Information About Azure Virtual WAN Integration
Azure Virtual WAN Hub Integration with Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN
Minimum supported releases: Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN Release 17.4.1a and Cisco vManage Release 20.4.1
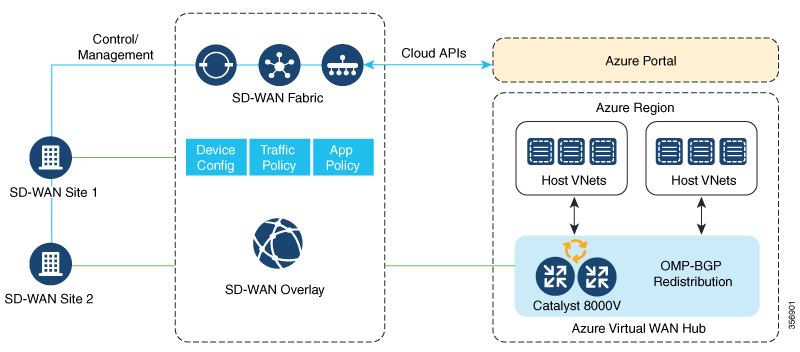
The integration of the Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN solution with Azure virtual WAN enhances Cloud OnRamp for Multicloud deployments and enables configuring Cisco Catalyst 8000V Edge Software (Cisco Catalyst 8000V) as a network virtual appliance (NVA) in Azure Virtual WAN Hubs.
This integration simplifies the consumption model for cloud services because it eliminates the need to create a transit virtual network (VNet) and you can control your host VNet connectivity directly through the Azure Virtual WAN Hub. Azure Virtual WAN is a networking service that provides optimized and automated branch-to-branch connectivity through Microsoft Azure. It enables you to connect and configure branch devices that can communicate with Azure. Configuring Cisco Catalyst 8000V instances inside Azure virtual hubs provides higher speeds and bandwidth and overcomes the speed and bandwidth limitation of using transit VNets.
Cloud OnRamp for IaaS Versus Cloud OnRamp for Multicloud
This table lists the differences between Cloud OnRamp for IaaS and Cloud OnRamp for Multicloud in the context of Microsoft Azure Integration.
|
Cloud OnRamp for IaaS for Azure |
Cloud OnRamp for Multicloud for Azure |
|---|---|

|
|
|
Enables automated provisioning of transit VNets through the Cloud OnRamp for IaaS workflow in Cisco SD-WAN Manager |
Enables automated provisioning of Azure virtual hubs through the Cloud OnRamp for Multicloud workflow in Cisco SD-WAN Manager |
|
Cisco SD-WAN Manager automatically provisions two Cisco Cloud Services Router 1000V Series (Cisco CSR1000V) devices inside the transit VNet |
Cisco SD-WAN Manager automatically provisions two Cisco Catalyst 8000V instances inside the Azure virtual hub |
For information on Cloud OnRamp for IaaS with Azure and how to configure transit VNets, see Configure Cloud OnRamp for IaaS for Azure.
How Virtual WAN Hub Integration Works
The connection between the overlay network and a public-cloud application is provided by a pair of redundant Cisco Catalyst 8000V instances that are configured inside the Azure virtual WAN hub as part of the Cloud OnRamp for Multicloud workflow for Azure. Using redundant routers to form the transit offers path resiliency to the public cloud.
The Cloud OnRamp for Multicloud flow in Cisco SD-WAN Manager discovers your existing VNets in geographical cloud regions and allows you to connect select VNets to the overlay network. In such a scenario, Cloud OnRamp for Multicloud allows simple integration between legacy public-cloud connections and the Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN overlay network.
A configuration wizard in Cisco SD-WAN Manager automates the bring-up of the Azure Virtual WAN Hub to connect with your public cloud account. The wizard also automates the connections between public-cloud applications and the users of those applications at branches in the overlay network. Using tags, Cisco SD-WAN Manager enables you to map the service VPNs in your branches with specific VNets in your public cloud infrastructure.
