Perform System Administration Tasks
This topic contains the following sections:
Overview of System Administration
The S-Series appliance provides a variety of tools for managing the system. Functionality on System Administration tab helps you manage the following tasks:
- Appliance configuration
- Feature keys
- Adding, editing, and removing user accounts
- AsyncOS software upgrades and updates
- System time
Saving, Loading, and Resetting the Appliance Configuration
All configuration settings within the Secure Web Appliance are managed using a single XML configuration file.
Viewing and Printing the Appliance Configuration
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > Configuration Summary. |
|
Step 2 |
View or print the Configuration Summary page as required. |
Saving the Appliance Configuration File
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > Configuration File. |
||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Complete the Configuration File options.
|
||||||||
|
Step 3 |
Click Submit. |
Loading the Appliance Configuration File
 Caution |
Loading configuration will permanently remove all of your current configuration settings. It is strongly recommended that you save your configuration before performing these actions. We do not recommend loading configurations from a previous release into the latest version. You can retain the configuration settings by upgrading the paths. Configuration files loaded with manual changes may result in performance and functional issues. |
 Note |
If a compatible configuration file is based on an older version of the set of URL categories than the version currently installed on the appliance, policies and identities in the configuration file may be modified automatically. |
 Note |
If you encounter a certificate validation error when loading the configuration file, upload the rootCA of the certificate to the trusted root directory of the Secure Web Appliance and then load the configuration file again. To know how to upload the rootCA, see Certificate Management. |
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > Configuration File. |
||
|
Step 2 |
Choose Load Configuration options and a file to load. Note:
|
||
|
Step 3 |
Click Load. |
||
|
Step 4 |
Read the warning displayed. If you understand the consequences of proceeding, click Continue. |
Resetting the Appliance Configuration to Factory Defaults
You can choose whether or not to retain existing network settings when you reset the appliance configuration.
This action does not require a commit.
Before you begin
Save your configuration to a location off the appliance.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > Configuration File. |
|
Step 2 |
Scroll down to view the Reset Configuration section. |
|
Step 3 |
Read the information on the page and select options. |
|
Step 4 |
Click Reset. |
Saving Configuration File Backup
The configuration file backup feature records the appliance configuration on every commit and sends the previous configuration file prior to the current one to a remotely located backup server through FTP or SCP.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > Configuration File |
|
Step 2 |
Select Enable Config Backup checkbox. |
|
Step 3 |
Choose Yes to include the passphrase in the configuration file. Alternatively, choose No to exclude the passphrase in the configuration file. |
|
Step 4 |
Choose the retrieval method. The available options are :
|
|
Step 5 |
Click Submit. You can also enable the configuration file backup feature by using the CLI command |
Cisco Secure Web Appliance Licensing
Working with Feature Keys
Feature keys enable specific functionality on your system.Keys are specific to the serial number of your appliance (you cannot re-use a key from one system on another system).
Displaying and Updating Feature Keys
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > Feature Keys. |
|
Step 2 |
To refresh the list of pending keys, click Check for New Keys to refresh the list of pending keys. |
|
Step 3 |
To add a new feature key manually, paste or type the key into the Feature Key field and click Submit Key. If the feature key is valid, the feature key is added to the display. |
|
Step 4 |
To activate a new feature key from the Pending Activation list, mark its “Select” checkbox and click Activate Selected Keys. You can configure your appliance to automatically download and install new keys as they are issued. In this case, the Pending Activation list will always be empty. You can tell AsyncOS to look for new keys at any time by clicking the Check for New Keys button, even if you have disabled the automatic checking via the Feature Key Settings page. |
Changing Feature Key Update Settings
The Feature Key Settings page is used to control whether your appliance checks for and downloads new feature keys, and whether or not those keys are automatically activated.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > Feature Key Settings. |
||||
|
Step 2 |
Click Edit Settings. |
||||
|
Step 3 |
Change the Feature Key Settings as required.
|
||||
|
Step 4 |
Submit and commit your changes. |
Smart Software Licensing
Overview
Smart Software Licensing enables you to manage and monitor Cisco Secure Web Appliance licenses seamlessly. To activate Smart Software licensing, you must register your appliance with Cisco Smart Software Manager (CSSM) which is the centralized database that maintains the licensing details about all the Cisco products that you purchase and use. With Smart Licensing, you can register with a single token rather than registering them individually on the website using Product Authorization Keys (PAKs).
Once you register the appliance, you can track your appliance licenses and monitor license usage through the CSSM portal. The Smart Agent installed on the appliance connects the appliance with CSSM and passes the license usage information to the CSSM to track the consumption.
See https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/technology/mesh/8-2/b_Smart_Licensing_ Deployment_Guide.html to know about Cisco Smart Software Manager.
 Note |
AsyncOS version 15.0 is the last release to support the Classic license. The next major release of AsyncOS will support only Smart Licenses. |
Before you begin
-
Make sure that your appliance has internet connectivity.
-
Contact Cisco sales team to create a smart account in Cisco Smart Software Manager portal (https://software.cisco.com/#module/SmartLicensing) or install a Cisco Smart Software Manager Satellite on your network.
See https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/technology/mesh/8-2/b_Smart_Licensing_ Deployment_Guide.html to know more about Cisco Smart Software Manager user account creation or installing a Cisco Smart Software Manager Satellite.
For users who do not want to directly send the license usage information to the internet, the Smart Software Manager Satellite can be installed on the premises, and it provides a subset of CSSM functionality. Once you download and deploy the satellite application, you can manage licenses locally and securely without sending data to CSSM using the internet. The CSSM Satellite periodically transmits the information to the cloud.

Note
If you want to use Smart Software Manager Satellite, use Smart Software Manager Satellite Enhanced Edition 6.1.0.
-
The existing users of classic licenses (traditional) should migrate their classic licenses to smart licenses.
-
The system clock of the appliance must be in sync with that of the CSSM. Any deviation in the system clock of the appliance with that of the CSSM, will result in failure of smart licensing operations.
 Note |
If you have internet connectivity and want to connect to the CSSM through a proxy, you must use the same proxy that is configured for the appliance using System Administration-> Upgrade and Update Settings |
 Note |
For virtual users, every time you receive a new PAK file (new or renewal), generate the license file and load the file on the appliance. After loading the file, you must convert the PAK to Smart Licensing. In Smart Licensing mode, the feature keys section in the license file will be ignored while loading the file and only the certificate information will be used. |
 Note |
The appliance will move from the Smart Licensing mode to Classic Licensing mode when you revert the appliance to a previous veriosn of AsyncOS. You must enable Smart Licensing manually and request for required licences. |
You must perform the following procedures to activate Smart Software Licensing for your appliance:
|
Do This |
More Informaton |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Step 1 |
Enable Smart Software Licensing |
|
|
Step 2 |
Register the appliance with Cisco Smart Software Manager |
|
|
Step 3 |
Request for licenses (feature keys) |
Enabling Smart Software Licensing
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > Smart Software Licensing. |
|
Step 2 |
Click Enable Smart Software Licensing. To know about Smart Software Licensing, click on the Learn More about Smart Software Licensing link. |
|
Step 3 |
Click OK after reading the information about Smart Software Licensing. |
|
Step 4 |
Commit your changes. |
What to do next
After you enable Smart Software Licensing, all the features in the Classic Licensing mode will be automatically available in the Smart Licensing mode. If you are an existing user in Classic Licensing mode, you have 90-days evaluation period to use the Smart Software Licensing feature without registering your appliance with the CSSM.
You will get notifications on regular intervals (90th, 60th, 30th, 15th, 5th, and last day) prior to the expiry and also upon expiry of the evaluation period. You can register your appliance with the CSSM during or after the evaluation period.
 Note |
|
Registering the Appliance with Cisco Smart Software Manager
You must enable the Smart Software Licensing feature under System Administration menu in order to register your appliance with the Cisco Smart Software Manager.
 Note |
You cannot register multiple appliances in a single instance. You should register appliances one by one. |
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose . |
||
|
Step 2 |
Select the Smart License Registration option. |
||
|
Step 3 |
Click Confirm. 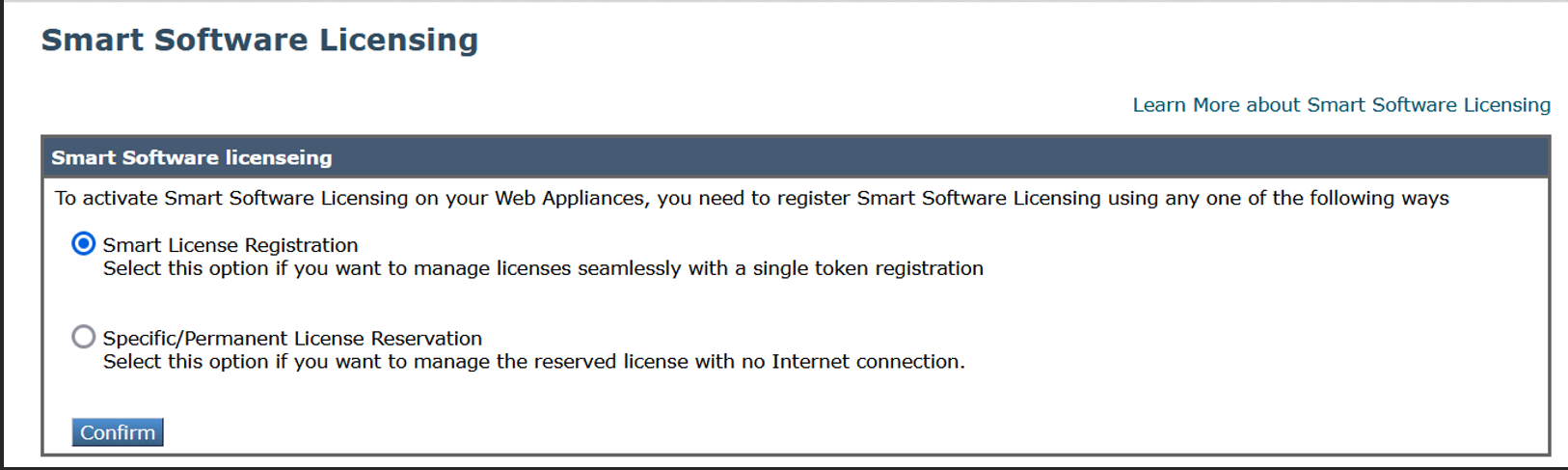 |
||
|
Step 4 |
Click Edit, if you want to change the Transport Settings. The available options are:
|
||
|
Step 5 |
(Optional) Test Interface: Choose Management or Data interface while registering the appliance for the smart licensing feature. This is applicable only when you enable split routing and register for smart licensing.
