Release Notes for Cisco Aironet Access Points for Cisco IOS Release 15.3(3)JBB5
Available Languages
Table of Contents
Release Notes for Cisco Aironet Access Points for Cisco IOS Release 15.3(3)JBB5
Supported Cisco Aironet Access Points
Finding the Cisco IOS Software Release
Upgrading to a New Software Release
Converting a Lightweight Access Point Back to Autonomous Mode
Disabling Radios to Prevent Unexpected Reboots When Upgrading the System Software
New Features and Platforms in this Release
Cisco Aironet Universal Access Points
Cisco 1040/1140 series Access Points May Record "watchdog timer expired" as Last Reset Reason
Point-to-Point and Point-to-Multipoint Bridging Support for 802.11n Platforms
Low Throughput Seen on Access Points with 16 BSSIDs Configured
802.11n HT Rates Apply Only to No Encryption or WPA2/AES Encryption
Layer 3 Not Supported with NAC for MBSSID
Change to Default IP Address Behavior
Changes to the Default Configuration—Radios Disabled and No Default SSID
Clients Using WPA/WPA2 and Power Save May Fail to Authenticate
Default Username and Password Are Cisco
Some Client Devices Cannot Associate When QoS Is Configured
Some Devices Disassociate When Multiple BSSIDs Are Added or Deleted
Enabling MBSSIDs Without VLANs Disables Radio Interface
Cannot Set Channel on DFS-Enabled Radios in Some Regulatory Domains
TACACS+ and DHCP IP Address Sometimes Locks Out Administrators
Access Points Do Not Support Loopback Interface
Throughput Option for 802.11g Radio Blocks Association by 802.11b Clients
Use Auto for Ethernet Duplex and Speed Settings
Using the force-reload Option with archive download-sw Command
Radio MAC Address Appears in Access Point Event Log
Mask Field on IP Filters Page Behaves the Same As in CLI
Repeater Access Points Cannot Be Configured as WDS Access Points
Corrupt EAP Packet Sometimes Causes an Error Message
Removal of WPA/TKIP configuration
Cisco CKM Supports SpectraLink Phones
Non-Cisco Aironet Clients Sometimes Fail 802.1X Authentication
Pings and Link Tests Sometimes Fail to Clients with Both Wired and Wireless Network Connections
Layer 3 Mobility Not Supported on Repeaters and Workgroup Bridges
Autonomous AP Will Treat The Sub-interface Tied To Bridge-group1 As The Native Vlan
DHCP Failure When Access Point Renewal Time Is Greater Than Rebind Time
Configuring the radius server using the old cli
Upgrade from IOS 12.4 to IOS 15 breaks access point L3 Co nnectivity
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
Release Notes for Cisco Aironet Access Points for Cisco IOS Release 15.3(3)JBB5
This document describes features, enhancements, and caveats for autonomous mode access points using Cisco IOS Release 15.3(3)JBB5.
The release notes for lightweight Cisco Aironet Access Points are included in the Release Notes for Cisco Wireless Controllers and Lightweight Access Points for Cisco Wireless Release 8.1.120.0, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/controller/release/notes/crn81mr2.html
Supported Cisco Aironet Access Points
This release supports the following Cisco Aironet access points in autonomous mode:
- AP 802
- AP 702I
- AP 700W
- AP 1040
- AP 1140
- AP 1260
- AP 1530
- AP 1550 (128 MB only supported)
- AP 1570
- AP 1600
- AP 1700
- AP 2600
- AP 2700
- AP 3500
- AP 3600 (AIR-RM3000AC- x -K9 802.11ac module is not supported)
- AP 3700 (AIR-RM3000AC- x -K9 802.11ac module is not supported)

Warning![]() Install only Cisco IOS Release 15.3(3)JA1 and newer releases on Cisco Aironet Universal Access Point models. Do not install older Cisco IOS releases on Cisco Aironet Universal Access Point models as that is a violation of local radio regulations and laws.
Install only Cisco IOS Release 15.3(3)JA1 and newer releases on Cisco Aironet Universal Access Point models. Do not install older Cisco IOS releases on Cisco Aironet Universal Access Point models as that is a violation of local radio regulations and laws.