VNet to VPN Mapping
The Intent Management workflow in Cisco SD-WAN Manager enables connectivity between Cisco SD-WAN VPNs (branch networks) and VNets, and VNets to VNets. VNets are represented by tags created under the Discover workflow for Cloud OnRamp for Multicloud. When VNets are mapped to connect them to the virtual WAN hubs, they are assigned a default route and propagate to the default label. When you create VNet tags within an Azure region, mapping is automatically created based on the other VNets and VPNs that share the same tag.
When Cisco SD-WAN Manager records the intent for connectivity, mapping is realized in cloud in regions where the cloud gateway is present. Mapping intents can be entered without cloud gateways being present in different regions. Your mapping intent is preserved and realized when a new cloud gateway or mapping change is discovered. As and when cloud gateways get instantiated or discovered in different regions, the mapping intents are realized in those regions. Similarly, tagging operations can influence the mapping in different regions as well and mappings as per the tags are realized in the cloud.
 Note |
The VPNs selected to be mapped to VNet tags must not have overlapping IP addresses. This is because segmentation is not supported in Microsoft Azure Virtual WAN. |
Inter-region Azure Hub-to-Hub connectivity is enabled by creating VNet tags and mapping them to your VPN sites. No additional configuration is required to enable inter-region hub-to-hub connectivity. VNets are associated with the Virtual WAN Hub for their respective regions. If VNets in different Azure regions share the same VNet tag, the connectivity between such VNets is automatically established and is carried out through the respective Virtual WAN Hubs that the VNets are connected to.
Components of Azure Virtual WAN Integration Workflow
A cloud gateway to connect your branches and data centers to the public cloud infrastructure is a logical object that hosts Cisco Catalyst 8000V instances. It comprises Azure Resource Groups, Azure Virtual WAN, and Azure Virtual WAN Hub.
Resource Groups
All Azure networking resources belong to a resource group and resource groups are created under Azure subscriptions. For Azure cloud gateways, Azure virtual WAN, and Azure Virtual WAN Hub are created under a resource group.
The first step to create an Azure cloud gateways is therefore to create a resource group.
After a resource group is created, you can configure Azure Virtual WAN.
Azure Virtual WAN
Azure Virtual WAN is the backbone of the Azure networking service. It's created under an existing Azure resource group. An Azure Virtual WAN can contain multiple Azure virtual hubs within it, as long as each virtual hub belongs to a different Azure region. Only one virtual hub per Azure region is supported.
After a virtual WAN has been defined under a resource group in a region, the next step is to create an Azure Virtual WAN Hub.
Azure Virtual WAN Hubs
The Azure virtual WAN Hub manages the core connectivity between your VPN sites and NVAs, and VNets. Once a virtual hub is created, the Cisco Catalyst 8000V instances can be integrated into the Azure networking service.
Connectivity Models
With the Integration of Azure Virtual WAN with the Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN solution, the following connectivity models are supported:
-
Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN branch to Azure Host VNets within the same Azure region
-
Inter-region Azure virtual hub-to-virtual hub connectivity
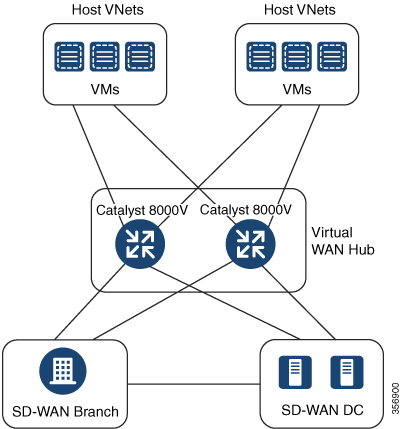
Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Branch to Azure Host VNets (Single-region)
In this scenario, the virtual hub is standalone and isn't connected to the virtual hubs in other Azure regions. In such cases, the VNets belong to the same region as the virtual hub, and are connected to your branch VPNs using VNet tags that are defined in Cisco SD-WAN Manager.
Virtual WAN Hub to Virtual WAN Hub (Inter-region)

This image represents hub-to-hub connectivity with Azure backbone. This connectivity need not be configured separately. It's automatically achieved if VNets in different Azure regions share the same VNet tag.