|
||
|
Step 6 |
Access the Cisco Smart Software Manager portal (https://software.cisco.com/#module/SmartLicensing) using your login credentials. Navigate to the Virtual Account page of the portal and access the General tab to generate a new token. Copy the Product Instance Registration Token for your appliance. See https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/technology/mesh/8-2/b_Smart_Licensing_ Deployment_Guide.html to know about Product Instance Registration Token creation. 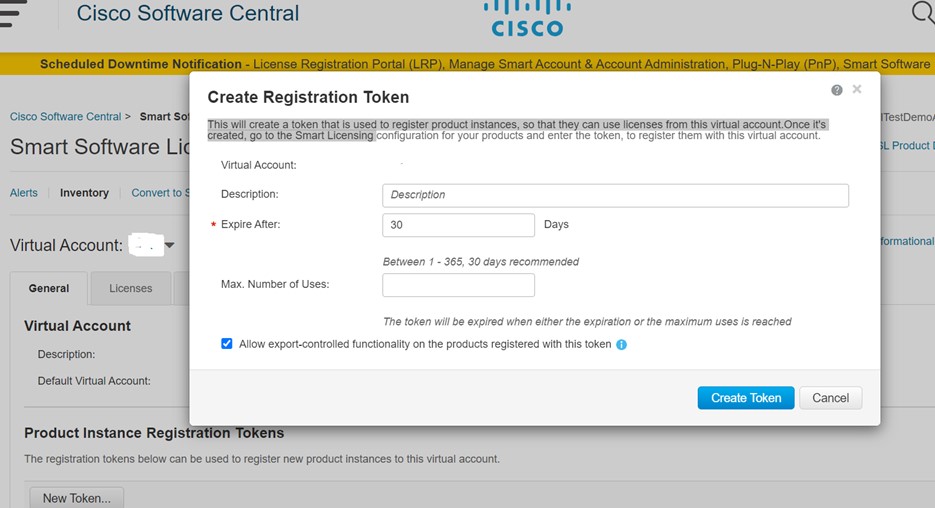 |
||
|
Step 7 |
Switch back to your appliance and click Register. 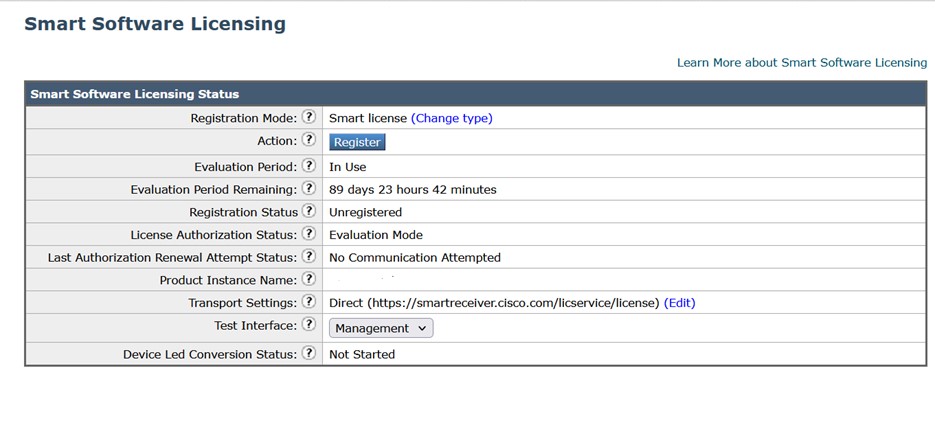 |
||
|
Step 8 |
Paste the Product Instance Registration Token in the textbox. On the Smart Software Licensing page, you can select the Reregister this product instance if it is already registered check box to reregister your appliance. 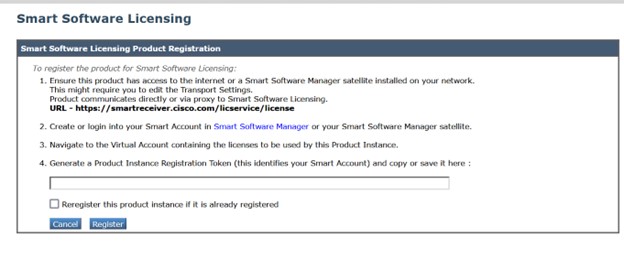 |
What to do next
The product registration process takes a few minutes and you can view the registration status on the Smart Software Licensing page.
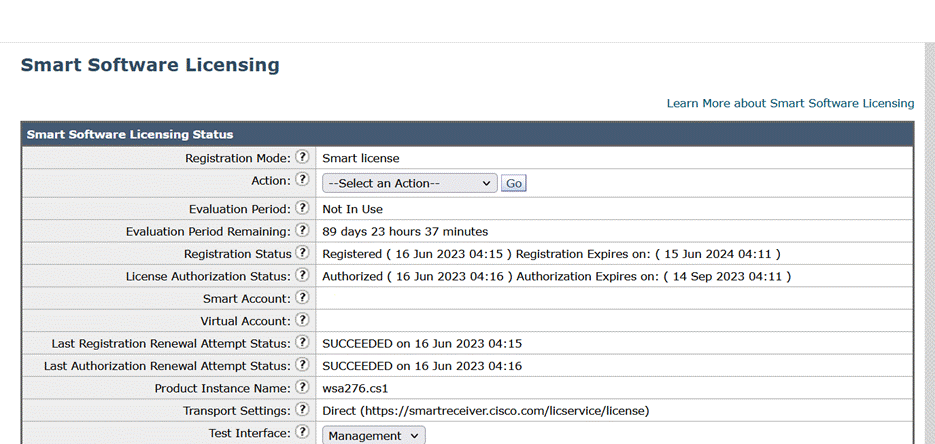
Requesting for Licenses
Once you complete the registration process successfully, you must request for licenses for the appliance's features as required.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > Licenses. |
|
Step 2 |
Click Edit Settings. |
|
Step 3 |
Check the checkboxes under the License Request/Release column corresponding to the licenses you want to request for. |
|
Step 4 |
Click Submit. 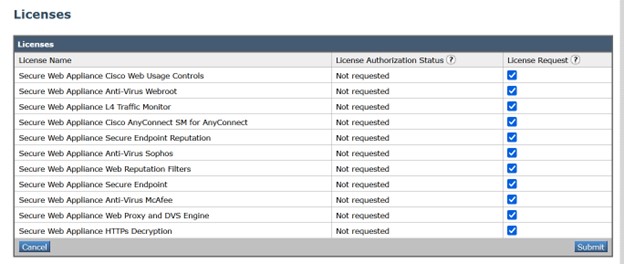 |
What to do next
When the licenses are overused or expired, they will go into out of compliance (OOC) mode and 30-days grace period is provided to each license. You will get notifications on regular intervals (30th, 15th, 5th, and last day) prior to the expiry and also upon the expiry of the OOC grace period.
After the expiry of the OOC grace period, you cannot use the licenses and the features will be unavailable. To access the features again, you must update the licenses on the CSSM portal and renew the authorization.
Releasing Licenses
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > Licenses. |
|
Step 2 |
Click Edit Settings. |
|
Step 3 |
Uncheck the checkboxes under the License Request column corresponding to the licenses you want to release. |
|
Step 4 |
Click Submit. |
Deregistering the Appliance from Smart Cisco Software Manager
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > Smart Software Licensing. |
|
Step 2 |
From the Action drop-down list, choose Deregister and click Go. |
|
Step 3 |
Click Submit. |
Reregistering the Appliance with Smart Cisco Software Manager
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > Smart Software Licensing. |
|
Step 2 |
From the Action drop-down list, choose Reregister and click Go. |
What to do next
See Registering the Appliance with Cisco Smart Software Manager to know about registration process.
You can reregister the appliance after you reset the appliance configurations during unavoidable scenarios.
Changing Transport Settings
You can change the transport settings only before registering the appliance with CSSM.
 Note |
You can change the transport settings only when the smart licensing feature is enabled.If you have already registered your appliance, you must deregister the appliance to change the transport settings. After changing the transport settings, you must register the appliance again. |
See Registering the Appliance with Cisco Smart Software Manager to know how to change the transport settings.
Renewing Authorization and Certificate
After you register your appliance with the Smart Cisco Software Manager, you can renew the certificate.
 Note |
You can renew authorization only after the successful registration of the appliance. |
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > Smart Software Licensing. |
|
Step 2 |
From the Action drop-down list, choose the appropriate option:
|
|
Step 3 |
Click Go. |
What to do next
Updating Smart Agent
To update the Smart Agent version installed on your appliance, perform the following steps:
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > Smart Software Licensing. |
||
|
Step 2 |
In the Smart Agent Update Status section, click Update Now and follow the process.
|
Alerts
You will receive notifications on the following scenarios:
-
Smart Software Licensing successfully enabled
-
Smart Software Licensing enabling failed
-
Beginning of the evaluation period
-
Expiry of evaluation period (on regular intervals during evaluation period and upon expiry)
-
Successfully registered
-
Registration failed
-
Successfully authorized
-
Authorization failed
-
Successfully deregistered
-
Deregistration failed
-
Successfully renewed Id certificate
-
Renewal of Id certificate failed
-
Expiry of authorization
-
Expiry of Id certificate
-
Expiry of out of compliance grace period (on regular intervals during out of compliance grace period and upon expiry).
-
First instance of the expiry of a feature
Command Line Interface
license_smart
Description
Configure smart software licensing feature.
Usage
Commit: This command requires a 'commit'.
Batch Command: This command supports a batch format. For details, see the inline help by typing the command: help license_smart.
Example: Configuring Port for Smart Agent Service
example.com> license_smart
Choose the operation you want to perform:
- ENABLE - Enables Smart Licensing on the product.
- SETAGENTPORT - Set port to run Smart Agent service.
[]> setagentport
Enter the port to run smart agent service.
[65501]>Example: Enabling Smart Licensing
example.com> license_smart
Choose the operation you want to perform:
- ENABLE - Enables Smart Licensing on the product.
[]> enable
After enabling Smart Licensing on your appliance, follow below steps to activate
the feature keys (licenses):
a) Register the product with Smart Software Manager using license_smart > register command in the CLI.
b) Activate the feature keys using license_smart > requestsmart_license command in the CLI.
Note: If you are using a virtual appliance, and have not enabled any of the
features in the classic licensing mode; you will not be able to activate the
licenses, after you switch to the smart licensing mode. You need to first register
your appliance, and then you can activate the licenses (features) in the smart licensing mode.
Commit your changes to enable the Smart Licensing mode on your appliance.
All the features enabled in the Classic Licensing mode will be available in the Evaluation period.
Type "Y" if you want to continue, or type "N" if you want to use the classic licensing mode [Y/N] []> y
> commit
Please enter some comments describing your changes:
[]>
Do you want to save the current configuration for rollback? [Y]>
Example: Registering the Appliance with the Smart Software Manager
example.com> license_smart
To start using the licenses, please register the product.
Choose the operation you want to perform:
- REGISTER - Register the product for Smart Licensing.
- URL - Set the Smart Transport URL.
- STATUS - Show overall Smart Licensing status.
- SUMMARY - Show Smart Licensing status summary.
[]> register
Reregister this product instance if it is already registered [N]> n
Enter token to register the product:
[]>
ODRlOTM5MjItOTQzOS00YjY0LWExZTUtZTdmMmY3OGNlNDZmLTE1MzM3Mzgw%0AMDEzNTR8WlpCQ1lMbGVMQWRx
OXhuenN4OWZDdktFckJLQzF5V3VIbzkyTFgx%0AQWcvaz0%3D%0A
Product Registration is in progress. Use license_smart > status command to check status of registration.
Example: Status of Smart Licensing
example.com> license_smart
To start using the licenses, please register the product.
Choose the operation you want to perform:
- REQUESTSMART_LICENSE - Request licenses for the product.
- RELEASESMART_LICENSE - Release licenses of the product.
- REGISTER - Register the product for Smart Licensing.
- URL - Set the Smart Transport URL.
- STATUS - Show overall Smart Licensing status.
- SUMMARY - Show Smart Licensing status summary.
[]> status
Smart Licensing is: Enabled
Evaluation Period: In Use
Evaluation Period Remaining: 89 days 23 hours 53 minutes
Registration Status: Unregistered
License Authorization Status: Evaluation Mode
Last Authorization Renewal Attempt Status: No Communication Attempted
Product Instance Name: mail.example.com
Transport Settings: Direct (https://smartreceiver.cisco.com/licservice/license)
Example: Status Summary of Smart Licensing
example.com> license_smart
To start using the licenses, please register the product.
Choose the operation you want to perform:
- REGISTER - Register the product for Smart Licensing.
- URL - Set the Smart Transport URL.
- STATUS - Show overall Smart Licensing status.
- SUMMARY - Show Smart Licensing status summary.
[]> summary
FeatureName LicenseAuthorizationStatus
Web Security Appliance Cisco Eval
Web Usage Controls
Web Security Appliance Anti-Virus Webroot Eval
Web Security Appliance Anti-Virus Sophos EvalExample: Setting the Smart Transport URL
example.com> license_smart
Choose the operation you want to perform:
- REQUESTSMART_LICENSE - Request licenses for the product.
- RELEASESMART_LICENSE - Release licenses of the product.
- REGISTER - Register the product for Smart Licensing.
- URL - Set the Smart Transport URL.
- STATUS - Show overall Smart Licensing status.
- SUMMARY - Show Smart Licensing status summary.