Introduction
The Cisco Aironet Access Point is a wireless LAN transceiver that acts as the connection point between wireless and wired networks or as the center point of a standalone wireless network. In large installations, the roaming functionality provided by multiple access points enables wireless users to move freely throughout the facility while maintaining uninterrupted access to the network.
System Requirements
You can install the 32 MB Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)JB3a on all 802, 1040, 1140, 1260, 1550, 1600, 2600, 3500, and 3600 series access points. New APs 702 and 1530 support 128 MB minimum flash and AP 3700 supports 64 MB minimum flash.
Finding the Cisco IOS Software Release
To find the version of Cisco IOS software that is running on your access point, use a Telnet session to log into the access point, and enter the show version EXEC command. This example shows command output from an access point that is running Cisco IOS Release 15.3(3)JBB5:
On access points running Cisco IOS software, you can also find the software release on the System Software Version page in the access point’s web-browser interface. If your access point does not run Cisco IOS software, the software release appears at the top left of most pages in the web-browser interface.
Upgrading to a New Software Release
To upgrade your access point or bridge software, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Follow this link to the Cisco home page:
Follow this link to the Cisco home page:
Step 2![]() Click Support. The Support and Documentation page appears.
Click Support. The Support and Documentation page appears.
Step 3![]() Under the Select a Product Name, click Wireless. The Product/Technology Support page appears.
Under the Select a Product Name, click Wireless. The Product/Technology Support page appears.
Step 4![]() Under the Make a Selection to Continue section, click Access Point. Products and Access Point are highlighted.
Under the Make a Selection to Continue section, click Access Point. Products and Access Point are highlighted.
Step 5![]() Select the access point model for which you need the information. For example, click the Cisco Aironet 1600 series. A list of documents appears.
Select the access point model for which you need the information. For example, click the Cisco Aironet 1600 series. A list of documents appears.
Step 6![]() Click Configure. A list of configuration documents appears.
Click Configure. A list of configuration documents appears.
Step 7![]() Click Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide for Cisco Aironet Access Points, 15.3(3)JBB5.
Click Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide for Cisco Aironet Access Points, 15.3(3)JBB5.
Step 8![]() Navigate to the Managing Firmware and Software chapter.
Navigate to the Managing Firmware and Software chapter.
For information on Cisco IOS software, click this link to browse to the Cisco IOS Software Center on Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/cisco/software/navigator.html
The new Cisco IOS software is supported only in these versions of 1550 series:

Note![]() AP 1550 does not support 64 MB Cisco IOS Release starting from 15.2(4)JA1 in autonomous mode.
AP 1550 does not support 64 MB Cisco IOS Release starting from 15.2(4)JA1 in autonomous mode.
Converting a Lightweight Access Point Back to Autonomous Mode
You can convert an access point from lightweight mode back to autonomous mode by loading a Cisco IOS Release that supports autonomous mode. If the access point is associated with a controller, you can use the controller to load the Cisco IOS release. If the access point is not associated with a controller, you can load the Cisco IOS release using TFTP. The image files and their supported access points are listed in Table 1 .

Note![]() Conversions from an 8.0 Wireless LAN Controller unified release AP image to autonomous 15.3(3) k9w7 image will get aborted with a message "AP image integrity check failed." To overcome this, load any previous autonomous k9w7 image and then upgrade to the 15.3(3) JAB k9w7 images. For more information, see caveat CSCuq53889.
Conversions from an 8.0 Wireless LAN Controller unified release AP image to autonomous 15.3(3) k9w7 image will get aborted with a message "AP image integrity check failed." To overcome this, load any previous autonomous k9w7 image and then upgrade to the 15.3(3) JAB k9w7 images. For more information, see caveat CSCuq53889.
Disabling Radios to Prevent Unexpected Reboots When Upgrading the System Software
If your access point runs Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)JA, 12.2(11)JA1, or 12.2(11)JA2, your access point might unexpectedly reboot after you upgrade to a later Cisco IOS release. However, after the access point reboots, the upgrade is complete and the access point operates normally. It is recommended to disable the radio interfaces before upgrading the software to prevent the access point from rebooting unexpectedly.
To disable the radio interfaces using the access point’s web-browser interface, which you can access through the access point's Ethernet port, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Browse to the Network Interfaces: Radio Settings page. Figure 1 shows the top portion of the Network Interfaces: Radio Settings page.