Routing Traffic Flow to a Secured Virtual Hub or a Local Firewall
Minimum supported releases: Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN Release 17.6.1a and Cisco vManage Release 20.6.1
The Microsoft Azure environment includes a virtual hub that enables connectivity between Azure Virtual Network (VNet) workloads and local branch devices. The integration of Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN and the Azure environment enables the following firewall options:
-
Routing outgoing internet traffic in the Azure Virtual WAN hub to a firewall on a local branch router
-
Routing outgoing internet traffic from a local branch router to an Azure secured virtual hub, to be subject to the security policies of the Azure Firewall Manager.

Note
An Azure secured virtual hub is an Azure Virtual WAN hub that has security and routing policy managed by the Azure Firewall Manager.
In both cases, return traffic follows the same path as outgoing internet traffic, so the same firewall policy applies to traffic in both directions.
Azure Virtual WAN Audit
Minimum supported releases: Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN Release 17.7.1a and Cisco vManage Release 20.7.1
The multicloud audit service compares the information from the Cisco SD-WAN Manager database with the information in the Azure cloud database. This information includes Azure virtual WAN, virtual hubs, network virtual appliances, virtual networks, and VPN-to-virtual network mapping. Later, Cloud OnRamp for Multicloud compares the results, identifies the discrepancies, and displays a list of Microsoft Azure objects with and without errors.
From Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN Release 17.8.1a and Cisco vManage Release 20.8.1, the audit function incorporates the following enhancements:
-
After you initiate an on-demand audit, the Cloud OnRamp for Multicloud audit service identifies and lists discrepancies between the information in the Cisco SD-WAN Manager database and the information in the Azure cloud. You can choose to fix all the discrepancies together or select a discrepancy and fix it individually. When you check a check box adjacent to an individual discrepancy, a brief explanation of the issue appears below the discrepancy.
For more details about the audit discrepancies and resolutions, see Audit Discrepancies and Resolutions.
-
You can now enable or disable periodic audits. For details, see Enable Periodic Audit.
Information About Periodic Audit
Minimum supported releases: Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN Release 17.8.1a and Cisco vManage Release 20.8.1
From Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN Release 17.8.1a and Cisco vManage Release 20.8.1, Cisco SD-WAN Manager provides an optional periodic audit with an interval of two hours. This automatic audit takes place in the background and generates a report of the discrepancies. If you enable the auto correct option, Cisco SD-WAN Manager automatically resolves recoverable issues, if any, that are found during the periodic audit. For more details about the periodic audit and its resolutions, see Audit Discrepancies and Resolutions.
 Note |
If you are upgrading the Cisco SD-WAN Manager version, the periodic audit and auto correct options are disabled by default. You can enable them from the Cloud Global Settings window. For details, see Add and Manage Global Cloud Settings. |
Audit Discrepancies and Resolutions
The following table provides details about the audit discrepancies and resolutions.
|
Discrepancy |
Description |
Resolution |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
On-Demand Audit Fix Sync Issues Button |
Periodic Audit and Auto Correct |
||||||||
|
Unavailability of VNet in the tags |
If VNet is tagged in the Cisco SD-WAN Manager database, but not available in the Azure portal. |
To remove VNet from the Cisco SD-WAN Manager database, click Fix Sync Issues. |
Removes VNet from the Cisco SD-WAN Manager database. See note 2. |
||||||
|
If the VNet tag is removed from the Azure portal, or if there is a VNet tag mismatch between Cisco SD-WAN Manager and Azure portal. |
To apply the VNet tags to the Azure portal from the Cisco SD-WAN Manager database, click Fix Sync Issues. |
Adds the VNet tags to the Azure portal from the Cisco SD-WAN Manager database. |
|||||||
|
Unavailability of storage accounts (stores configuration of NVAs) |
If the storage account is not available in the Azure portal, but is available in the Cisco SD-WAN Manager database. |
To remove the storage account from the Cisco SD-WAN Manager database, click Fix Sync Issues. |
Deletes the storage account from the Cisco SD-WAN Manager database. See note 2. |
||||||
|
Unavailability of virtual WAN, vHub, and NVA |
If virtual WAN, vHub, or NVA is not available in the Azure portal. |
|
See note 2. |
||||||
|
Unavailability of mapping in Azure portal See note 1. |
Mapping is found in the Cisco SD-WAN Manager database but not found in the Azure portal. |
To add the mapping back to the Azure portal, click Fix Sync Issues. |
Adds the mapping back to the Azure portal. |
||||||
|
Unavailability of mapping in Cisco SD-WAN Manager database
|
Mapping is found in the Azure portal, but not found in the Cisco SD-WAN Manager database. |
To add the mapping back to the Cisco SD-WAN Manager database, you must manually tag and map VNet using the Cisco SD-WAN Manager workflow.