[]> url
1. DIRECT - Product communicates directly with the cisco license servers
2. TRANSPORT_GATEWAY - Product communicates via transport gateway or smart software manager satellite.
Choose from the following menu options:
[1]> 1
Note: The appliance uses the Direct URL
(https://smartreceiver.cisco.com/licservice/license) to communicate with Cisco
Smart Software Manager (CSSM) via the proxy server configured using the updateconfig command.
Transport settings will be updated after commit.
Example: Requesting Licenses
 Note |
Users of virtual appliance must register their appliance to request for or release the licenses. |
example.com> license_smart
Choose the operation you want to perform:
- REQUESTSMART_LICENSE - Request licenses for the product.
- RELEASESMART_LICENSE - Release licenses of the product.
- REGISTER - Register the product for Smart Licensing.
- URL - Set the Smart Transport URL.
- STATUS - Show overall Smart Licensing status.
- SUMMARY - Show Smart Licensing status summary.
[]> requestsmart_license
Feature Name License Authorization Status
1. Web Security Appliance Anti-Virus Sophos Not Requested
2. Web Security Appliance Not requested
L4 Traffic Monitor
Enter the appropriate license number(s) for activation.
Separate multiple license with comma or enter range:
[]> 1
Activation is in progress for following features:
Web Security Appliance Anti-Virus Sophos
Use license_smart > summary command to check status of licenses.Example: Releasing Licenses
example.com> license_smart
Choose the operation you want to perform:
- REQUESTSMART_LICENSE - Request licenses for the product.
- RELEASESMART_LICENSE - Release licenses of the product.
- REGISTER - Register the product for Smart Licensing.
- URL - Set the Smart Transport URL.
- STATUS - Show overall Smart Licensing status.
- SUMMARY - Show Smart Licensing status summary.
[]> releasesmart_license
Feature Name License Authorization Status
1. Web Security Appliance Cisco Eval
Web Usage Controls
2. Web Security Appliance Eval
Anti-Virus Webroot
3. Web Security Appliance Eval
L4 Traffic Monitor
4. Web Security Appliance Cisco Eval
AnyConnect SM for AnyConnect
5. Web Security Appliance Advanced Eval
Malware Protection Reputation
6. Web Security Appliance Eval
Anti-Virus Sophos
7. Web Security Appliance Eval
Web Reputation Filters
8. Web Security Appliance Advanced Eval
Malware Protectionshow_license
Description
Show Smart Licensing status and summary of status.
Example: Status of Smart Licensing
example.com> showlicense_smart
Choose the operation you want to perform:
- STATUS- Show overall Smart Licensing status.
- SUMMARY - Show Smart Licensing summary.
[]> status
Smart Licensing is: Enabled
Evaluation Period: In Use
Evaluation Period Remaining: 89 days 23 hours 53 minutes
Registration Status: Unregistered
License Authorization Status: Evaluation Mode
Last Authorization Renewal Attempt Status: No Communication Attempted
Product Instance Name: example.com
Transport Settings: Direct (https://smartreceiver.cisco.com/licservice/license)
Example: Status Summary of Smart Licensing
example.com> showlicense_smart
Choose the operation you want to perform:
- STATUS- Show overall Smart Licensing status.
- SUMMARY - Show Smart Licensing summary.
[]> summary
FeatureName LicenseAuthorizationStatus
Web Security Appliance Cisco Eval
Web Usage Controls
Web Security Appliance Eval
Anti-Virus Webroot
Web Security Appliance Eval
Anti-Virus Sophos
cloudserviceconfig
-
Example: Enabling Cisco Cloud Services on Secure Web Appliance
-
Example: Disabling Cisco Cloud Services on Secure Web Appliance
-
Example: Registering Secure Web Appliance with Cisco Cloud Services Portal
-
Example: Automatically Registering Secure Web Appliance with Cisco Cloud Services Portal
-
Example: Deregistering Secure Web Appliance from Cisco Cloud Services Portal
Description
The cloudserviceconfig command is used to:
-
Enable the Cisco Cloud Services portal on Secure Web Appliance.
-
Disable the Cisco Cloud Services portal on Secure Web Appliance.
-
Register your Secure Web Appliance with the Cisco Cloud Services portal.
-
Automatically register your Secure Web Appliance with the Cisco Cloud Services portal.
-
Deregister your Secure Web Appliance from the Cisco Cloud Services portal.
-
Choose the Cisco Secure Cloud server to connect Secure Web Appliance to the Cisco Cloud Services portal.
-
Download the Cisco Cloud Services Certificate and key from the Cisco Talos Intelligence Services portal.
-
Uploading the Client Certificate and the key.
 Note |
This command is applicable only in Smart Licensing mode. |
Usage
-
Commit: This command does not require a 'commit.
-
Batch Command: This command supports a batch format.
Example: Enabling Cisco Cloud Services on Secure Web Appliance
In the following example, you can use the cloudserviceconfig > enable sub command to enable Cisco Cloud Services on
Secure Web Appliance
example.com > cloudserviceconfig
Choose the operation you want to perform:
- ENABLE - The Cisco Cloud Service is currently disabled on your appliance.
[]> enable
The Cisco Cloud Service is currently enabled on your appliance.
Currently configured Cisco Secure Cloud Server is: api.apj.sse.itd.cisco.com
Available list of Cisco Secure Cloud Servers:
1. AMERICAS (api-sse.cisco.com)
2. APJC (api.apj.sse.itd.cisco.com)
3. EUROPE (api.eu.sse.itd.cisco.com)
Enter Cisco Secure Cloud Server to connect to the Cisco Cloud Service portal.:
[]> 1
Selected Cisco Secure Cloud Server is api-sse.cisco.com.
Make sure you run "commit" to make these changes active.
example.com > commit
Please enter some comments describing your changes:
[]> commit changes
Do you want to save the current configuration for rollback? [Y]>
Changes committed: Tue Dec 29 13:23:19 2020 GMTexample.com >Example: Disabling Cisco Cloud Services on Secure Web Appliance
In the following example, you can use the cloudserviceconfig > disable sub command to disable Cisco Cloud Services on
Secure Web Appliance.
example.com > cloudserviceconfig
The appliance is not registered with the Cisco Cloud Service portal.
Currently configured Cisco Cloud Server is api-sse.cisco.com
Choose the operation you want to perform:
- DISABLE - The Cisco Cloud Service is currently enabled on your appliance.
- REGISTER - To register the appliance with the Cisco Cloud Service portal.
- SETTRS - Set the Cisco Secure Cloud Server to connect to the Cisco Cloud
Service portal.
[]> disable
The Cisco Cloud Service is currently disabled on your appliance.
example.com > commit
Please enter some comments describing your changes:
[]> commit changes
Do you want to save the current configuration for rollback? [Y]>
Changes committed: Tue Dec 29 13:01:07 2020 GMT
example.com >Example: Registering Secure Web Appliance with Cisco Cloud Services Portal
In the following example, you can use the cloudserviceconfig > register sub command to register the
Secure Web Appliance with the Cisco Cloud Services portal.
 Note |
You can only use this sub command if Smart Software licensing is not enabled, and Secure Web Appliance is not registered with Cisco Smart Software Manager |
example.com > cloudserviceconfig
Registration/deregistration of the device with cloud service:
Choose the operation you want to perform:
- DISABLE - The Cisco Cloud Service is currently enabled on your appliance.
- REGISTER - To register the appliance with the Cisco Cloud Service portal.
- SETTRS - Set the Cisco Secure Cloud Server to connect to the Cisco Cloud Service portal.
- STATUS - Check the appliance registration status with the Cisco Cloud Service portal.
[]> register
Enter a registration token key to register your appliance
[]> c51fa32bd9a31227eaab50dea873062c
Registering
The Web Security appliance is successfully registered with the Cisco Cloud Service portal.
example.com >
Example: Automatically Registering Secure Web Appliance with Cisco Cloud Services Portal
In the following example, you can use the cloudserviceconfig > autoregister command to register the
Secure Web Appliance with the Cisco cloud Service Portal.
example.com > cloudserviceconfig
Registration/deregistration of the device with cloud service:
Choose the operation you want to perform:
- AUTOREGISTER - register the appliance with the Cisco Cloud Service portal automatically using SL Payload.
- SETTRS - Set the Cisco Secure Cloud Server to connect to the Cisco Cloud Service portal.
- STATUS - Check the appliance registration status with the Cisco Cloud Service portal.
[]> autoregister
The Web Security appliance successfully auto-registered with the Cisco Cloud Service portal.
Example: Deregistering Secure Web Appliance from Cisco Cloud Services Portal
In the following example, you can use the cloudserviceconfig > deregister sub command to deregister the
Secure Web Appliance from the Cisco Cloud Services portal.
example.com > cloudserviceconfig
Registration/deregistration of the device with cloud service:
Choose the operation you want to perform:
- DISABLE - The Cisco Cloud Service is currently enabled on your appliance.
- DEREGISTER - To deregister the appliance from the Cisco Cloud Service portal.
- STATUS - Check the appliance registration status with the Cisco Cloud Service portal.
[]> deregister
Do you want to deregister your appliance from the Cisco Cloud Service portal.
If you deregister, you will not be able to access the Cloud Service features. [N]> y
The Web Security appliance successfully deregistered from the Cisco Cloud Service portal.
example.com >
Example: Choosing Cisco Secure Cloud Server to connect Secure Web Appliance to Cisco Cloud Services Portal
In the following example, you can use the cloudserviceconfig > settrs sub command to choose the required Cisco Secure Cloud Server to connect the
Secure Web Appliance to the Cisco Cloud Services portal.
example.com > cloudserviceconfig
The appliance is not registered with the Cisco Cloud Service portal.
Currently configured Cisco Cloud Server is api-sse.cisco.com
Choose the operation you want to perform:
- DISABLE - The Cisco Cloud Service is currently enabled on your appliance.
- REGISTER - To register the appliance with the Cisco Cloud Service portal.
- SETTRS - Set the Cisco Secure Cloud Server to connect to the Cisco Cloud
Service portal.
[]> settrs
Currently configured Cisco Secure Cloud Server is: api-sse.cisco.com
Available list of Cisco Secure Cloud Servers:
1. AMERICAS (api-sse.cisco.com)
2. APJC (api.apj.sse.itd.cisco.com)
3. EUROPE (api.eu.sse.itd.cisco.com)
Enter Cisco Secure Cloud Server to connect to the Cisco Cloud Service portal.:
[]> 3
Selected Cisco Secure Cloud Server is api.eu.sse.itd.cisco.com.
Make sure you run "commit" to make these changes active.
example.com > commit
Please enter some comments describing your changes:
[]> commit changes
Do you want to save the current configuration for rollback? [Y]>
Changes committed: Tue Dec 29 13:37:40 2020 GMTExample: Downloading Cisco Cloud Services Certificate and Key from Cisco Talos Intelligence Services Portal
In the following example, you can use the cloudserviceconfig > fetchcertificate sub command to download the Cisco Cloud Services certificate and key from the Cisco Talos Intelligence Services portal..
 Note |
You can only use this sub command when the existing Cisco Cloud Services certificate is expired and if you have registered the Secure Web Appliance with Cisco Smart Software Manager. |
example.com > cloudserviceconfig
Registration/deregistration of the device with cloud service:
Choose the operation you want to perform:
- FETCHCERTIFICATE - Download the Cisco Talos certificate and key
- SETTRS - Set the Cisco Secure Cloud Server to connect to the Cisco Cloud Service portal.
- STATUS - Check the appliance registration status with the Cisco Cloud Service portal.
