Begrijp werklastverdeling met BGP in single/multihomed omgevingen
Downloadopties
Inclusief taalgebruik
De documentatie van dit product is waar mogelijk geschreven met inclusief taalgebruik. Inclusief taalgebruik wordt in deze documentatie gedefinieerd als taal die geen discriminatie op basis van leeftijd, handicap, gender, etniciteit, seksuele oriëntatie, sociaaleconomische status of combinaties hiervan weerspiegelt. In deze documentatie kunnen uitzonderingen voorkomen vanwege bewoordingen die in de gebruikersinterfaces van de productsoftware zijn gecodeerd, die op het taalgebruik in de RFP-documentatie zijn gebaseerd of die worden gebruikt in een product van een externe partij waarnaar wordt verwezen. Lees meer over hoe Cisco gebruikmaakt van inclusief taalgebruik.
Over deze vertaling
Cisco heeft dit document vertaald via een combinatie van machine- en menselijke technologie om onze gebruikers wereldwijd ondersteuningscontent te bieden in hun eigen taal. Houd er rekening mee dat zelfs de beste machinevertaling niet net zo nauwkeurig is als die van een professionele vertaler. Cisco Systems, Inc. is niet aansprakelijk voor de nauwkeurigheid van deze vertalingen en raadt aan altijd het oorspronkelijke Engelstalige document (link) te raadplegen.
Inhoud
Inleiding
In dit document wordt workloadverdeling beschreven waarmee een router het uitgaande en inkomende verkeer tussen meerdere paden kan verdelen.
Voorwaarden
Vereisten
Zorg ervoor dat u aan deze vereisten voldoet voordat u deze configuratie probeert:
-
Kennis van het BGP-algoritme voor beste padselectie
-
Kennis van het configureren van BGP
Gebruikte componenten
Dit document is niet beperkt tot specifieke software- en hardware-versies.
De informatie in dit document is gebaseerd op de apparaten in een specifieke laboratoriumomgeving. Alle apparaten die in dit document worden beschreven, hadden een opgeschoonde (standaard)configuratie. Als uw netwerk live is, moet u zorgen dat u de potentiële impact van elke opdracht begrijpt.
Achtergrondinformatie
De inkomende en uitgaande verkeerspaden worden statisch of met dynamische protocollen zoals:
-
Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
-
Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP)
-
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)-protocol
In de standaardinstelling wordt met BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) slechts één best pad geselecteerd en wordt geen taakverdeling uitgevoerd. Dit document beschrijft hoe u het delen van ladingen in verschillende scenario's kunt uitvoeren met behulp van BGP. Zie Hoe werkt de taakverdeling voor aanvullende informatie over de taakverdeling?.
Het delen van de lading met het Loopback Adres als BGP Buurman
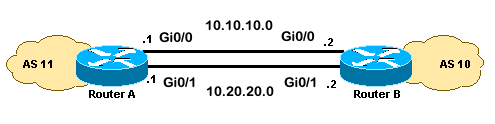
Dit scenario laat zien hoe u werklastverdeling kunt realiseren wanneer er meerdere (tot maximaal zes) gelijkwaardige koppelingen zijn. De links worden afgesloten in één router op een lokaal autonoom systeem (AS) en in een andere router op een extern AS in een single-homed BGP-omgeving. Het netwerkdiagram dient als voorbeeld.
Netwerkdiagram
In deze sectie wordt gebruik gemaakt van de volgende netwerkinstellingen:
Configuraties
In deze sectie worden de volgende configuraties gebruikt:
RouterA
interface loopback 0 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.255 interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ip address 10.20.20.1 255.255.255.0 interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0 router bgp 11 neighbor 192.168.2.2 remote-as 10 neighbor 192.168.2.2 update-source loopback 0 !--- Use the IP address of the loopback interface for TCP connections.
neighbor 192.168.2.2 ebgp-multihop !--- You must configure ebgp-multihop whenever the external BGP (eBGP) connections are not on the same network address.
router eigrp 12
network 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0
network 10.0.0.0
no auto-summary
RouterB
interface loopback 0 ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.255 interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ip address 10.20.20.2 255.255.255.0 interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.0 router bgp 10 neighbor 192.168.1.1 remote-as 11 neighbor 192.168.1.1 update-source loopback 0 !--- Use the IP address of the loopback interface for TCP connections.
neighbor 192.168.1.1 ebgp-multihop !--- You must configure ebgp-multihop whenever the eBGP connections are not on the same network address.
router eigrp 12
network 192.168.2.2 0.0.0.0
network 10.0.0.0 no auto-summary
Opmerking: u kunt statische routes gebruiken in plaats van een routeringsprotocol om twee gelijkwaardige paden te introduceren om de bestemming te bereiken. Maar in dit voorbeeld, werd EIGRP gebruikt om de loopbackinformatie te delen.
Verifiëren
Gebruik dit gedeelte om te bevestigen dat uw configuratie correct werkt.
De Cisco CLI Analyzer (alleen geregistreerde klanten) ondersteunt bepaalde show-opdrachten. Gebruik de Cisco CLI Analyzer om een analyse van show opdrachtoutput te bekijken.
