Identificar e Solucionar Problemas de VXLAN Multisite com CloudSec na Topologia Quadrada
Opções de download
Linguagem imparcial
O conjunto de documentação deste produto faz o possível para usar uma linguagem imparcial. Para os fins deste conjunto de documentação, a imparcialidade é definida como uma linguagem que não implica em discriminação baseada em idade, deficiência, gênero, identidade racial, identidade étnica, orientação sexual, status socioeconômico e interseccionalidade. Pode haver exceções na documentação devido à linguagem codificada nas interfaces de usuário do software do produto, linguagem usada com base na documentação de RFP ou linguagem usada por um produto de terceiros referenciado. Saiba mais sobre como a Cisco está usando a linguagem inclusiva.
Sobre esta tradução
A Cisco traduziu este documento com a ajuda de tecnologias de tradução automática e humana para oferecer conteúdo de suporte aos seus usuários no seu próprio idioma, independentemente da localização. Observe que mesmo a melhor tradução automática não será tão precisa quanto as realizadas por um tradutor profissional. A Cisco Systems, Inc. não se responsabiliza pela precisão destas traduções e recomenda que o documento original em inglês (link fornecido) seja sempre consultado.
Contents
Introdução
Este documento descreve a configuração de vários locais VXLAN e a solução de problemas com o CloudSec entre gateways de borda conectados na topologia quadrada.
Pré-requisitos
Requisitos
A Cisco recomenda que você esteja familiarizado com estes tópicos:
- Software Nexus NXOS ©.
- Tecnologia VXLAN EVPN.
- BGP e protocolos de roteamento OSPF.
Componentes Utilizados
As informações neste documento são baseadas nas seguintes versões de software e hardware:
- Cisco Nexus 9000
- NXOS versão 10.3(4a).
As informações neste documento foram criadas a partir de dispositivos em um ambiente de laboratório específico. Todos os dispositivos utilizados neste documento foram iniciados com uma configuração (padrão) inicial. Se a rede estiver ativa, certifique-se de que você entenda o impacto potencial de qualquer comando.
Configurar
Diagrama de Rede
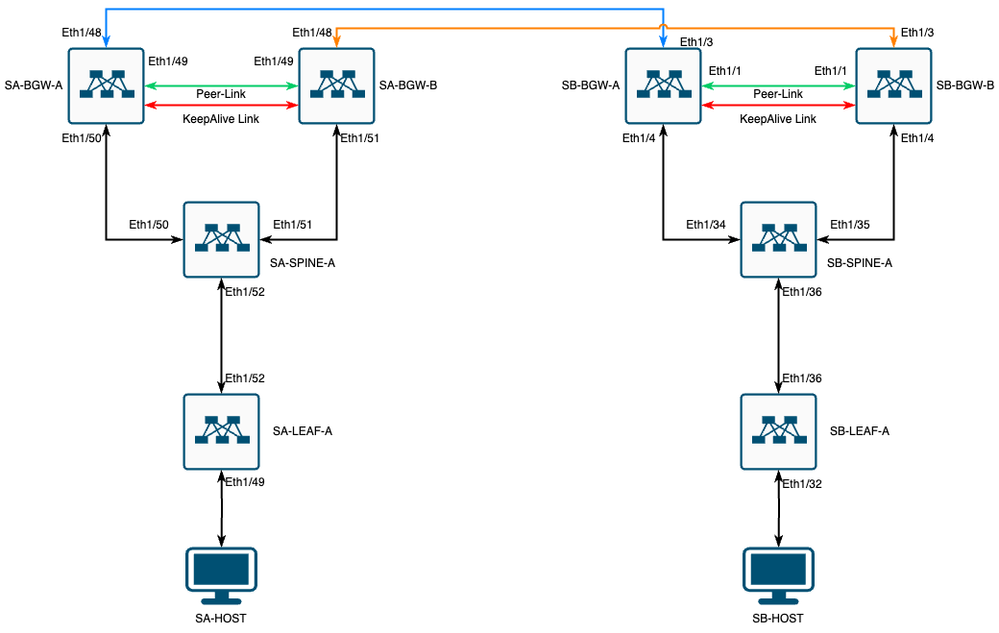 VXLAN MultiSite com CloudSec na topologia quadrada
VXLAN MultiSite com CloudSec na topologia quadrada
Detalhes da topologia
- Estrutura EVPN VXLAN de vários locais de dois locais.
- Ambos os locais são configurados com gateways de borda vPC.
- Os endpoints são hospedados na VLAN 1100.
- Os gateways de borda em cada site têm vizinhança IPv4 iBGP entre si na interface Vlan3600 do SVI.
- Os gateways de borda em um site têm vizinhança IPv4 eBGP somente com gateway de borda diretamente conectado no outro site.
- Os gateways de borda no site A têm vizinhança EVPN L2VPN eBGP com gateways de borda no site B.
Plano de endereçamento
Os endereços IP na tabela são usados durante a configuração:
| LOCAL A | LOCAL B | |||||||||||
| Função do dispositivo | ID da interface | IP Int Físico | IP de loop RID | IP de loop NVE | MSITE-VIP | IP do SVI de backup | ID da interface | IP Int Físico | IP de loop RID | IP de loop NVE | MSITE-VIP | IP do SVI de backup |
| FOLHA | Eth1/52 | 192.168.1.1/30 | 192.168.2.1/32 | 192.168.3.1/32 | N/A | N/A | Eth1/36 | 192.168.11.1/30 | 192.168.12.1/32 | 192.168.13.1/32 | N/A | N/A |
| COLUNA | Eth1/52 | 192.168.1.2/30 | N/A | Eth1/36 | 192.168.11.2/30 | N/A | ||||||
| Eth1/50 | 192.168.1.5/30 | 192.168.2.2/32 | N/A | N/A | N/A | Eth1/34 | 192.168.11.5/30 | 192.168.12.2/32 | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Eth1/51 | 192.168.1.9/30 | N/A | Eth1/35 | 192.168.11.9/30 | N/A | |||||||
| BGW-A | Eth1/51 | 192.168.1.6/30 | 192.168.2.3/32 | 192.168.3.2/32 | 192.168.100.1/32 | 192.168.4.1/30 | Eth1/4 | 192.168.11.6/30 | 192.168.12.3/32 | 192.168.13.2/32 | 192.168.200.1/32 | 192.168.14.1/30 |
| Eth1/48 | 10.12.10.1/30 | 192.168.3.254/32 | Eth1/3 | 10.12.10.2/30 | 192.168.13.254/32 | |||||||
| BGW-B | Eth1/51 | 192.168.1.10/30 | 192.168.2.4/32 | 192.168.3.3/32 | 192.168.100.1/32 | 192.168.4.2/30 | Eth1/4 | 192.168.11.10/30 | 192.168.12.4/32 | 192.168.13.3/32 | 192.168.200.1/32 | 192.168.14.2/30 |
| Eth1/48 | 10.12.10.5/30 | 192.168.3.254/32 | Eth1/3 | 10.12.10.6/30 | 192.168.13.254/32 |
Configurações
- Observe que neste guia somente a configuração relacionada a vários sites é mostrada. Para obter a configuração completa, você pode usar o guia de documentação oficial da Cisco para o Guia de configuração de VXLAN do Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS VXLAN, versão 10.3(x)
Para habilitar o CloudSec, o dci-advertise-pip comando deve ser configurado no gateway de borda de vários sites da vpn:
| SA-BGW-A e SA-BGW-B | SB-BGW-A e SB-BGW-B |
|
|
configuração de BGP
Essa configuração é específica do site.
| SA-BGW-A e SA-BGW-B | SB-BGW-A e SB-BGW-B |
|
|
- O comando maximum-path permite receber vários caminhos EVPN L2VPN eBGP do vizinho.
- O comando additional-path instrui o processo BGP para anunciar que o dispositivo é capaz de enviar/receber caminhos adicionais
Para todos os VRFs L3VNI nos gateways de borda, o multipath também deve ser configurado:
| SA-BGW-A e SA-BGW-B | SB-BGW-A e SB-BGW-B |
|
|
Configuração de criptografia de túnel
Essa configuração deve ser a mesma em todos os gateways de borda:
key chain CloudSec_Key_Chain1 tunnel-encryption key 1000 key-octet-string Cl0udSec! cryptographic-algorithm AES_128_CMAC feature tunnel-encryption tunnel-encryption must-secure-policy tunnel-encryption source-interface loopback0 tunnel-encryption policy CloudSec_Policy1Essa configuração é específica do site. O comandotunnel-encryption deve ser aplicado somente à interface que tem o evpn multisite dci-trackingcomando.
| SA-BGW-A e SA-BGW-B | SB-BGW-A e SB-BGW-B |
|
|
Depois de ativar a criptografia de túnel, atributos adicionais são adicionados ao loopback local ao anunciar rotas para o vizinho e todos os vizinhos unicast IPv4 do eBGP devem ver este atributo:
SA-BGW-A# show ip bgp 192.168.2.3 BGP routing table information for VRF default, address family IPv4 Unicast BGP routing table entry for 192.168.2.3/32, version 1320 Paths: (2 available, best #1) Flags: (0x000002) (high32 00000000) on xmit-list, is not in urib Multipath: eBGP iBGP Advertised path-id 1 Path type: local, path is valid, is best path, no labeled nexthop AS-Path: NONE, path locally originated 0.0.0.0 (metric 0) from 0.0.0.0 (192.168.2.3) Origin IGP, MED not set, localpref 100, weight 32768 Tunnel Encapsulation attribute: Length 152 !---This is a new attribute Path type: redist, path is valid, not best reason: Locally originated, no labeled nexthop AS-Path: NONE, path locally originated 0.0.0.0 (metric 0) from 0.0.0.0 (192.168.2.3) Origin incomplete, MED 0, localpref 100, weight 32768 Path-id 1 advertised to peers: 10.12.10.2 192.168.4.2 SA-BGW-A# Para o tipo de rota 2, também há um novo atributo:
SA-BGW-A# show bgp l2vpn evpn 00ea.bd27.86ef BGP routing table information for VRF default, address family L2VPN EVPN Route Distinguisher: 65002:31100 BGP routing table entry for [2]:[0]:[0]:[48]:[00ea.bd27.86ef]:[0]:[0.0.0.0]/216, version 7092 Paths: (2 available, best #2) Flags: (0x000202) (high32 00000000) on xmit-list, is not in l2rib/evpn, is not in HW Multipath: eBGP iBGP Path type: external, path is valid, not best reason: Router Id, multipath, no labeled nexthop Imported to 1 destination(s) Imported paths list: L2-31100 AS-Path: 65002 , path sourced external to AS 192.168.13.3 (metric 0) from 192.168.12.4 (192.168.12.4) Origin IGP, MED 2000, localpref 100, weight 0 Received label 31100 Received path-id 1 Extcommunity: RT:65001:31100 ENCAP:8 ESI: 0300.0000.00fd.ea00.0309 Advertised path-id 1 Path type: external, path is valid, is best path, no labeled nexthop Imported to 1 destination(s) Imported paths list: L2-31100 AS-Path: 65002 , path sourced external to AS 192.168.13.2 (metric 0) from 192.168.12.3 (192.168.12.3) Origin IGP, MED 2000, localpref 100, weight 0 Received label 31100 Received path-id 1 Extcommunity: RT:65001:31100 ENCAP:8 ESI: 0300.0000.00fd.ea00.0309 Path-id 1 not advertised to any peer Route Distinguisher: 192.168.2.3:33867 (L2VNI 31100) BGP routing table entry for [2]:[0]:[0]:[48]:[00ea.bd27.86ef]:[0]:[0.0.0.0]/216, version 7112 Paths: (2 available, best #1) Flags: (0x000212) (high32 0x000400) on xmit-list, is in l2rib/evpn, is not in HW Multipath: eBGP iBGP Advertised path-id 1 Path type: external, path is valid, is best path, no labeled nexthop, in rib Imported from 65002:31100:[2]:[0]:[0]:[48]:[00ea.bd27.86ef]:[0]:[0.0.0.0]/216 AS-Path: 65002 , path sourced external to AS 192.168.13.2 (metric 0) from 192.168.12.3 (192.168.12.3) Origin IGP, MED 2000, localpref 100, weight 0 Received label 31100 Received path-id 1 Extcommunity: RT:65001:31100 ENCAP:8 ESI: 0300.0000.00fd.ea00.0309 Path type: external, path is valid, not best reason: Router Id, multipath, no labeled nexthop, in rib Imported from 65002:31100:[2]:[0]:[0]:[48]:[00ea.bd27.86ef]:[0]:[0.0.0.0]/216 AS-Path: 65002 , path sourced external to AS 192.168.13.3 (metric 0) from 192.168.12.4 (192.168.12.4) Origin IGP, MED 2000, localpref 100, weight 0 Received label 31100 Received path-id 1 Extcommunity: RT:65001:31100 ENCAP:8 ESI: 0300.0000.00fd.ea00.0309 !---Ethernet Segment Identifier (ESI) is also new attribute Path-id 1 (dual) advertised to peers: 192.168.2.2 SA-BGW-A# Verificar
VerificarAntes de habilitar o cloudsec, é bom verificar se a configuração está funcionando bem sem ele:
SA-BGW-A(config)# show clock Warning: No NTP peer/server configured. Time may be out of sync. 10:02:01.016 UTC Fri Jul 19 2024 Time source is NTP SA-BGW-A(config)# show tunnel-encryption session Tunnel-Encryption Peer Policy Keychain RxStatus TxStatus ------------------------ ---------------------------------------- ---------------------------------------- ----------------- ----------------- =============================================== SA-HOST-A# show clock Warning: No NTP peer/server configured. Time may be out of sync. 10:02:21.592 UTC Fri Jul 19 2024 Time source is NTP SA-HOST-A# ping 10.100.20.10 count unlimited interval 1 PING 10.100.20.10 (10.100.20.10): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=0 ttl=254 time=1.583 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1 ttl=254 time=10.407 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=2 ttl=254 time=1.37 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=3 ttl=254 time=1.489 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=4 ttl=254 time=6.685 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=5 ttl=254 time=1.547 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=6 ttl=254 time=1.859 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=7 ttl=254 time=5.219 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=8 ttl=254 time=1.337 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=9 ttl=254 time=3.528 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=10 ttl=254 time=4.057 msApós a configuração de cloudsec também, o endpoint em SA deve efetuar ping com êxito no endpoint no site B. Mas, em alguns casos, o ping pode ser malsucedido. Depende de qual peer cloudsec foi selecionado pelo dispositivo local para enviar o tráfego criptografado cloudsec.
SA-HOST-A# ping 10.100.20.10 PING 10.100.20.10 (10.100.20.10): 56 data bytes Request 0 timed out Request 1 timed out Request 2 timed out Request 3 timed out Request 4 timed out --- 10.100.20.10 ping statistics --- 5 packets transmitted, 0 packets received, 100.00% packet loss SA-HOST-A# Troubleshooting
TroubleshootingVerifique a tabela ARP local no ponto final de origem:
SA-HOST-A# ping 10.100.20.10 count unlimited interval 1 Request 352 timed out Request 353 timed out Request 354 timed out 356 packets transmitted, 0 packets received, 100.00% packet loss SA-HOST-A# clear ip arp delete-force SA-HOST-A# show ip arp Flags: * - Adjacencies learnt on non-active FHRP router + - Adjacencies synced via CFSoE # - Adjacencies Throttled for Glean CP - Added via L2RIB, Control plane Adjacencies PS - Added via L2RIB, Peer Sync RO - Re-Originated Peer Sync Entry D - Static Adjacencies attached to down interface IP ARP Table for context default Total number of entries: 1 Address Age MAC Address Interface Flags 10.100.20.10 00:00:02 00ea.bd27.86ef Vlan1100 SA-HOST-A# Essa saída comprova que o tráfego de BUM está passando e o plano de controle está funcionando. A próxima etapa é verificar o status da criptografia do túnel:
SA-BGW-A# show tunnel-encryption session Tunnel-Encryption Peer Policy Keychain RxStatus TxStatus ------------------------ ---------------------------------------- ---------------------------------------- ----------------- ----------------- 192.168.13.2 CloudSec_Policy1 CloudSec_Key_Chain1 Secure (AN: 0) Secure (AN: 0) 192.168.13.3 CloudSec_Policy1 CloudSec_Key_Chain1 Secure (AN: 0) Secure (AN: 0) SA-BGW-A# Esta saída mostra que a sessão do CloudSec foi estabelecida. Como próxima etapa, você pode executar ping ilimitado em SA-HOST-A:
SA-HOST-A# ping 10.100.20.10 count unlimited interval 1A partir desse ponto, você deve verificar os dispositivos no site A e ver se o tráfego está chegando a esses dispositivos. Você pode realizar essa tarefa com o ELAM em todos os dispositivos ao longo do caminho no site A. Alterar in-select do valor padrão de 6 para 9 permite que o faça a correspondência com base nos cabeçalhos internos. Leia mais sobre o ELAM neste link: Nexus 9000 Cloud Scale ASIC (Tahoe) NX-OS ELAM.