Browse to the Network Interfaces: Radio Settings page. Figure 1 shows the top portion of the Network Interfaces: Radio Settings page.
Figure 1 Network Interfaces: Radio Settings Page
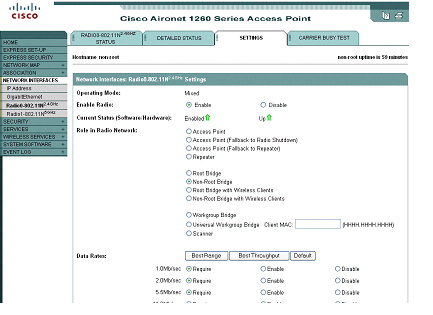
Step 2![]() Choose Disable to disable the radio.
Choose Disable to disable the radio.
Step 3![]() Click Apply at the bottom of the page.
Click Apply at the bottom of the page.
Step 4![]() If your access point has two radios, repeat these steps for the second radio.
If your access point has two radios, repeat these steps for the second radio.
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps to disable the access point radios using the access point CLI:
Enters interface configuration mode for the radio interface. The 2.4-GHz radio is radio 0, and the 5-GHz radio is radio 1. |
||
If your access point has two radios, repeat these steps for the second radio. Use the no form of the shutdown command to enable the radio.
New Features and Platforms in this Release
There are no new features or platforms included in this release in comparison to the previous release.
Important Notes
This section describes important information about access points and bridges.
Cisco Aironet Universal Access Points
Install only Cisco IOS Release 15.3(3)JA1 and newer releases on Cisco Aironet Universal Access Point models. Do not install older Cisco IOS releases on Cisco Aironet Universal Access Point models as that is a violation of local radio regulations and laws.
Cisco 1040/1140 series Access Points May Record "watchdog timer expired" as Last Reset Reason
This error message sometimes appears as the last reset reason when the access points are power cycled:
This symptom is observed only in the Cisco 1040/1140 series access point and does not have any impact on functionality. Ignore the “watchdog timer expired” reason after an access point has been power cycled. You can also overwrite the reset reason to “reload” by rebooting with command operation.
Regulatory Update for Japan
This release supports the U regulatory domain for the W52 frequency set (channels 36, 40, 44, and 48) in Japan for the Cisco Aironet 1230 series. This support was added for the Cisco Aironet 1130 series in Cisco IOS Software Release 12.4(3G)JA, which shipped previously. Cisco access points specified for this new domain ship with a U domain radio. Installed J domain access points are automatically upgraded to the U domain status with this release.
For the latest Cisco WLAN compliance status, visit this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/wireless/ps5679/ps5861/product_data_sheet0900aecd80537b6a_ps430_Products_Data_Sheet.html .
Point-to-Point and Point-to-Multipoint Bridging Support for 802.11n Platforms
The point-to-point and point-to-multipoint bridging is supported on the Cisco Aironet 1040, 1140, 1260, 1600, 2600, 3500 and 3600 series access points (802.11n platforms). The 5-GHz bands support 20 and 40-MHz channel widths, and the 2.4-GHz bands support only a 20-MHz channel width.
The following items are supported for AP1040, AP1140, AP1260, AP1600, AP2600, AP3500, and AP3600 bridging:
- MIMO, short-range bridging (on campus or inter-building bridge deployments), with dipole and MIMO antennas (line of sight and short range) under 1 km.
- 20-MHz and 40-MHz 802.11n support.
- Workgroup bridge (WGB) short-range support.
- SISO (single-in, single-out), MCS 0-7 and legacy bridge rates (802.11 a/b/g and 802.11n) using one outdoor antenna.

Note![]() This is only supported using short range links and is not a replacement for the 1530, 1550, and 1570 series access points which support bridging.
This is only supported using short range links and is not a replacement for the 1530, 1550, and 1570 series access points which support bridging.
The following are not supported on AP 702, AP1040, AP1140, AP1260, AP1600, AP2600, AP3500 and AP3600 for bridging:
Low Throughput Seen on Access Points with 16 BSSIDs Configured
If your network uses 16 BSSIDs with 1 and 2-Mbps data rates, access points might experience very low throughput due to high management traffic.
