10.1.1.2 |
| 发往备用路由器 (ICMP, Telnet) 的实际 IP 地址的数据包 | PC1 (0000.0c00.0001) | 路由器 B Ethernet 0 BIA (4000.0000.0020) | 10.1.1.10 | 10.1.1.3 |
HSRP 故障排除案例分析
案例分析 1:HSRP 备用 IP 地址被报告为重复 IP 地址
可能出现以下错误消息:
Oct 12 13:15:41: %STANDBY-3-DUPADDR: Duplicate address 10.25.0.1 on Vlan25, sourced by 0000.0c07.ac19 Oct 13 16:25:41: %STANDBY-3-DUPADDR: Duplicate address 10.25.0.1 on Vlan25, sourced by 0000.0c07.ac19 Oct 15 22:31:02: %STANDBY-3-DUPADDR: Duplicate address 10.25.0.1 on Vlan25, sourced by 0000.0c07.ac19 Oct 15 22:41:01: %STANDBY-3-DUPADDR: Duplicate address 10.25.0.1 on Vlan25, sourced by 0000.0c07.ac19
这些错误消息不一定指示 HSRP 问题。相反,错误消息可能指示一个生成树协议 (STP) 环路或路由器/交换机配置问题。这些错误消息只是另一个问题的症状。
另外,这些错误消息不妨碍 HSRP 正常操作。将忽略重复的 HSRP 数据包。这些错误消息被扼杀在 30 秒的时间间隔。然而,网络运行缓慢和数据包丢失可能源自网络不稳定性,这导致产生 HSRP 地址的 STANDBY-3-DUPADDR 错误消息。
这些消息明确表示路由器收到来自VLAN 25上的HSRP IP地址的数据包,其MAC地址为0000.0c07.ac19。由于HSRP MAC地址为0000.0c07.ac19,因此相关路由器要么收到自己的数据包,要么是HSRP组中的两个路由器都进入活动状态。因为路由器收到其自己的数据包,所以问题很可能出在网络而不是路由器上。有多种问题可能导致此行为。可能导致该错误消息的网络问题包括:
-
短暂的 STP 环路
-
EtherChannel 配置问题
-
重复帧
排除这些错误消息故障时,请参阅本文档的Catalyst交换机的HSRP故障排除部分中的故障排除步骤。所有故障排除模块均适用于本部分,其中包括配置模块。另外,必要时应记下交换机日志中的所有错误并参考其他案例研究。
您可以使用访问列表以防止活动路由器收到其自己的多播 hello 数据包。但是,这只是这些错误消息的一种解决方法,并且实际上会隐藏问题的症状。解决方法是对 HSRP 接口应用扩展入站访问列表。访问列表阻塞从物理 IP 地址发送到所有路由器多播地址 224.0.0.2 的所有流量。
access-list 101 deny ip host 172.16.12.3 host 224.0.0.2 access-list 101 permit ip any any interface GigabitEthernet 0/0 ip address 172.16.12.3 255.255.255.0 standby 1 ip 172.16.12.1 ip access-group 101 in
案例分析 2:HSRP 状态不断更改(活动、备用、对话)或 %HSRP-6-STATECHANGE
可能出现以下错误消息:
Jan 9 08:00:42.623: %STANDBY-6-STATECHANGE: Standby: 49: Vlan149 state Standby -> Active Jan 9 08:00:56.011: %STANDBY-6-STATECHANGE: Standby: 49: Vlan149 state Active -> Speak Jan 9 08:01:03.011: %STANDBY-6-STATECHANGE: Standby: 49: Vlan149 state Speak -> Standby Jan 9 08:01:29.427: %STANDBY-6-STATECHANGE: Standby: 49: Vlan149 state Standby -> Active Jan 9 08:01:36.808: %STANDBY-6-STATECHANGE: Standby: 49: Vlan149 state Active -> Speak Jan 9 08:01:43.808: %STANDBY-6-STATECHANGE: Standby: 49: Vlan149 state Speak -> Standby
Jul 29 14:03:19.441: %HSRP-5-STATECHANGE: Vlan10 Grp 110 state Standby -> Active
Jul 29 16:27:04.133: %HSRP-5-STATECHANGE: Vlan10 Grp 110 state Active -> Speak
Jul 29 16:31:49.035: %HSRP-5-STATECHANGE: Vlan10 Grp 110 state Speak -> Standby这些错误消息描述的是备用 HSRP 路由器没有从其 HSRP 对等体接收到三个连续 HSRP hello 数据包这种情况。输出显示备用路由器从 standby 状态变为 active 状态。紧接着,路由器回到 standby 状态。除非此错误消息在初始安装时出现,否则很可能不是 HSRP 问题导致此错误消息。此错误消息指示在对等体之间发生 HSRP hello 丢失。当您排除此故障时,您必须验证 HSRP 对等体之间的通信。对等体之间数据通信的随机、短暂丢失,是导致产生这些消息的最常见问题。HSRP 状态更改经常是因为高 CPU 使用率。如果错误消息是由于高 CPU 使用率所致,则在网络中放置嗅探器并跟踪导致高 CPU 使用率的系统。
有几种原因可能导致对等体之间丢失 HSRP 数据包。最常见的问题是物理层问题、生成树问题造成的过度网络流量,或每个 Vlan 造成的过度流量。与案例研究#1一样,所有故障排除模块都适用于HSRP状态更改的解决,特别是第3层HSRP调试。
如果对等体之间丢失 HSRP 数据包是由于上述由每个 VLAN 造成的过多流量,您可以调整或增加 SPD,并保持队列大小以克服输入队列丢弃的问题。
要增加选择性数据包丢弃(SPD)大小,请转到配置模式并在Cat6500交换机上执行以下命令:
(config)#ip spd queue max-threshold 600 !--- Hidden Command (config)#ip spd queue min-threshold 500 !--- Hidden Command
要增加保持队列大小,请转至 VLAN 接口模式并执行以下命令:
(config-if)#hold-queue 500 in
在增加SPD和保持队列大小后,如果执行clear counter interface命令,则可以清除接口计数器。
案例分析 3:HSRP 无法识别对等体
此部分中的路由器输出显示一个针对 HSRP 进行了配置但无法识别其 HSRP 对等体的路由器。要发生此情况,路由器必须不能从相邻路由器接收 HSRP hello。当您排除此故障时,请参阅本文档中的验证物理层连接部分和验证 HSRP 路由器配置部分。如果物理层连接是正确的,请检查是否存在不匹配的 VTP 模式。
Vlan8 - Group 8 Local state is Active, priority 110, may preempt Hellotime 3 holdtime 10 Next hello sent in 00:00:01.168 Hot standby IP address is 10.1.2.2 configured Active router is local Standby router is unknown expired Standby virtual mac address is 0000.0c07.ac08 5 state changes, last state change 00:05:03
案例分析 4:HSRP 状态更改且交换机在 Syslog 中报告“SYS-4-P2_WARN:1/Host <mac_address> Is Flapping Between Port <port_1> and Port <port_2>”
可能出现以下错误消息:
2001 Jan 03 14:18:43 %SYS-4-P2_WARN: 1/Host 00:00:0c:14:9d:08 is flapping between port 2/4 and port 2/3
Feb 4 07:17:44 AST: %SW_MATM-4-MACFLAP_NOTIF: Host 0050.56a9.1f28 in vlan 1027 is flapping between port Te1/0/7 and port Te2/0/2在Catalyst交换机中,交换机报告一个主机MAC地址,如果主机MAC地址在15秒内移动两次,该地址将移动。可能的原因是STP环路。交换机大约在 15 秒内丢弃来自此主机的数据包,以尝试将 STP 环路的影响降至最低。如果被报告在两个端口之间移动的 MAC 地址是 HSRP 虚拟 MAC 地址,那么问题很可能是两个 HSRP 路由器都进入了 active 状态。
如果被报告的 MAC 地址不是 HSRP 虚拟 MAC 地址,则问题可能表明数据包在网络中被循环、重复或反射。这些类型的情况可能造成 HSRP 问题。导致 MAC 地址移动的最常见原因是生成树问题或物理层问题。
当您排除此错误消息故障时,请完成以下步骤:
-
确定主机 MAC 地址的正确源(端口)。
-
断开不能源主机MAC地址的端口。
-
记录每个 VLAN 的 STP 拓扑结构并且检查 STP 故障。
-
验证端口信道配置。
-
错误的端口信道配置可能导致主机 MAC 地址产生错误消息抖动。这是由于端口信道的负载均衡本质所致。
-
案例分析 5:非对称路由和 HSRP(在带运行 HSRP 的路由器的网络中单播流量过度泛洪)
使用非对称路由时,传输和接收数据包在主机与其通信的对等体之间使用不同的路径。此数据包流是基于HSRP优先级(将HSRP设置为活动或备用)在HSRP路由器之间配置负载均衡的结果。交换环境中的这种数据包流可能导致未知的单播过度泛洪。此外,可能会缺失多层交换 (MLS) 条目。当交换机将单播数据包大量传出所有端口时,会发生未知单播泛洪。由于没有目标 MAC 地址条目,交换机将滥发数据包。因为仍在转发数据包,所以此行为不会中断连接。但是该行为的确造成了主机端口充斥过量的额外数据包。此案例分析不对称路由行为,并且分析发生单播泛洪的原因。
不对称路由的症状包括:
-
过多单播数据包泛洪
-
缺少流的 MLS 条目
-
嗅探器踪迹显示主机端口上的数据包的目的地不是该主机
-
基于第二层的数据包重写引擎(如服务器负载平衡器、Web 缓存设备和网络设备)增大了网络延迟
示例包括 Cisco LocalDirector 和 Cisco Cache Engine。
-
连接的主机和工作站因为不能处理附加单播泛洪流量负载而丢弃数据包
注意:路由器上的默认 ARP 缓存老化时间是四小时。交换机内容可寻址存储器 (CAM) 条目的默认老化时间是五分钟。主机工作站的 ARP 老化时间对本讨论并不重要。但本例将 ARP 老化时间设置为四小时。
本图表说明此问题。此拓扑结构示例包括在每台交换机中使用多层交换机功能卡 (MSFC) 的 Catalyst 6500 系列。虽然此示例使用 MSFC,但是您可以使用任何路由器而不是 MSFC。您可以使用的示例路由器包括路由交换模块 (RSM)、千兆交换路由器 (GSR) 和 Cisco 7500。直接将主机连接到交换机上的端口。交换机通过为 VLAN 1 和 VLAN 2 传输流量的中继互相连接。
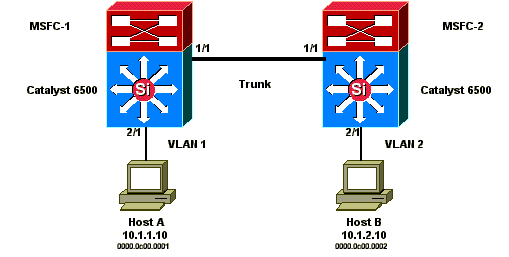
这些输出节选自每个 MSF 的 show standby 命令配置。
MSFC1
interface Vlan 1 mac-address 0003.6bf1.2a01 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 no ip redirects standby 1 ip 10.1.1.1 standby 1 priority 110 interface Vlan 2 mac-address 0003.6bf1.2a01 ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0 no ip redirects standby 2 ip 10.1.2.1 MSFC1#show standby Vlan1 - Group 1 Local state is Active, priority 110 Hellotime 3 holdtime 10 Next hello sent in 00:00:00.696 Hot standby IP address is 10.1.1.1 configured Active router is local Standby router is 10.1.1.3 expires in 00:00:07 Standby virtual mac address is 0000.0c07.ac01 2 state changes, last state change 00:20:40 Vlan2 - Group 2 Local state is Standby, priority 100 Hellotime 3 holdtime 10 Next hello sent in 00:00:00.776 Hot standby IP address is 10.1.2.1 configured Active router is 10.1.2.3 expires in 00:00:09, priority 110 Standby router is local 4 state changes, last state change 00:00:51 MSFC1#exit Console> (enable)
MSFC2
interface Vlan 1
mac-address 0003.6bf1.2a02
ip address 10.1.1.3 255.255.255.0
no ip redirects
standby 1 ip 10.1.1.1
interface Vlan 2
mac-address 0003.6bf1.2a02
ip address 10.1.2.3 255.255.255.0
no ip redirects
standby 2 ip 10.1.2.1
standby 2 priority 110
MSFC2#show standby
Vlan1 - Group 1
Local state is Standby, priority 100
Hellotime 3 holdtime 10
Next hello sent in 00:00:01.242
Hot standby IP address is 10.1.1.1 configured
Active router is 10.1.1.2 expires in 00:00:09, priority 110
Standby router is local
7 state changes, last state change 00:01:17
Vlan2 - Group 2
Local state is Active, priority 110
Hellotime 3 holdtime 10
Next hello sent in 00:00:00.924
Hot standby IP address is 10.1.2.1 configured
Active router is local
Standby router is 10.1.2.2 expires in 00:00:09
Standby virtual mac address is 0000.0c07.ac02
2 state changes, last state change 00:40:08
