About Management Center High Availability
To ensure the continuity of operations, the high availability feature allows you to designate redundant management centers to manage devices. The management centers support Active/Standby high availability where one appliance is the active unit and manages devices. The standby unit does not actively manage devices. The active unit writes configuration data into a data store and replicates data for both units, using synchronization where necessary to share some information with the standby unit.
Active/Standby high availability lets you configure a secondary management center to take over the functionality of a primary management center if the primary fails. When the primary management center fails, you must promote the secondary management center to become the active unit.
Event data streams from managed devices to both management centers in the high availability pair. If one management center fails, you can monitor your network without interruption using the other management center.
Note that management centers configured as a high availability pair do not need to be on the same trusted management network, nor do they have to be in the same geographic location.
 Caution |
Because the system restricts some functionality to the active management center, if that appliance fails, you must promote the standby management center to active. |
 Note |
Triggering a switchover on management center immediately after a successful change deployment can lead to preview configuration not working on the new active management center. This does not impact policy deploy functionality. It is recommended to trigger a switchover on the management center after the necessary sync is completed. Similarly, when management center HA synchronization is in degraded state, triggering a switchover or changing roles could make management center HA to damage the database and it can become catastrophic. We recommend that you immediately contact Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) for further assistance to resolve this issue. This HA synchronization can end up in degraded state due to various reasons. The Replacing Management Centers in a High Availability Pair section in this chapter covers some of the failure scenarios and the subsequent procedure to fix the issue. If the reason or scenario of degraded state matches to the scenarios explained, follow the steps to fix the issue. For other reasons, we recommend that you contact TAC. |