De output van het showip routebevel toont beide wegen aan het 192.168.2.2 netwerk, die door EIGRP worden geleerd. Het showip bgp summiere bevel toont aan dat de buur BGP met Loopback van de verre router werd gebouwd. De output van het traceroute bevel wijst op de lading wordt verdeeld tussen twee seriële verbindingen. In dit scenario wordt het delen van de lading per pakket uitgevoerd. U kunt de ip route-cache opdracht geven op de seriële interfaces om het delen van de lading per bestemming uit te voeren. U kunt ook taakverdeling per pakket en per bestemming configureren met Cisco Express Forwarding. Raadpleeg Cisco Express Forwarding configureren voor meer informatie over het configureren van Cisco Express Forwarding.
RouterA#show ip route Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP a - application route + - replicated route, % - next hop override, p - overrides from PfR Gateway of last resort is not set 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 2 masks C 10.10.10.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0 L 10.10.10.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0 C 10.20.20.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 L 10.20.20.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 192.168.1.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets C 192.168.1.1 is directly connected, Loopback0 192.168.2.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets D 192.168.2.2 [90/130816] via 10.20.20.2, 00:02:01, GigabitEthernet0/1 [90/130816] via 10.10.10.2, 00:02:01, GigabitEthernet0/0 RouterA#RouterA#show ip bgp summary BGP router identifier 192.168.1.1, local AS number 11 BGP table version is 1, main routing table version 1 Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd 192.168.2.2 4 10 20 20 1 0 0 00:15:05 0RouterA#traceroute 192.168.2.2 Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to 192.168.2.2 VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id) 1 10.10.10.2 2 msec 10.20.20.2 2 msec 10.10.10.2 2 msec RouterA#
Problemen oplossen
Er is momenteel geen specifieke informatie beschikbaar om deze configuratie problemen op te lossen.
Het delen van de lading wanneer dubbel-Homed aan één Internet Service Provider (ISP) door één enkele lokale router
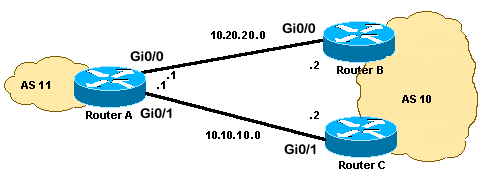
Dit scenario toont hoe u werklastverdeling kunt bereiken wanneer er meerdere koppelingen bestaan tussen een externe AS en een lokale AS. Deze koppelingen worden in één router op de lokale AS en op meerdere routers op externe AS’s in een single-homed BGP-omgeving beëindigd. Het netwerkdiagram is een voorbeeld van een dergelijk netwerk.
Deze voorbeeldconfiguratie gebruikt de opdracht maximum-paden. Standaard kiest BGP één beste pad uit de mogelijke paden met gelijke kosten die van één AS worden geleerd. U kunt echter het maximale aantal toegestane parallelle gelijkwaardige paden wijzigen. Om deze wijziging te maken, moet u de opdracht Maximum-Path Path opnemen onder de BGP-configuratie. Gebruik een getal tussen 1 en 6 voor het argument paden.
Netwerkdiagram
In deze sectie wordt gebruik gemaakt van de volgende netwerkinstellingen:
Configuraties
In deze sectie worden de volgende configuraties gebruikt:
RouterA
interface Loopback0 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.255 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip address 10.20.20.1 255.255.255.0 ! ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0 ! ! router bgp 11 neighbor 10.20.20.2 remote-as 10 neighbor 10.10.10.2 remote-as 10 network 192.168.1.1 mask 255.255.255.255 maximum-paths 2 !--- This command specifies the maximum number of paths to install in the routing table for a specific destination.
RouterB
interface GigabitEthernet0/2 ip address 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip address 10.20.20.2 255.255.255.0 ! ! router bgp 10 neighbor 10.20.20.1 remote-as 11 network 172.16.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0
RouterC
interface GigabitEthernet0/2 ip address 172.16.2.2 255.255.255.0 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.0 ! ! router bgp 10 neighbor 10.10.10.1 remote-as 11 network 172.16.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0
Verifiëren
Gebruik dit gedeelte om te bevestigen dat uw configuratie correct werkt.
De Cisco CLI Analyzer (alleen geregistreerde klanten) ondersteunt bepaalde show-opdrachten. Gebruik de Cisco CLI Analyzer om een analyse van show opdrachtoutput te bekijken.
De output van het showip routebevel toont beide wegen aan het 172.16.2.0 netwerk door BGP worden geleerd. De output van het traceroute bevel wijst op de lading wordt verdeeld tussen twee seriële verbindingen. In dit scenario vindt het delen van de lading plaats per bestemming. Het opdracht show ip bgp geeft de geldige vermeldingen voor het 172.16.2.0-netwerk.