MSFC2#exit
注意:在 MSFC1 上 VLAN 1 处于 HSRP active 状态,并且 VLAN 2 处于 HSRP standby 状态。在 MSFC2 上 VLAN 2 处于 HSRP active 状态,并且 VLAN 1 处于 HSRP standby 状态。每台主机的默认网关是各自的备用 IP 地址。
-
最初,所有缓存都为空。主机 A 使用 MSFC1 作为其默认网关。主机 B 使用 MSFC2。
Ping 启动之前的 ARP 和 MAC 地址表主机 A ARP 表 交换机 1 MAC 地址表 MAC VLAN 端口 MSFC1 ARP 表 MSFC2 ARP 表 交换机 2 MAC 地址表 MAC VLAN 端口 主机 B ARP 表 0003.6bf1.2a01 1 15/1 0003.6bf1.2a02 1 15/1 0003.6bf1.2a01 2 15/1 0003.6bf1.2a02 2 15/1 0000.0c07.ac01 1 15/1 0000.0c07.ac01 1 1/1 0000.0c07.ac02 2 1/1 0000.0c07.ac02 2 15/1 0003.6bf1.2a02 1 1/1 0003.6bf1.2a01 1 1/1 0003.6bf1.2a02 2 1/1 0003.6bf1.2a01 2 1/1 注意:为简要起见,在此部分出现的其他表中不包括路由器 HSRP 的交换机 1 MAC 地址和 MAC 地址。
-
主机 A ping 主机 B,这意味着主机 A 发送一个 ICMP echo 数据包。由于每台主机位于单独的 VLAN 上,主机 A 将要发送给主机 B 的数据包转发到其默认网关。要发生此过程,主机 A 必须发送一个 ARP,才能解析其默认网关的 MAC 地址 10.1.1.1。
主机 A 向默认网关发送 ARP 之后的 ARP 和 MAC 地址表主机 A ARP 表 交换机 1 MAC 地址表 MAC VLAN 端口 MSFC1 ARP 表 MSFC2 ARP 表 交换机 2 MAC 地址表 MAC VLAN 端口 主机 B ARP 表 10.1.1.1 :0000.0c07.ac01 0000.0c00.0001 1 2/1 10.1.1.10 :0000.0c00.0001 -
MSFC1 接收数据包,重写数据包,并将数据包转发到主机 B。为了重写数据包,MSFC1 将向主机 B 发送 ARP 请求,因为该主机位于直接连接的接口。MSFC2 仍需接收此流中的所有数据包。当 MSFC1 从主机 B 收到 ARP 应答时,两台交换机获知与主机 B 关联的源端口。
主机A发送信息包到默认网关,以及MSFC1向主机B发送ARP之后,显示ARP和MAC地址表。主机 A ARP 表 交换机 1 MAC 地址表 MAC VLAN 端口 MSFC1 ARP 表 MSFC2 ARP 表 交换机 2 MAC 地址表 MAC VLAN 端口 主机 B ARP 表 10.1.1.1 :0000.0c07.ac01 0000.0c00.0001 1 2/1 10.1.1.10 :0000.0c00.0001 0000.0c00.0002 2 2/1 10.1.2.2 :0003.6bf1.2a01 0000.0c00.0002 2 1/1 10.1.2.10 :0000.0c00.0002 -
主机B通过MSFC1从主机A接收回应数据包。主机B现在必须向主机A发送回应应答。由于主机A位于不同的VLAN上,因此主机B通过其默认网关MSFC2转发应答。为了通过转发数据包,主机B必须为其默认网关IP地址10.1.2.1发送ARP。
在主机 B 向其默认网关发送 ARP 之后的 ARP 和 MAC 地址表主机 A ARP 表 交换机 1 MAC 地址表 MAC VLAN 端口 MSFC1 ARP 表 MSFC2 ARP 表 交换机 2 MAC 地址表 MAC VLAN 端口 主机 B ARP 表 10.1.1.1 :0000.0c07.ac01 0000.0c00.0001 1 2/1 10.1.1.10 :0000.0c00.0001 10.1.2.10 0000.0c00.0002 0000.0c00.0002 2 2/1 10.1.2.2 (0003.6bf1.2a01) 0000.0c00.0002 2 1/1 10.1.2.10 :0000.0c00.0001 10.1.2.1 (0000.0c07.ac02) -
主机B现在将回应应答数据包转发到MSFC2。MSFC2向主机A发送ARP请求,因为它直接连接到VLAN 1。交换机2使用主机B的MAC地址填充其MAC地址表。
在主机 A 收到 echo 数据包之后的 ARP 和 MAC 地址表主机 A ARP 表 交换机 1 MAC 地址表 MAC VLAN 端口 MSFC1 ARP 表 MSFC2 ARP 表 交换机 2 MAC 地址表 MAC VLAN 端口 主机 B ARP 表 10.1.1.1 :0000.0c07.ac01 0000.0c00.0001 1 2/1 10.1.1.10 :0000.0c00.0001 10.1.2.10 0000.0c00.0002 0000.0c00.0002 2 2/1 10.1.2.2(0003.6bf1.2a01) 10.1.1.3 :0003.6bf1.2a0 0000.0c00.0002 2 1/1 10.1.2.10 :0000.0c00.0001 10.1.1.10 0000.0c00.0001 0000.0c00.00001 1 1/1 10.1.2.1 (0000.0c07.ac02) -
回声应答到达主机 A,整个流是完整的。
非对称路由的后果
考虑由主机 A 连续对主机 B 执行 ping 操作的情况。请记住,主机 A 将回应数据包发送到 MSFC1,主机 B 将回应应答发送到 MSFC2,后者处于非对称路由状态。交换机1了解主机B的源MAC的唯一时间是主机B回复来自MSFC1的ARP请求。这是因为主机B使用MSFC2作为其默认网关,不会向MSFC1发送数据包,因此不会向交换机1发送数据包。由于ARP超时默认为四小时,因此交换机1在默认情况下五分钟后会延长主机B的MAC地址。交换机2在五分钟后使主机A老化。结果,交换机 1 必须将具有主机 B 目标 MAC 的所有数据包当作未知单播进行处理。交换机将从主机 A 发往主机 B 的数据包从所有端口大量送出。另外,因为交换机 1 中没有 MAC 地址条目主机 B,因而也不会有 MLS 条目。
在由主机 A 连续 Ping 主机 B 5 分钟之后,显示的 ARP 和 MAC 地址表
| 主机 A ARP 表 | 交换机 1 MAC 地址表 MAC VLAN 端口 | MSFC1 ARP 表 | MSFC2 ARP 表 | 交换机 2 MAC 地址表 MAC VLAN 端口 | 主机 B ARP 表 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10.1.1.1 :0000.0c07.ac01 | 0000.0c00.0001 1 2/1 | 10.1.1.10 :0000.0c00.0001 | 10.1.2.10 0000.0c00.0002 | 0000.0c00.0002 2 2/1 | 10.1.2.2 :0003.6bf1.2a01 |
| 10.1.1.3 :0003.6bf1.2a0 | 10.1.2.10 :0000.0c00.0001 | 10.1.1.10 0000.0c00.0001 | 10.1.2.1 :0000.0c07.ac01 |
来自主机B的回应应答数据包在交换机2上主机A的MAC地址条目老化后也遇到同样的问题。主机B将回应应答转发到MSFC2,MSFC2反过来路由数据包,并在VLAN 1上将其发送出去。交换机的MAC地址表中没有条目主机A,因此必须将数据包从VLAN 1中的所有端口泛洪出去。
非对称路由问题不会中断连接。但是,非对称路由可能会导致单播过度泛洪和丢失 MLS 项。有三种配置更改可以解决此问题:
-
将各个交换机的上 MAC 老化时间调整为 14,400 秒(四小时)或更长时间。
-
将路由器上的 ARP 超时更改为五分钟(300 秒)。
-
将 MAC 老化时间和 ARP 超时更改为同一超时值。
首选方法是将 MAC 老化时间更改为 14,400 秒。以下是配置的指导原则:
-
Cisco IOS 软件:
mac address-table aging-time <seconds> vlan <vlan_id>
案例分析 6:HSRP 虚拟 IP 地址被报告为不同的 IP 地址
当因交换机中的桥接环路而存在 interVLAN 泄漏时,将出现 STANDBY-3-DIFFVIP1 错误消息。
如果收到此错误消息,并且因交换机中的桥接环路而存在 interVLAN 泄漏,请完成这些步骤以解决此错误:
-
确定数据包在终端节点之间采用的路径。
如果此路径上存在路由器,请完成以下步骤:
-
排除从第一台交换机到路由器的路径上的故障。
-
排除从路由器到第二台交换机的路径上的故障。
-
-
连接到路径上的每台交换机,并且检查路径上终端节点之间使用的端口的状态。
案例分析 7:HSRP 导致安全端口上出现 MAC 违规
当在连接到启用 HSRP 的路由器的交换机端口上配置端口安全时,将导致 MAC 违规,因为您不能在多个接口上具有同一个安全 MAC 地址。在以下情况之一中,安全端口上将发生安全违规:
-
添加到地址表中的安全 MAC 地址数量已达到最大,而其 MAC 地址不在该地址表中的工作站试图访问接口。
-
在一个安全接口上获知或配置的地址出现在同一个 VLAN 中的另一个安全接口上。
默认情况下,端口安全违规导致交换机接口因错误而被禁用并立即关闭,从而阻止在路由器之间传送 HSRP 状态消息。
解决方法
-
在路由器上发出 standby use-bia 命令。这强制路由器使用固化地址用于 HSRP,而不是虚拟 MAC 地址。
-
禁用连接到已启用 HSRP 的路由器的交换机端口上的端口安全。
案例分析 9:%Interface Hardware Cannot Support Multiple Groups
如果在接口上创建了多个 HSRP 组,将收到此错误消息:
%Interface hardware cannot support multiple groups
收到此错误消息是因为某些路由器或交换机上的硬件限制。用任何软件方法都不可能克服此限制。问题是每个 HSRP 组使用接口上的另一个 MAC 地址,因此以太网 MAC 芯片必须支持多个可编程 MAC 地址,以启用多个 HSRP 组。
解决方法是使用 standby use-bia 接口配置命令,该命令使用接口的固化地址 (BIA) 作为其虚拟 MAC 地址,而不是预先分配的 MAC 地址。
排除Catalyst交换机中的HSRP故障
A.检验HSRP路由器配置
1. 验证唯一路由器接口 IP 地址
逐接口验证每台 HSRP 路由器为每个子网提供了唯一的 IP 地址。并且,验证每个接口的线路协议是否 up。为了快速验证每个接口的当前状态,请发出 show ip interface brief 命令。例如:
Router_1#show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol Vlan1 192.168.1.1 YES manual up up Vlan10 192.168.10.1 YES manual up up Vlan11 192.168.11.1 YES manual up upRouter_2#show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol Vlan1 192.168.1.2 YES manual up up Vlan10 192.168.10.2 YES manual up up Vlan11 192.168.11.2 YES manual upup
2. 验证备用 (HSRP) IP 地址和备用组号码
验证被配置的备用 (HSRP) IP 地址和备用组号码与每个参与 HSRP 的路由器相匹配。如果备用组或 HSRP 备用地址不匹配,则可能引起 HSRP 问题。show standby 命令详细显示每个接口的备用组和备用 IP 地址配置。例如:
Router_1#show standby
Vlan10 - Group 110
State is Active
2 state changes, last state change 00:01:34
Virtual IP address is 192.168.10.100
Active virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac6e (MAC In Use)
Local virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac6e (v1 default)
Hello time 3 sec, hold time 10 sec
Next hello sent in 0.144 secs
Preemption enabled
Active router is local
Standby router is 192.168.10.2, priority 109 (expires in 10.784 sec)
Priority 110 (configured 110)
Group name is "hsrp-Vl10-110" (default)
FLAGS: 0/1
Vlan11 - Group 111
State is Active
2 state changes, last state change 00:00:27
Virtual IP address is 192.168.11.100
Active virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac6f (MAC In Use)
Local virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac6f (v1 default)
Hello time 3 sec, hold time 10 sec
Next hello sent in 2.096 secs
Preemption enabled
Active router is local
Standby router is 192.168.11.2, priority 109 (expires in 8.944 sec)
Priority 110 (configured 110)
Group name is "hsrp-Vl11-111" (default)
FLAGS: 0/1
Router_2#show standby
Vlan10 - Group 110
State is Standby
1 state change, last state change 00:03:15
Virtual IP address is 192.168.10.100
Active virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac6e (MAC Not In Use)
Local virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac6e (v1 default)
Hello time 3 sec, hold time 10 sec
Next hello sent in 1.088 secs
Preemption disabled
Active router is 192.168.10.1, priority 110 (expires in 11.584 sec)
Standby router is local
Priority 109 (configured 109)
Group name is "hsrp-Vl10-110" (default)
FLAGS: 0/1
Vlan11 - Group 111
State is Standby
1 state change, last state change 00:02:53
Virtual IP address is 192.168.11.100