802.11n HT Rates Apply Only to No Encryption or WPA2/AES Encryption
As per the 802.11n amendment, the 802.11n HT rates apply only to no encryption or WPA2/AES encryption. They do not apply to WEP or WPA encryption. If WEP or TKIP encryption is used, the access point and any 802.11n clients will not transmit at HT rates. Legacy rates (802.11a/b/g) will be used for any clients using WEP or TKIP encryption.
Layer 3 Not Supported with NAC for MBSSID
Layer 3 is not supported with NAC for MBSSID in this release.
Change to Default IP Address Behavior
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(2)JA and later releases change the default behavior of access points that request an IP address from a DHCP server
When you connect a 1040, 1130, 1140, 1250, or 1260 series access point or a 1300 series outdoor access point/bridge with a default configuration to a LAN, the access point requests an IP address from a DHCP server and, if it does not receive an address, continues to send requests indefinitely.
Changes to the Default Configuration—Radios Disabled and No Default SSID
The radio or radios are disabled by default, and there is no default SSID. You must create an SSID and enable the radio or radios before the access point allows wireless associations from other devices. These changes to the default configuration improve the security of newly installed access points.
Clients Using WPA/WPA2 and Power Save May Fail to Authenticate
Certain clients using WPA/WPA2 key management and power save can take many attempts to authenticate or, in some cases, fail to authenticate. Any SSID that is defined to use authentication key-management WPA, together with clients using power save mode and authenticating using WPA/WPA2, can experience this problem.
A hidden configure level command, dot11 wpa handshake timeout, can be used to increase the timeout between sending the WPA key packets from the default value (100 ms) to a value between 101 and 2000 ms. The command stores its value in the configuration across device reloads.
Default Username and Password Are Cisco
When you open the access point interface, you must enter a username and a password. The default username for administrator login is Cisco, and the default password is Cisco. Both the username and password are case sensitive.
Some Client Devices Cannot Associate When QoS Is Configured
Some wireless client devices, including Dell Axim handhelds and Hewlett-Packard iPaq HX4700 handhelds, cannot associate to an access point when the access point is configured for QoS. To allow these clients to associate, disable QoS on the access point. You can use the QoS Policies page on the access point GUI to disable QoS or enter this command on the CLI:
Some Devices Disassociate When Multiple BSSIDs Are Added or Deleted
Devices on your wireless LAN that are configured to associate to a specific access point based on the access point MAC address (such as client devices, repeaters, hot standby units, or workgroup bridges) might lose their association when you add or delete multiple BSSIDs. When you add or delete multiple BSSIDs, check the association status of devices that are configured to associate to a specific access point. If necessary, reconfigure the disassociated device to use the BSSID new MAC address.
Enabling MBSSIDs Without VLANs Disables Radio Interface
If you use the mbssid configuration interface command to enable multiple BSSIDs on a specific radio interface but VLANs are not configured on the access point, the access point disables the radio interface. To re-enable the radio, you must shut down the radio, disable multiple BSSIDs, and re-enable the radio.
This example shows how to re-enable the radio:
After you re-enable the radio, you can enable VLANs on the access point and enable multiple BSSIDs.
Cannot Set Channel on DFS-Enabled Radios in Some Regulatory Domains
Access points with 5-GHz radios configured at the factory for use in Europe, Singapore, Korea, Japan, Taiwan, and Israel now comply with regulations that require radio devices to use Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) to detect radar signals and to avoid interfering with them. You cannot manually set the channel on DFS-enabled radios that are configured for these regulatory domains.
TACACS+ and DHCP IP Address Sometimes Locks Out Administrators
When you configure an access point for TACACS+ administration and you request for an IP address from the DHCP server, you might be locked out of the access point after it reboots if you do not have a local username and password configured on the access point. This is because the AP gets a newer IP address which is not yet added in TACACS. If you have been locked out, you must regain access by resetting the unit to default settings.
This issue does not affect access points that are configured with a static IP address.
Access Points Do Not Support Loopback Interface
You must not configure a loopback interface on the access point.

Throughput Option for 802.11g Radio Blocks Association by 802.11b Clients
When you configure the 802.11g access point radio for best throughput, the access point sets all data rates to basic (required). This setting blocks association from 802.11b client devices. The best throughput option appears on the web-browser interface Express Setup and Radio Settings pages and in the speed CLI configuration interface command.