RouterA#show ip route Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP a - application route + - replicated route, % - next hop override, p - overrides from PfR Gateway of last resort is not set 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 2 masks C 10.10.10.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 L 10.10.10.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 C 10.20.20.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0 L 10.20.20.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0 172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets B 172.16.2.0 [20/0] via 10.20.20.2, 00:08:51 [20/0] via 10.10.10.2, 00:08:51 192.168.1.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets C 192.168.1.1 is directly connected, Loopback0RouterA#traceroute 172.16.2.2 source loopback0 Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to 172.16.2.2 VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id) 1 10.10.10.2 3 msec 10.20.20.2 3 msec 10.10.10.2 3 msec RouterA#RouterA#show ip bgp BGP table version is 4, local router ID is 192.168.1.1 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, t secondary path, Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *m 172.16.2.0/24 10.10.10.2 0 0 10 i *> 10.20.20.2 0 0 10 i *> 192.168.1.1/32 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
Problemen oplossen
Er is momenteel geen specifieke informatie beschikbaar om deze configuratie problemen op te lossen.
Het delen van de lading wanneer dubbel-Homed aan één ISP door Veelvoudige Lokale Routers
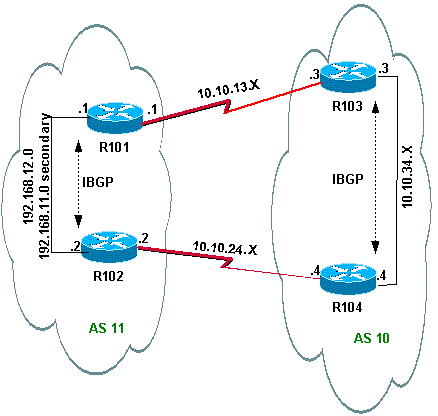
Dit scenario toont hoe u werklastverdeling kunt bereiken wanneer er meerdere verbindingen met dezelfde ISP zijn via meerdere lokale routers. De twee eBGP-peers worden op twee afzonderlijke lokale routers beëindigd. Taakverdeling op de twee koppelingen is niet mogelijk omdat BGP de beste single path kiest uit de netwerken die van eBGP en interne BGP zijn geleerd (iBGP). Taakverdeling tussen de meerdere paden naar AS 10 is de best mogelijke optie. Met dit type van lading het delen, reist het verkeer naar specifieke netwerken, op basis van vooraf bepaald beleid, door beide verbindingen. Daarnaast fungeert elke link als een back-up van de andere link, voor het geval dat één link mislukt.
Ga voor eenvoud ervan uit dat het BGP-routeringsbeleid voor AS1 als volgt is:
-
AS11 accepteert de lokale routes vanaf AS10, samen met een standaard voor de rest van de internetroutes.
-
Het uitgaande verkeersbeleid is:
-
Al het verkeer dat vanaf R101 voor het internet bestemd is, verloopt via de R101-R103-link.
-
Als de koppeling R101-R103 mislukt, gaat al het verkeer naar het internet van R101 door R102 naar AS 10.
-
Op dezelfde manier gaat al het verkeer dat vanaf R102 naar internet gaat door de R102-R104-link.
-
Als de koppeling R102-R104 mislukt, gaat al het verkeer naar het internet van R102 door R101 naar AS 10.
-
-
Het inkomende verkeersbeleid is:
-
Het verkeer dat is bestemd voor het netwerk 192.168.11.0/24 van het internet komt van de R103-R101 link.
-
Het verkeer dat is bestemd voor het netwerk 192.168.12.0/24 van het internet komt van de R104-R102 link.
-
Als één link naar AS 10 mislukt, routeert de andere link het verkeer dat bestemd is voor alle netwerken terug naar AS 11 vanaf het internet.
-
Om dit te bereiken, wordt 192.168.11.0 aangekondigd van R101 tot R103 met een kortere AS_PATH dan aangekondigd van R102 tot R104. AS 10 vindt het beste pad door de R103-R101 link. Ook 192.168.12.0 wordt aangekondigd met een korter pad door de R102-R104 link. AS 10 geeft de voorkeur aan de R104-R102-koppeling voor verkeer dat is gebonden aan 192.168.12.0 in AS 11.
Voor uitgaand verkeer bepaalt BGP het beste pad op basis van routes die door eBGP zijn geleerd. Deze routes zijn te verkiezen boven routes die door iBGP worden geleerd. Zo leert R101 10.10.34.0 van R103 door eBGP en van R102 door iBGP. Het externe pad wordt over het interne pad geselecteerd. Als u de BGP tabel in de R101 configuratie bekijkt, zou de route naar 10.10.34.0 door de R101-R103 link, met de volgende hop 10.10.13.3 zijn. Op R102 loopt de route naar 10.10.34.0 via de koppeling R102-R104, met de volgende hop 10.10.24.4. Dit bereikt lastverdeling voor verkeer bestemd voor 10.10.34.0. Een soortgelijke reden geldt voor de standaardroutes op R101 en R102. Zie BGP-algoritme voor beste padselectie voor meer informatie over de BGP-padselectiecriteria.