Active virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac6f (MAC Not In Use)
Local virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac6f (v1 default)
Hello time 3 sec, hold time 10 sec
Next hello sent in 2.352 secs
Preemption disabled
Active router is 192.168.11.1, priority 110 (expires in 9.120 sec)
Standby router is local
Priority 109 (configured 109)
Group name is "hsrp-Vl11-111" (default)
FLAGS: 0/13. 验证每个接口的备用 (HSRP) IP 地址是否各不相同
验证备用 (HSRP) IP 地址是否与每个接口上配置的 IP 地址不同。show standby 命令是查看此信息的快速参考。例如:
Router_1#show standby
Vlan10 - Group 110
State is Active
2 state changes, last state change 00:01:34
Virtual IP address is 192.168.10.100
Active virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac6e (MAC In Use)
Local virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac6e (v1 default)
Hello time 3 sec, hold time 10 sec
Next hello sent in 0.144 secs
Preemption enabled
Active router is local
Standby router is 192.168.10.2, priority 109 (expires in 10.784 sec)
Priority 110 (configured 110)
Group name is "hsrp-Vl10-110" (default)
FLAGS: 0/1
Vlan11 - Group 111
State is Active
2 state changes, last state change 00:00:27
Virtual IP address is 192.168.11.100
Active virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac6f (MAC In Use)
Local virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac6f (v1 default)
Hello time 3 sec, hold time 10 sec
Next hello sent in 2.096 secs
Preemption enabled
Active router is local
Standby router is 192.168.11.2, priority 109 (expires in 8.944 sec)
Priority 110 (configured 110)
Group name is "hsrp-Vl11-111" (default)
FLAGS: 0/1
Router_2#show standby
Vlan10 - Group 110
State is Standby
1 state change, last state change 00:03:15
Virtual IP address is 192.168.10.100
Active virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac6e (MAC Not In Use)
Local virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac6e (v1 default)
Hello time 3 sec, hold time 10 sec
Next hello sent in 1.088 secs
Preemption disabled
Active router is 192.168.10.1, priority 110 (expires in 11.584 sec)
Standby router is local
Priority 109 (configured 109)
Group name is "hsrp-Vl10-110" (default)
FLAGS: 0/1
Vlan11 - Group 111
State is Standby
1 state change, last state change 00:02:53
Virtual IP address is 192.168.11.100
Active virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac6f (MAC Not In Use)
Local virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac6f (v1 default)
Hello time 3 sec, hold time 10 sec
Next hello sent in 2.352 secs
Preemption disabled
Active router is 192.168.11.1, priority 110 (expires in 9.120 sec)
Standby router is local
Priority 109 (configured 109)
Group name is "hsrp-Vl11-111" (default)
FLAGS: 0/1 4.何时使用standy use-bia命令
除非令牌环接口上配置了 HSRP,否则 standby use-bia 命令应该只用于特殊情况。此命令通知路由器使用其 BIA 而不是虚拟 HSRP MAC 地址用于 HSRP 组。在令牌环网络中,如果源路由桥接 (SRB) 处于使用状态,那么 standby use-bia 命令将允许新的活动路由器通过无故 ARP 更新主机的路由信息字段 (RIF) 缓存。但并不是所有的主机实现都能正确地处理无故 ARP。standby use-bia 命令的另一个注意事项涉及代理 ARP。备用路由器不能取代故障活动路由器已丢失的代理 ARP 数据库。
5. 验证访问列表配置
验证在所有 HSRP 对等体上配置的访问列表是否未过滤在其接口上配置的任何 HSRP 地址。特别地,验证为了将流量发送到子网上所有路由器而使用的多播地址 (224.0.0.2)。 同时,验证目标为 HSRP 端口 1985 的 UDP 流量是否未被过滤。HSRP 使用此地址和端口在对等体之间发送 hello 数据包。作为快速参考发出 show access-lists 命令,以记下路由器上配置的访问列表。例如:
Router_1#show access-lists
Standard IP access list 77
deny 10.19.0.0, wildcard bits 0.0.255.255
permit any
Extended IP access list 144
deny pim 238.0.10.0 0.0.0.255 any
permit ip any any (58 matches)
B. 验证 Catalyst Fast EtherChannel 和中继配置
1. 验证中继配置
如果中继用来连接 HSRP 路由器,请验证路由器和交换机上的中继配置。有五个可能的中继模式:
-
在
-
desirable
-
auto(自动)
-
off
-
nonegotiate(非协商)
验证配置的中继模式是否提供期望的中继方法。
当您排除 HSRP 故障时,请使用 desirable 配置用于交换机到交换机连接。此配置可以隔离交换机端口无法正确建立中继的问题。因为多数 Cisco IOS 路由器不支持中继协商,请将路由器到交换机配置设置为非协商。
对于IEEE 802.1Q(dot1q)中继模式,检验中继两端是否配置为使用相同的本地VLAN和封装。由于默认情况下思科产品不标记本地 VLAN,本地 VLAN 配置不匹配会导致在错配的 VLAN 上无法连通。最后,验证是否已经配置中继来传输路由器上配置的 VLAN,同时验证 VLAN 是否未被修剪并且处于 STP 状态,以供与路由器连接的端口使用。发出show interfaces <interface> trunk命令,以获得显示此信息的快速参考。例如:
L2Switch_1#show interfaces gigabitEthernet1/0/13 trunk Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Gi1/0/13 on 802.1q trunking 1 Port Vlans allowed on trunk Gi1/0/13 1-4094 Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain Gi1/0/13 1,10-11,70,100,300-309 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Gi1/0/13 1,10-11,70,100,300-309
Router_1#show interfaces gigabitEthernet1/0/1 trunk Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Gi1/0/1 on 802.1q trunking 1 Port Vlans allowed on trunk Gi1/0/1 1-4094 Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain Gi1/0/1 1,10-11,100,206,301,307,401,900,3001-3002 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Gi1/0/1 1,10-11,100,206,301,307,401,900,3001-30022. 验证 Fast EtherChannel(端口信道)配置
如果用端口信道连接 HSRP 路由器,请验证路由器和交换机上的 EtherChannel 配置。在至少一端将交换机对交换机端口信道配置为 desirable。另一边可以处于任何以下模式:
-
在
-
desirable
-
auto(自动)
但是,在本示例中,接口不是port-channel的成员:
Router_1#show etherchannel summary
Flags: D - down P - bundled in port-channel
I - stand-alone s - suspended
H - Hot-standby (LACP only)
R - Layer3 S - Layer2
U - in use f - failed to allocate aggregator
M - not in use, minimum links not met
u - unsuitable for bundling
w - waiting to be aggregated
d - default port
A - formed by Auto LAG
Number of channel-groups in use: 0
Number of aggregators: 0
Group Port-channel Protocol Ports
------+-------------+-----------+-----------------------------------------------
Router_1#
Router_2#show etherchannel summary
Flags: D - down P - bundled in port-channel
I - stand-alone s - suspended
H - Hot-standby (LACP only)
R - Layer3 S - Layer2
U - in use f - failed to allocate aggregator
M - not in use, minimum links not met
u - unsuitable for bundling
w - waiting to be aggregated
d - default port
A - formed by Auto LAG
Number of channel-groups in use: 0
Number of aggregators: 0
Group Port-channel Protocol Ports
------+-------------+-----------+-----------------------------------------------
Router_2#3.检查交换机MAC地址转发表
验证 HSRP 路由器的交换机上的 MAC 地址表中是否存在 HSRP 虚拟 MAC 地址和物理 BIA 的条目。路由器上的 show standby 命令提供虚拟 MAC 地址。show interface 命令提供物理 BIA。以下是示例输出:
Router_1#show standby Vlan10 - Group 110 State is Active 2 state changes, last state change 00:37:03 Virtual IP address is 192.168.10.100 Active virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac6e (MAC In Use) Local virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac6e (v1 default) Hello time 3 sec, hold time 10 sec Next hello sent in 0.768 secs Preemption enabled Active router is local Standby router is 192.168.10.2, priority 109 (expires in 10.368 sec) Priority 110 (configured 110) Group name is "hsrp-Vl10-110" (default) FLAGS: 0/1 Vlan11 - Group 111 State is Active 2 state changes, last state change 00:35:56 Virtual IP address is 192.168.11.100 Active virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac6f (MAC In Use) Local virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac6f (v1 default) Hello time 3 sec, hold time 10 sec Next hello sent in 1.472 secs Preemption enabled Active router is local Standby router is 192.168.11.2, priority 109 (expires in 8.336 sec) Priority 110 (configured 110) Group name is "hsrp-Vl11-111" (default) FLAGS: 