[]> fetchcertificate
Successfully downloaded the Cisco Talos certificate and key
example.com >
Example: Client Certificate updateconfig
In the following example, you can use the Updateconfig > clientcertificate sub command to upload the certificate and the key.
example.com > updateconfig
Service (images): Update URL:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Web Reputation Filters Cisco Servers
Support Request updates Cisco Servers
Timezone rules Cisco Servers
How-Tos Updates Cisco Servers
HTTPS Proxy Certificate Lists Cisco Servers
Cisco AsyncOS upgrades Cisco Servers
Smart License Agent Updates Cisco Servers
Service (list): Update URL:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Web Reputation Filters Cisco Servers
Support Request updates Cisco Servers
Timezone rules Cisco Servers
How-Tos Updates Cisco Servers
HTTPS Proxy Certificate Lists Cisco Servers
Cisco AsyncOS upgrades Cisco Servers
Smart License Agent Updates Cisco Servers
Update interval for Web Reputation and Categorization: 5m
Update interval for all other services: 5m
Proxy server: not enabled
HTTPS Proxy server: not enabled
Routing table for updates: Management
The following services will use this routing table:
- Web Reputation Filters
- Support Request updates
- Timezone rules
- How-Tos Updates
- HTTPS Proxy Certificate Lists
- Cisco AsyncOS upgrades
- Smart License Agent Updates
Upgrade notification: enabled
Choose the operation you want to perform:
- SETUP - Edit update configuration.
- CLIENTCERTIFICATE - Upload the client certificate and key.
- VALIDATE_CERTIFICATES - Validate update server certificates
- TRUSTED_CERTIFICATES - Manage trusted certificates for updates
[]> clientcertificate
Current Cisco certificate is valid for 179 days
Do you like to overwrite the existing certificate and key [Y|N] ? []> y
Paste the certificate.
Press CTRL-D on a blank line when done.
^D
Paste your certificate and private key details. Certificate and key are stored successfully.
Smart Software Licensing Key Points for AsyncOS 14.0 and later
-
When smart software licensing is enabled and registered, Cisco Cloud Service will be enabled and registered automatically.
-
If the Cisco Cloud Services certificate is expired, you can now download a new certificate from the Cisco Talos Intelligence Services portal using the
cloudserviceconfig>fetchcertificatesub command in the CLI. -
You cannot perform Cisco Cloud Service auto registration when smart license is in evaluation mode.
Virtual Appliance License
The Cisco Web Security Virtual appliance requires an additional license to run the virtual appliance on a host.
For more information about virtual appliance licensing, see the Cisco Content Security Virtual Appliance Installation Guide , available from http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/security/web-security-appliance/products-installation-guides-list.html.
 Note |
You cannot open a Technical Support tunnel before installing the virtual appliance license. |
After the license expires, the appliance will continue to serve as a web proxy without security services for180 days. Security service updates do not occur during this period.
You can configure the appliance so you receive alerts about license expiration.
Related Topics
Installing a Virtual Appliance License
See the Cisco Content Security Virtual Appliance Installation Guide, available from http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/security/web-security-appliance/products-installation-guides-list.html
Enabling Remote Power Cycling
Before you begin
-
Cable the dedicated Remote Power Cycle (RPC) port directly to a secure network. For information, see the hardware guide for your appliance model. For the location of this document, see Documentation Set.
-
Ensure that the appliance is accessible remotely; for example, open any necessary ports through the firewall.
-
This feature requires a unique IPv4 address for the dedicated Remote Power Cycle interface. This interface is configurable only via the procedure described in this section; it cannot be configured using the ipconfig command.
-
In order to cycle appliance power, you will need a third-party tool that can manage devices that support the Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) version 2.0. Ensure that you are prepared to use such a tool.
-
For more information about accessing the command-line interface, see Command Line Interface
After you configure RPC and commit the changes, wait for 10 to 15 minutes before sending the calls to RPC. Secure Web Appliance initializes the RCP services during this wait time.
The ability to remotely reset the power for the appliance chassis is available on x80, x90, and x95 series hardware.
If you want to be able to remotely reset appliance power, you must enable and configure this functionality in advance, using the procedure described in this section.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Use SSH or the serial console port to access the command-line interface. |
|
Step 2 |
Sign in using an account with Administrator access. |
|
Step 3 |
Enter the following commands:
|
|
Step 4 |
Follow the prompts to specify the following:
|
|
Step 5 |
Enter
|
|
Step 6 |
Test your configuration to be sure that you can remotely manage appliance power. |
|
Step 7 |
Ensure that the credentials that you entered will be available to you in the indefinite future. For example, store this information in a safe place and ensure that administrators who may need to perform this task have access to the required credentials. |
What to do next
Related Topics
Administering User Accounts
The following types of users can log into the appliance to manage it:
-
Local users. You can define users locally on the appliance itself.
-
Users defined in an external system. You can configure the appliance to connect to an external LDAP or RADIUS server to authenticate users logging into the appliance.
 Note |
Any user you define can log into the appliance using any method, such as logging into the web interface or using SSH. |
Related Topics
Managing Local User Accounts
You can define any number of users locally on the Secure Web Appliance.
The default system admin account has all administrative privileges. You can change the admin account passphrase, but you cannot edit or delete this account.
 Note |
If you have lost the admin user passphrase, contact your Cisco support provider. For more details, see Reset Your Administrator Password and Unlock the Administrator User Account. |
Adding Local User Accounts
Before you begin
Define the passphrase requirements that all user accounts must follow. See Setting Passphrase Requirements for Administrative Users.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > Users. |
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Click Add User |
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
Enter a username, noting the following rules:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Enter a full name for the user. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Select a user type.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
Enter or generate a passphrase. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
Submit and commit your changes. |
Deleting User Accounts
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > Users. |
|
Step 2 |
Click the trash can icon corresponding to the listed user name and confirm when prompted. |
|
Step 3 |
Submit and commit your changes. |
Editing User Accounts
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > Users. |
|
Step 2 |
Click the user name. |
|
Step 3 |
Make changes to the user on the Edit User page as required. |
|
Step 4 |
Submit and commit your changes. |
Changing Passphrases
To change the passphrase of the account currently logged in, select Options > Change Passphrase from the top right-hand side of the window.
For other accounts, edit the account and change the passphrase in the Local User Settings page.
Related Topics
Configuring Restrictive User Account and Passphrase Settings
You can define user account and passphrase restrictions to enforce organizational passphrase policies. The user account and passphrase restrictions apply to local users defined on the Cisco appliance. You can configure the following settings:
-
User account locking.You can define how many failed login attempts cause the user to be locked out of the account. You can set the number of user login attempts from 1 to 60. The default value is 5.
-
Passphrase lifetime rules.You can define how long a passphrase can exist before the user is required to change the passphrase after logging in.
-
Passphrase rules.You can define what kinds of passphrases users can choose, such as which characters are optional or mandatory.

Note
From AsyncOS version 14.0 onwards, the passphrase rules are enabled by default except for Reject 3 or more repetitive or sequential characters in passphrases and List of words to disallow in passphrases rules.
-
Passphrase strength. You can display a passphrase-strength indicator when an administrative user enters a new passphrase.
For more information, see Setting Passphrase Requirements for Administrative Users.
You define user account and passphrase restrictions on the System Administration > Users page in the Local User Account & Passphrase Settings section.
RADIUS User Authentication
The Secure Web Appliance can use a RADIUS directory service to authenticate users that log in to the appliance using HTTP, HTTPS, SSH, and FTP. You can configure the appliance to contact multiple external servers for authentication, using either PAP or CHAP authentication. You can map groups of external users to different Secure Web Appliance user role types.
Sequence of Events For Radius Authentication
When external authentication is enabled and a user logs into the Secure Web Appliance, the appliance:
-
Determines if the user is the system-defined “admin” account.
-
If not, checks the first configured external server to determine if the user is defined there.
-
If the appliance cannot connect to the first external server, it checks the next external server in the list.
-
If the appliance cannot connect to any external server, it tries to authenticate the user as a local user defined on the Secure Web Appliance.
-
If the user does not exist on any external server or on the appliance, or if the user enters the wrong passphrase, access to the appliance is denied.
Enabling External Authentication Using RADIUS
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
On the System Administration > Users page, click Enable External Authentication. |
||||||
|
Step 2 |
Choose RADIUS as the Authentication Type. |
||||||
|
Step 3 |
Enter the host
name, port number, and Shared Secret passphrase for the RADIUS server. Default
port is
|
||||||
|
Step 4 |
Enter the number of seconds the appliance is to wait for a response from the server before timing out. |
||||||
|
Step 5 |
Choose the authentication protocol used by the RADIUS server. |
||||||
|
Step 6 |
(Optional) Click Add Row to add another RADIUS server. Repeat Steps 1 – 5 for each RADIUS server.
|
||||||
|
Step 7 |
In the External Authentication Cache Timeout field, enter the number of seconds AsyncOS stores the external authentication credentials before contacting the RADIUS server again to re-authenticate. Default is zero.
|
||||||
|
Step 8 |
Configure Group Mapping—Select whether to map all externally authenticated users to the Administrator role or to different appliance-user role types.
|
||||||
|
Step 9 |
Submit and commit your changes. |
What to do next
Related Topics
Defining User Preferences
Preference settings, such as reporting display formats, are stored for each user and are the same regardless from which client machine the user logs into the appliance.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose Options > Preferences. |
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
On the User Preferences page, click Edit Preferences. |
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
Configure the preference settings as required.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Submit and commit your changes. |
Configuring Administrator Settings
Setting Passphrase Requirements for Administrative Users
To set passphrase requirements for locally-defined administrative users of the appliance:
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Select System Administration > Users. |
||||||
|
Step 2 |
In the Passphrase Settings section, click Edit Settings. |
||||||
|
Step 3 |
Choose options:
|
||||||
|
Step 4 |
Submit and commit your changes. |
Additional Security Settings for Accessing the Appliance
You can use the CLI command adminaccessconfig to configure the
Secure Web Appliance to have stricter access requirements for administrators logging into the appliance.
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Configures the appliance to display any text you specify when an administrator tries to log in. The custom log-in banner appears when an administrator accesses the appliance through any interface; for example, via the Web UI, CLI, or FTP. You can load the custom text either by pasting it into the CLI prompt, or by copying it from a text file located on the Secure Web Appliance. To upload the text from a file, you must first transfer the file to the configuration directory on the appliance using FTP. |
|
|
This is a
post-log-in banner, displayed after successful administrator log-in. This text
is added to the appliance configuration by the same means as the log-in
|
|
|
Controls from which IP addresses administrators access the Secure Web Appliance. Administrators can access the appliance from any machine, or from machines with an IP address from a list you specify. When restricting access to an allow list, you can specify IP addresses, subnets, or CIDR addresses. By default, when you list the addresses that can access the appliance, the IP address of your current machine is listed as the first address in the allow list. You cannot delete the IP address of your current machine from the allow list. This information also can be provided using the Web UI; see User Network Access. |
|
|
Enable/disable Web UI cross-site request forgery protection, used to identify and protect against malicious or spoofed requests. For best security, it is recommended that CSRF protection be enabled. |
|
|
Configure use of host header in HTTP requests. By default,
the Web UI responds with the host header sent by the Web client in an HTTP
request. For increased security, you can configure the Web UI to respond with
only the appliance-specific host name; that is, the appliance’s configured name
(for example,
|
|
|
Provide an inactivity time-out interval; that is, the number of minutes users can be inactive before being logged out. This value can be between five and 1440 minutes (24 hours); the default value is 30 minutes. This information also can be provided using the Web UI; see User Network Access. |
|
|
Enable walkthroughs that assist you in accomplishing specific configuration tasks. |
|
|
Configures the appliance so administrators log into the web interface on port 8443 using stronger SSL ciphers (greater than 56 bit encryption). When you configure the appliance to require stronger SSL ciphers, the change only applies to administrators accessing the appliance using HTTPS to manage the appliance. It does not apply to other network traffic connected to the Web Proxy using HTTPS. |
|
|
Configure the number of days for which the login history is retained. |
|
|
Configure the maximum number of concurrent login sessions (CLI and web interface). |
User Network Access
You can specify how long a user can be logged into the appliance before AsyncOS logs the user out due to inactivity. You also can specify the type of user connections allowed.
The session timeout applies to all users, including administrators, logged into either the Web UI or the CLI. When AsyncOS logs a user out, the user is redirected to the appliance log-in page.