|
To add the mapping back to the Cisco SD-WAN Manager database, you must manually tag and map VNet using the Cisco SD-WAN Manager workflow.
|
||||||
 Note |
1. From Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN Release 17.8.1a and Cisco vManage Release 20.8.1, you can view this discrepancy and fix it. |
 Note |
2. From Cisco vManage Release 20.9.x, the auto correct option is not available. Instead, display the cloud services audit as follows: From the Cisco SD-WAN Manager menu, choose , then in the Intent Management pane, click Audit. Select the cloud provider. Cisco SD-WAN Manager shows the audit report. |
SKU Scale Value of Network Virtual Appliances
Minimum supported releases: Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN Release 17.7.1a and Cisco vManage Release 20.7.1
You can edit the SKU scale value of a Cisco Catalyst 8000V Edge instance in Azure. In releases earlier than Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN Release 17.7.1a and Cisco vManage Release 20.7.1, the SKU scale value is not editable. If you want to change the SKU scale value, you must delete and re-create the cloud gateway with a new SKU scale value.
You can opt for higher SKU scale values for better performance and lower values for cost-effectiveness.
For more information on how to update SKU scale values, see Configure SKU Scale Value.
 Note |
After editing the SKU scale value, expect a network downtime of 3 to 4 minutes. |
For details about the supported SKU scales, see Supported Azure Instances for Azure Virtual WAN Integration.
Security Rules Configuration of Network Virtual Appliances
Minimum supported releases: Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN Release 17.7.1a and Cisco vManage Release 20.7.1
Microsoft Azure has an option to edit the security rules of Network Virtual Appliances (NVAs). Cisco SD-WAN Manager supports the configuration of these security rules for NVAs.
Cisco Catalyst 8000V NVAs that are launched during cloud gateway creation prohibit the use of all the inbound ports, except Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN-related ports. The Security Rules Configuration of NVA feature allows you to enable a particular port as required, for example, for debugging purposes. After you add a new NVA rule to enable a port, it remains active only for two hours. Simultaneously, adding another NVA rule restarts the timer, and now all the enabled ports remain active for two hours.
 Note |
|
Information About Azure ExpressRoute Connection to NVA
Minimum supported releases: Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN Release 17.8.1a and Cisco vManage Release 20.8.1
From Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN Release 17.8.1a and Cisco vManage Release 20.8.1, Cisco SD-WAN Manager supports ExpressRoute connections from branch offices to NVAs through SD-WAN tunnels. Express route connections are private networks that offer high reliability, few latencies, and fast connections for data transfer.
For further details about Azure ExpressRoute Connection to NVA, see Alternative Azure Designs.
Information about Multiple Virtual Hubs in Each Region
Minimum supported release: Cisco vManage Release 20.11.1
 Note |
This feature is supported on both Azure Cloud and Azure Government Cloud. |
For organizations with thousands of sites connected to Azure in a single region, Microsoft supports creation of multiple cloud gateways, and up to eight virtual hubs for a single region.
For Cisco vManage Release 20.10.1 and earlier releases, the Azure Virtual WAN solution supports only a single virtual hub in a single region. From Cisco vManage Release 20.11.1, the solution supports multiple virtual hubs in each region.
The cloud gateway attachment to a virtual network is based on a load balancing algorithm. When you add a tag to the cloud gateway attachment, you can choose Auto which distributes the VNets based on the load balancing algorithm. When you create a new cloud gateway, you can choose to redistribute VNets to load balance the existing VNets among all the cloud gateways. You can only reassign VNets across cloud gateways when you choose the Auto VNet tag. You cannot reassign the dedicated VNet tags that are attached to cloud gateways.
 Feedback
Feedback