0/1Router_1#show interfaces vlan 10 Vlan10 is up, line protocol is up , Autostate Enabled Hardware is Ethernet SVI, address is d4e8.801f.4846 (bia d4e8.801f.4846) Internet address is 192.168.10.1/24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 1000000 Kbit/sec, DLY 10 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set Keepalive not supported ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input 00:00:00, output 00:00:01, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Input queue: 0/375/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0 Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue: 0/40 (size/max) 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 9258 packets input, 803066 bytes, 0 no buffer Received 0 broadcasts (0 IP multicasts) 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles 0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored 3034 packets output, 368908 bytes, 0 underruns Output 0 broadcasts (0 IP multicasts) 0 output errors, 2 interface resets 0 unknown protocol drops 0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped outL2Switch_1#show mac address-table address 0000.0c07.ac6e Mac Address Table ------------------------------------------- Vlan Mac Address Type Ports ---- ----------- -------- ----- 10 0000.0c07.ac6e DYNAMIC Gi1/0/13 Total Mac Addresses for this criterion: 1
L2Switch_1#show mac address-table address 0000.0c07.ac6f Mac Address Table ------------------------------------------- Vlan Mac Address Type Ports ---- ----------- -------- ----- 11 0000.0c07.ac6f DYNAMIC Gi1/0/13 Total Mac Addresses for this criterion: 1
请务必检查 CAM 老化时间,以便确定条目的老化速度。如果时间等于 STP 转发延迟的配置值(默认情况下为 15 秒),则网络中很可能存在 STP 环路。示例命令输出如下:
L2Switch_1#show mac address-table aging-time vlan 10
Global Aging Time: 300
Vlan Aging Time
---- ----------
10 300
L2Switch_1#show mac address-table aging-time vlan 11
Global Aging Time: 300
Vlan Aging Time
---- ----------
11 300C. 验证物理层连接
如果 HSRP 组内有多个路由器处于活动状态,则这些路由器不会一致从其他 HSRP 对等体那里接收到 hello 数据包。物理层问题可能会阻止流量在对等体之间持续通过并导致此情况。排除 HSRP 故障时,请务必验证 HSRP 对等体之间的物理连接和 IP 连接。发出 show standby 命令以验证连接。例如:
Router_1#show standby Vlan10 - Group 110 State is Active 2 state changes, last state change 00:54:03 Virtual IP address is 192.168.10.100 Active virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac6e (MAC In Use) Local virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac6e (v1 default) Hello time 3 sec, hold time 10 sec Next hello sent in 0.848 secs Preemption enabled Active router is local Standby router is unknown Priority 110 (configured 110) Group name is "hsrp-Vl10-110" (default) FLAGS: 0/1 Vlan11 - Group 111 State is Active 2 state changes, last state change 00:52:56 Virtual IP address is 192.168.11.100 Active virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac6f (MAC In Use) Local virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac6f (v1 default) Hello time 3 sec, hold time 10 sec Next hello sent in 0.512 secs Preemption enabled Active router is local Standby router is unknown Priority 110 (configured 110) Group name is "hsrp-Vl11-111" (default) FLAGS: 0/1Router_2#show standby Vlan10 - Group 110 State is Init (interface down) 2 state changes, last state change 00:00:42 Virtual IP address is 192.168.10.100 Active virtual MAC address is unknown (MAC Not In Use) Local virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac6e (v1 default) Hello time 3 sec, hold time 10 sec Preemption disabled Active router is unknown Standby router is unknown Priority 109 (configured 109) Group name is "hsrp-Vl10-110" (default) FLAGS: 0/1 Vlan11 - Group 111 State is Init (interface down) 2 state changes, last state change 00:00:36 Virtual IP address is 192.168.11.100 Active virtual MAC address is unknown (MAC Not In Use) Local virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac6f (v1 default) Hello time 3 sec, hold time 10 sec Preemption disabled Active router is unknown Standby router is unknown Priority 109 (configured 109) Group name is "hsrp-Vl11-111" (default) FLAGS: 0/1
1.检查接口状态
检查接口。验证是否所有配置 HSRP 的接口均处于 up/up 状态,如以下示例所示:
Router_1#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Vlan1 192.168.1.1 YES manual up up
Vlan10 192.168.10.1 YES manual up up
Vlan11 192.168.11.1 YES manual up up
Router_2#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Vlan1 192.168.1.2 YES manual up up
Vlan10 192.168.10.2 YES manual administratively down down
Vlan11 192.168.11.2 YES manual administratively down down 如果任何接口在管理上处于 down/down 状态,请在路由器上进入配置模式并发出接口特定的 no shutdown 命令。例如:
Router_2#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router_2(config)#interface vlan 10 Router_2(config-if)#no shutdown Router_2(config-if)#endRouter_2#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router_2(config)#interface vlan 11 Router_2(config-if)#no shutdown Router_2(config-if)#endRouter_2#show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol Vlan1 192.168.1.2 YES manual up up Vlan10 192.168.10.2 YES manual up down Vlan11 192.168.11.2 YES manual up up
如果其中任一接口处于 down/down 或 up/down 状态,请检查日志中是否有接口更改通知。对基于 Cisco IOS 软件的交换机而言,在链路打开/关闭情况下会出现下列消息:
%LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface "interface", changed state to up %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface "interface", changed state to down Router_1#show log 3d04h: %STANDBY-6-STATECHANGE: Standby: 0: Vlan10 state Active-> Speak 3d04h: %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Vlan10, changed state to down 3d04h: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Vlan10, changed state to down
检查端口、电缆和 HSRP 对等体之间的所有收发器或其他设备。是否有人移除或松开了任何连接?是否有任何接口经常丢失链路?使用的电缆类型是否适当?检查接口是否存在任何错误,如下例所示:
Router_2#show interface vlan 10Vlan10 is down, line protocol is down , Autostate Enabled Hardware is Ethernet SVI, address is 1880.90d8.5946 (bia 1880.90d8.5946) Internet address is 192.168.10.2/24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 1000000 Kbit/sec, DLY 10 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set Keepalive not supported ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input 00:00:10, output 00:00:08, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Input queue: 0/375/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0 Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue: 0/40 (size/max) 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 1243 packets input, 87214 bytes, 0 no buffer Received 0 broadcasts (0 IP multicasts) 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles 0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored 23 packets output, 1628 bytes, 0 underruns Output 0 broadcasts (0 IP multicasts) 0 output errors, 2 interface resets 0 unknown protocol drops 0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
2. 链路更改和端口错误
检查交换机端口链路更改和其他错误。发出以下命令并检查输出:
-
show logging
-
show interfaces <interface> counters
-
show interfaces <interface> status
这些命令可帮助您确定交换机和其他设备之间是否存在连接问题。
对于链路打开/关闭情况,以下消息是正常的:
L2Switch_1#show logging
Syslog logging: enabled (0 messages dropped, 5 messages rate-limited, 0 flushes, 0 overruns, xml disabled, filtering disabled)
No Active Message Discriminator.