 Note |
You also can use
the CLI
|
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > Network Access. |
|
Step 2 |
Click Edit Settings. |
|
Step 3 |
In the Session Inactivity Timeout field, enter the number of minutes users can be inactive before being logged out. You can define a time-out interval between five and 1440 minutes (24 hours); the default value is 30 minutes. |
|
Step 4 |
In the User Access section, you control users’ system access: choose either Allow Any Connection or Only Allow Specific Connections. If you choose Only Allow Specific Connections, define the specific connections as IP addresses, IP ranges, or CIDR ranges. Along with the client IP address, the appliance IP address is automatically added in the User Access section. |
|
Step 5 |
Submit and commit your changes. |
Resetting the Administrator Passphrase
Before you begin
- If you do not know the passphrase for the admin account, contact your customer support provider to reset the passphrase.
- Understand that changes to the passphrase take effect immediately and do not require you to commit the change.
Any administrator-level user can change the passphrase for the “admin” user.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Select Management Appliance > System Administration > Users. |
|
Step 2 |
Click the admin link in the Users list. |
|
Step 3 |
Select Change the passphrase. |
|
Step 4 |
Generate or enter the new passphrase. |
Configuring the Return Address for Generated Messages
You can configure the return address for mail generated by AsyncOS for reports.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > Return Addresses. |
|
Step 2 |
Click Edit Settings. |
|
Step 3 |
Enter the display name, user name, and domain name. |
|
Step 4 |
Submit and commit your changes. |
Managing Alerts
Alerts are email notifications containing information about events occurring on the Cisco Secure Web Appliance. These events can be of varying levels of importance (or severity) from minor (Informational) to major (Critical) and pertain generally to a specific component or feature on the appliance.
 Note |
To receive alerts and email notifications, you must configure the SMTP relay host that the appliance uses to send the email messages. |
Alert Classifications and Severities
The information contained in an alert is determined by an alert classification and a severity. You can specify which alert classifications, at which severity, are sent to any alert recipient.
Alert Classifications
AsyncOS sends the following types of alert:
-
System
-
Hardware
-
Updater
-
Web Proxy
-
Anti-Malware
-
AMP
-
L4 Traffic Monitor
-
External URL Categories
-
Policy Expiration
Alert Severities
Alerts can be sent for the following severities:
- Critical: Requires immediate attention.
- Warning: Problem or error requiring further monitoring and potentially immediate attention.
- Information: Information generated in the routine functioning of this device.
Managing Alert Recipients
 Note |
If you enabled AutoSupport during System Setup, the email address you specified will receive alerts for all severities and classes by default. You can change this configuration at any time. |
Adding and Editing Alert Recipients
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > Alerts. |
|
Step 2 |
Click on a recipient in the Alert Recipients list to edit it, or click Add Recipient to add a new recipient. |
|
Step 3 |
Add or edit the recipient’s email address. You can enter multiple addresses, separated by commas. |
|
Step 4 |
Select which alert severities to receive for each alert type. |
|
Step 5 |
Submit and commit your changes. |
Deleting Alert Recipients
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > Alerts. |
|
Step 2 |
Click the trash can icon corresponding to the alert recipient in the Alert Recipient listing and confirm. |
|
Step 3 |
Commit your changes. |
Configuring Alert Settings
Alert settings are global settings, meaning that they affect how all of the alerts behave.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > Alerts. |
||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Click Edit Settings. |
||||||||
|
Step 3 |
Configure the alert settings as required.
|
||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Submit and commit your changes. |
Alert Listing
The following sections list alerts by classification. The table in each section includes the alert name (internally used descriptor), actual text of the alert, description, severity (critical, information, or warning) and the parameters (if any) included in the text of the message.
Hardware Alerts
The following table contains a list of the various hardware alerts that can be generated by AsyncOS, including a description of the alert and the alert severity:
|
Message |
Alert Severity |
Parameters |
|---|---|---|
|
A RAID-event has occurred: $error |
Warning |
$error: Text of the RAID error. |
System Alerts
The following table contains a list of the various system alerts that can be generated by AsyncOS, including a description of the alert and the alert severity:
|
Message |
Alert Severity |
Parameters |
|---|---|---|
|
Startup script $name exited with error: $message |
Critical. |
$name: Name of the script. $message: Error message text. |
|
System halt failed: $exit_status: $output', |
Critical. |
$exit_status: Exit code of the command. $output: Output from the command. |
|
System reboot failed: $exit_status: $output |
Critical. |
$exit_status: Exit code of the command. $output: Output from the command. |
|
Process $name listed $dependency as a dependency, but it does not exist. |
Critical. |
$name: Name of the process. $dependency: Name of the dependency that was listed. |
|
Process $name listed $dependency as a dependency, but $dependency is not a wait_init process. |
Critical. |
$name: Name of the process. $dependency: Name of the dependency that was listed. |
|
Process $name listed itself as a dependency. |
Critical. |
$name: Name of the process. |
|
Process $name listed $dependency as a dependency multiple times. |
Critical. |
$name: Name of the process. $dependency: Name of the dependency that was listed. |
|
Dependency cycle detected: $cycle. |
Critical. |
$cycle: The list of process names involved in the cycle. |
|
An error occurred while attempting to share statistical data through the Network Participation feature. Please forward this tracking information to your support provider: Error: $error. |
Warning. |
$error: The error message associated with the exception. |
|
There is an error with “$name”. |
Critical. |
$name: Name of the process that generated a core file. |
|
An application fault occurred: “$error” |
Critical. |
$error: Text of the error, typically a traceback. |
|
Appliance: $appliance, User: $username, Source IP: $ip, Event: Account locked due to X failed login attempts. User $username is locked after X consecutive login failures. Last login attempt was from $ip. |
Information. |
$appliance: Identifier of the specific Secure Web Appliance. $username: Identifier of the specific user account. $ip: - IP address from which the login attempt occurred. |
|
Tech support: Service tunnel has been enabled, port $port |
Information. |
$port: Port number used for the service tunnel. |
|
Tech support: Service tunnel has been disabled. |
Information. |
Not applicable. |
|
Warning. |
$ip - IP address from which a login attempt occurred. Description: IP addresses that try to connect to the appliance over SSH but do not provide valid credentials are added to the SSH blocked list if more than 10 failed attempts occur within two minutes. When a user logs in successfully from the same IP address, that IP address is added to the allowed list. Addresses on the allowed list are allowed access even if they are also on the blocked list. Entries are automatically removed from the blocked list after about a day. |
 Note |
System alerts include Feature Key Alerts, Logging Alerts, and Reporting Alerts. You will receive these alerts after configuring them as part of the system alerts. |
Feature Key Alerts
The following table contains a list of the various feature key alerts that can be generated by AsyncOS, including a description of the alert and the alert severity:
|
Message |
Alert Severity |
Parameters |
|---|---|---|
|
A “$feature” key was downloaded from the key server and placed into the pending area. EULA acceptance required. |
Information. |
$feature: Name of the feature. |
|
Your “$feature” evaluation key has expired. Please contact your authorized sales representative. |
Warning. |
$feature: Name of the feature. |
|
Your “$feature” evaluation key will expire in under $days day(s). Please contact your authorized sales representative. |
Warning. |
$feature: Name of the feature. $days: The number of days that will pass before the feature key will expire. |
Logging Alerts
The following table contains a list of the various logging alerts that can be generated by AsyncOS, including a description of the alert and the alert severity:
|
Message |
Alert Severity |
Parameters |
|---|---|---|
|
$error. |
Information. |
$error: The traceback string of the error. |
|
Log Error: Subscription $name: Log partition is full. |
Critical. |
$name: Log subscription name. |
|
Log Error: Push error for subscription $name: Failed to connect to $ip: $reason. |
Critical. |
$name: Log subscription name. $ip: IP address of the remote host. $reason: Text describing the connect error |
|
Log Error: Push error for subscription $name: An FTP command failed to $ip: $reason. |
Critical. |
$name: Log subscription name. $ip: IP address of the remote host. $reason: Text describing what went wrong. |
|
Log Error: Push error for subscription $name: SCP failed to transfer to $ip:$port: $reason', |
Critical. |
$name: Log subscription name. $ip: IP address of the remote host. $port: Port number on the remote host. $reason: Text describing what went wrong. |
|
Log Error: 'Subscription $name: Failed to connect to $hostname ($ip): $error. |
Critical. |
$name: Log subscription name. $hostname: Hostname of the syslog server. $ip: IP address of the syslog server. $error: Text of the error message. |
|
Log Error: Subscription $name: Network error while sending log data to syslog server $hostname ($ip): $error |
Critical. |
$name: Log subscription name. $hostname: Hostname of the syslog server. $ip: IP address of the syslog server. $error: Text of the error message. |
|
Subscription $name: Timed out after $timeout seconds sending data to syslog server $hostname ($ip). |
Critical. |
$name: Log subscription name. $timeout: Timeout in seconds. $hostname: Hostname of the syslog server. $ip: IP address of the syslog server. |
|
Subscription $name: Syslog server $hostname ($ip) is not accepting data fast enough. |
Critical. |
$name: Log subscription name. $hostname: Hostname of the syslog server. $ip: IP address of the syslog server. |
|
Subscription $name: Oldest log file(s) were removed because log files reached the maximum number of $max_num_files. Files removed include: $files_removed. |
Information. |
$name: Log subscription name. $max_num_files: Maximum number of files allowed per log subscription. $files_removed: List of files that were removed. |
Reporting Alerts
The following table contains a list of the various reporting alerts that can be generated by AsyncOS, including a description of the alert and the alert severity:
|
Message |
Alert Severity |
Parameters |
|---|---|---|
|
The reporting system is unable to maintain the rate of data being generated. Any new data generated will be lost. |
Critical. |
Not applicable. |
|
The reporting system is now able to handle new data. |
Information. |
Not applicable. |
|
A failure occurred while building periodic report ‘$report_title’. This subscription should be examined and deleted if its configuration details are no longer valid. |
Critical. |
$report_title: Title of the report. |
|
A failure occurred while emailing periodic report ‘$report_title’. This subscription has been removed from the scheduler. |
Critical. |
$report_title: Title of the report. |
|
Processing of collected reporting data has been disabled due to lack of logging disk space. Disk usage is above $threshold percent. Recording of reporting events will soon become limited and reporting data may be lost if disk space is not freed up (by removing old logs, etc). Once disk usage drops below $threshold percent, full processing of reporting data will be restarted automatically. |
Warning. |
$threshold: Threshold value. |
|
PERIODIC REPORTS: While building periodic report $report_title' the expected domain specification file could not be found at ‘$file_name’. No reports were sent. |
Critical. |
$report_title: Title of the report. $file_name: Name of the file. |
|
Counter group “$counter_group” does not exist. |
Critical. |
$counter_group: Name of the counter_group. |
|
PERIODIC REPORTS: While building periodic report $report_title’ the domain specification file ‘$file_name’ was empty. No reports were sent. |
Critical. |
$report_title: Title of the report. $file_name: Name of the file. |
|
PERIODIC REPORTS: Errors were encountered while processing the domain specification file ‘$file_name’ for the periodic report ‘$report_title’. Any line which has any reported problem had no report sent. $error_text |
Critical. |
$report_title: Title of the report. $file_name: Name of the file. $error_text: List of errors encountered. |
|
Processing of collected reporting data has been disabled due to lack of logging disk space. Disk usage is above $threshold percent. Recording of reporting events will soon become limited and reporting data may be lost if disk space is not freed up (by removing old logs, etc). Once disk usage drops below $threshold percent, full processing of reporting data will be restarted automatically. |
Warning. |
$threshold: Threshold value. |
|
The reporting system has encountered a critical error while opening the database. In order to prevent disruption of other services, reporting has been disabled on this machine. Please contact customer support to have reporting enabled. The error message is: $err_msg |
Critical. |
$err_msg: Error message text. |
Updater Alerts
The following table contains a list of the various updater alerts that can be generated by AsyncOS, including a description of the alert and the alert severity:
|
Message |
Alert Severity |
Parameters |
|---|---|---|
|
The $app application tried and failed $attempts times to successfully complete an update. This may be due to a network configuration issue or temporary outage. |
Warning. |
$app: Secure Web Appliance security service name. $attempts: Number of attempts tried. |
|
The updater has been unable to communicate with the update server for at least $threshold. |
Warning. |
$threshold: Threshold value time. |
|
Unknown error occurred: $traceback. |
Critical. |
$traceback: Traceback information. |
|
Certificate Revoke: OCSP validation failed for the UPDATER Server Certificate ($host:$port). Ensure the certificate is valid. |
Critical |
$host: The hostname of the UPDATER Server. $port: The port of the UPDATER Server. |
Anti-Malware Alerts
For information about alerts related to Secure Endpoint, see Ensuring That You Receive Alerts About Secure Endpoint Issues.
