ENCS Switch Commands
See, Cisco Enterprise Network Compute System Switch Command Reference for switch commands.
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Access to the ENCS switch is restricted through Consent Token. Consent Token is a security feature that is used to authenticate the network administrator of an organization to access system shell with mutual consent from the network administrator and Cisco Technical Assistance Centre (Cisco TAC).
 Note |
From the switch console, there is access to debug mode and an advanced debug mode. Credentials of the local user are synchronized to access debug mode. Advanced debug uses unique credentials for each device that allows for additional debugging options for Cisco engineering. To enter either debug mode permission must be granted through Consent Token. |
See, Cisco Enterprise Network Compute System Switch Command Reference for switch commands.
See, API Reference for Cisco Enterprise Network Function Virtualization Infrastructure Software for switch related APIs.
The Switch option from the Cisco Enterprise NFVIS portal allows you to configure STP/RSTP, VLAN on specified ranges, RADIUS based authentication, and port channel load balancing for various switch ports. This section describes how to configure settings on the ENCS switch portal.
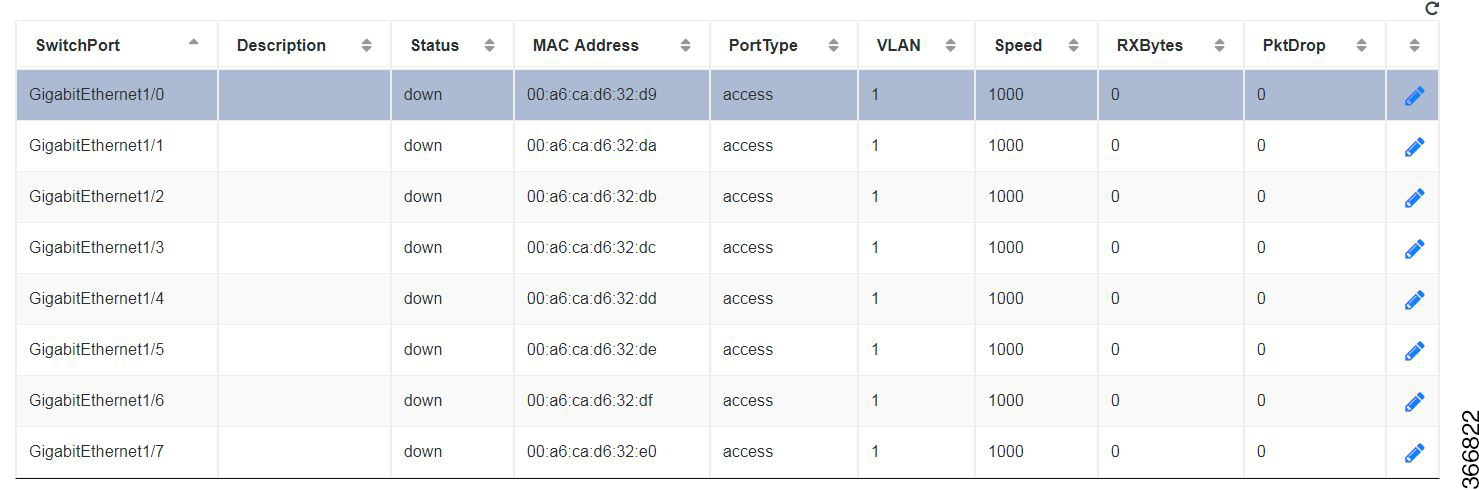
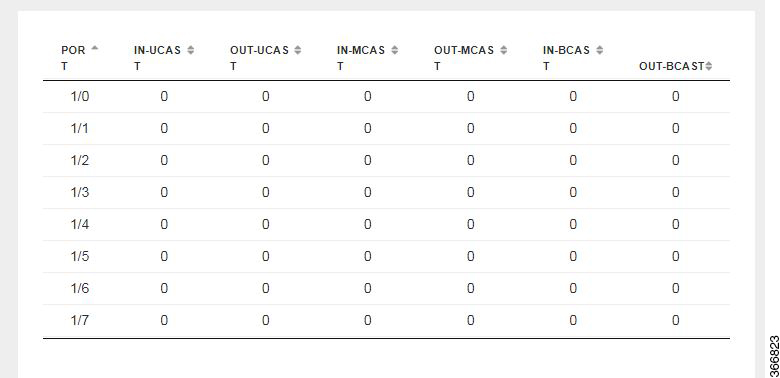
You can view the Switch Interface operational data and the statistics parameters in the following table:
|
Parameter |
Description |
Values |
|
SwitchPort |
Specifies the switch interface name. |
|
|
Description |
Specifies the description of the interface. |
|
|
Status |
Specifies the status of the interface. |
up or down |
|
MAC Address |
Specifies the MAC address of the interface. |
|
|
PortType |
Specifies the mode of the port interface. |
Supported types are:
|
|
VLAN |
Specifies the VLAN ID. |
Range: 1-2349 and 2450-4093 |
|
Speed |
Specifies the speed of the interface. |
Speed:
|
|
RxBytes |
Specifies the received data on interface in bytes. |
|
|
PktDrop |
Specifies the number of packet drops. |
|
|
PORT |
Specifies the port number. |
|
|
IN-UCAST |
Specifies the number of incoming unicast packets at the interface. |
|
|
OUT-UCAST |
Specifies the number of outgoing unicast packets at the interface. |
|
|
IN-MCAST |
Specifies the number of incoming multicast packets at the interface. |
|
|
OUT-MCAST |
Specifies the number of outgoing multicast packets at the interface. |
|
|
IN-BCAST |
Specifies the number of incoming broadcast packets at the interface. |
|
|
OUT-BCAST |
Specifies the number of outgoing broadcast packets at the interface. |
