Release Notes for Cisco IOS Release 15.7(3)M2 on the 5900 Embedded Services Routers
Available Languages
Table of Contents
Release Notes for Cisco IOS Release 15.7(3)M2
Image Information and Supported Platforms
Generalized TTL Security Mechanism (GTSM) Support
Web Services Management Agent (WSMA)
Connected Grid Network Agent (CGNA)
SCEP Enrollment with Custom Device Credential
Changes to the SCEP Enrollment EEM policy
Virtual WPAN (VWPAN) Interface and Mesh-security
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
Release Notes for Cisco IOS Release 15.7(3)M2
The following release notes support Cisco IOS Releases 15.7(3)M2 and higher releases. These releases support the Cisco 5900 Embedded Services Routers (ESR) platforms. These release notes are updated to describe new features, limitations, troubleshooting, recommended configurations, caveats, and how to obtain support and documentation.
Image Information and Supported Platforms

Note![]() You must have a Cisco.com account to download the software.
You must have a Cisco.com account to download the software.
Cisco IOS Release 15.7(3)M2 includes the following Cisco IOS images:
Related Documentation
The following documentation is available:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/routers/5900-series-embedded-services-routers/tsd-products-support-series-home.html
http://www.cisco.com/cisco/web/psa/default.html?mode=prod&level0=268438303
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/15-7m/release/notes/15-7-3-m-rel-notes.html
New Features Supported
This release supports software changes made in IOS that exist on other platforms.
DLEP Compliance to RFC 8175
The DLEP protocol runs between a router and its attached modem devices, allowing the modem to communicate link characteristics as they change, and convergence events (acquisition and loss of potential routing next-hops). DLEP provides an event driven mechanism instead of a timer-driver one and enables routing protocols to be radio-aware. Support includes a generalized TTL security mechanism for UDP in order to be compliant with RFC 8175.
Generalized TTL Security Mechanism (GTSM) Support
GTSM is designed to protect a router's IP-based control plane from CPU-utilization based attacks. The GTSM mechanism is equally applicable to both TTL (IPv4) and Hop Limit (IPv6).
- If a DLEP signal is received with a TTL value that is NOT equal to 255 (254 for IPv4), the receiving implementation MUST ignore the Signal.
- If a DLEP packet in the TCP stream is received with a TTL value other than 255 (254 for IPv4), the receiving implementation MUST immediately transition to the Session Reset state.
Web Services Management Agent (WSMA)
WSMA is a family of embedded agents, used by a point-point management application to fully manage a device. It provide users access to similar capabilities as the CNS agents (CONFIG, EXEC, FILE SYSTEM, DIAGNOSTICS) but via an open standards point-to-point connection. These agents leverage the knowledge and code base of the CNS agents and provide comparable mechanisms in a point-point environment rather than the Event Bus which is the basis of CNS.
CNS agents have proven to be a useful set of management interfaces for scalable management of Cisco devices, but with the following deficiencies:
- Proprietary TIBCO communication bus
- Inflexible protocol interfaces
- Steep application developer learning curve
- Requires a proxy agent (no direct access)
The WSMA addresses these deficiencies. The WSMA is accessible over SSH and HTTP(S) transports. The WSMA transport layer is configurable to be run in both session initiator and listener mode. This allows the WSMA on IOS to run in server mode regardless of how the transport connection is made to the device. The WSMA is accessed directly over the SOAP/SSH or SOAP/HTTP(S) transport.
Additional information can be found in the WSMA Configuration Guide.
Connected Grid Network Agent (CGNA)
The CGNA is a helper to facilitate NMS operations. It is a light-weight process/task in IOS, communicating with NMS via WSMA and HTTPS sessions. The following functions are supported by the CGNA:
Additional information can be found in the Cisco Connected Grid WPAN Module for CGR 1000 Series Installation and CG-Mesh Configuration Guide (Cisco IOS)
SCEP Enrollment with Custom Device Credential
The following section describes the use of custom device credential for the SCEP enrollment on the ESR5921.
Changes to the SCEP Enrollment EEM policy
On the ESR5921, there are several changes to the existing SCEP enrollment EEM policy compared to the CGR1K platform. The changes are logged in the header of the policy script tm_ztd_scep.tcl.
New control environment variables:
Requirements
For a custom device credential, there needs to be three parts:
- A device specific certificate (for example: cust_sudi.crt)
- A private key associated with the device certificate (for example: cust_sudi.prv)
- The certificate of the CA server signing the device certificate (for example: cust_sudi.ca)
In the device certificate, it should contain the PID and serial number for this device in its subject name, which can be used on the RA server for authorization through AAA. In order to minimize the compatibility issue, use Cisco CA servers to generate credentials.
Example Installation
Custom credentials are presented as cust_sudi (.crt.prv.ca) in PEM format. Other setups and configurations are identical to the CGR1K SCEP enrollment. The following section describes the differences.
On the ESR5921
This procedure assumes the custom sudi files are available on nvram:
Additional Notes
For compatibility issues with the enrollment credential on the ESR5921, you may test it on the ESR5921 to make sure it can be accepted by Cisco IOS. Use these steps:
1.![]() Make sure the credential files are named as previously stated. (.ca. prv and.crt respectively)
Make sure the credential files are named as previously stated. (.ca. prv and.crt respectively)
2.![]() Issue the following command, assuming the credential files are cust_sudi.ca, cust_sudi.prv and cust_sudi.crt:
Issue the following command, assuming the credential files are cust_sudi.ca, cust_sudi.prv and cust_sudi.crt:
Virtual WPAN interface
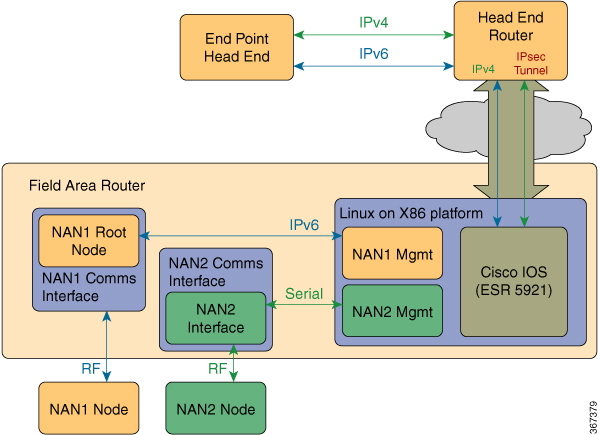
A new Virtual WPAN interface is included in Cisco IOS release 15.7(3)M1 or higher to provide 802.1X and Mesh-security services on the ESR C5921 running on field area routers. This interface serves as the anchor to the Port Access Entity (PAE) for the partner module and the end-points. It also provides configuration and monitoring of CLI commands.
The VWPAN interface has three main subsystems:
- Partner Module
The module connects directly to Linux using USB. The partner module must have an embedded 802.1X supplicant. - Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) relay application
A partner-developed GOS application that functions as an EAP relay between the module and IOS. EAP packets received from the module are forwarded to Cisco IOS and are processed in the reverse direction. The application uses an API library (libvwpan) that Cisco provides to communicate with Cisco IOS. - Cisco IOS Virtual WPAN interface
Provides the 802.1X and Mesh-security services for partner module and mesh endpoints.
The following graphic illustrates the high level architecture:
IEEE802.1x
IEEE802.1x is an essential component to support WPAN and mesh security. This feature is ported in the ESR5921.
Mesh-Security
802.11i based mesh security module monitors and manages the PTKs and GTKs in the wireless mesh networks. Porting this feature to ESR is also required.
For the mesh network keys' storage, the integration partner provides an ACT2 equivalent module secure storage with related APIs. Use this interface for the mesh security master key access, which encrypts the clients' session keys and stores them on the flash.
On ESR 5921, there is no real security storage feature, which is a mandatory requirement for VWPAN and mesh security feature of storing sessions. On Cisco platforms, it is usually implemented through ACT. But for ESR running on customer's platform, it needs to integrate with the platform's HSM (hardware security module).
The approach is explained in the following: (Library Name: libesrhsm.so)
- A set of public APIs for store/retrieve securities (such as AES keys) are defined.
- APIs should be implemented by customers according to their specific requirement with DSO (dynamic shared object).
- ESR will dynamically load the library and use these sets of APIs to store and retrieve securities as needed.