Policy Expiration Alerts
The following table contains a list of the various Policy Expiration alerts that can be generated by AsyncOS, including a description of the alert and the alert severity:
|
Message |
Alert Severity |
Parameters |
|---|---|---|
|
'$PolicyType': '$GroupName' has been disbaled due to expiry configuration. |
Information |
$PolicyType: Access policy / decryption policy based on the web policy type. $GroupName:Policy group name. |
|
'$PolicyType' : '$GroupName' will expire in days : 3. |
Information |
$PolicyType: Access policy / decryption policy based on the web policy type. $GroupName: Policy group name. |
FIPS Compliance
Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) specify requirements for cryptographic modules that are used by all government agencies to protect sensitive but unclassified information. FIPS help ensure compliance with federal security and data privacy requirements. FIPS, developed by the National Institute for Standards and Technology (NIST), are for use when no voluntary standards exist to meet federal requirements.
The Secure Web Appliance achieves FIPS 140-2 compliance in FIPS mode using Cisco Common Cryptographic Module (C3M). By default, FIPS mode is disabled.
Related Topics
FIPS Certificate Requirements
FIPS mode requires that all enabled encryption services on the Secure Web Appliance use a FIPS-compliant certificate. This applies to the following encryption services:
-
HTTPS Proxy
-
Authentication
-
Identity Provider for SaaS
-
Appliance Management HTTPS Service
-
Secure ICAP External DLP Configuration
-
Identity Services Engine
-
SSL Configuration
-
SSH Configuration
 Note |
The Appliance Management HTTPS Service must be configured with a FIPS Complaint certificate before FIPS mode can be enabled. The other encryption services need not be enabled. |
A FIPS-compliant certificate must meet these requirements:
|
Certificate |
Algorithm |
Signature Algorithm |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
|
X509 |
RSA |
sha1WithRSAEncryption sha256WithRSAEncryption |
Cisco recommends a bit key size of 1024 for best decryption performance and sufficient security. A larger bit size will increase security, but impact decryption performance. |
FIPS Certificate Validation
When you enable FIPS mode, the appliance performs the following certificate checks:
-
All certificates uploaded to the Secure Web Appliance, whether by means of the UI or the
certconfigCLI command, are validated to comply strictly with CC standards. Any certificate without a proper trust path in the Secure Web Appliance’s trust store cannot be uploaded. -
Certificate Signature with a trusted path validation; Certificate/Public Key tampering with
basicConstrainsandCAFlagset validated for all signer certificates. -
OCSP validation is available to validate a certificate against a revocation list. This is configurable using the
certconfigCLI command.
Note
A new subcommandOCSPVALIDATION_FOR_SERVER_CERTis added under the main CLI commandcertconfig. Using the new subcommand you can enable the OCSP validation for LDAP and Updater server certificates. If the certificate validation is enabled, you will receive an alert if the certificates involved in communication are revoked.
See also Strict Certificate Validation.
Enabling or Disabling FIPS Mode
Before you begin
-
Make a back-up copy of the appliance configuration; see Saving the Appliance Configuration File
-
Ensure the certificates to be used in FIPS mode use FIPS 140-2 approved public key algorithms (see FIPS Certificate Requirements).
 Note |
|
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > FIPS Mode. |
|
Step 2 |
Click Edit Settings. |
|
Step 3 |
Check Enable FIPS Compliance to enable FIPS compliance. When you check Enable FIPS Compliance, the Enable encryption of Critical Sensitive Parameters (CSP) check box is enabled. |
|
Step 4 |
Check Enable encryption of Critical Sensitive Parameters (CSP) to enable encryption of configuration data such as passwords, authentication information, certificates, shared keys, and so on. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Submit. |
|
Step 6 |
Click Continue to allow the appliance to reboot. |
System Date and Time Management
Setting the Time Zone
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > Time Zone. |
|
Step 2 |
Click Edit Settings. |
|
Step 3 |
Select your region, country, and time zone or select the GMT offset. |
|
Step 4 |
Submit and commit the changes. |
Synchronizing the System Clock with an NTP Server
Cisco recommends that you set your Secure Web Appliance to track the current date and time by querying a Network Time Protocol (NTP) server, not by manually setting the time on the appliance. This is especially true if your appliance integrates with other devices. All integrated devices should use the same NTP server.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > Time Settings. |
||
|
Step 2 |
Click Edit Settings. |
||
|
Step 3 |
Select Use Network Time Protocol as the Time Keeping Method. |
||
|
Step 4 |
Enter the fully qualified hostname or IP address of the NTP server, clicking Add Row as needed to add servers. |
||
|
Step 5 |
(Optional) Choose the routing table associated with an appliance network interface type, either Management or Data, to use for NTP queries. This is the IP address from which NTP queries should originate.
|
||
|
Step 6 |
Submit and commit your changes. |
SSL Configuration
For enhanced security, you can enable and disable SSL v3 and various versions of TLS for several services. Disabling SSL v3 for all services is recommended for best security. By default, all versions of TLS are enabled, and SSL is disabled.
 Note |
You also can use the
|
 Note |
Restart the application when you modify or change the SSL configuration that results in disabling the TLS ciphers. |
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > SSL Configuration. |
||||
|
Step 2 |
Click Edit Settings. |
||||
|
Step 3 |
Check the corresponding boxes to enable SSL v3 and TLS v1.x for these services:
|
||||
|
Step 4 |
Click Submit. |
Certificate Management
 Note |
The Certificate Management page takes a long time to load and results in a timed-out error when the appliance is not connected to the internet. In addition, the "Failed to fetch manifest" network error is displayed in the Certificate Updates list after loading the certificate. |
Related Topics
Strict Certificate Validation
With the release of the FIPS-mode updates in AsyncOS 10.5, all presented certificates are validated strictly to comply with Common Criteria (CC) standards before uploading, and OCSP validation is available to validate certificates against a revocation list.
You must ensure that proper, valid certificates are uploaded to the Secure Web Appliance, and that valid, secure certificates are configured on all related servers to facilitate smooth SSL handshakes with those servers.
Strict certificate validation is applied for the following certificate uploads:
-
HTTPS Proxy (Security Services > HTTPS Proxy)
-
File Analysis Server (Security Services > Anti-Malware and Reputation > Advanced Settings for File Analysis > File Analysis Server: Private Cloud & Certificate Authority: Use Uploaded Certificate Authority)
-
Trusted Root Certificates (Network > Certificate Management)
-
Global Authentication Settings (Network > Authentication > Global Authentication Settings)
-
Identity Provider for SaaS (Network > Identity Provider for SaaS)
-
Identity Services Engine (Network > Identity Services Engine)
-
External DLP Servers (Network > External DLP Servers)
-
LDAP & Secure LDAP (Network > Authentication > Realm)
See also FIPS Compliance.
About Certificates and Keys
When a browser prompts its user to authenticate, the browser sends the authentication credentials to the Web Proxy using a secure HTTPS connection. By default, the Secure Web Appliance uses the “Cisco Web Security Appliance Demo Certificate” that comes with it to create an HTTPS connection with the client. Most browsers will warn users that the certificate is not valid. To prevent users from seeing the invalid certificate message, you can upload a certificate and key pair that your applications recognize automatically.
Related Topics
Managing Trusted Root Certificates
The Secure Web Appliance ships with and maintains a list of trusted root certificates. Web sites with trusted certificates do not require decryption.
You can manage the trusted certificate list, adding certificates to it and functionally removing certificates from it. While the Secure Web Appliance does not delete certificates from the primary list, it allows you to override trust in a certificate, which functionally removes the certificate from the trusted list.
To add, override or download a trusted root certificate:
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose Network > Certificate Management. |
|
Step 2 |
Click Manage Trusted Root Certificates on the Certificate Management page. |
|
Step 3 |
To add a custom trusted root certificate with a signing authority not on the Cisco-recognized list: Click Import and then browse to, select, and Submit the certificate file. |
|
Step 4 |
To override the trust for one or more Cisco-recognized certificates:
|
|
Step 5 |
To download a copy of a particular certificate:
|
Certificate Updates
The Updates section lists version and last-updated information for the Cisco trusted-root-certificate and blocked list bundles on the appliance. These bundles are updated periodically.
Procedure
|
Click Update Now on the Certificate Management page to update all bundles for which updates are available. |
Viewing Blocked Certificates
To view a list of certificates which Cisco has determined to be invalid, and has blocked:
Procedure
|
Click View Blocked Certificates. |
Uploading or Generating a Certificate and Key
Certain AsyncOS features require a certificate and key to establish, confirm or secure a connection Identity Services Engine (ISE) and . You can either upload an existing certificate and key, or you can generate one when you configure the feature.
Uploading a Certificate and Key
A certificate you upload to the appliance must meet the following requirements:
- It must use the X.509 standard.
- It must include a matching private key in PEM format. DER format is not supported.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Select Use Uploaded Certificate and Key. |
||
|
Step 2 |
In the Certificate field, click Browse; locate the file to upload.
|
||
|
Step 3 |
In the Key field, click Browse; locate the file to upload.
|
||
|
Step 4 |
If the key is encrypted, select Key is Encrypted. |
||
|
Step 5 |
Click Upload Files. |
Generating a Certificate and Key
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Select Use Generated Certificate and Key. |
|
Step 2 |
Click Generate New Certificate and Key. |
|
Step 3 |
Click Download Certificate to download the new certificate for upload to the appliance. |
|
Step 4 |
Click Download Certificate Signing Request to download the new certificate file for transmission to a Certificate Authority (CA) for signing. See Certificate Signing Requests for more information about this process.
|
Certificate Signing Requests
The Secure Web Appliance cannot generate Certificate Signing Requests (CSR) for certificates uploaded to the appliance. Therefore, to have a certificate created for the appliance, you must issue the signing request from another system. Save the PEM-formatted key from this system because you will need to install it on the appliance later.
You can use any UNIX machine with a recent version of OpenSSL installed. Be sure to put the appliance hostname in the CSR. Use the guidelines at the following location for information on generating a CSR using OpenSSL:
http://www.modssl.org/docs/2.8/ssl_faq.html#ToC28
Once the CSR has been generated, submit it to a certificate authority (CA). The CA will return the certificate in PEM format.
If you are acquiring a certificate for the first time, search the Internet for “certificate authority services SSL server certificates,” and choose the service that best meets the needs of your organization. Follow the service’s instructions for obtaining an SSL certificate.
 Note |
You can also generate and sign your own certificate. Tools for doing this are included with OpenSSL, free software from http://www.openssl.org .
|
Intermediate Certificates
In addition to root certificate authority (CA) certificate verification, AsyncOS supports the use of intermediate certificate verification. Intermediate certificates are certificates issued by a trusted root CA which are then used to create additional certificates. This creates a chained line of trust. For example, a certificate may be issued by example.com who, in turn, is granted the rights to issue certificates by a trusted root CA. The certificate issued by example.com must be validated against example.com’s private key as well as the trusted root CA’s private key.
Servers send a “certificate chain” in an SSL handshake in order for clients (for example, browsers and in this case the Secure Web Appliance, which is a HTTPS proxy) to authenticate the server. Normally, the server certificate is signed by an intermediate certificate which in turn is signed by a trusted root certificate, and during the handshake, the server certificate and the entire certificate chain are presented to the client. As the root certificate is typically present in the Trusted Certificate store of the Secure Web Appliance, verification of the certificate chain is successful.
However, sometimes when the end-point entity certificate is changed on the server, necessary updates for the new chain are not performed. As a result, going forward the server presents only the server certificate during the SSL handshake and the Secure Web Appliance proxy is unable to verify the certificate chain since the intermediate certificate is missing.