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 protocol that runs on bridges and switches. The main purpose of STP is to ensure that you do not create loops when you have redundant paths in your network.
The Spanning Tree option is enabled by default. You can click on edit and make the necessary settings or disable Spanning Tree if required.


The configuration of spanning tree has the following parameters when it is enabled:
|
Parameter |
Description |
Values |
|
Spanning Tree |
Specifies the state of the Spanning Tree. |
Enable or Disable The default value is Enable. |
|
Mode |
Specifies the mode of the Spanning Tree. |
stp or rstp |
|
Forward Time |
Specifies the Spanning Tree forward time in seconds. |
Range: 4-30 seconds |
|
Hello Time |
Specifies the Hello time in seconds. |
Range: 1 to10 seconds |
|
Max Age |
Specifies the spanning-tree bridge maximum age in seconds. |
Range: 6 to 40 seconds |
|
Loopback Guard |
Specifies the loopback guard status. |
Enable or Disable |
|
Path Cost Method |
Specifies the speed of the interface. |
Method:
|
|
Priority |
Specifies the port priority. |
Range: 0 to 61440 in steps of 4096 The default value is 32768. |
|
BPDU Filtering |
Specifies that BPDU packets are filtered when the spanning tree is disabled on an interface. |
|
|
BPDU Flooding |
Specifies that BPDU packets are flooded unconditionally when the spanning tree is disabled on an interface. |
This chapter describes how to configure dot1x port-based authentication on the Cisco Enterprise NFVIS portal. dot1x prevents unauthorized devices (clients) from gaining access to the network. It is a standard for media-level (Layer 2) access control, offering the capability to permit or deny network connectivity based on the identity of the end user or device. The dot1x is disabled by default. You can click on edit to enable dot1x.
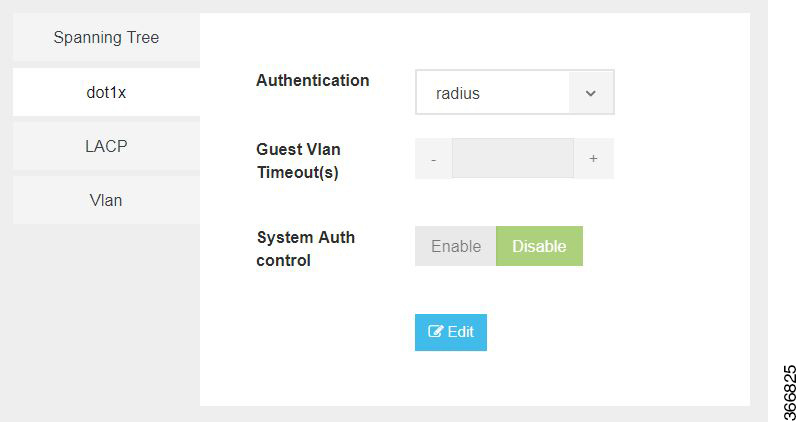
The configuration of dot1x has the following parameters:
|
Parameter |
Description |
Values |
|
Authentication |
Specifies the authentication type for the port. |
radius or none The default value is radius. |
|
Guest VLAN Timeout(s) |
Specifies the time delay in seconds between enabling Dot1X (or port up) and adding the port to the guest VLAN. |
Range: 30 to 180 seconds |
|
System Auth control |
Specifies the authentication control. |
Enable or Disable |
The Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) enables you to bundle several physical ports together to form a single logical channel. LACP enables you to form a single Layer 2 link automatically from two or more Ethernet links. This protocol ensures that both ends of the Ethernet link are functional and are part of the aggregation group.
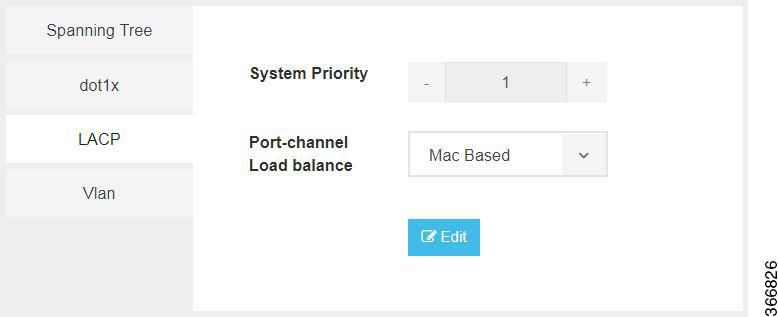
LACP uses the following parameters to control aggregation:
|
Parameter |
Description |
Values |
|
System Priority |
Specifies the port priority. |
Range: 1 to 65535 |
|
Port-channel load balance |
Specifies the load balance of the port channel. |
Mac Based or IP Based |
You can use virtual LANs (VLANs) to divide the network into separate logical areas. VLANs can also be considered as broadcast domains. Any switch port can belong to a VLAN, and unicast, broadcast, and multicast packets are forwarded and flooded only to end stations in that VLAN. Each VLAN is considered a logical network, and packets destined for stations that do not belong to the VLAN must be forwarded through a router.
You can configure VLANs in the range <1-2349>|<2450-4093> for a specified switch port.

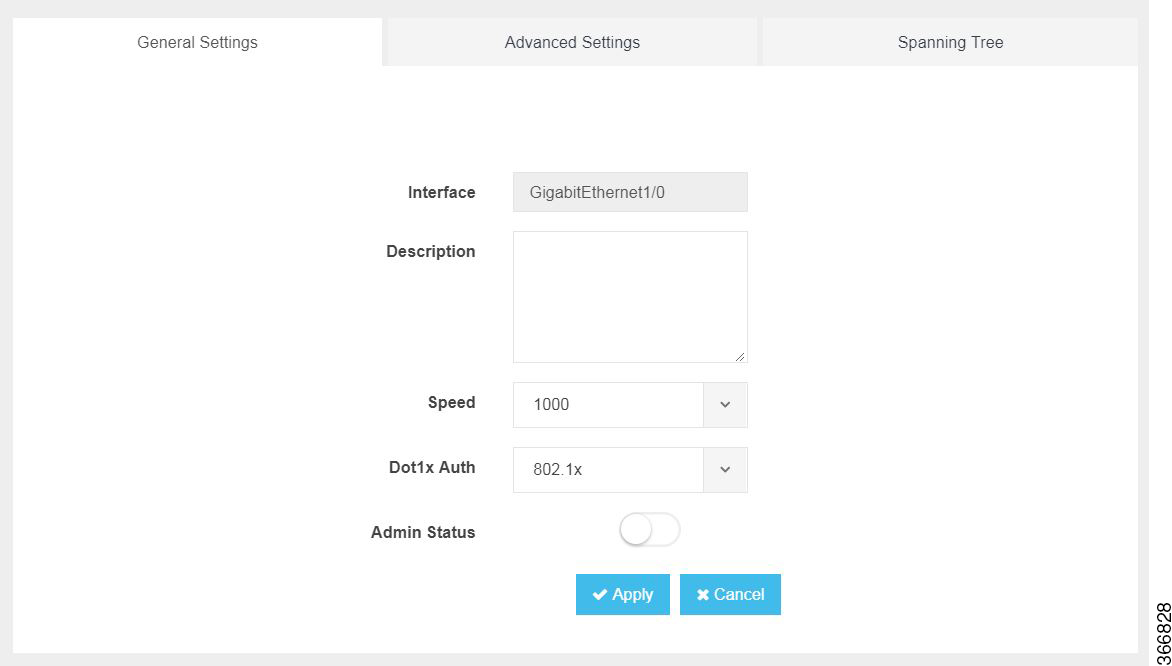
You can configure general settings using the following parameters for each switch interface:
Interface—Name of the interface
Description—Set the description per interface
Speed—10/100/1000 MBPS
Dot1x Auth—802.1x, mac or both
PoE Method—auto, never or four-pair
PoE Limit—0-60000mW
Admin Status—enable or disable
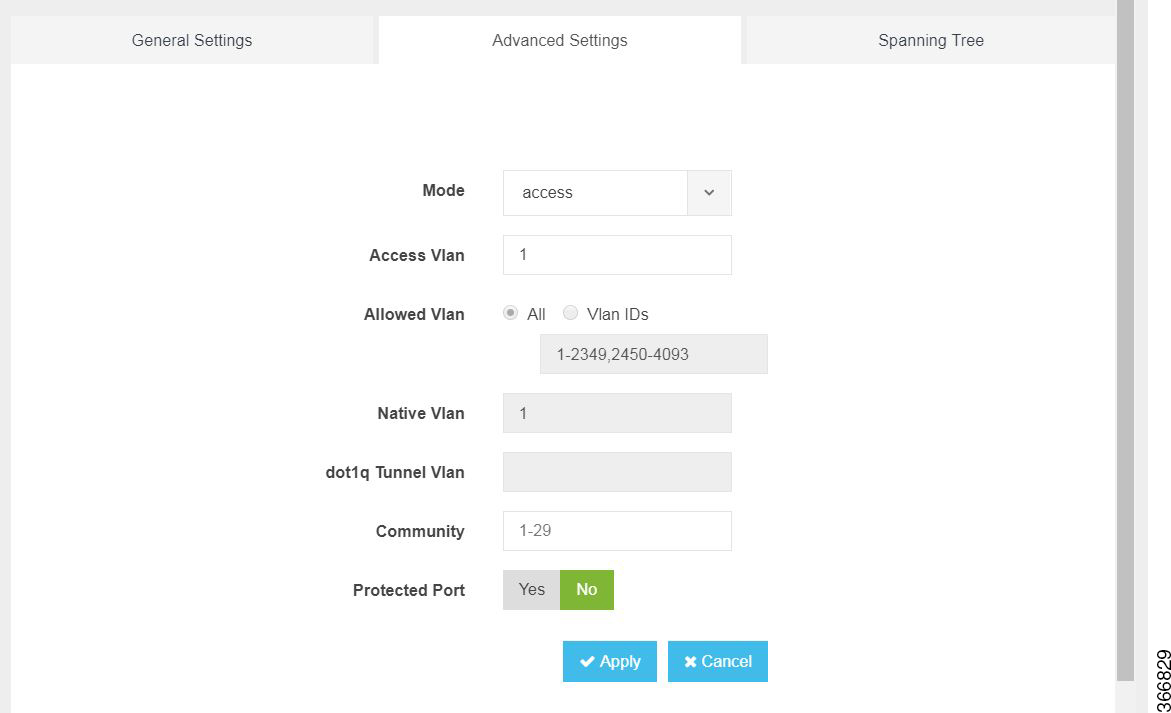
You can make the advanced settings using the following parameters for each switch interface:
Mode—access, dot1q-tunnel, private-vlan, or trunk
Access Vlan—Specifies the number of VLANs.
Allowed Vlan—All or VLAN IDs
Native Vlan—Specifies the VLAN ID. You can enter a value from one of the following ranges:
1 to 2349
2450 to 4093
Dot1q Tunnel Vlan—Specifies the Layer 2 tunnel port.
Community—Specifies the community number. Range: 1 to 29
Protected Port—Yes or No
 Note |
The VLAN configuration takes effect only if the global VLANs are also configured with the same values in Configuring VLAN. |
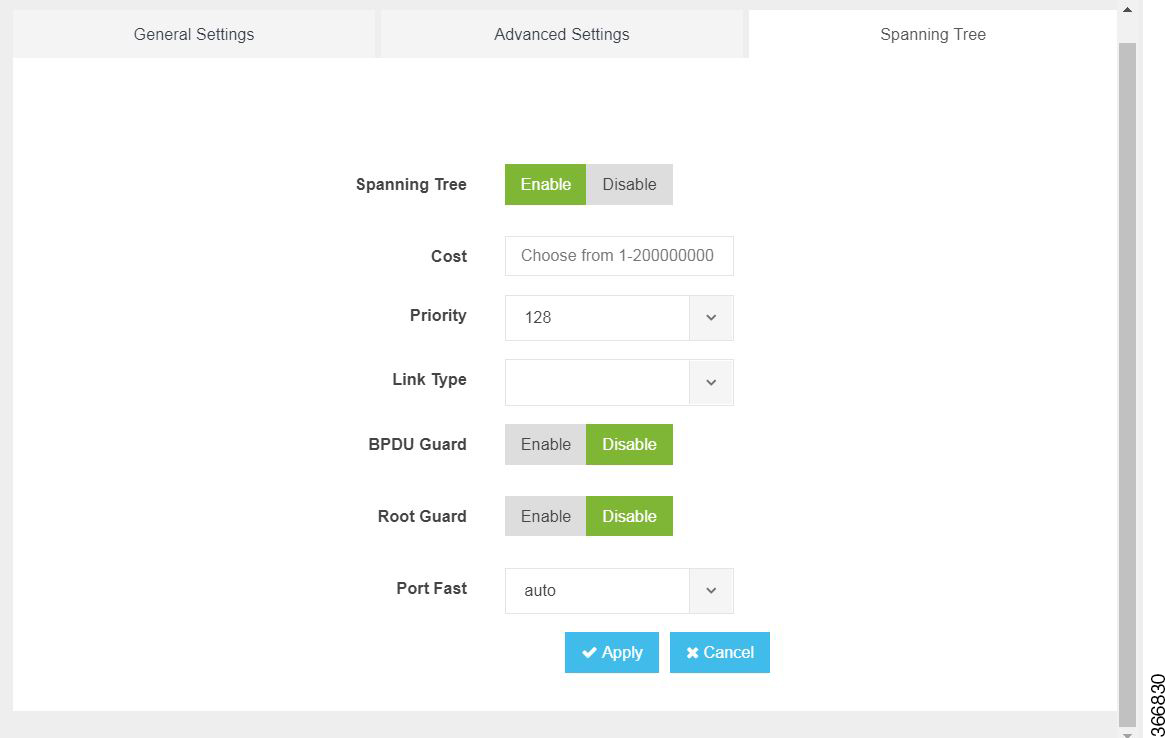
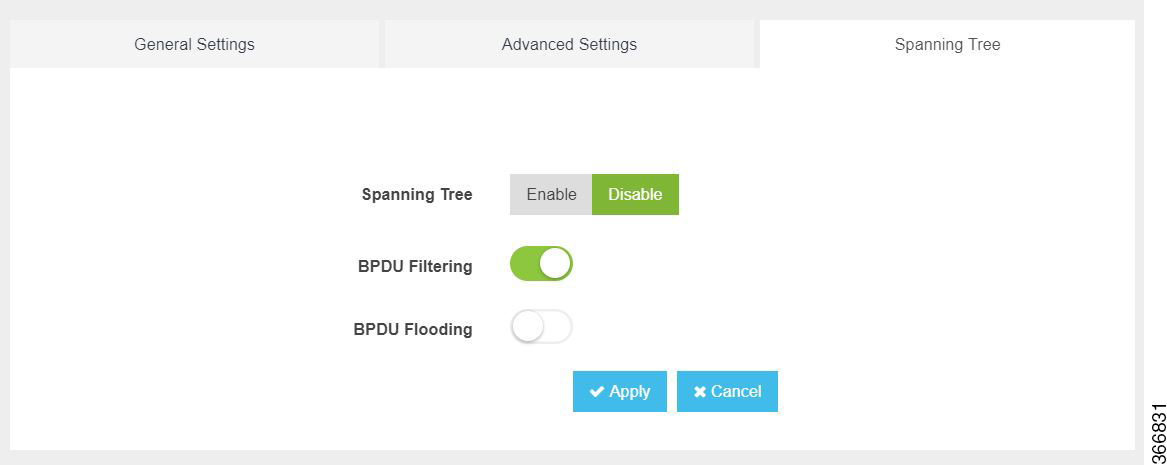
You can configure spanning tree for each switch interface using the following parameters:
Spanning Tree—Enable or Disable
Cost—Specifies the cost. Range: 1 to 200000000
Priority—Specifies the port priority. Range: 0 to 240, default value is 128
Link Type—point-to-point or shared
BPDU Guard—Enable or Disable
Root Guard—Enable or Disable
Port Fast—auto or enable
BPDU Filtering—Specifies that BPDU packets are filtered when the spanning tree is disabled
BPDU Flooding—Specifies that BPDU packets are flooded when the spanning tree is disabled