No Inactive Message Discriminator.
Console logging: level informational, 319 messages logged, xml disabled,
filtering disabled
Monitor logging: level debugging, 0 messages logged, xml disabled,
filtering disabled
Buffer logging: level debugging, 467 messages logged, xml disabled,
filtering disabled
Exception Logging: size (4096 bytes)
Count and timestamp logging messages: disabled
File logging: disabled
Persistent logging: disabled
No active filter modules.
Trap logging: level informational, 327 message lines logged
Logging Source-Interface: VRF Name:
Log Buffer (10000 bytes):
*Jul 26 17:52:07.526: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface GigabitEthernet1/0/13, changed state to up
*Jul 26 17:52:09.747: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface GigabitEthernet1/0/13, changed state to down
*Jul 26 17:57:11.716: %SPANTREE-7-RECV_1Q_NON_TRUNK: Received 802.1Q BPDU on non trunk GigabitEthernet1/0/16 VLAN307.
*Jul 26 17:57:11.716: %SPANTREE-7-BLOCK_PORT_TYPE: Blocking GigabitEthernet1/0/16 on VLAN0307. Inconsistent port type.
*Jul 26 17:57:13.583: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface GigabitEthernet1/0/16, changed state to up
*Jul 26 17:57:16.237: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface GigabitEthernet1/0/16, changed state to down
*Jul 26 18:02:16.481: %SPANTREE-7-RECV_1Q_NON_TRUNK: Received 802.1Q BPDU on non trunk GigabitEthernet1/0/16 VLAN307.
*Jul 26 18:02:16.481: %SPANTREE-7-BLOCK_PORT_TYPE: Blocking GigabitEthernet1/0/16 on VLAN0307. Inconsistent port type.
*Jul 26 18:02:18.367: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface GigabitEthernet1/0/16, changed state to up
*Jul 26 18:02:20.561: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface GigabitEthernet1/0/16, changed state to down发出show interfaces <interface> status命令以确定端口的常规运行状况。例如:
L2Switch_1#show interfaces gigabitEthernet 1/0/13 status
Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type
Gi1/0/13 connected trunk a-full a-1000 10/100/1000BaseTX接口状态是connected、notconnect还是errdisable?如果状态是 notconnect,请检查两端电缆是否均已插入。检查使用的电缆是否适当。如果状态是 errdisable,请查看计数器看是否存在过多错误。有关详细信息,请参阅恢复Cisco IOS平台上的Errdisable端口状态。
此端口是针对什么 VLAN 配置的?请确保连接的另一端是为同一 VLAN 配置的。如果将链路配置为中继,则应保证中继的两端都承载同样的 VLAN。
速度和双工配置如何?如果在设置前面加上了一个 a-,则该端口配置为自动协商速度和双工。否则,网络管理员已预先确定此配置。在配置链路的速度和双工时,链路两端的设置必须匹配。如果一个交换机端口配置为自动协商,则链路另一端也必须配置为自动协商。如果一端被硬编码为特定速度和双工,另一端也必须进行硬编码。如果留下一端自动协商,同时另一端为硬编码时,则会中断自动协商进程。
L2Switch_1#show interfaces gi1/0/13 counters errors Port Align-Err FCS-Err Xmit-Err Rcv-Err UnderSize OutDiscards Gi1/0/13 0 0 0 0 0 0 Port Single-Col Multi-Col Late-Col Excess-Col Carri-Sen Runts Gi1/0/13 0 0 0 0 0 0 是否有很多 Align-Err、FCS-Err 或 Runts?这些指示端口和连接设备之间的速度或双工不匹配。请更改该端口的速度和双工设置,以便帮助正确这些错误。
发出 show mac 命令以验证端口是否有流量通过。In和Out列指示在特定端口上接收和传输的单播、组播和广播数据包的数量。底部的计数器显示有多少数据包被丢弃或丢失,以及这些数据包是否是入站或出站流量的一部分。Lrn-Discrd、In-Lost 和 Out-Lost 计算由于缓冲区不足而错误转发或丢弃的数据包数量。
L2Switch_1#show interfaces gi1/0/13 counters
Port InOctets InUcastPkts InMcastPkts InBcastPkts
Gi1/0/13 304933333 1180453 1082538 14978
Port OutOctets OutUcastPkts OutMcastPkts OutBcastPkts
Gi1/0/13 282752538 276716 824562 588960
3. 验证 IP 连接
验证 IP 连接。从相关路由器对远程HSRP设备发出IP ping。这有助于暴露所有连接的短暂丢失。扩展 ping 仅在 enable 模式中可用。示例命令输出如下:
Router_1#show run interface vlan 10
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 141 bytes
!
interface Vlan10
ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
standby 110 ip 192.168.10.100
standby 110 priority 110
standby 110 preempt
end
Router_2#show run interface vlan 10
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 120 bytes
!
interface Vlan10
ip address 192.168.10.2 255.255.255.0
standby 110 ip 192.168.10.100
standby 110 priority 109
end
Router_1#ping 192.168.10.2 repeat 1500
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 1500, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.10.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (1500/1500), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/2/9 ms从每个 HSRP 路由器发出到其对等体的 ping 以确定连接的故障位置。
4.检查单向链路
检查交换机是否存在 HSRP 对等体之间的单向链路。每当邻居可收到链路上的本地设备传输的流量,而本地设备无法接收邻居传输的流量时,就会产生单向链路。此功能称作单向链路检测 (UDLD) 主动模式。UDLD 仅在连接的两端均支持此功能时才可用。UDLD 主动模式运行在 L2 层,以确定链路是否已正确连接,以及流量是否在正确的邻居之间双向流动。示例命令输出如下:
注意:导航到配置UDLD协议功能的下一个链接,该功能取决于使用的平台。
另一个在UDLD不可用时有助于验证单向链路的选项是使用Cisco发现协议(CDP)。 启用 CDP 是另一种检测单向链路是否存在的方法。如果只有链路的一端能发现其相邻设备,请替换设备之间的电缆,并且检查有故障的接口。
Router_1#show cdpGlobal CDP information: Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Sending a holdtime value of 180 seconds Sending CDPv2 advertisements is enabled Router_1#show cdp neighbors gi1/0/1 detail ------------------------- Device ID: L2Switch_1.cisco.com Entry address(es): IP address: 192.168.70.1 IPv6 address: 2001:420:140E:2101::1 (global unicast) IPv6 address: FE80::2FE:C8FF:FED3:86C7 (link-local) Platform: cisco WS-C3650-12X48UR, Capabilities: Router Switch IGMP Interface: GigabitEthernet1/0/1, Port ID (outgoing port): GigabitEthernet1/0/13 Holdtime : 173 sec Version : Cisco IOS Software [Denali], Catalyst L3 Switch Software (CAT3K_CAA-UNIVERSALK9-M), Version 16.3.8, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc3) Technical Support: http://www.cisco.com/techsupport Copyright (c) 1986-2019 by Cisco Systems, Inc. Compiled Wed 13-Feb-19 03:00 by mcpre advertisement version: 2 VTP Management Domain: 'CALOnet' Native VLAN: 1 Duplex: full Management address(es): IP address: 192.168.70.1 Spare Pair PoE: Yes, Spare Pair Detection Required: No Spare Pair PD Config: Disable, Spare Pair PSE Operational: No Total cdp entries displayed : 1
5. 其他物理层故障排除参考
请参阅以下文档:
D. 第三层 HSRP 调试
如果HSRP状态频繁更改,请在路由器上使用HSRP debug命令(在启用模式下)以观察HSRP活动。此信息可帮助您确定哪些 HSRP 数据包是由路由器接收和发送的。如果创建 Cisco 技术支持服务请求,请收集此信息。调试输出还显示 HSRP 状态信息,以及详细的 HSRP hello 数据包统计。
1. 标准 HSRP 调试
在Cisco IOS中,使用命令debug standby启用HSRP调试功能。对于间歇性的、仅影响几个接口的问题,此信息非常有用。通过调试,您可以确定所涉及的 HSRP 路由器是否以特定时间间隔接收和传输 HSRP hello 数据包。如果路由器未收到 hello 数据包,您可以推断对等体未传输 hello 数据包或网络丢弃了数据包。
| 命令 | 目的 |
|---|---|
| debug standby | 启用 HSRP 调试 |
示例命令输出如下:
Router_1#debug standby HSRP debugging is onJul 29 16:12:16.889: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello out 192.168.10.1 Active pri 110 vIP 192.168.10.100 Jul 29 16:12:16.996: HSRP: Vl11 Grp 111 Hello in 192.168.11.2 Standby pri 109 vIP 192.168.11.100 Jul 29 16:12:17.183: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello in 192.168.10.2 Standby pri 109 vIP 192.168.10.100Jul 29 16:12:17.366: HSRP: Vl11 Grp 111 Hello out 192.168.11.1 Active pri 110 vIP 192.168.11.100 Jul 29 16:12:18.736: HSRP: Vl10 Interface adv in, Passive, active 0, passive 1, from 192.168.10.2 Jul 29 16:12:19.622: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello out 192.168.10.1 Active pri 110 vIP 192.168.10.100
2. 条件 HSRP 调试(根据备用组和/或 VLAN 限制输出)
Cisco IOS 软件版本 12.0(3) 引入 debug condition,它允许根据接口和组号码过滤 debug standby 命令的输出。该命令使用在 Cisco IOS 软件版本 12.0 中引入的 debug condition 示例。
| 命令 | 目的 |
|---|---|
| debug condition standby <interface> <group> | 启用组的HSRP条件调试(0-255) |
接口必须是可以支持 HSRP 的有效接口。组可以是从0到255的任何组。可以为不存在的组设置调试条件。这允许在新组的初始化期间捕获调试。必须启用 debug standby,才能生成任何调试输出。如果不存在备用 debug condition,则将为所有接口上的所有组生成调试输出。如果存在至少一个备用 debug condition,则应根据所有备用 debug condition,对备用调试输出进行过滤。示例命令输出如下:
Router_1#debug condition standby vlan 10 110 Condition 1 set Router_1# Jul 29 16:16:20.284: Vl10 HSRP110 Debug: Condition 1, hsrp Vl10 HSRP110 triggered, count 1 Router_1#debug standby HSRP debugging is on Router_1# Jul 29 16:16:44.797: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello out 192.168.10.1 Active pri 110 vIP 192.168.10.100
Jul 29 16:16:45.381: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello in 192.168.10.2 Standby pri 109 vIP 192.168.10.100
Jul 29 16:16:47.231: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello out 192.168.10.1 Active pri 110 vIP 192.168.10.100
Jul 29 16:16:48.248: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello in 192.168.10.2 Standby pri 109 vIP 192.168.10.100
