Configure a Public Server with Cisco ASDM
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document discuss on how to configure a public server using Cisco Adaptive Security Device Manager, ASDM. Public servers are those application servers that are used by the external world to use their resources. A new feature called, Public Server, is introduced from Cisco ASDM software release 6.2 .
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
Cisco ASA 5500 series Adaptive Security Appliances running software version 8.2 and later
-
Cisco Adaptive Security Device Manager software version 6.2 and later
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Background Information
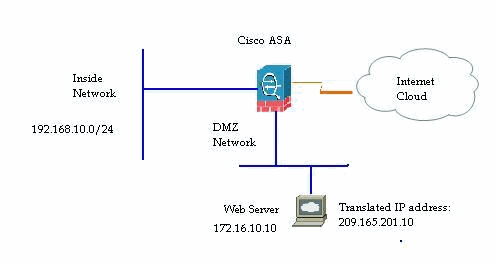
A web server with internal IP address, 172.16.10.10 is in the DMZ network and should be accessed from the Outside world. You need these items in order to accomplish this:.
-
Create a translation entry specific to this web server.
-
Create an ACL entry to permit this connection.
But, from Cisco ASDM software release version 6.2 and later, a new wizard for the public server is introduced. From now, you do not need to separately configure the NAT translations and the ACL permits. Instead, you need to specify simple details such as public interface, private interface, public IP address, private address and service.
Configure
In this section, you are presented with the information to configure the features described in this document.
Note: Use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) to obtain more information on the commands used in this section.
Network Diagram
This document uses this network setup:
ASDM Configuration
Complete these steps in order to configure a public server with the wizard.
-
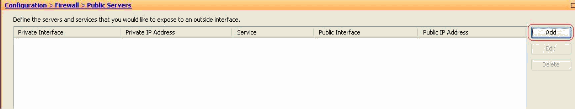
Choose Configuration > Firewall > Public servers.
-
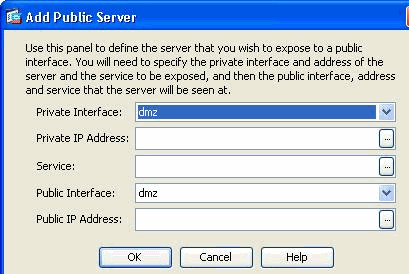
Click Add. Then the Add Public Server window appears.
-
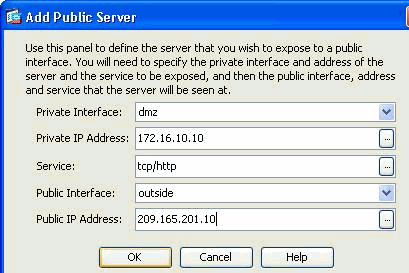
Now specify these parameters:
-
Private Interface—The interface to which the real server is connected.
-
Private IP Address—The real IP address of the server.
-
Private Service—The actual service that is running on the real server.
-
Public Interface—The interface through which outside users can access the real server.
-
Public Address—The IP address that is seen by outside users.
-
-
Click OK.
-
You can view the related configuration entry in the Public Servers pane.
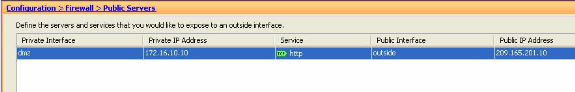
-
The equivalent CLI configuration is shown here for your reference:
Cisco ASA access-list inside_access_in extended permit tcp any host 209.165.201.10 eq www access-group inside_access_in in interface outside static (dmz,outside) 209.165.201.10 172.16.10.10 netmask 255.255.255.255
Support for Static PAT
When you use Cisco ASDM version 6.2, you can configure the public server for a static NAT only, but not with a static PAT. It means the public server is accessible at the same service that it is actually exposed to outside world. From Cisco ASDM software release 6.3 and later, support for static NAT with Port Address Translation is available, which means that you can access the public server at a different service to what it is actually exposed.
This is a sample ASDM screen shot of the Add Public Server window for ASDM software release 6.3.
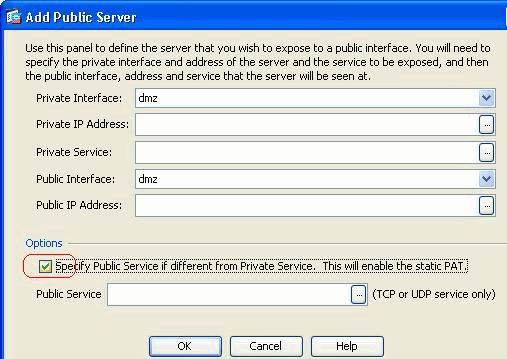
In this case, the public service can be different from the private service. Refer to Static NAT with Port Address Translation for more information.
More explanation about CLI
This feature is exclusively introduced from ASDM perspective for the ease of the Administrator to configure Public Servers. No equivalent new CLI commands are introduced. When you configure a public server using ASDM, the equivalent set of commands for the static and access-list are created automatically and can be viewed in the corresponding ASDM panes. A modification to these entries also result in the modification in the public server entry.
Verify
There is currently no verification procedure available for this configuration.
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
25-Jan-2012 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)




 Feedback
Feedback