Previously, the solution was manual intervention by the
Secure Web Appliance administrator, who would upload the necessary intermediate certificate to the Trusted Certificate store. Now you can use
the CLI command advancedproxyconfig > HTTPS > Do you want to enable automatic discovery and download of missing Intermediate Certificates? to enable “intermediate certificate discovery,” a process the
Secure Web Appliance uses in an attempt to eliminate the manual step in these situations.
Intermediate certificate discovery uses a method called “AIA chasing”: when presented with an untrusted certificate, the Secure Web Appliance examines it for an extension named “Authority Information Access.” This extension includes an optional CA Issuers URI field, which can be queried for the Issuer Certificate used to sign the server certificate in question. If it is available, the Secure Web Appliance fetches the issuer’s certificate recursively until the root CA certificate is obtained, and then tries to verify the chain again.
AsyncOS for Web Upgrades and Updates
Cisco periodically releases upgrades (new software versions) and updates (changes to current software versions) for AsyncOS for Web and its components.
Best Practices For Upgrading AsyncOS for Web
-
Before you start the upgrade, save the XML configuration file off the Secure Web Appliance from the System Administration > Configuration File page or by using the saveconfig command.
-
Save other files stored on the appliance, such as PAC files or customized end-user notification pages.
-
When upgrading, do not pause for long amounts of time at the various prompts. If the TCP session times out during the download, the upgrade may fail.
-
After the upgrade completes, save the configuration information to an XML file.
Related Topics
Upgrading and Updating AsyncOS and Security Service Components
Downloading and Installing an Upgrade
Before you begin
Save the appliance configuration file (see Saving, Loading, and Resetting the Appliance Configuration).
 Note |
When downloading and upgrading AsyncOS in a single operation from a local server instead of from a Cisco server, the upgrade installs immediately while downloading. A banner is displayed for 10 seconds at the beginning of the upgrade process. While this banner is displayed, you can type Control-C to exit the upgrade process before downloading starts. |
 Note |
While performing an upgrade, if the secure authentication certificate is not FIPs-complaint, it will be replaced with the default certificate of the latest path to which your appliance is upgraded to. This happens only when the customer has used the default certificate before the upgrade. |
You can download and install in a single operation, or download in the background and install later.
Upgrade fails if any configuration value stored in varstore files have non-ASCII characters.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > System Upgrade. |
||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Click Upgrade Options. Select upgrade options and an upgrade image:
|
||||||||
|
Step 3 |
Click Proceed. If you are installing: |
Viewing Status of, Canceling, or Deleting a Background Download
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > System Upgrade. |
||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Click Upgrade Options. |
||||||||
|
Step 3 |
Choose an option:
|
||||||||
|
Step 4 |
(Optional) View the Upgrade Logs. |
What to do next
Related Topics
Automatic and Manual Update and Upgrade Queries
AsyncOS periodically queries the update servers for new updates to all security service components, but not for new AsyncOS upgrades. To upgrade AsyncOS, you must manually prompt AsyncOS to query for available upgrades. You can also manually prompt AsyncOS to query for available security service updates. For more information, see Reverting to a Previous Version of AsyncOS for Web.
When AsyncOS queries an update server for an update or upgrade, it performs the following steps:
-
Contacts the update server.
Cisco allows the following sources for update servers:
- Cisco update servers. For more information, see Updating and Upgrading from the Cisco Update Servers.
- Local server. For more information, see Upgrading from a Local Server.
-
Receives an XML file that lists the available updates or AsyncOS upgrade versions. This XML file is known as the “manifest.”
-
Downloads the update or upgrade image files.
Manually Updating Security Service Components
By default, each security service component periodically receives updates to its database tables from the Cisco update servers. However, you can manually update the database tables.
 Note |
Some updates are available on demand from the GUI pages related to the feature. |
 Tip |
View a record of update activity in the updater log file. Subscribe to the updater log file on the System Administration > Log Subscriptions page. |
 Note |
Updates that are in-progress cannot be interrupted. All in-progress updates must complete before new changes can be applied. |
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > Upgrade and Update Settings. |
|
Step 2 |
Click Edit Update Settings. |
|
Step 3 |
Specify the location of the update files. |
|
Step 4 |
Initiate the update using the Update Now function key on the component page located on the Security Services tab. For example, Security Services > Web Reputation Filters page. The CLI and the Web application interface may be sluggish or unavailable during the update process. |
Local And Remote Update Servers
By default, AsyncOS contacts the Cisco update servers for both update and upgrade images and the manifest XML file. However, you can choose from where to download the upgrade and update images and the manifest file. Using a local update server for the images or manifest file for any of the following reasons:
- You have multiple appliances to upgrade simultaneously. You can download the upgrade image to a web server inside your network and serve it to all appliances in your network.
- Your firewall settings require static IP addresses for the Cisco update servers. The Cisco update servers use dynamic IP addresses. If you have strict firewall policies, you may need to configure a static location for updates and AsyncOS upgrades. For more information, see Configuring a Static Address for the Cisco Update Servers.
 Note |
Local update servers do not automatically receive security service updates, only AsyncOS upgrades. After using a local update server for upgrading AsyncOS, change the update and upgrade settings back to use the Cisco update servers so the security services update automatically again. |
Updating and Upgrading from the Cisco Update Servers
A Secure Web Appliance can connect directly to Cisco update servers and download upgrade images and security service updates. Each appliance downloads the updates and upgrade images separately.
Configuring a Static Address for the Cisco Update Servers
The Cisco update servers use dynamic IP addresses. If you have strict firewall policies, you may need to configure a static location for updates and AsyncOS upgrades.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Contact Cisco Customer Support to obtain the static URL address. |
|
Step 2 |
Navigate to the System Administration > Upgrade and Update Settings page, and click Edit Update Settings. |
|
Step 3 |
On the Edit Update Settings page, in the “Update Servers (images)” section, choose Local Update Servers and enter the static URL address received in step 1. |
|
Step 4 |
Verify that Cisco Update Servers is selected for the “Update Servers (list)” section. |
|
Step 5 |
Submit and commit your changes. |
Upgrading from a Local Server
The Secure Web Appliance can download AsyncOS upgrades from a server within your network instead of obtaining upgrades directly from the Cisco update servers. When you use this feature, you download the upgrade image from Cisco once only, and then serve it to all Secure Web Appliances in your network.
The following figure shows how Secure Web Appliances download upgrade images from local servers.

Hardware and Software Requirements for Local Upgrade Servers
For downloading AsyncOS upgrade files, you must have a system in your internal network that has a web browser and Internet access to the Cisco update servers.
 Note |
If you need to configure a firewall setting to allow HTTP access to this address, you must configure it using the DNS name and not a specific IP address. |
For hosting AsyncOS upgrade files, a server on the internal network must have a web server, such as Microsoft IIS (Internet Information Services) or the Apache open source server, which has the following features:
-
Supports the display of directory or filenames in excess of 24 characters.
-
Has directory browsing enabled.
-
Is configured for anonymous (no authentication) or Basic (“simple”) authentication.
-
Contains at least 350MB of free disk space for each AsyncOS upgrade image.
Configuring Upgrades from a Local Server
 Note |
Cisco recommends changing the update and upgrade settings to use the Cisco update servers (using dynamic or static addresses) after the upgrade is complete to ensure the security service components continue to update automatically. |
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Configure a local server to retrieve and serve the upgrade files. |
|
Step 2 |
Download the upgrade zip file. Using a browser on the local server, go to http://updates.ironport.com/fetch_manifest.html to download a zip file of an upgrade image. To download the image, enter your serial number (for a physical appliance) or VLN (for a virtual appliance) and the version number of the appliance. You will then be presented with a list of available upgrades. Click on the upgrade version that you want to download. |
|
Step 3 |
Unzip the zip file in the root directory on the local server while keeping the directory structure intact. |
|
Step 4 |
Configure the appliance to use the local server using the System Administration > Upgrade and Update Settings page or the updateconfig command. |
|
Step 5 |
On the System Administration > System Upgrade page, click Available Upgrades or run the upgrade command. |
Differences Between Local and Remote Upgrading Methods
The following differences apply when upgrading AsyncOS from a local server rather than from a Cisco update server:
-
The upgrading installs immediately while downloading .
-
A banner displays for 10 seconds at the beginning of the upgrade process. While this banner is displayed, you have the option to type Control+C to exit the upgrade process before downloading starts.
Configuring Upgrade and Service Update Settings
You can configure how the Secure Web Appliance downloads security services updates and AsyncOS for Web upgrades. For example, you can choose which network interface to use when downloading the files, configure the update interval or disable automatic updates.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose System Administration > Upgrade and Update Settings. |
||||||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Click Edit Update Settings. |
||||||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
Configure the settings, referencing the following information:
|
||||||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Submit and commit your changes. |
What to do next
Related Topics
Reverting to a Previous Version of AsyncOS for Web
AsyncOS for Web supports the ability to revert the AsyncOS for Web operating system to a previous qualified build for emergency uses.
 Note |
You cannot revert to a version of AsyncOS for Web earlier than version 7.5. |
Reverting AsyncOS on Virtual Appliances Impacts the License
If you revert to AsyncOS 8.0, there is no 180-day grace period during which the appliance processes web transactions without security features. License expiration dates are unaffected.
Configuration File Use in the Revert Process
Effective in version 7.5, when you upgrade to a later version, the upgrade process automatically saves the current system configuration to a file on the Secure Web Appliance. (However, Cisco recommends manually saving the configuration file to a local machine as a backup.) This allows AsyncOS for Web to load the configuration file associated with the earlier release after reverting to the earlier version. However, when it performs a reversion, it uses the current network settings for the management interface.
Reverting AsyncOS for an Appliance Managed by the SMA
You can revert AsyncOS for Web from the Secure Web Appliance. However, if the Secure Web Appliance is managed by a Security Management appliance, consider the following rules and guidelines:
-
When Centralized Reporting is enabled on the Secure Web Appliance, AsyncOS for Web finishes transferring the reporting data to the Security Management appliance before it starts the reversion. If the files take longer than 40 seconds to transfer to the Security Management appliance, AsyncOS for Web prompts you to continue waiting to transfer the files, or continue the reversion without transferring all files.
-
You must associate the Secure Web Appliance with the appropriate Primary Configuration after reverting. Otherwise, pushing a configuration from the Security Management appliance to the Secure Web Appliance might fail.
Reverting AsyncOS for Web to a Previous Version
 Caution |
Reverting the operating system on a Secure Web Appliance is a very destructive action and destroys all configuration logs and databases. Reversion also disrupts web traffic handling until the appliance is reconfigured. Depending on the initial Secure Web Appliance configuration, this action may destroy network configuration. If this happens, you will need physical local access to the appliance after performing the reversion. |
 Caution |
Smart Licensing configuration cannot be preserved if the operating system on a Secure Web Appliance is reverted to the previous version with Smart Licensing enabled. When you have successfully reverted to previous AsyncOS version, you should enable Smart Licensing and register it with the CSSM portal. If the Specific/Permanent License Reservation option was selected when Smart Software Licensing was activated, it is recommended to release the licenses used by the appliance before reverting the operation and de-register the appliance from CSSM portal. You can contact Cisco support for assistance if the licenses were not released or the appliance was not de-registered before the revert operation. |
 Note |
If updates to the set of URL categories are available, they will be applied after AsyncOS reversion. |
Before you begin
-
Contact Cisco Quality Assurance to confirm that you can perform the intended reversion. (BS: this is a summary of the Available Versions section in the original topic. Have asked if this is correct.)
-
Back up the following information from the Secure Web Appliance to a separate machine:
-
System configuration file (with passphrases unmasked).
-
Log files you want to preserve.
-
Reports you want to preserve.
-
Customized end-user notification pages stored on the appliance.
-
PAC files stored on the appliance.
-
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Log into the CLI of the appliance you want to revert.
|
||
|
Step 2 |
Enter the
|
||
|
Step 3 |
Confirm twice that you want to continue with the reversion. |
||
|
Step 4 |
Choose one of the available versions to revert to. The appliance reboots twice.