3. 增强的 HSRP 调试功能
Cisco IOS 软件版本 12.1(1) 添加了增强的 HSRP 调试功能。为了帮助找到有用的信息,增强的 HSRP 调试功能限制定期 Hello 消息中的噪声并且包括其他状态信息。当您创建服务请求以与 Cisco 技术支持工程师一起工作时,此信息特别有用。
| 命令 | 目的 |
|---|---|
| debug standby | 显示所有 HSRP 错误、事件和数据包 |
| debug standby errors | 显示 HSRP 错误 |
| debug standby events [[all] | [hsrp |冗余 | track]] [detail] | 显示 HSRP 事件 |
| debug standby packets [[all | terse] | [通告 |政变 | hello | resign]] [detail] | 显示 HSRP 数据包 |
| debug standby terse | 显示有限范围的HSRP错误、事件和数据包 |
示例命令输出如下:
Router_2#debug standby terse
HSRP:
HSRP Errors debugging is on
HSRP Events debugging is on
(protocol, neighbor, redundancy, track, ha, arp, interface)
HSRP Packets debugging is on
(Coup, Resign)
Router_2#
*Jul 29 16:49:35.416: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Resign in 192.168.10.1 Active pri 110 vIP 192.168.10.100
*Jul 29 16:49:35.416: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Standby: i/Resign rcvd (110/192.168.10.1)
*Jul 29 16:49:35.416: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Active router is local, was 192.168.10.1
*Jul 29 16:49:35.416: HSRP: Vl10 Nbr 192.168.10.1 no longer active for group 110 (Standby)
*Jul 29 16:49:35.417: HSRP: Vl10 Nbr 192.168.10.1 Was active or standby - start passive holddown
*Jul 29 16:49:35.417: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Standby router is unknown, was local
*Jul 29 16:49:35.417: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Standby -> Active
*Jul 29 16:49:35.418: %HSRP-5-STATECHANGE: Vlan10 Grp 110 state Standby -> Active
*Jul 29 16:49:35.418: HSRP: Peer not present
*Jul 29 16:49:35.418: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Redundancy "hsrp-Vl10-110" state Standby -> Active
*Jul 29 16:49:35.419: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Added 192.168.10.100 to ARP (0000.0c07.ac6e)
*Jul 29 16:49:35.420: HSRP: Vl10 IP Redundancy "hsrp-Vl10-110" standby, local -> unknown
*Jul 29 16:49:35.421: HSRP: Vl10 IP Redundancy "hsrp-Vl10-110" update, Standby -> Active
*Jul 29 16:49:38.422: HSRP: Vl10 IP Redundancy "hsrp-Vl10-110" update, Active -> Active您可以使用接口和/或 HSRP 组条件调试以对此调试输出进行过滤。
| 命令 | 目的 |
|---|---|
| debug condition interface interface | 启用接口条件调试 |
| debug condition standby <interface> <group> | 启用 HSRP 条件调试 |
在本示例中,路由器加入事先存在的 HSRP 组:
Rotuer_2#debug condition standby vlan 10 110
Condition 1 set
Router_2#debug condition interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/1 vlan-id 10
Condition 2 set
Router_2#debug standby
HSRP debugging is on
Router_2#
*Jul 29 16:54:12.496: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello out 192.168.10.2 Active pri 109 vIP 192.168.10.100
*Jul 29 16:54:15.122: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello out 192.168.10.2 Active pri 109 vIP 192.168.10.100
*Jul 29 16:54:17.737: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello out 192.168.10.2 Active pri 109 vIP 192.168.10.100
*Jul 29 16:54:18.880: HSRP: Vl10 Nbr 192.168.10.1 is passive
*Jul 29 16:54:20.316: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello out 192.168.10.2 Active pri 109 vIP 192.168.10.100
*Jul 29 16:54:20.322: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Coup in 192.168.10.1 Listen pri 110 vIP 192.168.10.100
*Jul 29 16:54:20.323: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Active: j/Coup rcvd from higher pri router (110/192.168.10.1)
*Jul 29 16:54:20.323: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Active router is 192.168.10.1, was local
*Jul 29 16:54:20.323: HSRP: Vl10 Nbr 192.168.10.1 is no longer passive
*Jul 29 16:54:20.324: HSRP: Vl10 Nbr 192.168.10.1 active for group 110
*Jul 29 16:54:20.324: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Active -> Speak
*Jul 29 16:54:20.325: %HSRP-5-STATECHANGE: Vlan10 Grp 110 state Active -> Speak
*Jul 29 16:54:20.325: HSRP: Peer not present
*Jul 29 16:54:20.325: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Redundancy "hsrp-Vl10-110" state Active -> Speak
*Jul 29 16:54:20.326: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Removed 192.168.10.100 from ARP
*Jul 29 16:54:20.326: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Deactivating MAC 0000.0c07.ac6e
*Jul 29 16:54:20.327: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Removing 0000.0c07.ac6e from MAC address filter
*Jul 29 16:54:20.328: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello out 192.168.10.2 Speak pri 109 vIP 192.168.10.100
*Jul 29 16:54:20.328: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello in 192.168.10.1 Active pri 110 vIP 192.168.10.100
*Jul 29 16:54:23.104: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello out 192.168.10.2 Speak pri 109 vIP 192.168.10.100
*Jul 29 16:54:23.226: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello in 192.168.10.1 Active pri 110 vIP 192.168.10.100
*Jul 29 16:54:25.825: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello in 192.168.10.1 Active pri 110 vIP 192.168.10.100
*Jul 29 16:54:25.952: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello out 192.168.10.2 Speak pri 109 vIP 192.168.10.100
*Jul 29 16:54:28.427: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello in 192.168.10.1 Active pri 110 vIP 192.168.10.100
*Jul 29 16:54:28.772: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello out 192.168.10.2 Speak pri 109 vIP 192.168.10.100
*Jul 29 16:54:30.727: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Speak: d/Standby timer expired (unknown)
*Jul 29 16:54:30.727: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Standby router is local
*Jul 29 16:54:30.727: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Speak -> Standby
*Jul 29 16:54:30.727: %HSRP-5-STATECHANGE: Vlan10 Grp 110 state Speak -> Standby
*Jul 29 16:54:30.728: HSRP: Peer not present
*Jul 29 16:54:30.728: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Redundancy "hsrp-Vl10-110" state Speak -> Standby
*Jul 29 16:54:30.728: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello out 192.168.10.2 Standby pri 109 vIP 192.168.10.100
*Jul 29 16:54:31.082: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello in 192.168.10.1 Active pri 110 vIP 192.168.10.100
*Jul 29 16:54:33.459: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello out 192.168.10.2 Standby pri 109 vIP 192.168.10.100
*Jul 29 16:54:33.811: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello in 192.168.10.1 Active pri 110 vIP 192.168.10.100
*Jul 29 16:54:36.344: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello out 192.168.10.2 Standby pri 109 vIP 192.168.10.100
*Jul 29 16:54:36.378: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello in 192.168.10.1 Active pri 110 vIP 192.168.10.100
*Jul 29 16:54:38.856: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello in 192.168.10.1 Active pri 110 vIP 192.168.10.100
*Jul 29 16:54:38.876: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello out 192.168.10.2 Standby pri 109 vIP 192.168.10.100
*Jul 29 16:54:41.688: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello out 192.168.10.2 Standby pri 109 vIP 192.168.10.100
*Jul 29 16:54:41.717: HSRP: Vl10 Grp 110 Hello in 192.168.10.1 Active pri 110 vIP 192.168.10.100E. 生成树故障排除
网络中的 STP 环路或不稳定性可能会阻止 HSRP 对等体正常通信。由于这种不正常通信,每个对等体都成为活动路由器。STP 环路能导致广播风暴、重复帧和 MAC 表不一致。所有这些问题将影响整个网络,特别是 HSRP。HSRP 错误消息可能是 STP 问题的第一个征兆。
当您排除 STP 故障时,您必须了解每个 VLAN 上的网络 STP 拓扑。您必须确定哪个交换机是根网桥,并且该交换机的哪些端口处于阻塞和转发状态。由于每个 VLAN 有其自己的 STP 拓扑,在每个 VLAN 上,此信息是非常重要的。
1. 验证生成树配置
请确保在网络中的每台交换机和桥接设备上配置 STP。请记下每台交换机所认为的根网桥位置。还要记下以下计时器的值:
-
根最大老化时间
-
沟通时间
-
转发延迟
发出show spanning-tree命令以查看所有这些信息。默认情况下,命令显示所有VLAN的此信息。但是,如果您使用命令提供VLAN编号,则还可以过滤其他VLAN信息。当您排除 STP 故障时,此信息将非常有用。
您在show spanning-tree输出中记录的这三个计时器是从根网桥获取的。这些计时器不需要与特定网桥上设置的计时器匹配。但请确保计时器与根网桥相匹配,以防出现此交换机在任一点成为根网桥的情况。计时器与根网桥相匹配有助于维护管理的连续性和便于管理。匹配还可以防止使用了不正确计时器的交换机导致网络瘫痪。