About Remote Access VPN High Availability
If the primary device has Remote Access VPN configuration with an identity certificate enrolled using a CertEnrollment object, the secondary device must have an identity certificate enrolled using the same CertEnrollment object. The CertEnrollment object can have different values for the primary and secondary devices due to device-specific overrides. The limitation is only to have the same CertEnrollment object enrolled on the two devices before the high availability formation.
SNMP Behavior in Management Center High Availability
In an SNMP-configured HA pair, when you deploy an alert policy, the primary management center sends the SNMP traps. When the primary management center fails, the secondary management center which becomes the active unit, sends the SNMP traps without the need for any additional configuration.
Roles v. Status in Management Center High Availability
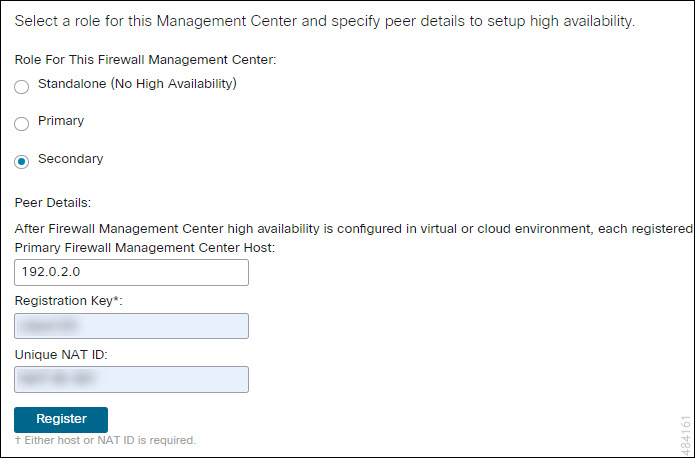
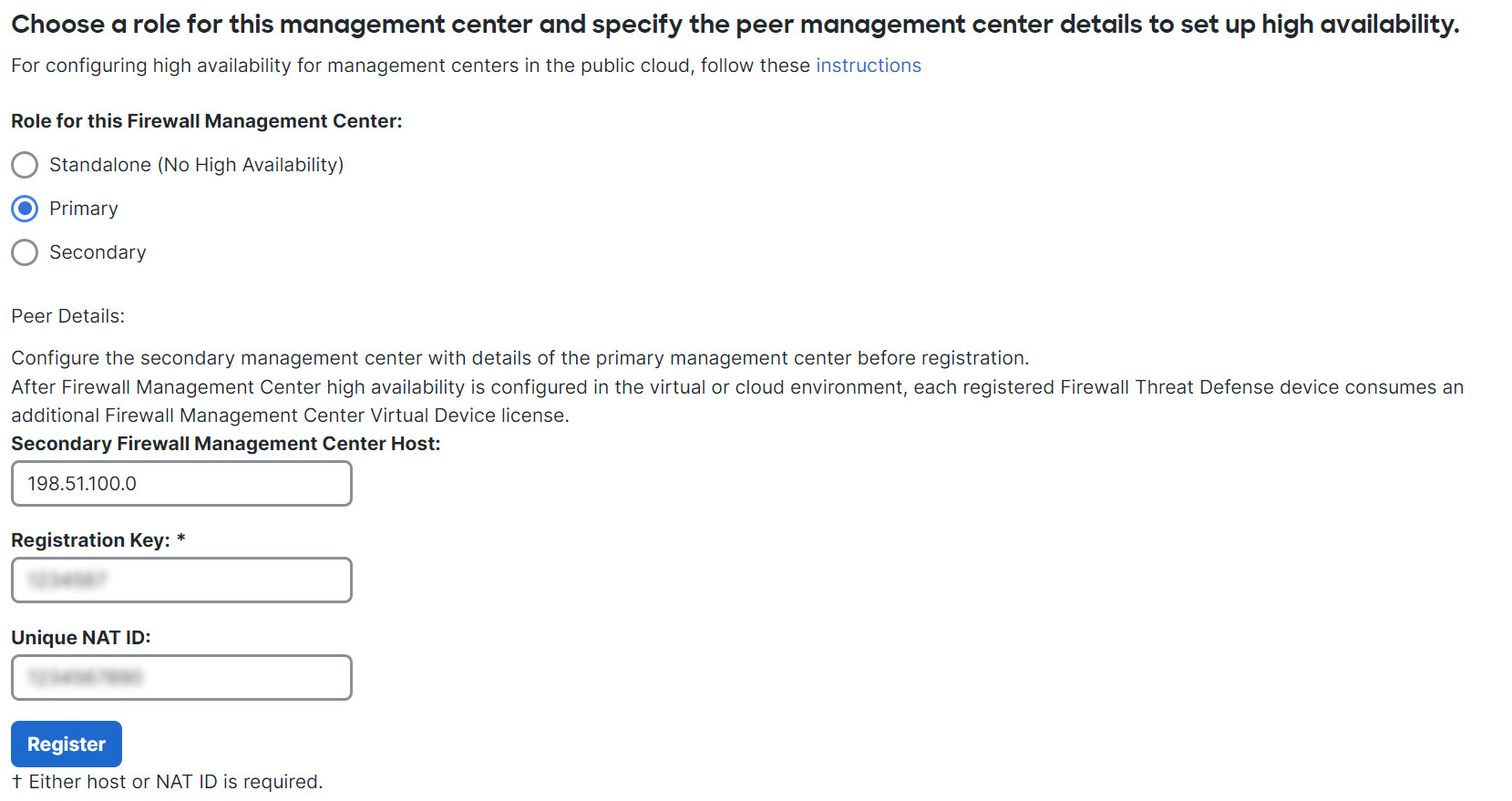
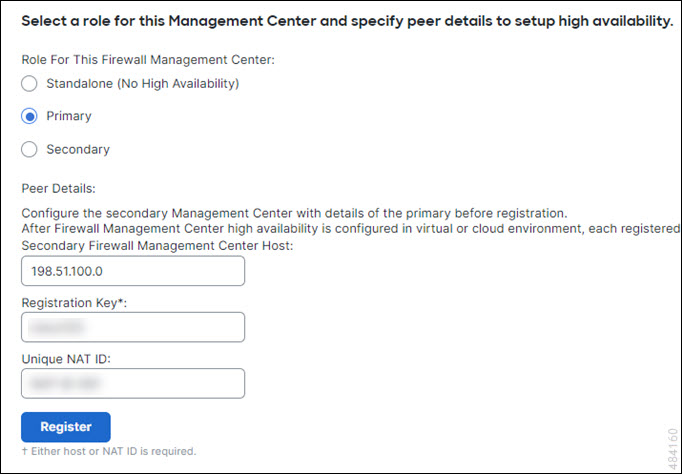
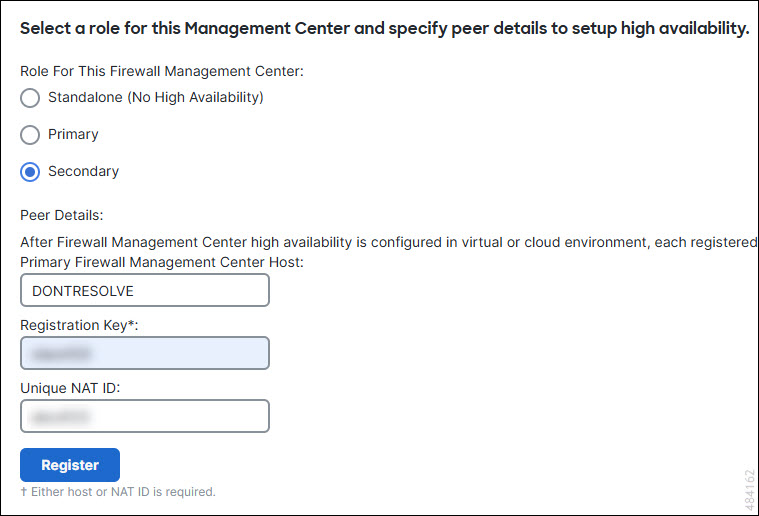
Primary/Secondary Roles
When setting up Secure Firewall Management Centers in a high availability pair, you configure one Secure Firewall Management Center to be primary and the other as secondary. During configuration, the primary unit's policies are synchronized to the secondary unit. After this synchronization, the primary Secure Firewall Management Center becomes the active peer, while the secondary Secure Firewall Management Center becomes the standby peer, and the two units act as a single appliance for managed device and policy configuration.
Active/Standby Status
The main differences between the two Secure Firewall Management Centers in a high availability pair are related to which peer is active and which peer is standby. The active Secure Firewall Management Center remains fully functional, where you can manage devices and policies. On the standby Secure Firewall Management Center, functionality is hidden; you cannot make any configuration changes.
Event Processing on Management Center High Availability Pairs
Since both management centers in a high availability pair receive events from managed devices, the management IP addresses for the appliances are not shared. This means that you do not need to intervene to ensure continuous processing of events if one of the management center fails.