The appliance should now run using the selected AsyncOS for Web version. You can access the web interface from a web browser. |
Monitoring System Health and Status Using SNMP
The AsyncOS operating system supports system status monitoring via SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol). (For more information about SNMP, see RFCs 1065, 1066, and 1067.)
Please note:
-
SNMP is off by default.
-
SNMP SET operations (configuration) are not implemented.
-
AsyncOS supports SNMPv1, v2, and v3. For more information on SNMPv3, see RFCs 2571-2575.
-
Message authentication and encryption are mandatory when enabling SNMPv3. Passphrases for authentication and encryption should be different. The encryption algorithm can be AES (recommended) or DES. The authentication algorithm can be SHA-1 (recommended) or MD5. The snmpconfig command “remembers” your passphrases the next time you run the command.
-
The SNMPv3 username is: v3get.
> snmpwalk -v 3 -l AuthNoPriv -u v3get -a MD5 serv.example.com -
If you use only SNMPv1 or SNMPv2, you must set a community string. The community string does not default to
public. -
For SNMPv1 and SNMPv2, you must specify a network from which SNMP GET requests are accepted.
-
To use traps, an SNMP manager (not included in AsyncOS) must be running and its IP address entered as the trap target. (You can use a host name, but if you do, traps will only work if DNS is working.)
MIB Files
MIB files are available from http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/security/web-security-appliance/tsd-products-support-series-home.html
Use the latest version of each MIB file.
There are multiple MIB files:
-
asyncoswebsecurityappliance-mib.txt — an SNMPv2 compatible description of the Enterprise MIB for Secure Web Appliances.
-
ASYNCOS-MAIL-MIB.txt — an SNMPv2 compatible description of the Enterprise MIB for Email Security appliances.
-
IRONPORT-SMI.txt — This “Structure of Management Information” file defines the role of the asyncoswebsecurityappliance-mib.
This release implements a read-only subset of MIB-II as defined in RFCs 1213 and 1907.
See https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/security/web-security-appliance/118415-technote-wsa-00.html to know about monitoring CPU usage on the appliance using SNMP.
Enabling and Configuring SNMP Monitoring
To configure SNMP to gather system status information for the appliance, use the snmpconfig command in the command-line interface (CLI). After you choose and configure values for an interface, the appliance responds to SNMPv3 GET requests.
When you use SNMP monitoring, keep the following points in mind:
- These version 3 requests must include a matching passphrase.
- By default, version 1 and 2 requests are rejected.
- If enabled, version 1 and 2 requests must have a matching community string.
Hardware Objects
Hardware sensors conforming to the Intelligent Platform Management Interface Specification (IPMI) report information such as temperature, fan speed, and power supply status.
To determine the hardware-related objects available for monitoring (for example, the number of fans or the operating temperature range), see the hardware guide for your appliance model.
Related Topics
SNMP Traps
SNMP provides the ability to send traps, or notifications, to advise an administration application when one or more conditions have been met. Traps are network packets that contain data relating to a component of the system sending the trap. Traps are generated when a condition has been met on the SNMP agent (in this case, the Cisco Secure Web Appliance). After the condition has been met, the SNMP agent then forms an SNMP packet and sends it to the host running the SNMP management console software.
You can configure SNMP traps (enable or disable specific traps) when you enable SNMP for an interface.
To specify multiple trap targets: when prompted for the trap target, you may enter up to 10 comma separated IP addresses.
Related Topics
About the connectivityFailure SNMP Trap
The
connectivityFailure trap is intended to monitor your appliance’s connection to
the internet. It does this by attempting to connect and send an HTTP GET
request to a single external server every 5 to 7 seconds. By default, the
monitored URL is
downloads.ironport.com on port 80.
To change the
monitored URL or port, run the
snmpconfig command and enable the connecivityFailure
trap, even if it is already enabled. You will see a prompt to change the URL.
 Tip |
To simulate
connectivityFailure traps, you can use the
|
CLI Example: snmpconfig
wsa.example.com> snmpconfig
Current SNMP settings:
SNMP Disabled.
Choose the operation you want to perform:
- SETUP - Configure SNMP.
[]> SETUP
Do you want to enable SNMP?
[Y]>
Please choose an IP interface for SNMP requests.
1. Management (198.51.100.1: wsa.example.com)
[1]>
Which port shall the SNMP daemon listen on interface "Management"?
[161]>
Please select SNMPv3 authentication type:
1. MD5
2. SHA
[1]> 2
Please select SNMPv3 privacy protocol:
1. DES
2. AES
[1]> 2
Enter the SNMPv3 authentication passphrase.
[]>
Please enter the SNMPv3 authentication passphrase again to confirm.
[]>
Enter the SNMPv3 privacy passphrase.
[]>
Please enter the SNMPv3 privacy passphrase again to confirm.
[]>
Service SNMP V1/V2c requests?
[N]> Y
Enter the SNMP V1/V2c community string.
[ironport]> public
Shall SNMP V2c requests be serviced from IPv4 addresses?
[Y]>
From which IPv4 networks shall SNMP V1/V2c requests be allowed? Separate
multiple networks with commas.
[127.0.0.1/32]>
Enter the Trap target as a host name, IP address or list of IP
addresses separated by commas (IP address preferred). Enter "None" to disable traps.
[127.0.0.1]> 203.0.113.1
Enter the Trap Community string.
[ironport]> tcomm
Enterprise Trap Status
1. CPUUtilizationExceeded Disabled
2. FIPSModeDisableFailure Enabled
3. FIPSModeEnableFailure Enabled
4. FailoverHealthy Enabled
5. FailoverUnhealthy Enabled
6. RAIDStatusChange Enabled
7. connectivityFailure Disabled
8. fanFailure Enabled
9. highTemperature Enabled
10. keyExpiration Enabled
11. linkUpDown Enabled
12. memoryUtilizationExceeded Disabled
13. powerSupplyStatusChange Enabled
14. resourceConservationMode Enabled
15. updateFailure Enabled
Do you want to change any of these settings?
[N]> Y
Do you want to disable any of these traps?
[Y]> n
Do you want to enable any of these traps?
[Y]> y
Enter number or numbers of traps to enable. Separate multiple numbers with
commas.
[]> 1,7,12
What threshold would you like to set for CPU utilization?
[95]>
What URL would you like to check for connectivity failure?
[http://downloads.ironport.com]>
What threshold would you like to set for memory utilization?
[95]>
Enter the System Location string.
[Unknown: Not Yet Configured]> Network Operations Center - west; rack #30, position 3
Enter the System Contact string.
[snmp@localhost]> wsa-admin@example.com
Current SNMP settings:
Listening on interface "Management" 198.51.100.1 port 161.
SNMP v3: Enabled.
SNMP v1/v2: Enabled, accepting requests from subnet 127.0.0.1/32 .
SNMP v1/v2 Community String: public
Trap target: 203.0.113.1
Location: Network Operations Center - west; rack #30, position 3
System Contact: wsa-admin@example.com
Choose the operation you want to perform:
- SETUP - Configure SNMP.
[]>
wsa.example.com> commit
Please enter some comments describing your changes:
[]> Enable and configure SNMP
Changes committed: Fri Nov 06 18:13:16 2015 GMT
wsa.example.com> Web Traffic Tap
Before You Begin:Enabling Web Traffic Tap feature will result in reduced transaction handling capacity (requests per second) for the appliance as appliance will need additional CPU cycles and memory to copy the messages to the tap interface.
 Note |
For reducing the performance impact due to Web Traffic Tap feature, reduce the amount of traffic that gets tapped by setting appropriate Web Traffic Tap policies. This feature is not supported on Amazon Web Services (AWS) |
Web Traffic Tap feature allows you to tap the HTTP and HTTPS web traffic that passes through the appliance and copy it to a Secure Web Appliance interface in-line with the real time data traffic. You can select the Secure Web Appliance interface to which the tapped traffic data is sent. If the tapped traffic includes HTTPS data, the appliance decrypts them based on the decryption policies before sending them to the tap interface. See Decryption Policies.
The selected tap interface must be directly connected to an external security device for analysis, forensics, and archiving. Alternatively, it may be connected to a L2 switch on a dedicated VLAN.
 Note |
The traffic mirrored on the tap interface is broadcast over Ethernet layer and not IP routable. Therefore a dedicated VLAN is required if connected to a L2 switch. |
This feature also enables you to set Web Traffic Tap policies. Based on these customer defined policy filters, the appliance mirrors the web traffic that is available for the external security device. Web Traffic Tap feature provides visibility to the HTTPS traffic.
The term tapping refers to the reconstruction of complete TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) streams as if occurring between a directly connected client and server.
Virtual Secure Web Appliances support Web Traffic Tap feature.
 Note |
The act of inspecting SSL traffic might be subject to corporate policy guidelines and/or national legislation. Cisco is not responsible for any legal obligations and it is your sole responsibility to ensure that your use of Web Traffic Tap feature on Secure Web Appliance is in accordance with any such legal or policy requirements. |
You must perform the following procedures to tap the web traffic using the appliance:
-
Enable Web Traffic Tap feature
-
Configure Web Traffic Tap policies
Related Topics
Enabling Web Traffic Tap
Before you begin
The Web Traffic Tap feature is disabled by default. You must enable the feature before you define the Web Traffic Tap policies using Web Security Manager > Web Traffic Tap Policies.
 Note |
Decryption policies must be defined in order to tap HTTPS transactions. See Decryption Policies. |
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose Network > Web Traffic Tap. |
||
|
Step 2 |
Click Edit Settings. |
||
|
Step 3 |
In the Edit Web Traffic Tap page, check the Enable check box to enable Web Traffic Tap feature.
|
||
|
Step 4 |
From the Tap Interface drop-down list, choose the Secure Web Appliance interface to which the tapped traffic data is sent. The interface options are P1, P2, T1, and T2. See Connect the Appliance to know about interfaces.
|
||
|
Step 5 |
Click Submit and commit your changes. |
Configuring Web Traffic Tap Policies
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose Web Security Manager > Web Traffic Tap Policies. |
||||||
|
Step 2 |
Click Add Policy. Follow the instructions in Creating a Policyto add a new Web Traffic Tap policy.
|
||||||
|
Step 3 |
Expand the Advanced section of the Policy Member Definition area to add the following additional group membership criteria for Web Traffic Tap.
See Creating a Policy to know more about defining additional group membership criteria.
You can also add URL categories from the URL Filtering table using Web Security Manager > Web Traffic Tap Policies.
See Policy Order to know about the Web Traffic Tap policy order. |
Configuring HTTP 2.0 Protocol
The Cisco AsyncOS 14.0 version supports HTTP 2.0 for web request and response over TLS.
HTTP 2.0 for web request and response over TLS. HTTP 2.0 support requires TLS ALPN based negotiation which is available only from TLS 1.2 version onwards.
In this release, the HTTPS 2.0 is not supported for the following features:
-
Web Traffic Tap
-
External DLP
-
Overall Bandwidth and Application Bandwidth
 Note |
By default, the HTTP 2.0 feature is disabled and use the CLI command HTTP 2 to enable the feature. |
The HTTP 2.0 feature supports:
-
A maximum of 4096 concurrent sessions and 128 concurrent streams
-
All HTTP protocol in ALPN and a maximum of seven protocols in advertised ALPN.
-
A maximum header size of 16k.
 Note |
CONNECT for explicit proxy in 2.0 also starts with HTTP1.1 |
A new CLI command HTTP2 is introduced to enable or disable HTTP 2.0 configurations. See
Secure Web Appliance CLI Commands.
You cannot enable or disable HTTP 2.0 and restrict domain for HTTP 2.0 through the appliance’s web user interface. The configuration of HTTP 2.0 is not supported through Cisco Secure Email and Web Manager (Cisco Content Security Management Appliances).
-
When URL fails in both HTTP 2 exception lists and passthrough URL Categories, HTTP 2 takes precedence over passthrough.
-
ALPN logging is not consistent for Passthrough URL Categories.
 Feedback
Feedback