ELAM no SA-LEAF-A
ELAM no SA-LEAF-ANa rede de produção, existem mais de um dispositivo SPINE. Para entender para qual coluna o tráfego foi enviado, você deve primeiro obter um ELAM no LEAF. Apesar do in-select 9 usado, na FOLHA conectada à origem, o cabeçalho ipv4 externo deve ser usado, já que o tráfego que chega a essa FOLHA não é criptografado por VXLAN. Em uma rede real, pode ser difícil capturar o pacote exato gerado. Nesses casos, você pode executar o ping com um comprimento específico e usar o cabeçalho Pkt len para identificar seu pacote. Por padrão, o pacote icmp tem 64 bytes de comprimento. Mais 20 bytes de cabeçalho IP, que em resumo lhe deu 84 bytes PKT Len:
SA-LEAF-A# debug platform internal tah elam SA-LEAF-A(TAH-elam)# trigger init in-select 9 Slot 1: param values: start asic 0, start slice 0, lu-a2d 1, in-select 9, out-select 0 SA-LEAF-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# set outer ipv4 src_ip 10.100.10.10 dst_ip 10.100.20.10 SA-LEAF-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# start SA-LEAF-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# report ELAM not triggered yet on slot - 1, asic - 0, slice - 0 SUGARBOWL ELAM REPORT SUMMARY slot - 1, asic - 0, slice - 1 ============================ Incoming Interface: Eth1/49 Src Idx : 0xc1, Src BD : 1100 Outgoing Interface Info: dmod 1, dpid 64 !---Note dpid value Dst Idx : 0xcd, Dst BD : 1100 Packet Type: IPv4 Outer Dst IPv4 address: 10.100.20.10 Outer Src IPv4 address: 10.100.10.10 Ver = 4, DSCP = 0, Don't Fragment = 0 Proto = 1, TTL = 255, More Fragments = 0 Hdr len = 20, Pkt len = 84, Checksum = 0xb4ae !---64 byte + 20 byte IP header Pkt len = 84 Inner Payload Type: CE L4 Protocol : 1 L4 info not available Drop Info: ---------- LUA: LUB: LUC: LUD: Final Drops: SA-LEAF-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show system internal ethpm info all | i i "dpid=64" !---Put dpid value here IF_STATIC_INFO: port_name=Ethernet1/52,if_index:0x1a006600,ltl=5940,slot=0, nxos_port=204,dmod=1,dpid=64,unit=0,queue=65535,xbar_unitbmp=0x0,ns_pid=255,slice_num=1,port_on_slice=24,src_id=48 SA-LEAF-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show cdp neighbors interface ethernet 1/52 Capability Codes: R - Router, T - Trans-Bridge, B - Source-Route-Bridge S - Switch, H - Host, I - IGMP, r - Repeater, V - VoIP-Phone, D - Remotely-Managed-Device, s - Supports-STP-Dispute Device-ID Local Intrfce Hldtme Capability Platform Port ID SA-SPINE-A(FDO242210CS) Eth1/52 130 R S s N9K-C93240YC-FX2 Eth1/52 Total entries displayed: 1 SA-LEAF-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# A partir dessa saída, você pode ver que o tráfego é alcançado pelo SA-LEAF-A e encaminhado pela interface Ethernet1/52, que está conectada ao SA-SPINE-A a partir da topologia.
ELAM em SA-SPINE-A
ELAM em SA-SPINE-AEm SPINE, o valor de Pkt Len será maior, já que o cabeçalho VXLAN de 50 bytes também foi adicionado. Por padrão, SPINE não pode corresponder em cabeçalhos internos sem vxlan-parse ou feature nv overlay . Portanto, você deve usar o vxlan-parse enable comando no SPINE:
SA-SPINE-A(config-if)# debug platform internal tah elam SA-SPINE-A(TAH-elam)# trigger init in-select 9 Slot 1: param values: start asic 0, start slice 0, lu-a2d 1, in-select 9, out-select 0 SA-SPINE-A(TAH-elam)# vxlan-parse enable SA-SPINE-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# set inner ipv4 src_ip 10.100.10.10 dst_ip 10.100.20.10 SA-SPINE-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# start SA-SPINE-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# report ELAM not triggered yet on slot - 1, asic - 0, slice - 0 HEAVENLY ELAM REPORT SUMMARY slot - 1, asic - 0, slice - 1 ============================ Incoming Interface: Eth1/52 Src Idx : 0xcd, Src BD : 4153 Outgoing Interface Info: dmod 1, dpid 72 Dst Idx : 0xc5, Dst BD : 4151 Packet Type: IPv4 Outer Dst IPv4 address: 192.168.100.1 Outer Src IPv4 address: 192.168.3.1 Ver = 4, DSCP = 0, Don't Fragment = 0 Proto = 17, TTL = 255, More Fragments = 0 Hdr len = 20, Pkt len = 134, Checksum = 0x7d69 !---84 bytes + 50 bytes VXLAN header Pkt len = 134 Inner Payload Type: IPv4 Inner Dst IPv4 address: 10.100.20.10 Inner Src IPv4 address: 10.100.10.10 L4 Protocol : 17 L4 info not available Drop Info: ---------- LUA: LUB: LUC: LUD: Final Drops: SA-SPINE-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show system internal ethpm info all | i i "dpid=72" IF_STATIC_INFO: port_name=Ethernet1/50,if_index:0x1a006200,ltl=5948,slot=0, nxos_port=196,dmod=1,dpid=72,unit=0,queue=65535,xbar_unitbmp=0x0,ns_pid=255,slice_num=1,port_on_slice=0,src_id=0 SA-SPINE-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show cdp neighbors interface ethernet 1/50 Capability Codes: R - Router, T - Trans-Bridge, B - Source-Route-Bridge S - Switch, H - Host, I - IGMP, r - Repeater, V - VoIP-Phone, D - Remotely-Managed-Device, s - Supports-STP-Dispute Device-ID Local Intrfce Hldtme Capability Platform Port ID SA-BGW-A(FDO242210CX) Eth1/50 169 R S s N9K-C93240YC-FX2 Eth1/50 Total entries displayed: 1 SA-SPINE-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# SA-SPINE-A envia tráfego para o SA-BGW-A de acordo com a saída.