注意:请一直启用所有 VLAN 的 STP,不管网络中是否存在冗余链路。如果在非冗余网络上启用 STP,可以防止中断。如果有人将交换机与集线器或其他交换机一起桥接,并偶然创建一个物理环路,就可能发生中断。在隔离特定问题时,STP 也是非常有用的。如果启用 STP 的启动影响了网络中的某种操作,则可能存在需要隔离出来的问题。
以下是show spanning-tree命令的输出示例:
L2Switch_1#show spanning-tree vlan 10
VLAN0010
Spanning tree enabled protocol rstp
Root ID Priority 32778
Address 00fe.c8d3.8680
This bridge is the root
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32778 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 10)
Address 00fe.c8d3.8680
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 300 sec
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Gi1/0/3 Desg FWD 4 128.3 P2p
Gi1/0/10 Desg FWD 4 128.10 P2p Edge
Gi1/0/11 Desg FWD 4 128.11 P2p
Gi1/0/13 Desg FWD 4 128.13 P2p
Gi1/0/14 Desg FWD 4 128.14 P2p
Gi1/0/15 Desg FWD 4 128.15 P2p
Gi1/0/16 Desg FWD 4 128.16 P2p
Gi1/0/35 Desg FWD 4 128.35 P2p
L2Switch_1#show spanning-tree vlan 11
VLAN0011
Spanning tree enabled protocol rstp
Root ID Priority 32779
Address 00fe.c8d3.8680
This bridge is the root
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32779 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 11)
Address 00fe.c8d3.8680
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 300 sec
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Gi1/0/3 Desg FWD 4 128.3 P2p
Gi1/0/10 Desg FWD 4 128.10 P2p Edge
Gi1/0/11 Desg FWD 4 128.11 P2p
Gi1/0/13 Desg FWD 4 128.13 P2p
Gi1/0/14 Desg FWD 4 128.14 P2p
Gi1/0/15 Desg FWD 4 128.15 P2p
Gi1/0/16 Desg FWD 4 128.16 P2p
Gi1/0/35 Desg FWD 4 128.35 P2p 交换机L2Switch_1是VLAN 10和VLAN 11的根。
2. 生成树环路
要发生 STP 环路,网络中必须存在 L2 物理冗余。如果不可能存在物理环路,则不会发生 STP。STP 环路的症状如下:
-
整个网络中断
-
连接 损耗
-
网络设备报告高进程和系统利用率
只要单个 VLAN 发生 STP 环路,就可能会拥塞链路,浪费其他 VLAN 的带宽。show interfaces <interface> controller命令会记录传输或接收过多数据包的端口。过多的广播和多播可能指示端口是 STP 环路的一部分。通常,只要多播或广播超过单播数据包的数量,就可以怀疑链路是否存在 STP 环路。
注意:交换机将接收和传输的 STP 网桥协议数据单元 (BPDU) 也视为多播帧。处于 STP 阻塞状态的端口仍然会传输和接收 STP BPDU。
Router_2#show interfaces gi1/0/1 controller
GigabitEthernet1/0/1 is up, line protocol is up (connected)
Hardware is Gigabit Ethernet, address is 1880.90d8.5901 (bia 1880.90d8.5901)
Description: PNP STARTUP VLAN
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 1000000 Kbit/sec, DLY 10 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Full-duplex, 1000Mb/s, media type is 10/100/1000BaseTX
input flow-control is on, output flow-control is unsupported
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input 00:00:00, output 00:00:04, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters never
Input queue: 0/2000/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue: 0/40 (size/max)
5 minute input rate 33000 bits/sec, 31 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 116000 bits/sec, 33 packets/sec
9641686 packets input, 1477317083 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 1913802 broadcasts (1151766 multicasts)
0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored
0 watchdog, 1151766 multicast, 0 pause input
0 input packets with dribble condition detected
10702696 packets output, 4241534645 bytes, 0 underruns
Output 3432 broadcasts (0 multicasts)
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 2 interface resets
9582 unknown protocol drops
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier, 0 pause output
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
Transmit GigabitEthernet1/0/1 Receive
4241534645 Total bytes 1477317083 Total bytes
10562003 Unicast frames 7727884 Unicast frames
4229489212 Unicast bytes 1291270617 Unicast bytes
137261 Multicast frames 1151766 Multicast frames
11812065 Multicast bytes 91096867 Multicast bytes
3432 Broadcast frames 762036 Broadcast frames
233368 Broadcast bytes 94949599 Broadcast bytes
0 System FCS error frames 0 IpgViolation frames
0 MacUnderrun frames 0 MacOverrun frames
0 Pause frames 0 Pause frames
0 Cos 0 Pause frames 0 Cos 0 Pause frames
0 Cos 1 Pause frames 0 Cos 1 Pause frames
0 Cos 2 Pause frames 0 Cos 2 Pause frames
0 Cos 3 Pause frames 0 Cos 3 Pause frames
0 Cos 4 Pause frames 0 Cos 4 Pause frames
0 Cos 5 Pause frames 0 Cos 5 Pause frames
0 Cos 6 Pause frames 0 Cos 6 Pause frames
0 Cos 7 Pause frames 0 Cos 7 Pause frames
0 Oam frames 0 OamProcessed frames
0 Oam frames 0 OamDropped frames
38144 Minimum size frames 4165201 Minimum size frames
4910833 65 to 127 byte frames 3126489 65 to 127 byte frames
1237675 128 to 255 byte frames 750243 128 to 255 byte frames
1029126 256 to 511 byte frames 1279281 256 to 511 byte frames
2205966 512 to 1023 byte frames 103668 512 to 1023 byte frames
1280952 1024 to 1518 byte frames 205229 1024 to 1518 byte frames
0 1519 to 2047 byte frames 11575 1519 to 2047 byte frames
0 2048 to 4095 byte frames 0 2048 to 4095 byte frames
0 4096 to 8191 byte frames 0 4096 to 8191 byte frames
0 8192 to 16383 byte frames 0 8192 to 16383 byte frames
0 16384 to 32767 byte frame 0 16384 to 32767 byte frame
0 > 32768 byte frames 0 > 32768 byte frames
0 Late collision frames 0 SymbolErr frames
0 Excess Defer frames 0 Collision fragments
0 Good (1 coll) frames 0 ValidUnderSize frames
0 Good (>1 coll) frames 0 InvalidOverSize frames
0 Deferred frames 0 ValidOverSize frames
0 Gold frames dropped 0 FcsErr frames
0 Gold frames truncated
0 Gold frames successful
0 1 collision frames
0 2 collision frames
0 3 collision frames
0 4 collision frames
0 5 collision frames
0 6 collision frames
0 7 collision frames
0 8 collision frames
0 9 collision frames
0 10 collision frames
0 11 collision frames
0 12 collision frames
0 13 collision frames
0 14 collision frames
0 15 collision frames
0 Excess collision frames
LAST UPDATE 2384 msecs AGO3. 拓扑结构更改通知
另一个对STP问题诊断至关重要的命令是show spanning-tree detail命令。此命令跟踪拓扑更改通知 (TCN) 消息,一直追溯到发送方。这些作为交换机间的特殊 BPDU 发送的消息表明交换机的拓扑结构发生过更改。该交换机将 TCN 传送出其根端口。TCN 上行移动到根网桥。根网桥然后将另一个特殊 BPDU(拓扑更改确认 (TCA))发送出其所有端口。根网桥在配置 BPDU 中设置 TCN 位。这会导致所有非根网桥将其 MAC 地址表老化计时器设置为配置 STP 转发延迟。
为了隔离此问题,请访问每个VLAN的根网桥,并对交换机连接的端口发出show spanning-tree <interface> detail命令。last change occurred条目提供接收上一个TCN的时间。在此情况下,要发现谁发送了导致可能的 STP 环路的 TCN,已经为时太晚。拓扑更改数条目可让您了解出现的TCN数量。在 STP 环路中,此计数器随时可能增加。有关详细信息,请参阅排除STP问题及相关设计注意事项。
其他有用的数据包括:
-
最后一个 TCN 的端口
-
最后一个 TCN 的时间
-
当前 TCN 计数
示例命令输出如下:
L2Switch_1#show spanning-tree vlan 10 detail
VLAN0010 is executing the rstp compatible Spanning Tree protocol
Bridge Identifier has priority 32768, sysid 10, address 00fe.c8d3.8680
Configured hello time 2, max age 20, forward delay 15, transmit hold-count 6
We are the root of the spanning tree
Topology change flag not set, detected flag not set
Number of topology changes 8 last change occurred 03:21:48 ago
from GigabitEthernet1/0/35
Times: hold 1, topology change 35, notification 2
hello 2, max age 20, forward delay 15
Timers: hello 0, topology change 0, notification 0, aging 300
Port 3 (GigabitEthernet1/0/3) of VLAN0010 is designated forwarding
Port path cost 4, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.3.
Designated root has priority 32778, address 00fe.c8d3.8680
Designated bridge has priority 32778, address 00fe.c8d3.8680
Designated port id is 128.3, designated path cost 0
Timers: message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1
Link type is point-to-point by default
BPDU: sent 6066, received 0
Port 10 (GigabitEthernet1/0/10) of VLAN0010 is designated forwarding
Port path cost 4, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.10.
Designated root has priority 32778, address 00fe.c8d3.8680
Designated bridge has priority 32778, address 00fe.c8d3.8680
Designated port id is 128.10, designated path cost 0
Timers: message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1
The port is in the portfast mode by portfast trunk configuration
Link type is point-to-point by default
BPDU: sent 6063, received 0
Port 11 (GigabitEthernet1/0/11) of VLAN0010 is designated forwarding
Port path cost 4, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.11.