Netwerkdiagram
In deze sectie wordt gebruik gemaakt van de volgende netwerkinstellingen:
Configuraties
In deze sectie worden de volgende configuraties gebruikt:
R101 NL
hostname R101 ! interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0 secondary ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Serial8/0 ip address 10.10.13.1 255.255.255.0 ! router bgp 11 no synchronization bgp log-neighbor-changes network 192.168.11.0 network 192.168.12.0 neighbor 10.10.13.3 remote-as 10 neighbor 10.10.13.3 route-map R101-103-MAP out !--- The AS_PATH is increased for 192.168.12.0. neighbor 192.168.12.2 remote-as 11 neighbor 192.168.12.2 next-hop-self maximum-paths 2 no auto-summary ! access-list 1 permit 192.168.12.0 access-list 2 permit 192.168.11.0 route-map R101-103-MAP permit 10 match ip address 1 set as-path prepend 11 11 11 ! route-map R101-103-MAP permit 20 match ip address 2
R102 NL
hostname R102 ! interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 192.168.11.2 255.255.255.0 secondary ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0 ! interface Serial8/0 ip address 10.10.24.2 255.255.255.0 ! router bgp 11 no synchronization bgp log-neighbor-changes network 192.168.11.0 network 192.168.12.0 neighbor 10.10.24.4 remote-as 10 neighbor 10.10.24.4 route-map R102-104-MAP out !--- The AS_PATH is increased for 192.168.11.0. neighbor 192.168.12.1 remote-as 11 neighbor 192.168.12.1 next-hop-self no auto-summary ! access-list 1 permit 192.168.11.0 access-list 2 permit 192.168.12.0 route-map R102-104-MAP permit 10 match ip address 1 set as-path prepend 11 11 11 ! route-map R102-104-MAP permit 20 match ip address 2
R103 NL
hostname R103 ! interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 10.10.34.3 255.255.255.0 ! interface Serial8/0 ip address 10.10.13.3 255.255.255.0 ! router bgp 10 no synchronization bgp log-neighbor-changes network 10.10.34.0 mask 255.255.255.0 neighbor 10.10.13.1 remote-as 11 neighbor 10.10.13.1 default-originate neighbor 10.10.34.4 remote-as 10 neighbor 10.10.34.4 next-hop-self no auto-summary
R104 +
hostname R104 ! interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 10.10.34.4 255.255.255.0 ! interface Serial8/0 ip address 10.10.24.4 255.255.255.0 ! router bgp 10 no synchronization bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 10.10.24.2 remote-as 11 neighbor 10.10.24.2 default-originate neighbor 10.10.34.3 remote-as 10 neighbor 10.10.34.3 next-hop-self no auto-summary
Verifiëren
Deze sectie bevat informatie over de manier waarop u kunt controleren of de configuratie goed werkt.
Bepaalde show commando's worden ondersteund door de Cisco CLI Analyzer (alleen geregistreerde klanten) , waarmee u een analyse van de show opdrachtoutput kunt bekijken.
Verificatie wanneer zowel de koppelingen tussen AS 11 en AS 10 omhoog zijn
Verificatie van uitgaand verkeer
Opmerking: het groter-dan-teken (>) in de opdrachtoutput van show-ip bgp vertegenwoordigt het beste pad dat voor dat netwerk moet worden gebruikt tussen de mogelijke paden. Raadpleeg de sectie BGP-algoritme voor selectie van het beste pad voor meer informatie.
De BGP-tabel in R101 toont dat het beste pad voor al het uitgaande verkeer naar internet via de R101-R103-link verloopt. De uitvoer van het routebevel van de show ip bevestigt de routes in de routeringstabel.
R101#show ip bgp BGP table version is 5, local router ID is 192.168.12.1 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path * i0.0.0.0 192.168.12.2 100 0 10 i *> 10.10.13.3 0 10 i !--- This is the next hop of R103. * i10.10.34.0/24 192.168.12.2 100 0 10 i *> 10.10.13.3 0 0 10 i !--- This is the next hop of R103. * i192.168.11.0 192.168.12.2 0 100 0 i *> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i * i192.168.12.0 192.168.12.2 0 100 0 i *> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i R101#show ip route !--- Output suppressed.
Gateway of last resort is 10.10.13.3 to network 0.0.0.0 C 192.168.12.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0 C 192.168.11.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0 10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets C 10.10.13.0 is directly connected, Serial8/0 B 10.10.34.0 [20/0] via 10.10.13.3, 00:08:53 !--- This is the next hop of R103.
B* 0.0.0.0/0 [20/0] via 10.10.13.3, 00:08:53 !--- This is the next hop of R103.
Hier zijn de BGP- en routeringstabellen voor R102. Op basis van het beleid wordt in R102 al het verkeer door de R102-R104-link naar AS 10 geleid:
R102#show ip bgp BGP table version is 7, local router ID is 192.168.12.2 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 0.0.0.0 10.10.24.4 0 10 i !--- This is the next hop of R104.
* i 192.168.12.1 100 0 10 i *> 10.10.34.0/24 10.10.24.4 0 10 i !--- This is the next hop of R104.
* i 192.168.12.1 0 100 0 10 i * i192.168.11.0 192.168.12.1 0 100 0 i *> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i * i192.168.12.0 192.168.12.1 0 100 0 i *> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i R102#show ip route !--- Output suppressed.
Gateway of last resort is 10.10.24.4 to network 0.0.0.0 C 192.168.12.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0 C 192.168.11.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0 10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets C 10.10.24.0 is directly connected, Serial8/0 B 10.10.34.0 [20/0] via 10.10.24.4, 00:11:21 !--- This is the next hop of R104.
B* 0.0.0.0/0 [20/0] via 10.10.24.4, 00:11:21 !--- This is the next hop of R104.
Verificatie van inkomend verkeer van AS 10 naar AS 11
De netwerken 192.168.11.0 en 192.168.12.0 behoren tot AS 11. Op basis van het beleid geeft AS 11 de voorkeur aan de R103-R101-link voor verkeer dat bestemd is voor het netwerk 192.168.11.0 en de R104-R102-link voor verkeer dat bestemd is voor het netwerk 192.168.12.0.
R103#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 4, local router ID is 10.10.34.3
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 10.10.34.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 192.168.11.0 10.10.13.1 0 0 11 i
!--- The next hop is R101.
* 192.168.12.0 10.10.13.1 0 0 11 11 11 11 i
*>i 10.10.34.4 0 100 0 11 i
!--- The next hop is R104.
R103#show ip route
!--- Output suppressed.
Gateway of last resort is not set
B 192.168.12.0/24 [200/0] via 10.10.34.4, 00:04:46
!--- The next hop is R104.
B 192.168.11.0/24 [20/0] via 10.10.13.1, 00:04:46
!--- The next hop is R101.
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets
C 10.10.13.0 is directly connected, Serial8/0
C 10.10.34.0 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
Het beste pad voor netwerk 192.168.11.0 op R103 is via de R103-R101 link, en het beste pad voor netwerk 192.168.12.0 loopt door R104 naar AS 11. In dit geval bepaalt de kortste pad lengte het beste pad.
Op dezelfde manier lijkt de BGP- en routeringstabel op de R104 op dit:
R104#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 13, local router ID is 10.10.34.4
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i10.10.34.0/24 10.10.34.3 0 100 0 i
*>i192.168.11.0 10.10.34.3 0 100 0 11 i
* 10.10.24.2 0 0 11 11 11 11 i
*> 192.168.12.0 10.10.24.2 0 0 11 i
R104#show ip route
!--- Output suppressed.
Gateway of last resort is not set
B 192.168.12.0/24 [20/0] via 10.10.24.2, 00:49:06
!--- The next hop is R102.
B 192.168.11.0/24 [200/0] via 10.10.34.3, 00:07:36
!--- The next hop is R103.
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets
C 10.10.24.0 is directly connected, Serial8/0
C 10.10.34.0 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
Verificatie wanneer link naar R101-R103 mislukt
Wanneer de R101-R103-link mislukt, moet alle verkeer door R102 worden omgeleid. In dit diagram wordt deze verandering geïllustreerd:
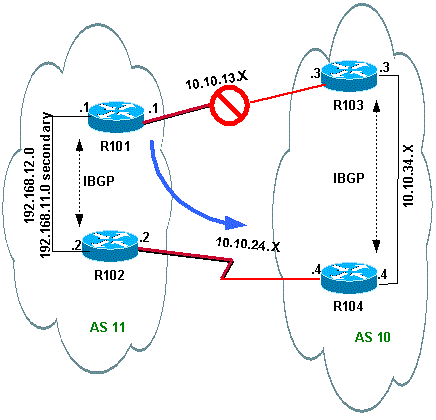
Schakel de koppeling R103-R101 op R103 uit om deze situatie te simuleren.
R103(config)#interface serial 8/0 R103(config-if)#shutdown *May 1 00:52:33.379: %BGP-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor 10.10.13.1 Down Interface flap *May 1 00:52:35.311: %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Serial8/0, changed state to administratively down *May 1 00:52:36.127: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial8/0, changed state to down
Controleer de uitgaande route naar AS 10.
R101#show ip bgp BGP table version is 17, local router ID is 192.168.12.1 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *>i0.0.0.0 192.168.12.2 100 0 10 i !--- This is the next hop of R102.
*>i10.10.34.0/24 192.168.12.2 100 0 10 i
!--- This is the next hop of R102.
* i192.168.11.0 192.168.12.2 0 100 0 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* i192.168.12.0 192.168.12.2 0 100 0 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
R101#show ip route
!--- Output suppressed.
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.12.2 to network 0.0.0.0
C 192.168.12.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
C 192.168.11.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 10.10.34.0 [200/0] via 192.168.12.2, 00:01:34
B* 0.0.0.0/0 [200/0] via 192.168.12.2, 00:01:34
!--- All outbound traffic goes through R102.
R102#show ip route
!--- Output suppressed.
Gateway of last resort is 10.10.24.4 to network 0.0.0.0
C 192.168.12.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
C 192.168.11.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets
C 10.10.24.0 is directly connected, Serial8/0
B 10.10.34.0 [20/0] via 10.10.24.4, 00:13:22
B* 0.0.0.0/0 [20/0] via 10.10.24.4, 00:55:22
!--- All outbound traffic on R102 goes through R104.
Controleer de inkomende verkeersroute wanneer R101-R103 is ingedrukt.
R103#show ip bgp BGP table version is 6, local router ID is 10.10.34.3 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 10.10.34.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i *>i192.168.11.0 10.10.34.4 0 100 0 11 11 11 11 i *>i192.168.12.0 10.10.34.4 0 100 0 11 i R103#show ip route !--- Output suppressed.
Gateway of last resort is not set
B 192.168.12.0/24 [200/0] via 10.10.34.4, 00:14:55
!--- The next hop is R104.
B 192.168.11.0/24 [200/0] via 10.10.34.4, 00:05:46
!--- The next hop is R104.
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 10.10.34.0 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
Op de R104 gaat het verkeer voor 192.168.11.0 en 192.168.12.0 door de R104-R102 verbinding.
R104#show ip route !--- Output suppressed.
Gateway of last resort is not set
B 192.168.12.0/24 [20/0] via 10.10.24.2, 00:58:35
!--- The next hop is R102.
B 192.168.11.0/24 [20/0] via 10.10.24.2, 00:07:57
!--- The next hop is R102.
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets
C 10.10.24.0 is directly connected, Serial8/0
C 10.10.34.0 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
Problemen oplossen
Er is momenteel geen specifieke informatie beschikbaar om deze configuratie problemen op te lossen.
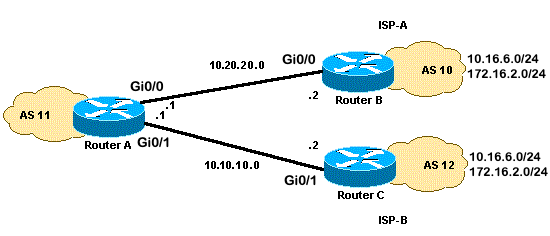
Het delen van de lading wanneer multihomed aan twee ISPs door één enkele lokale router
In dit scenario is taakverdeling geen optie in een multihomed omgeving, zodat u alleen taakverdeling kunt uitvoeren. U kunt geen taakverdeling uitvoeren omdat BGP slechts één optimaal pad naar een bestemming selecteert onder de BGP-routes die van de verschillende AS’s zijn geleerd. Het idee is om een betere metriek voor de routes in de waaier 1.0.0.x aan 128.0.0.x te plaatsen die van ISP (A) en betere metriek voor de rest routes worden geleerd die van ISP (B) worden geleerd. Het netwerkdiagram is een voorbeeld.
Raadpleeg Monsterconfiguratie voor BGP met twee verschillende serviceproviders (Multihoming) voor aanvullende informatie.
Netwerkdiagram
In deze sectie wordt gebruik gemaakt van de volgende netwerkinstellingen:
Configuraties
In deze sectie worden de volgende configuraties gebruikt:
RouterA
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 10.20.20.1 255.255.255.0
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0
router bgp 11
neighbor 10.20.20.2 remote-as 10
neighbor 10.20.20.2 route-map UPDATES-1 in
!--- This allows only the networks up to 128.0.0.x.
neighbor 10.10.10.2 remote-as 12
neighbor 10.10.10.2 route-map UPDATES-2 in
!--- This allows anything above the 128.0.0.x network.
route-map UPDATES-1 permit 10
match ip address 1
set weight 100
route-map UPDATES-1 permit 20
match ip address 2
route-map UPDATES-2 permit 10
match ip address 1
route-map UPDATES-2 permit 20
match ip address 2
set weight 100
access-list 1 permit 0.0.0.0 127.255.255.255
access-list 2 deny 0.0.0.0 127.255.255.255
access-list 2 permit any
RouterB
interface GigabitEthernet0/2 ip address 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0
interface GigabitEthernet0/3 ip address 10.16.6.1 255.255.255.0 interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip address 10.20.20.2 255.255.255.0 router bgp 10 neighbor 10.20.20.1 remote-as 11 network 172.16.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 10.16.6.0 mask 255.255.255.0
RouterC
interface GigabitEthernet0/3 ip address 10.16.6.2 255.255.255.0 interface GigabitEthernet0/2 ip address 172.16.2.2 255.255.255.0 interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.0 router bgp 12 neighbor 10.10.10.1 remote-as 11 network 172.16.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 10.16.6.0 mask 255.255.255.0
Verifiëren
Gebruik dit gedeelte om te bevestigen dat uw configuratie correct werkt.
De Cisco CLI Analyzer (alleen geregistreerde klanten) ondersteunt bepaalde show-opdrachten. Gebruik de Cisco CLI Analyzer om een analyse van show opdrachtoutput te bekijken.
De output van het bevel van de show ip route en de output van het traceroute bevel tonen om het even welk netwerk lager dan 128.0.0.x verlaten RouterA door 10.20.20.2. Deze route is de volgende hop uit seriële interface 0. De rest van de netwerken gaat door 10.10.10.2, wat de volgende hop uit seriële 1 interface is.
RouterA#show ip route
!--- Output suppressed.
Gateway of last resort is not set
B 172.16.2.0/24 [20/0] via 10.10.10.2, 00:13:16
!--- This is the next hop out through GigabitEthernet0/0.
B 10.16.6.0/24 [20/0] via 10.20.20.2, 00:13:16 !--- This is the next hop out through GigabitEthernet0/1.