To use this library provided by the integration partner, copy the library to the ESR flash and setup the emulation.conf file. The mesh-security feature uses it as the secure key storage without any additional configurations.
Caveats
Caveats describe unexpected behavior in Cisco IOS releases. Caveats listed as open in a prior release are carried forward to the next release as either open or closed (resolved).

Note![]() You must have a Cisco.com account to log in and access the Cisco Bug Search Tool. If you do not have one, you can register for an account.
You must have a Cisco.com account to log in and access the Cisco Bug Search Tool. If you do not have one, you can register for an account.
For more information about the Cisco Bug Search Tool, see the Bug Search Tool Help & FAQ.
Open Caveats
While using DLEP, heartbeat is not sent by the router, and the radio is closing the TCP connection.
For discovery and non-discovery cases, the client session is established. After a period of time, the heartbeat is not send by the router and radio waits for the heartbeat and closes the TCP connection.
SNMP is sending two packets per trap, one of which has the SNMP version set to 0.
Whenever an SNMP trap is generated, the additional one trap is generated with the name ?enterprisespecific? of which the version is 0. FND processes and ignores this trap.
TLS negotiation fails for DLEP when RFC 8175 is used between the radio and the router to establish the session.
Use normal TCP session for the connection between the radio and the router for DLEP RFC 8175.
ZTD script needs to improve Subject field parsing for custom sudi certs from different CA issuers.
Different signing CA issuers may re-arrange the order of elements in the Subject field of a signed custom SUDI certificate.
Closed Caveats
The following caveats are fixed with this release:
3rd Party SIP Phones not registering from CME 11.6
In a KVM setup, when the C5921 is accessed via swrvcon (virtual console) application and issued any CLI (example, show version) in swrvcon then the CPU spikes up around 40% in IOS thread and 20% in FP thread.
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, using the Cisco Bug Search Tool (BST), submitting a service request, and gathering additional information, see What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation at: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html.
Subscribe to What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation, which lists all new and revised Cisco technical documentation, as an RSS feed and deliver content directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free service.
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback