Monitoring Switch
The Switch menu includes the following submenus:
Viewing Switch CPU Information
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Choose Monitor > Switch > CPU. The CPU window is displayed. This window displays the CPU information for the switches in that scope. |
| Step 2 |
You can use the drop-down to filter the view by Last 10 Minutes, Last Hour, Last Day, Last Week, Last Month, and Last Year. |
| Step 3 |
In the Switch column, click the switch name to view the Switch Dashboard. |
| Step 4 |
Click the chart icon in the Switch column to view the CPU utilization. You can also change the chart timeline to Last 10 Minutes, Last Hour, Last Day, Last Week, Last Month, and Last Year. You can choose the chart type and chart options to show as well. |
Viewing Switch Memory Information
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Choose Monitor > Switch > Memory. The memory panel is displayed. This panel displays the memory information for the switches in that scope. |
| Step 2 |
Use the drop-down to filter the view by Last 10 Minutes, Last Hour, Last Day, Last Week, Last Month, and Last Year. |
| Step 3 |
Click the chart icon in the Switch column to see a graph of the memory usage of the switch. |
| Step 4 |
In the Switch column, click the switch name to view the Switch Dashboard. |
| Step 5 |
You can use the drop-down to view the chart in different time lines. Use the chart icons to view the memory utilization chart in varied views. |
Viewing Switch Traffic and Errors Information
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Choose Monitor > Switch > Traffic. The Switch Traffic panel is displayed. This panel displays the traffic on that device for the past 24 hours. |
| Step 2 |
Use the drop-down to filter the view by 24 hours, Week, Month, and Year. |
| Step 3 |
Click the Export icon in the upper-right corner to export the data into a spreadsheet. |
| Step 4 |
Click Save. |
| Step 5 |
Click the switch name to view the Switch Dashboard section. |
Viewing Switch Temperature
 Note |
It is not necessary to configure the LAN or SAN credentials under the Configure > Credentials Management > LAN Credentials screen to fetch the temperature monitoring data from the switches. |
To view the switch temperature information from the Cisco DCNM Web UI, perform the following steps:
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Choose Monitor > Switch > Temperature. The Switch Temperature window is displayed with the following columns.
|
| Step 2 |
From this list, each row has a chart icon, which you can click. |
Enabling Temperature Monitoring
You can enable the temperature monitoring feature for LAN switches from the LAN Collections screen, and for the SAN switches by setting a few properties under Administration > DCNM Server > Server Properties screens.
Enabling Temperature Monitoring for SAN Switches
-
From the menu bar, select Administration > DCNM Server > Server Properties.
-
Navigate to the # PERFORMANCE MANAGER > COLLECTIONS area.
-
Set the environment fields pm.collectSanTemperature & pm.sanSensorDiscovery to TRUE.
-
Click Apply Changes to save the configuration.
-
Restart Cisco DCNM.
Viewing Other Statistics
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Choose Monitor > Switch > User Defined. The Other window is displayed. |
| Step 2 |
You can use the drop-down to filter the view by 24 hours, Week, Month, and Year. There are variations to this procedure. In addition to these basic steps, you can also do the following:
|
Viewing Switch Custom Port Groups Information
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Choose Monitor > Switch > Custom Port Groups. The Custom Port Groups window shows statistics and performance details for custom port groups. |
| Step 2 |
You can use the drop-down to filter the view by 24 hours, Week, Month, and Year. |
| Step 3 |
Click the Export icon in the upper-right corner to export the data into a spreadsheet. |
| Step 4 |
Click Save. |
| Step 5 |
Click the switch name to view the Switch Dashboard. |
Viewing Accounting Information
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Choose Monitor > Switch > Accounting. The fabric name or the group name along with the accounting information is displayed. |
| Step 2 |
Select Advanced Filter beside the filter icon to search the accounting information by Source, Username,Time, and Description. Or select Quick Filter to search under each column. |
| Step 3 |
You can also select a row and click the Delete icon to delete accounting information from the list. |
| Step 4 |
You can use the Print icon to print the accounting details and use the Export icon to export the data to a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet. |
Viewing Events Information
To view the events and syslog from the Cisco DCNM Web UI, perform the following steps:
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Choose Monitor > Switch > Events. The fabrics along with the switch name and the events details are displayed. The Count column displays the number of times the same event has occurred during the time period as shown in the Last Seen and First Seen columns. Click a switch name in the Switch column to view the switch dashboard. |
| Step 2 |
Select an event in the table and click the Add Suppressor icon to open the shortcut of adding an event suppressor rule. |
| Step 3 |
Select one or more events from the table and click the Acknowledge icon to acknowledge the event information for the fabric.
|
| Step 4 |
Select the fabric and click the Unacknowledge icon to cancel an acknowledgment for a fabric. |
| Step 5 |
Select Advanced Filter beside the filter icon to search the accounting information by Source, Username,Time, and Description. Or select Quick Filter to search under each column. |
| Step 6 |
Select a fabric and use the Delete icon to delete the fabric and event information from the list. |
| Step 7 |
Click the Print icon to print the event details. |
| Step 8 |
Click the Export to Excel icon to export the data. |

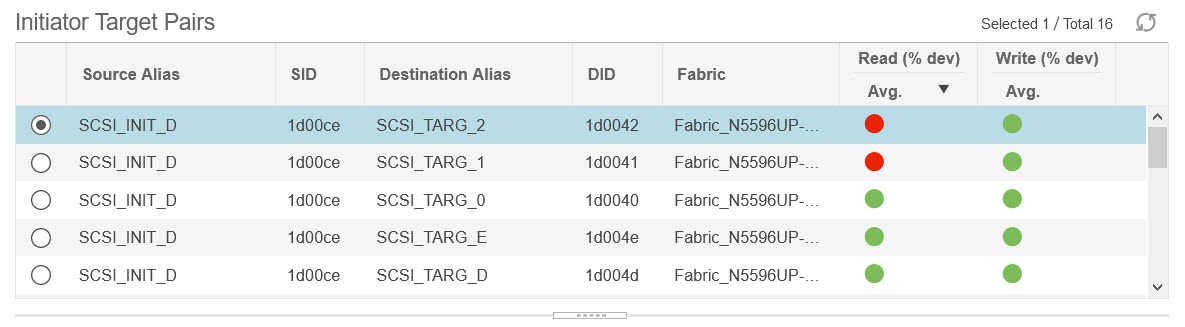
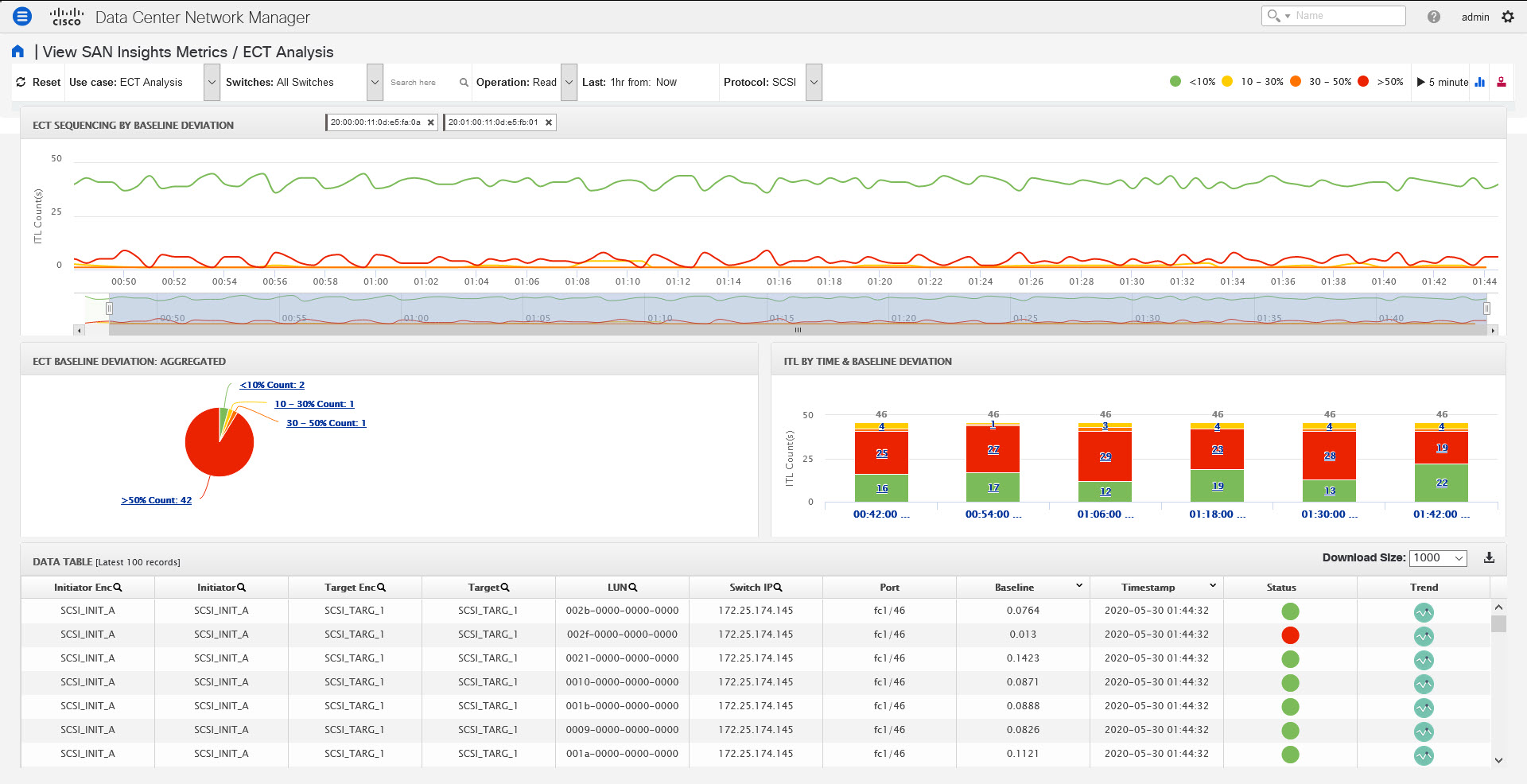
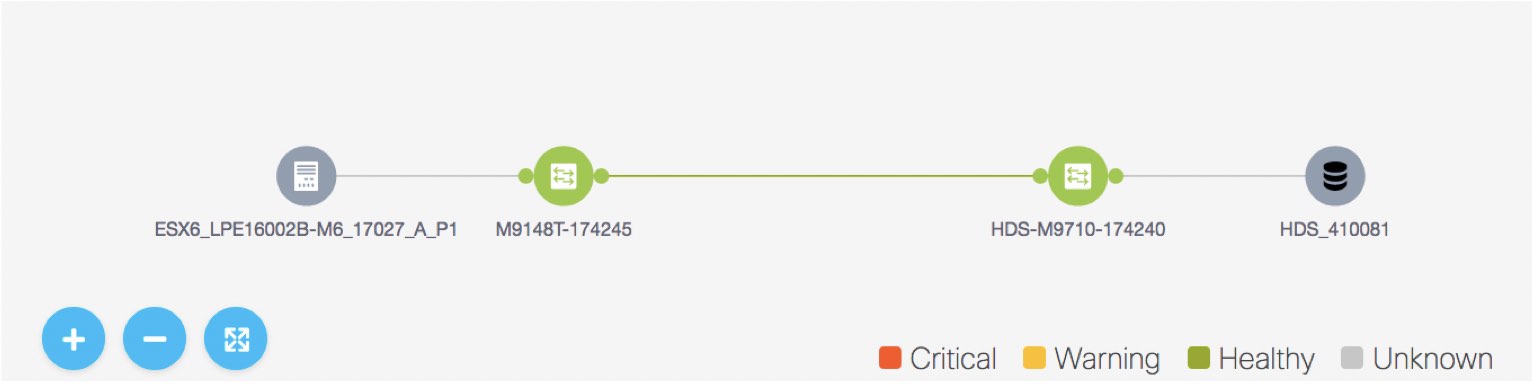

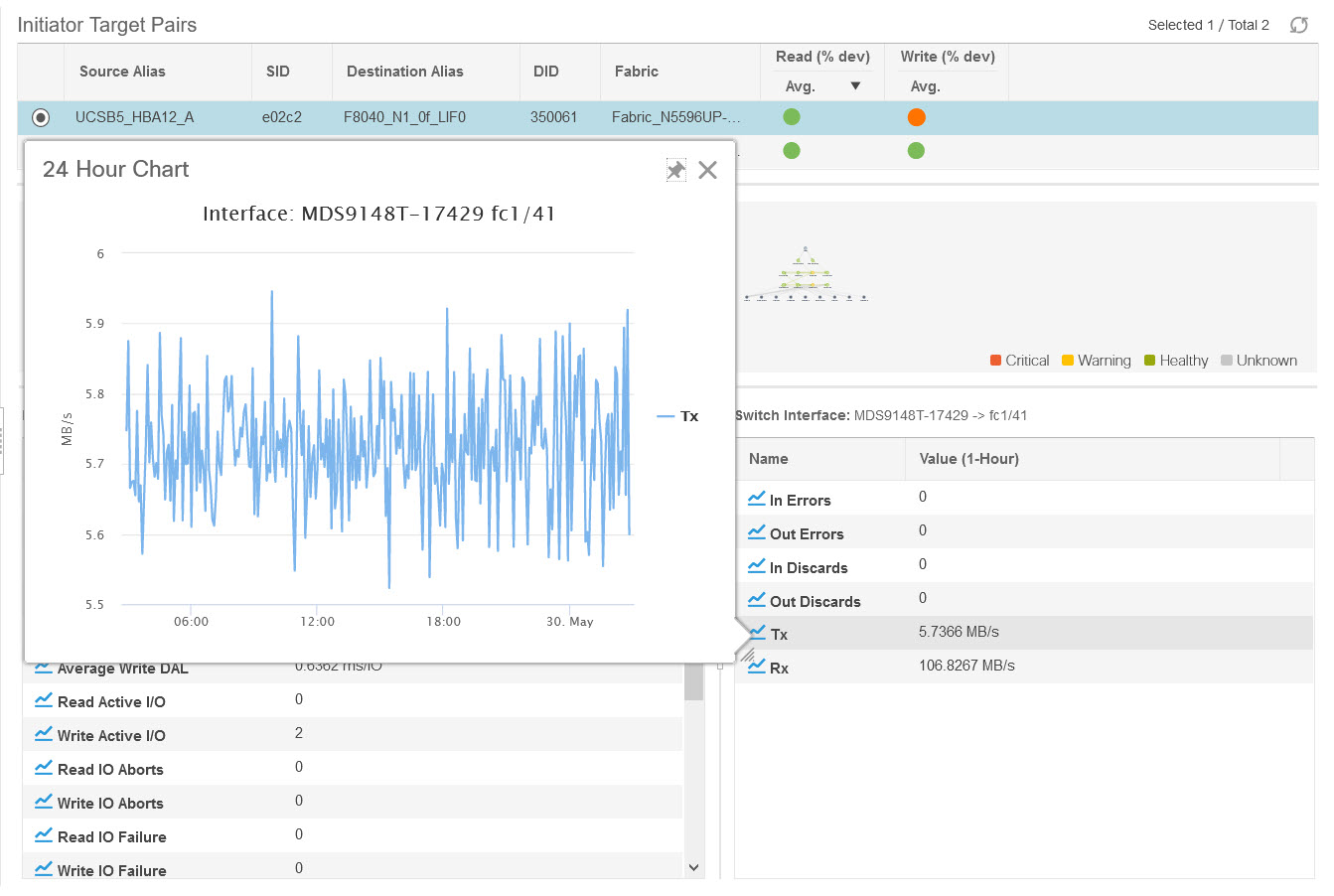
 icon to view the 24-hour chart.
icon to view the 24-hour chart.
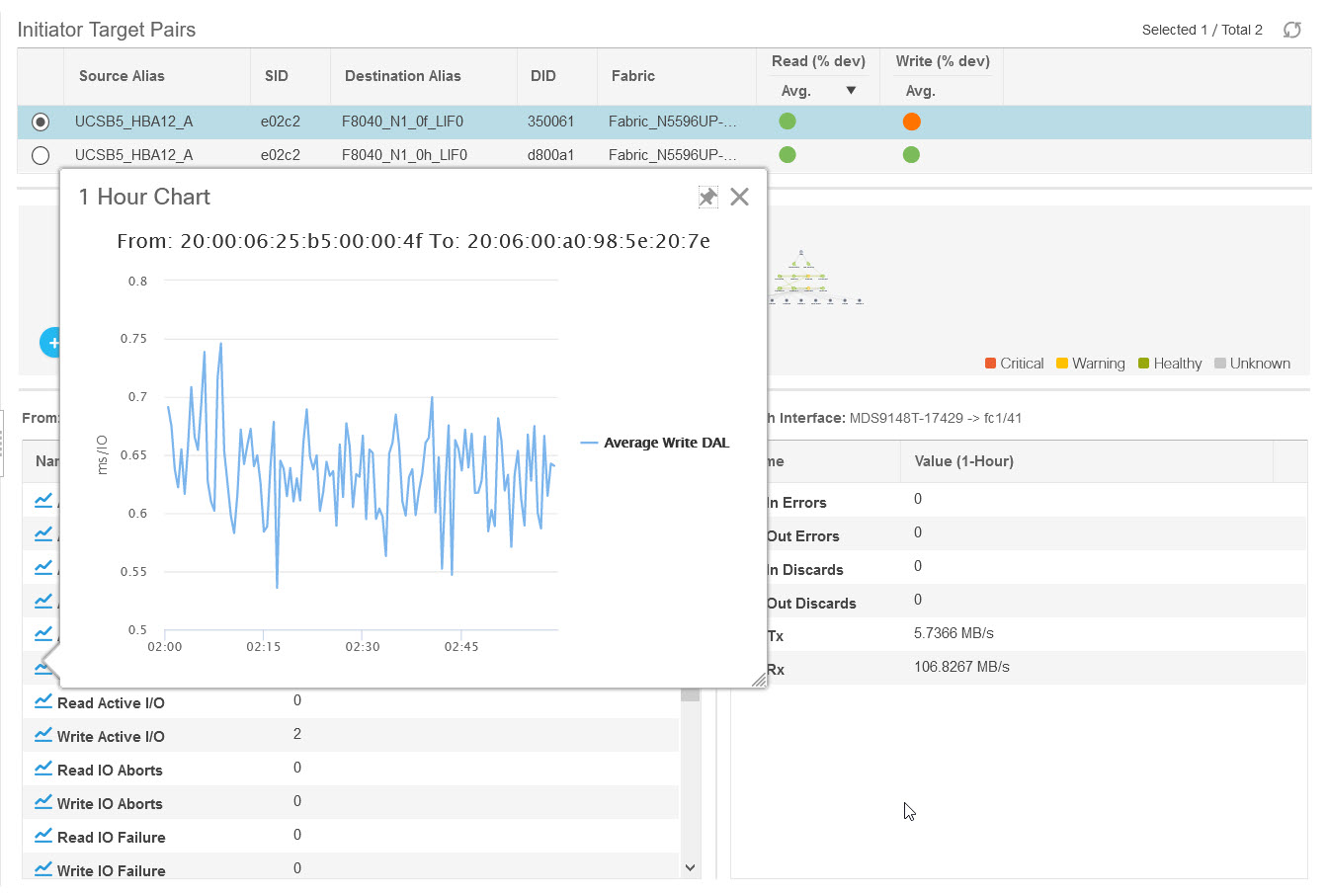
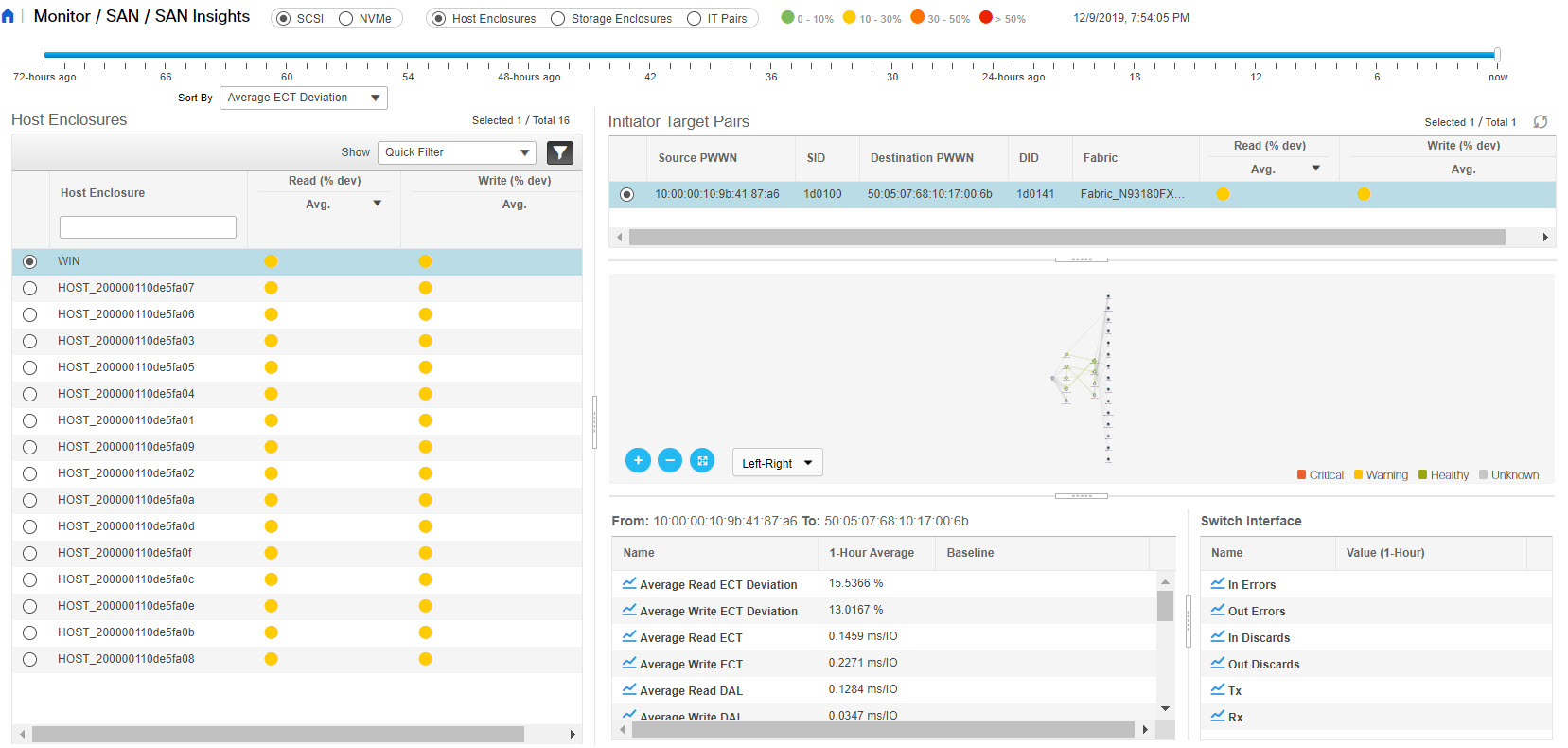
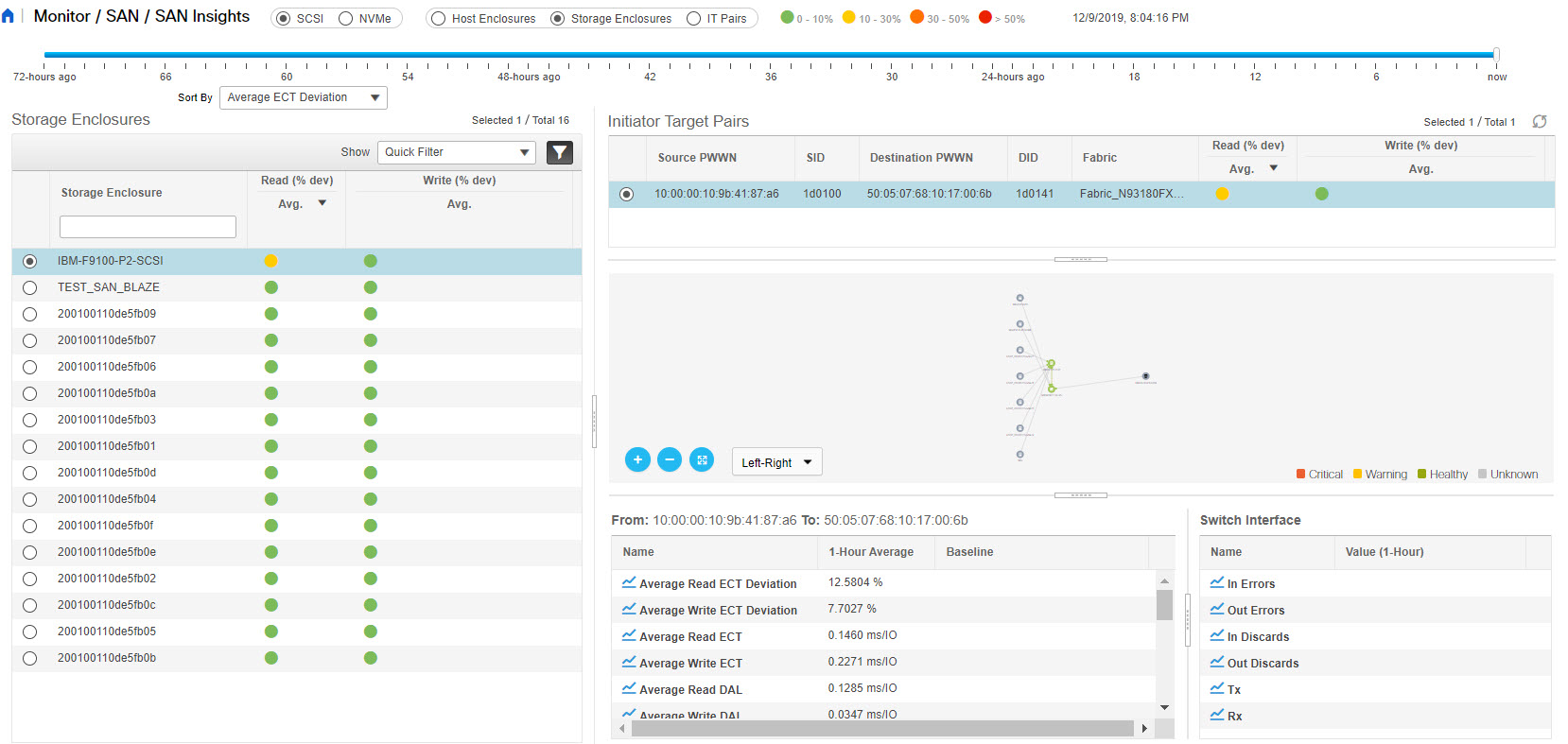