!--- Output suppressed.RouterA#show ip cef 172.16.2.0 172.16.2.0/24 nexthop 10.10.10.2 GigabitEthernet0/1 RouterA#show ip cef 10.16.6.0 10.16.6.0/24 nexthop 10.20.20.2 GigabitEthernet0/0RouterA#show ip bgp BGP table version is 10, local router ID is 192.168.1.1 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, t secondary path, Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 10.16.6.0/24 10.20.20.2 0 100 10 i * 10.10.10.2 0 0 12 i * 172.16.2.0/24 10.20.20.2 0 0 10 i *> 10.10.10.2 0 100 12 i *> 192.168.1.1/32 0.0.0.0 0 32768 iRouterA#traceroute 172.16.2.1 source loopback0 Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to 172.16.2.1 VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id) 1 10.10.10.2 2 msec 3 msec 2 msec 2 172.16.2.1 [AS 12] 3 msec 3 msec * RouterA#traceroute 10.16.6.1 source loopback0 Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to 10.16.6.1 VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id) 1 10.20.20.2 3 msec 2 msec * RouterA#
Problemen oplossen
Er is momenteel geen specifieke informatie beschikbaar om deze configuratie problemen op te lossen.
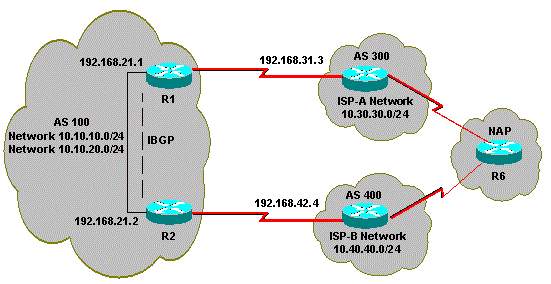
Het delen van de lading wanneer multihomed aan twee ISPs door Veelvoudige Lokale Routers
Taakverdeling is niet mogelijk in een omgeving met meerdere deelnemers en twee ISP’s. BGP selecteert alleen het beste pad naar een bestemming tussen de BGP-paden die van verschillende AS's zijn geleerd, waardoor taakverdeling onmogelijk is. Maar load sharing is mogelijk in zulke multihomed BGP-netwerken. Op basis van vooraf bepaald beleid wordt de verkeersstroom bepaald met verschillende BGP-kenmerken.
In deze sectie worden de meerlaagse configuraties besproken die het meest worden gebruikt. De configuratie toont hoe u werklastverdeling kunt realiseren. Zie het Netwerkdiagram, waarin multihome van AS100 betrouwbaarheid en werklastverdeling bereikt.
Opmerking: de IP-adressen in dit voorbeeld voldoen aan de RFC 1918-standaarden voor Private Address Space.
Ga voor eenvoud ervan uit dat het BGP-routeringsbeleid voor AS 100 als volgt is:
-
AS100 accepteert de lokale routes van beide providers, samen met een default voor de andere internetroutes.
-
Het uitgaande verkeersbeleid is:
-
Het verkeer naar AS 300 gaat door de R1-ISP(A) link.
-
Het verkeer naar AS 400 gaat door de R2-ISP(B) link.
-
Al het andere verkeer geeft de voorkeur aan standaardroute 0.0.0 via de R1-ISP(A) link.
-
Als de koppeling R1-ISP(A) mislukt, gaat al het verkeer door de koppeling R2-ISP(B).
-
-
Het inkomende verkeersbeleid is:
-
Het verkeer dat bestemd is voor het netwerk 10.10.10.0/24 van het internet komt van de ISP(A)-R1 link.
-
Het verkeer dat bestemd is voor het netwerk 10.10.20.0/24 van het internet komt van de ISP(B)-R2-link.
-
Als één ISP ontbreekt, leidt andere ISP verkeer terug naar AS 100 van Internet voor alle netwerken.
-
Netwerkdiagram
In deze sectie wordt gebruik gemaakt van de volgende netwerkinstellingen:
Configuraties
In deze sectie worden de volgende configuraties gebruikt:
V2
interface Ethernet0 ip address 192.168.21.2 255.255.255.0 ! interface Serial0 ip address 192.168.42.2 255.255.255.0 router bgp 100 no synchronization bgp log-neighbor-changes !--- The next two lines announce the networks to BGP peers. network 10.10.10.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 10.10.20.0 mask 255.255.255.0 !--- The next line configures iBGP on R1. neighbor 192.168.21.1 remote-as 100 neighbor 192.168.21.1 next-hop-self !--- The next line configures eBGP with ISP(B). neighbor 192.168.42.4 remote-as 400 !--- This is the incoming policy route map for the application of attributes to specific routes. neighbor 192.168.42.4 route-map AS-400-INCOMING in !--- This is the outgoing policy route map for the application of attributes to specific routes. neighbor 192.168.42.4 route-map AS-400-OUTGOING out no auto-summary !--- This line sets the AS path access list, it permits all routes within the routing domain of the provider. ip as-path access-list 1 permit ^400$ !--- These two lines set the access list. access-list 10 permit 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255 access-list 20 permit 10.10.20.0 0.0.0.255 !--- The next three lines configure LOCAL_PREF for routes that match AS path access list 1. route-map AS-400-INCOMING permit 10 match as-path 1 set local-preference 150 !--- Here, the route map prepends AS 100 to BGP updates for networks that are permitted by access list 10. route-map AS-400-OUTGOING permit 10 match ip address 10 set as-path prepend 100 !--- This line announces the network that is permitted by access list 20 without any changes in BGP attributes. route-map AS-400-OUTGOING permit 20 match ip address 20
R1