Designated root has priority 32778, address 00fe.c8d3.8680
Designated bridge has priority 32778, address 00fe.c8d3.8680
Designated port id is 128.11, designated path cost 0
Timers: message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1
Link type is point-to-point by default
BPDU: sent 6066, received 0
Port 13 (GigabitEthernet1/0/13) of VLAN0010 is designated forwarding
Port path cost 4, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.13.
Designated root has priority 32778, address 00fe.c8d3.8680
Designated bridge has priority 32778, address 00fe.c8d3.8680
Designated port id is 128.13, designated path cost 0
Timers: message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1
Link type is point-to-point by default
BPDU: sent 6066, received 3
Port 14 (GigabitEthernet1/0/14) of VLAN0010 is designated forwarding
Port path cost 4, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.14.
Designated root has priority 32778, address 00fe.c8d3.8680
Designated bridge has priority 32778, address 00fe.c8d3.8680
Designated port id is 128.14, designated path cost 0
Timers: message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1
Link type is point-to-point by default
BPDU: sent 6066, received 3
Port 15 (GigabitEthernet1/0/15) of VLAN0010 is designated forwarding
Port path cost 4, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.15.
Designated root has priority 32778, address 00fe.c8d3.8680
Designated bridge has priority 32778, address 00fe.c8d3.8680
Designated port id is 128.15, designated path cost 0
Timers: message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1
Link type is point-to-point by default
BPDU: sent 6067, received 0
Port 16 (GigabitEthernet1/0/16) of VLAN0010 is designated forwarding
Port path cost 4, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.16.
Designated root has priority 32778, address 00fe.c8d3.8680
Designated bridge has priority 32778, address 00fe.c8d3.8680
Designated port id is 128.16, designated path cost 0
Timers: message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1
Link type is point-to-point by default
BPDU: sent 6067, received 0
Port 35 (GigabitEthernet1/0/35) of VLAN0010 is designated forwarding
Port path cost 4, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.35.
Designated root has priority 32778, address 00fe.c8d3.8680
Designated bridge has priority 32778, address 00fe.c8d3.8680
Designated port id is 128.35, designated path cost 0
Timers: message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1
Link type is point-to-point by default
BPDU: sent 6067, received 0此输出显示从接口GigabitEthernet1/0/35连接的设备发生最后一次拓扑更改。接下来,从该设备发出相同的show spanning-tree detail命令以尝试跟踪问题。如果生成TCN的交换机仅连接到PC或终端,请确保在这些端口上启用STP PortFast。当端口转换状态时,STP PortFast 会抑制 STP TCN。
有关 STP 和如何排除与网络接口卡 (NIC) 关联的链路转换故障的信息,请参阅以下文档:
4. 断开阻塞端口
由于 Fast Etherchannel (FEC)(端口信道)负载均衡的本质,FEC 问题可能会造成 HSRP 和 STP 问题。当您对STP或HSRP进行故障排除时,可以删除任何FEC连接的配置。配置更改到位后,在两台交换机上发出show spanning-tree blockedports命令。确保在连接的每一端有至少一个端口开始阻塞。
有关EtherChannel的信息,请参阅以下文档:
5. 广播抑制
启用广播抑制可帮助削减广播风暴的影响。广播风暴是 STP 环路的主要副作用之一。示例命令输出如下:
L2Switch_1#show run interface TenGigabitEthernet1/1/5
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 279 bytes
!
interface TenGigabitEthernet1/1/5
switchport trunk allowed vlan 300-309
switchport mode trunk
storm-control broadcast level 30.00
storm-control multicast level 30.00
storm-control unicast level 30.00
spanning-tree guard root
end
L2Switch_1#show storm-control broadcast
Key: U - Unicast, B - Broadcast, M - Multicast
Interface Filter State Upper Lower Current Action Type
--------- ------------- ----------- ----------- ---------- --------- ----
Te1/1/5 Forwarding 30.00% 30.00% 0.00% None B
Te1/1/7 Link Down 30.00% 30.00% 0.00% None B
Te1/1/8 Forwarding 10.00% 10.00% 0.00% None B
L2Switch_1#show storm-control multicast
Key: U - Unicast, B - Broadcast, M - Multicast
Interface Filter State Upper Lower Current Action Type
--------- ------------- ----------- ----------- ---------- --------- ----
Te1/1/5 Forwarding 30.00% 30.00% 0.00% None M
Te1/1/7 Link Down 30.00% 30.00% 0.00% None M 6. 控制台和 Telnet 访问
在 STP 环路中,到交换机的控制台或 Telnet 流量经常变得太缓慢,以至于不能正确找到冲突设备。为了强制网络立刻恢复,请删除所有冗余物理链路。在允许 STP 在新的非冗余拓朴结构上重新收敛后,再一次重新连接一条冗余链路。如果在您添加某个特定段之后,重新出现 STP 环路,即已识别出冲突设备。
7. 生成树功能:Portfast、UplinkFast 和 BackboneFast
验证 PortFast、UplinkFast 和 BackboneFast 的配置是否正确。当您排除 STP 故障时,请禁用所有高级 STP(UplinkFast 和 BackboneFast)。 另外,请验证是否仅在直接连接到非桥接主机的端口上启用 STP PortFast。非桥接主机包括用户工作站和不带网桥组的路由器。请勿在连接到集线器或其他交换机的端口上启用 PortFast。下面是一些文档,可帮助了解并配置这些功能:
8. BPDU 防护
当您启用 PortFast BPDU 防护时,如果在非中继的、已启用 PortFast 的端口上收到 BPDU,则该端口将转入 errdisable 状态。此功能可帮助您查找 PortFast 配置不正确的端口。此功能还会检测设备在何处反映数据包或将STP BPDU注入网络。在对STP问题进行故障排除时,您可以启用此功能以帮助隔离STP问题。
L2Switch_1#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
L2Switch_1(config)#spanning-tree portfast bpduguard
L2Switch_1(config)#end9. VTP 修剪
当在网络中已启用 VTP 修剪时,它可能会导致 HSRP 组的设备转入活动状态。这会导致在网关之间出现 IP 冲突并造成了流量问题。请确保任何 HSRP 组的 VLAN 不被网络中的 VTP 修剪。
F.分治
如果隔离或解决 HSRP 的所有其他尝试失败,接下来就要使用“分开处理”的方法。此方法可帮助隔离组成网络的网络和组件。“分开处理”方法涉及以下列表中的任何一项指导原则:
注意:此列表重复了来自本文档中其他部分的一些指导原则。
-
为 HSRP 创建一个测试 VLAN 和隔离 VLAN 以与 HSRP 路由器交换。
-
断开所有冗余端口。
-
将 FEC 端口分成单个连接的端口。
-
将 HSRP 组成员数降低到仅含两名成员。
-
修剪中继端口,以便在这些端口上只传播必要的 VLAN。
-
断开网络中已连接的交换机,直到问题不再出现。
已知问题
将Cisco 2620/2621和Cisco 3600与快速以太网配合使用时,HSRP状态抖动/不稳定
当网络中断连接或向网络添加更加高优先级的 HSRP 路由器时,快速以太网接口可能会发生此问题。当 HSRP 状态从活动更改为对话时,路由器会重置接口,以便从接口 MAC 地址过滤器中删除该 HSRP MAC 地址。只有用于 Cisco 2600、3600 及 7500 系列的快速以太网接口上的特定硬件有此问题。路由器接口重置导致快速以太网接口上的链路状态更改,并且交换机检测到这一更改。如果交换机运行 STP,则更改会导致发生 STP 转换。STP 需要 30 秒的时间以将端口到转换为 forwarding 状态。此时间是默认转发延迟时间 15 秒的两倍。同时,对话路由器在 10 秒(这是 HSRP 保持时间)之后过渡到 standby 状态。STP 尚未转发,因此不会收到来自活动路由器的 HSRP hello 消息。这会导致备用路由器在大约 10 秒之后变成活动路由器。两个路由器现在都处于 active 状态。当 STP 端口变为转发状态时,优先级较低的路由器将从活动状态更改为对话状态,且整个进程将重复操作。
| Platform | 描述 | Cisco Bug ID | 修复程序 | 解决方法 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cisco 2620/2621 | 当配置了 HSRP,并且拔掉电缆时,快速以太网接口开始抖动。 | 软件升级;有关修订的详细信息,请参阅 Bug。 | 启用在连接的交换机端口上生成树 PortFast。 | |
| Cisco 2620/2621 | 在带快速以太网的 2600 上,HSRP 状态出现抖动。 | Cisco IOS 软件版本 12.1.3 | 启用在连接的交换机端口上生成树 PortFast。 | |
| 配备 NM-1FE-TX1的思科 3600 | 在 2600 和 3600 快速以太网上,HSRP 状态出现抖动。 | Cisco IOS 软件版本 12.1.3 | 启用在连接的交换机端口上生成树 PortFast。 | |
| 带快速以太网接口的 Cisco 4500 | 在 4500 快速以太网上,HSRP 状态出现抖动。 | Cisco IOS 软件版本 12.1.5 | 启用在连接的交换机端口上生成树 PortFast。 |
1NM-1FE-TX = 单端口快速以太网(10/100BASE-TX 接口)网络模块。
备选解决方法是调整 HSRP 计时器,以便 STP 转发延迟低于默认 HSRP 保持时间的一半。默认 STP 转发延迟是 15 秒,并且默认 HSRP 保持时间是 10 秒。
当在 HSRP 进程下使用 track 命令时,思科建议您使用特定的递减值,以避免 HSRP 摆动。
以下是使用 track 命令时 HSRP 主用路由器的配置示例:
standby 1 ip 10.0.0.1 standby 1 priority 105 standby 1 preempt delay minimum 60 standby 1 name TEST standby 1 track <object> decrement 15
其中15是对象摆动时的递减值值。要了解有关track命令的更多信息,请导航至HSRPv2配置示例中的文档跟踪选项。
相关信息
修订历史记录
| 版本 | 发布日期 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
3.0 |
13-Dec-2024 |
格式化。 |
2.0 |
09-Jan-2023 |
更新了技术内容,更新了内容。将格式、动词、机器翻译、样式要求、标题长度、SEO和图像更新为.png。 |
1.0 |
29-Nov-2001 |
初始版本 |
 反馈
反馈