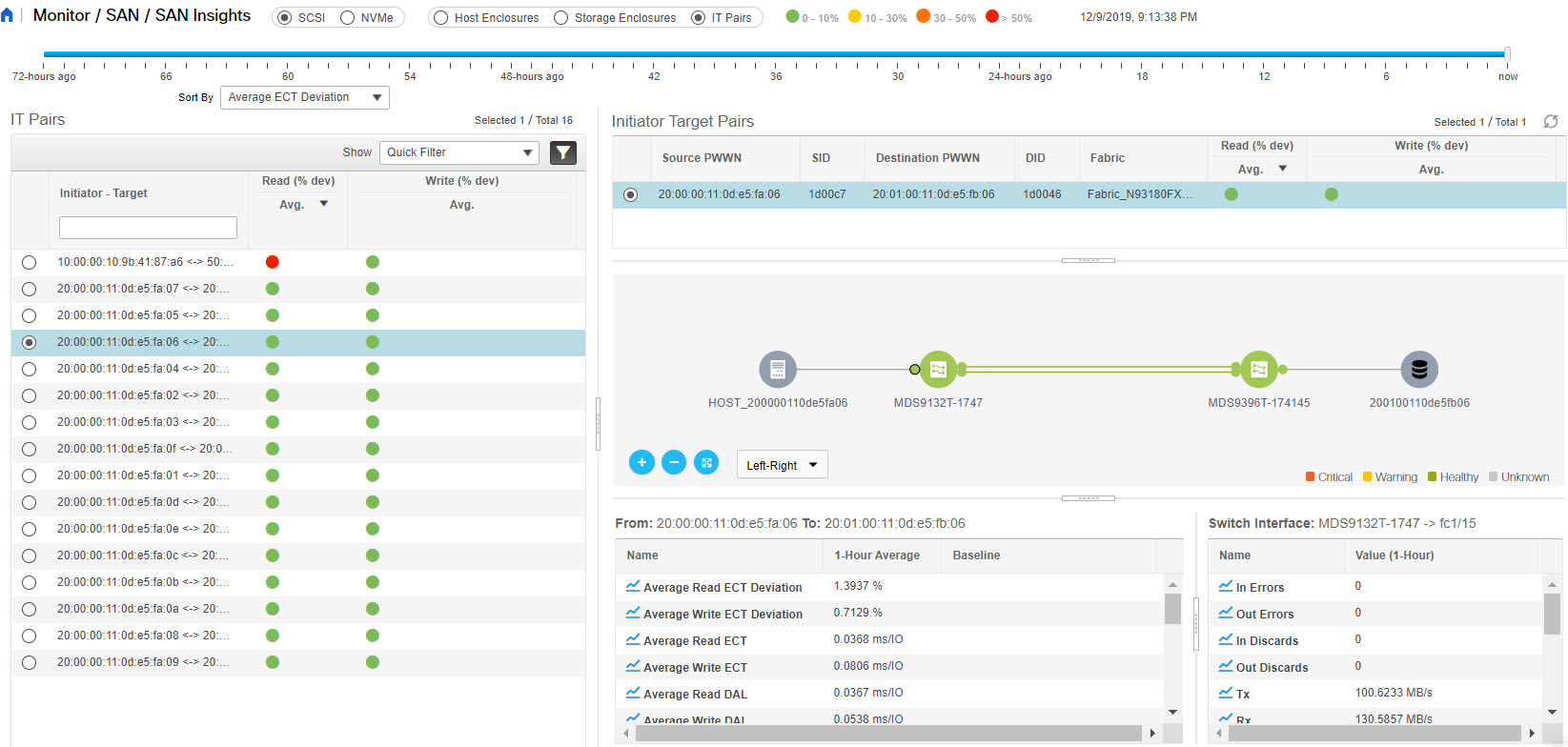

 Feedback
Feedback