AMP Cloud Connections and Malware Information
Although they share file policies and related configurations, management centers in a high availability pair share neither Cisco AMP cloud connections nor malware dispositions. To ensure continuity of operations, and to ensure that detected files’ malware dispositions are the same on both management centers, both primary and secondary management centers must have access to the AMP cloud.
URL Filtering and Security Intelligence
URL filtering and Security Intelligence configurations and information are synchronized between Secure Firewall Management Centers in a high availability deployment. However, only the primary Secure Firewall Management Center downloads URL category and reputation data for updates to Security Intelligence feeds.
If the primary Secure Firewall Management Center fails, not only must you make sure that the secondary Secure Firewall Management Center can access the internet to update threat intelligence data, but you must also use the web interface on the secondary Secure Firewall Management Center to promote it to active.
User Data Processing During Management Center Failover
If the primary management center fails, the Secondary management center propagates to managed devices user-to-IP mappings from the TS Agent identity source; and propagates SGT mappings from the ISE/ISE-PIC identity source. Users not yet seen by identity sources are identified as Unknown.
After the downtime, the Unknown users are re identified and processed according to the rules in your identity policy.
Configuration Management on Management Center High Availability Pairs
In a high availability deployment, only the active management center can manage devices and apply policies. Both management centers remain in a state of continuous synchronization.
If the active management center fails, the high availability pair enters a degraded state until you manually promote the standby appliance to the active state. Once the promotion is complete, the appliances leave maintenance mode.
Management Center High Availability Disaster Recovery
In case of a disaster recovery situation, a manual switchover must be performed. When the primary management center - FMC1 fails, access the web interface of the secondary management center - FMC2 and switch peers. This is applicable conversely also in case the secondary (FMC2) fails. For more information, see Switching Peers in the Management Center High Availability Pair.