Use Auto for Ethernet Duplex and Speed Settings
We recommend that you use auto, the default setting, for both the speed and duplex settings on the access point Ethernet port. When your access point receives inline power from a switch, any change in the speed or duplex settings that resets the Ethernet link reboots the access point. If the switch port to which the access point is connected is not set to auto, you can change the access point port to half or full to correct a duplex mismatch, and the Ethernet link is not reset. However, if you change from half or full back to auto, the link is reset, and, if your access point receives inline power from a switch, the access point reboots.

Note![]() The speed and duplex settings on the access point Ethernet port must match the Ethernet settings on the port to which the access point is connected. If you change the settings on the port to which the access point is connected, change the settings on the access point Ethernet port to match.
The speed and duplex settings on the access point Ethernet port must match the Ethernet settings on the port to which the access point is connected. If you change the settings on the port to which the access point is connected, change the settings on the access point Ethernet port to match.
Using the force-reload Option with archive download-sw Command
When you upgrade an access point or bridge system software by entering the archive download-sw command on the CLI, you must use the force-reload option. If the access point or bridge does not reload the flash memory after the upgrade, the pages in the web-browser interface might not reflect the upgrade. This example shows how to upgrade the system software by using the archive download-sw command:
Radio MAC Address Appears in Access Point Event Log
When a client device roams from an access point (such as access point alpha) to another access point (access point bravo), a message appears in the event log on access point alpha stating that the client roamed to access point bravo. The MAC address that appears in the event message is the MAC address for the radio in access point bravo. The MAC address for the access point Ethernet port is on the label on the back of the access point.
Mask Field on IP Filters Page Behaves the Same As in CLI
In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)JA and later releases, the mask that you enter in the Mask field on the IP Filters page in the access point GUI behaves the same way as a mask that you enter in the CLI. If you enter 255.255.255.255 as the mask, the access point accepts any IP address. If you enter 0.0.0.0, the access point looks for an exact match with the IP address that you entered in the IP Address field.
Repeater Access Points Cannot Be Configured as WDS Access Points
Repeater access points can participate in WDS, but they cannot provide WDS. You cannot configure a repeater access point as a main WDS access point, and if a root access point becomes a repeater in fallback mode, it cannot provide WDS.
Cannot Perform Link Tests on Non-Cisco Aironet Client Devices and on Cisco Aironet 802.11g Client Devices
The link test feature on the web-browser interface does not support non-Cisco Aironet client devices.
Corrupt EAP Packet Sometimes Causes an Error Message
During client authentication, the access point sometimes receives a corrupt EAP packet and displays this error message:
Removal of WPA/TKIP configuration
Wi-Fi certified access points no longer support a WPA/TKIP configuration. TKIP is only allowed in combination with WPA2/AES for backward compatibility to allow older TKIP-only devices to associate.
Authentication key-management WPA version 1 will be changed to authentication key-management WPA. The following message will be displayed:
WPA version 1 option has been removed from the authentication key-management wpa cli and configuring TKIP only under this interface is not supported. It will be changed to aes-ccm tkip to work on mixed mode with the following message on the ap console:
Cisco CKM Supports SpectraLink Phones
Cisco CKM (CCKM) key management is designed to support voice clients that require minimal roaming times. Voice clients must support Cisco Compatible Extensions to benefit from this feature, for the voice client security mode you selected, please refer to the following URL for the list of CCX versions and supported clients: http://www.cisco.com/web/partners/pr46/pr147/partners_pgm_concept_home.html
Non-Cisco Aironet Clients Sometimes Fail 802.1X Authentication
Some non-Cisco Aironet client adapters do not perform 802.1X authentication to the access point unless you configure Open authentication with EAP. To allow both Cisco Aironet clients using LEAP and non-Cisco Aironet clients using LEAP to associate using the same SSID, you might need to configure the SSID for both Network EAP authentication and Open authentication with EAP.