ELAM no SA-BGW-A
ELAM no SA-BGW-ASA-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# set inner ipv4 src_ip 10.100.10.10 dst_ip 10.100.20.10 SA-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# start SA-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# report ELAM not triggered yet on slot - 1, asic - 0, slice - 0 HEAVENLY ELAM REPORT SUMMARY slot - 1, asic - 0, slice - 1 ============================ Incoming Interface: Eth1/50 Src Idx : 0xc5, Src BD : 1100 Outgoing Interface Info: dmod 1, dpid 48 Dst Idx : 0xbd, Dst BD : 1100 Packet Type: IPv4 Outer Dst IPv4 address: 192.168.100.1 Outer Src IPv4 address: 192.168.3.1 Ver = 4, DSCP = 0, Don't Fragment = 0 Proto = 17, TTL = 254, More Fragments = 0 Hdr len = 20, Pkt len = 134, Checksum = 0x7e69 Inner Payload Type: IPv4 Inner Dst IPv4 address: 10.100.20.10 Inner Src IPv4 address: 10.100.10.10 L4 Protocol : 17 L4 info not available Drop Info: ---------- LUA: LUB: LUC: LUD: Final Drops: SA-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show system internal ethpm info all | i i "dpid=48" IF_STATIC_INFO: port_name=Ethernet1/48,if_index:0x1a005e00,ltl=5956,slot=0, nxos_port=188,dmod=1,dpid=48,unit=0,queue=65535,xbar_unitbmp=0x0,ns_pid=255,slice_num=0,port_on_slice=48,src_id=96 SA-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show cdp neighbors interface ethernet 1/48 Capability Codes: R - Router, T - Trans-Bridge, B - Source-Route-Bridge S - Switch, H - Host, I - IGMP, r - Repeater, V - VoIP-Phone, D - Remotely-Managed-Device, s - Supports-STP-Dispute Device-ID Local Intrfce Hldtme Capability Platform Port ID SB-BGW-A(FDO2452070B) Eth1/48 122 R S s N9K-C93216TC-FX2 Eth1/3 Total entries displayed: 1 SA-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# De acordo com a saída do SA-BGW-A, o tráfego saiu da Ethernet1/48 em direção ao SB-BGW-A. A próxima etapa é verificar o SB-BGW-A:
SB-BGW-A# debug platform internal tah elam SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam)# trigger init in-select 9 Slot 1: param values: start asic 0, start slice 0, lu-a2d 1, in-select 9, out-select 0 SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# set inner ipv4 src_ip 10.100.10.10 dst_ip 10.100.20.10 SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# start SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# report ELAM not triggered yet on slot - 1, asic - 0, slice - 0 ELAM not triggered yet on slot - 1, asic - 0, slice - 1 !---Reset the previous filter and start again just in case if packet was not captured. SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# reset SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# set inner ipv4 src_ip 10.100.10.10 dst_ip 10.100.20.10 SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# start SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# report ELAM not triggered yet on slot - 1, asic - 0, slice - 0 ELAM not triggered yet on slot - 1, asic - 0, slice - 1 SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# De acordo com a saída do SB-BGW-A, o ELAM nem sequer foi acionado. Isso significa que o SB-BGW-B está recebendo os pacotes e não está sendo capaz de descriptografá-los e analisá-los corretamente, ou não os recebe de forma alguma. Para entender o que aconteceu com o tráfego de cloudsec, você pode executar um ELAM no SB-BGW-A novamente, mas o filtro de gatilho deve ser definido como endereço IP externo que é usado para cloudsec, pois não há como ver o cabeçalho interno do pacote de trânsito criptografado do cloudsec. A partir da saída anterior, você sabe, que o SA-BGW-A tratou o tráfego, o que significa que o SA-BGW-A criptografa o tráfego com o cloudsec. Assim, você pode usar o IP NVE de SA-BGW-A como um filtro acionador para ELAM. A partir das saídas anteriores, o comprimento do pacote ICMP criptografado da VXLAN é de 134 bytes. Além disso, o cabeçalho cloudsec de 32 bytes em resumo fornece 166 bytes:
SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# reset SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# set outer ipv4 src_ip 192.168.3.2 SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# start SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# report ELAM not triggered yet on slot - 1, asic - 0, slice - 0 HEAVENLY ELAM REPORT SUMMARY slot - 1, asic - 0, slice - 1 ============================ Incoming Interface: Eth1/3 Src Idx : 0x9, Src BD : 4108 Outgoing Interface Info: dmod 1, dpid 130 Dst Idx : 0xd, Dst BD : 4109 Packet Type: IPv4 Outer Dst IPv4 address: 192.168.13.3 !---NVE IP address of SB-BGW-B Outer Src IPv4 address: 192.168.3.2 Ver = 4, DSCP = 0, Don't Fragment = 0 Proto = 17, TTL = 254, More Fragments = 0 Hdr len = 20, Pkt len = 166, Checksum = 0xd546 !---134 byte VXLAN packet + 32 byte cloudsec header Pkt len = 166 Inner Payload Type: CE L4 Protocol : 17 L4 info not available Drop Info: ---------- LUA: LUB: LUC: LUD: Final Drops: !---To reach SB-BGW-B NVE IP traffic was sent out of Ethernet1/4 which is connected to SB-SPINE-A SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show system internal ethpm info all | i i "dpid=130" IF_STATIC_INFO: port_name=Ethernet1/4,if_index:0x1a000600,ltl=6132,slot=0, nxos_port=12,dmod=1,dpid=130,unit=0,queue=65535,xbar_unitbmp=0x0,ns_pid=255,slice_num=1,port_on_slice=58,src_id=116
SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show cdp neighbors interface ethernet 1/4 Capability Codes: R - Router, T - Trans-Bridge, B - Source-Route-Bridge S - Switch, H - Host, I - IGMP, r - Repeater, V - VoIP-Phone, D - Remotely-Managed-Device, s - Supports-STP-Dispute Device-ID Local Intrfce Hldtme Capability Platform Port ID SB-SPINE-A(FDO22302CJ0) Eth1/4 131 R S s N9K-C9236C Eth1/34 Total entries displayed: 1 SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show ip route 192.168.13.3 IP Route Table for VRF "default" '*' denotes best ucast next-hop '**' denotes best mcast next-hop '[x/y]' denotes [preference/metric] '%<string>' in via output denotes VRF <string> 192.168.13.3/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0 *via 192.168.11.5, Eth1/4, [110/6], 00:56:13, ospf-UNDERLAY, intra via 192.168.14.2, [200/0], 01:13:46, bgp-65002, internal, tag 65002 !---The device still have a route for SB-BGW-B NVE IP via SVI
SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show ip route 192.168.14.2 IP Route Table for VRF "default" '*' denotes best ucast next-hop '**' denotes best mcast next-hop '[x/y]' denotes [preference/metric] '%<string>' in via output denotes VRF <string> 192.168.14.2/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached *via 192.168.14.2, Vlan3600, [250/0], 01:15:05, am SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show ip arp 192.168.14.2 Flags: * - Adjacencies learnt on non-active FHRP router + - Adjacencies synced via CFSoE # - Adjacencies Throttled for Glean CP - Added via L2RIB, Control plane Adjacencies PS - Added via L2RIB, Peer Sync RO - Re-Originated Peer Sync Entry D - Static Adjacencies attached to down interface IP ARP Table Total number of entries: 1 Address Age MAC Address Interface Flags 192.168.14.2 00:00:13 ecce.1324.c803 Vlan3600 SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show mac address-table address ecce.1324.c803 Legend: * - primary entry, G - Gateway MAC, (R) - Routed MAC, O - Overlay MAC age - seconds since last seen,+ - primary entry using vPC Peer-Link, (T) - True, (F) - False, C - ControlPlane MAC, ~ - vsan, (NA)- Not Applicable VLAN MAC Address Type age Secure NTFY Ports ---------+-----------------+--------+---------+------+----+------------------ G 3600 ecce.1324.c803 static - F F vPC Peer-Link(R) SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# A partir dessa saída, você pode ver que o tráfego de cloudsec é encaminhado para o SB-BGW-B através da interface Ethernet1/4, com base na tabela de roteamento. De acordo com o Guia de configuração do Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS VXLAN, versão 10.3(x), diretrizes e limitações:
-
O tráfego do CloudSec destinado ao switch deve entrar no switch através dos uplinks DCI.
De acordo com a seção Suporte do vPC Border Gateway para Cloudsec do mesmo guia, se o BGW do vPC aprender o endereço IP do BGW do vPC e anunciar no lado do DCI, os atributos de caminho do BGP de ambos os BGW do vPC serão os mesmos. Portanto, os nós intermediários de DCI podem acabar escolhendo o caminho do vPC BGW que não possui o endereço PIP. Neste cenário, o link MCT é usado para tráfego criptografado proveniente do site remoto. Mas, nesse caso, a interface em direção ao SPINE é usada, apesar disso, os BGWs também têm uma adjacência OSPF através do SVI de backup.
SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show ip ospf neighbors OSPF Process ID UNDERLAY VRF default Total number of neighbors: 2 Neighbor ID Pri State Up Time Address Interface 192.168.12.4 1 FULL/ - 01:33:11 192.168.14.2 Vlan3600 192.168.12.2 1 FULL/ - 01:33:12 192.168.11.5 Eth1/4 SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)#Motivo do problema e correção
Motivo do problema e correçãoO motivo é o custo OSPF da interface SVI. Por padrão, a largura de banda de referência de custo automático do NXOS é 40G. As interfaces SVI têm uma largura de banda de 1 Gbps, enquanto a interface física tem uma largura de banda de 10 Gbps:
SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show ip ospf interface brief OSPF Process ID UNDERLAY VRF default Total number of interface: 5 Interface ID Area Cost State Neighbors Status Vlan3600 3 0.0.0.0 40 P2P 1 up <Output omitted> Eth1/4 5 0.0.0.0 1 P2P 1 up Nesse caso, a alteração administrativa do custo do SVI pode resolver o problema. O ajuste deve ser feito em todos os gateways de borda.
SB-BGW-A(config)# int vlan 3600 SB-BGW-A(config-if)# ip ospf cost 1 SB-BGW-A(config-if)# sh ip route 192.168.13.3 IP Route Table for VRF "default" '*' denotes best ucast next-hop '**' denotes best mcast next-hop '[x/y]' denotes [preference/metric] '%<string>' in via output denotes VRF <string> 192.168.13.3/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0 *via 192.168.14.2, Vlan3600, [110/2], 00:00:08, ospf-UNDERLAY, intra via 192.168.14.2, [200/0], 01:34:07, bgp-65002, internal, tag 65002 SB-BGW-A(config-if)#
!---The ping is started to work immediately
Request 1204 timed out Request 1205 timed out Request 1206 timed out 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1207 ttl=254 time=1.476 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1208 ttl=254 time=5.371 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1209 ttl=254 time=5.972 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1210 ttl=254 time=1.466 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1211 ttl=254 time=2.972 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1212 ttl=254 time=4.582 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1213 ttl=254 time=1.434 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1214 ttl=254 time=4.486 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1215 ttl=254 time=2.743 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1216 ttl=254 time=1.469 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1217 ttl=254 time=7.322 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1218 ttl=254 time=1.532 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1219 ttl=254 time=1.438 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1220 ttl=254 time=7.122 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1221 ttl=254 time=1.344 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1222 ttl=254 time=1.63 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1223 ttl=254 time=6.133 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1224 ttl=254 time=1.455 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1225 ttl=254 time=3.221 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1226 ttl=254 time=4.435 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1227 ttl=254 time=1.463 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1228 ttl=254 time=5.14 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1229 ttl=254 time=2.796 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1230 ttl=254 time=1.49 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1231 ttl=254 time=6.707 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1232 ttl=254 time=1.447 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1233 ttl=254 time=1.285 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1234 ttl=254 time=7.097 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1235 ttl=254 time=1.295 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1236 ttl=254 time=0.916 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1237 ttl=254 time=6.24 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1238 ttl=254 time=1.439 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1239 ttl=254 time=2.739 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1240 ttl=254 time=4.477 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1241 ttl=254 time=1.431 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1242 ttl=254 time=5.372 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1243 ttl=254 time=3.119 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1244 ttl=254 time=1.504 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1245 ttl=254 time=6.909 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1246 ttl=254 time=1.498 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1247 ttl=254 time=1.454 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1248 ttl=254 time=6.701 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1249 ttl=254 time=1.441 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1250 ttl=254 time=1.888 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1251 ttl=254 time=6.052 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1252 ttl=254 time=1.469 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1253 ttl=254 time=3.61 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1254 ttl=254 time=4.213 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1255 ttl=254 time=1.276 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1256 ttl=254 time=5.712 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1257 ttl=254 time=2.299 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1258 ttl=254 time=1.417 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1259 ttl=254 time=7.159 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1260 ttl=254 time=1.538 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1261 ttl=254 time=1.629 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1262 ttl=254 time=7.892 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1263 ttl=254 time=1.495 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1264 ttl=254 time=2.792 ms ^C --- 10.100.20.10 ping statistics --- 1265 packets transmitted, 58 packets received, 95.42% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 0.916/3.31/7.892 ms SA-HOST-A# Histórico de revisões
| Revisão | Data de publicação | Comentários |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
29-Jul-2024 |
Versão inicial |
Colaborado por engenheiros da Cisco
- Chingiz KhalafovEngenheiro de consultoria técnica
Contate a Cisco
- Abrir um caso de suporte

- (É necessário um Contrato de Serviço da Cisco)
 Feedback
Feedback