For restoring a failed management center, refer to Replacing Management Centers in a High Availability Pair.
Single Sign-On and High Availability Pairs
Management Centers in a high availability configuration can support Single Sign-On, but you must keep the following considerations in mind:
-
SSO configuration is not synchronized between the members of the high availability pair; you must configure SSO separately on each member of the pair.
-
Both management centers in a high availability pair must use the same identity provider (IdP) for SSO. You must configure a service provider application at the IdP for each management center configured for SSO.
-
In a high availability pair of management centers where both are configured to support SSO, before a user can use SSO to access the secondary management center for the first time, that user must first use SSO to log into the primary management center at least once.
-
When configuring SSO for management centers in a high availability pair:
-
If you configure SSO on the primary management center, you are not required to configure SSO on the secondary management center.
-
If you configure SSO on the secondary management center, you are required to configure SSO on the primary management center as well. (This is because SSO users must log in to the primary management center at least once before logging into the secondary management center.)
-
Management Center High Availability Behavior During a Backup
When you perform a Backup on a management center high availability pair, the Backup operation pauses synchronization between the peers. During this operation, you may continue using the active management center, but not the standby peer.
After Backup is completed, synchronization resumes, which briefly disables processes on the active peer. During this pause, the High Availability page briefly displays a holding page until all processes resume.
Management Center High Availability Split-Brain
If the active management center in a high-availability pair goes down (due to power issues, network/connectivity issues), you can promote the standby management center to an active state. When the original active peer comes up, both peers can assume they are active. This state is defined as 'split-brain'. When this situation occurs, the system prompts you to choose an active appliance, which demotes the other appliance to standby.
If the active management center goes down (or disconnects due to a network failure), you may either break high availability or switch roles. The standby management center enters a degraded state.
 Note |
Whichever appliance you use as the intended standby loses all of its device registrations and policy configurations when you resolve split-brain. For example, you would lose modifications to any policies that existed on the intended standby but not on the intended active. If the management center is in a high availability split-brain scenario where both appliances are active, and you register managed devices and deploy policies before you resolve split-brain, you must export any policies and unregister any managed devices from the intended standby management center before re-establishing high availability. You may then register the managed devices and import the policies to the intended active management center. |
Troubleshooting Management Center High Availability
This section lists troubleshooting information for some common management center high availability operation errors.
|
Error |
Description |
Solution |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
You must reset your password on the active management center before you can log in to the standby. |
You attempted to log into the standby management center when a force password reset is enabled for your account. |
As the database is read-only for a standby management center, reset the password on the login page of the active management center. |
||
|
500 Internal |
May appear when attempting to access the web interface while performing critical management center high availability operations, including switching peer roles or pausing and resuming synchronization. |
Wait until the operation completes before using the web interface. |
||
|
System processes are starting, please wait Also, the web interface does not respond. |
May appear when the management center reboots (manually or while recovering from a power down) during a high availability or data synchronization operation. |
|
||
|
Device Registration Status:Host <string> is not reachable |
During the initial configuration of a threat defense, if the management center IP address and NAT ID are specified, the Host field can be left blank. However, in an HA environment with both the management centers behind a NAT, this error occurs when you add the threat defense on the secondary management center. |
|
||
|
Device Registration Status:Host <string> is not reachable |
The error occurs when adding threat defense device to the secondary management center center in a high-availability deployment where both the secondary management center and the threat defense device are behind NAT. |
On the standby management center web interface, click . Under the pending device registration table, click the IP address of the pending device, and then change the IP address to the public IP address of the threat defense. OR
|
||
|
Device configuration synchronization has been stopped between high availability management centers. |
The device configuration history files are now synced in parallel with other configuration data during a management center HA synchronization. The management center monitors the configuration history file sync task and notifies you if the sync has not happened for the last 6 hours. This health alert appears in both active and standby management centers. |
Both the active and standby management centers move to the degraded state. Contact Cisco TAC to troubleshoot the issue. |


 Feedback
Feedback