Pings and Link Tests Sometimes Fail to Clients with Both Wired and Wireless Network Connections
When you ping or run a link test from an access point to a client device installed in a PC running Microsoft Windows, the ping or link test sometimes fails when the client has both wired and wireless connections to the LAN. Microsoft does not recommend this configuration. For more information, refer to Microsoft Knowledge Base article 157025 at this URL:
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;en-us;157025&Product=win2000
Layer 3 Mobility Not Supported on Repeaters and Workgroup Bridges
Repeater access points and workgroup bridges cannot associate to an SSID that is configured for Layer 3 mobility. Layer 3 mobility is not supported on repeaters and workgroup bridges.
Potential RFC 3748 Violation
When the following command is configured under the SSID settings (for LEAP authentication):
if the first access-challenge returned by the Radius server after the access-request from the access point is not for the LEAP method but for EAP-MD5, the access point violates RFC 3748.
Instead of sending an EAP NAK requesting LEAP authentication, the access point sends the user's credentials with EAP-MD5 and drops the derived keys, since it cannot read the EAP-MD5 from the access-accept.
The workaround for this is to use the commands dot1x credentials and dot1x eap profile for LEAP authentication.
For configuration procedures, see the Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide for Cisco Aironet Access Points.
Autonomous AP Will Treat The Sub-interface Tied To Bridge-group1 As The Native Vlan
When using a configuration on an autonomous AP where there is no native VLAN defined, each interface is being dot1q tagged, communication will fail after upgrading to release 15.3(3)JBB5 or later. It appears that the configuration is still correct after the upgrade, but the AP sends the untagged frames for bridge-group 1, even though the encapsulation is not defined as native. The autonomous AP will treat the sub-interface tied to bridge-group 1 as the native VLAN, even if it is not defined with the native keyword: "encapsulation dot1 <vlan> native". The VLAN associated with bridge-group 1 must be set to native on the connecting switchport configuration
The workaround for this is to configure VLAN 100 as the native VLAN on the connected switchport trunk, even though the encapsulation is not specified as native on the AP.
DHCP Failure When Access Point Renewal Time Is Greater Than Rebind Time
An access point is unable to obtain IP through the same IOS DHCP server when the access point is running on 15.2x. The problem occurs because the Renewal (T1) time dhcp option 58 is larger than Rebinding (T2) time dhcp option 59.
Configuring the radius server using the old cli
This cli command was used in the previous releases to configure radius servers:
radius-server host { hostname | ip-address } [ auth-port port-number ] [ acct-port port-number ] [ timeout seconds ] [ retransmit retries ] [ key string ]
Though this command can still be used, we recommend that you use this new command:
radius server {server-name}[ auth-port port-number ] [ acct-port port-number ] [ timeout seconds ] [ retransmit retries ] [ key string ]
Caveats
This section lists Open Caveats and Resolved Caveats for access points and bridges in Cisco IOS Release 15.3(3)JBB5.
Cisco Bug Search Tool
The Bug Search Tool (BST), which is the online successor to Bug Toolkit, is designed to improve the effectiveness in network risk management and device troubleshooting. The BST allows partners and customers to search for software bugs based on product, release, and keyword, and aggregates key data such as bug details, product, and version. The tool has a provision to filter bugs based on credentials to provide external and internal bug views for the search input.
To view the details of a caveat listed in this document:
1.![]() Access the BST (use your Cisco user ID and password) at https://tools.cisco.com/bugsearch/.
Access the BST (use your Cisco user ID and password) at https://tools.cisco.com/bugsearch/.
2.![]() Enter the bug ID in the Search For: field.
Enter the bug ID in the Search For: field.

Note![]() To have a Cisco User ID and password, you need to be a registered cisco.com user, To become a registered cisco.com user, go to the following website:
To have a Cisco User ID and password, you need to be a registered cisco.com user, To become a registered cisco.com user, go to the following website:
https://tools.cisco.com/RPF/register/register.do
Open Caveats
Table 2 lists caveats that are open in Cisco IOS Release 15.3(3)JBB5.
Troubleshooting
For the most up-to-date, detailed troubleshooting information, refer to the Cisco TAC website at http://www.cisco.com/cisco/web/support/index.html. Click Technology Support, choose Wireless from the menu on the left, and click Wireless LAN.
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, using the Cisco Bug Search Tool (BST), submitting a service request, and gathering additional information, see What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation.
To receive new and revised Cisco technical content directly to your desktop, you can subscribe to the What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation RSS feed. The RSS feeds are a free service.

 Feedback
Feedback