interface Serial0/0 ip address 192.168.31.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet1/0 ip address 192.168.21.1 255.255.255.0 ! router bgp 100 no synchronization bgp log-neighbor-changes network 10.10.10.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 10.10.20.0 mask 255.255.255.0 !--- IBGP peering with R2
neighbor 192.168.21.2 remote-as 100 neighbor 192.168.21.2 next-hop-self !--- This line sets eBGP peering with ISP(A). neighbor 192.168.31.3 remote-as 300 !--- This is the incoming policy route map for the application of attributes to specific routes. neighbor 192.168.31.3 route-map AS-300-INCOMING in !--- This is the outgoing policy route map for the application of attributes to specific routes. neighbor 192.168.31.3 route-map AS-300-OUTGOING out no auto-summary !--- This line sets the AS path access list, it permits all routes within the routing domain of the provider. ip as-path access-list 1 permit ^300$ !--- These two lines set the IP access list. access-list 10 permit 10.10.20.0 0.0.0.255 access-list 20 permit 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255 !--- The next three lines configure LOCAL_PREF for routes that match AS path access list 1. route-map AS-300-INCOMING permit 10 match as-path 1 set local-preference 200 !--- Here, the route map prepends AS 100 to BGP updates for networks that are permitted by access list 10. route-map AS-300-OUTGOING permit 10 match ip address 10 set as-path prepend 100 !--- This line announces the network that is permitted by access list 20 without any changes in BGP attributes. route-map AS-300-OUTGOING permit 20 match ip address 20 !
Verifiëren
Gebruik dit gedeelte om te bevestigen dat uw configuratie correct werkt.
De Cisco CLI Analyzer (alleen geregistreerde klanten) ondersteunt bepaalde show-opdrachten. Gebruik de Cisco CLI Analyzer om een analyse van show opdrachtoutput te bekijken.
Geef het showip bgp-bevel uit om te verifiëren dat het uitgaande/inkomende beleid werkt.
Opmerking: het grotere dan-teken (>) in de output van ip bgp vertegenwoordigt het beste pad dat voor dat netwerk moet worden gebruikt tussen de mogelijke paden. Raadpleeg de sectie BGP-algoritme voor selectie van het beste pad voor meer informatie.
R1#show ip bgp BGP table version is 6, local router ID is 192.168.31.1 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete BGP table version is 6, local router ID is 192.168.31.1 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 0.0.0.0 192.168.31.3 200 0 300 i !--- This line shows that the default route 0.0.0.0/0 is preferred through AS 300, ISP(A).
* i10.10.10.0/24 192.168.21.2 0 100 0 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* i10.10.20.0/24 192.168.21.2 0 100 0 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 10.30.30.0/24 192.168.31.3 0 200 0 300 i
*>i10.40.40.0/24 192.168.21.2 0 150 0 400 i
!--- The route to network 10.30.30.0/24 (AS 300) is preferred through the R1-ISP(A) link.
!--- The route to network 10.40.40.0/24 (AS 400) is preferred through the R2-ISP(B) link.
Bekijk nu de ip bgp uitvoer op R2:
R2#show ip bgp BGP table version is 8, local router ID is 192.168.42.2 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path * 0.0.0.0 192.168.42.4 150 0 400 i *>i 192.168.21.1 200 0 300 i !--- This line shows that the default route 0.0.0.0/0 is preferred through AS 300, through the R2-ISP(B) link.
*> 10.10.10.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* i 192.168.21.1 0 100 0 i
*> 10.10.20.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* i 192.168.21.1 0 100 0 i
*>i10.30.30.0/24 192.168.21.1 0 200 0 300 i
*> 10.40.40.0/24 192.168.42.4 0 150 0 400 i !--- The route to network 10.30.30.0/24 (AS 300) is preferred through the R1-ISP(A) link.
!--- The route to network 10.40.40.0/24 (AS 400) is preferred through the R2-ISP(B) link.
Geef het showip bgp-bevel op router 6 uit om het inkomende beleid voor netwerken 10.10.10.0/24 en 10.10.20.0/24 waar te nemen:
R6#show ip bgp BGP table version is 15, local router ID is 192.168.64.6 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 10.10.10.0/24 192.168.63.3 0 300 100 100 i !--- This line shows that network 10.10.10.0/24 is routed through AS 300
!--- with the ISP(A)-R1 link.
* 192.168.64.4 0 400 100 100 100 i
* 10.10.20.0/24 192.168.63.3 0 300 100 100 i
*> 192.168.64.4 0 400 100 i
!--- This line shows that network 10.10.20.0/24 is routed through AS 400
!--- with the ISP(B)-R2 link.
*> 10.30.30.0/24 192.168.63.3 0 0 300 i
*> 10.40.40.0/24 192.168.64.4 0 0 400 i
Sluit de R1-ISP(A) link op R1 en neem de BGP-tabel in acht. Verwacht dat al het verkeer naar internet door de R2-ISP(B) link wordt geleid:
R1(config)#interface serial 0/0 R1(config-if)#shutdown *May 2 19:00:47.377: %BGP-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor 192.168.31.3 Down Interface flap *May 2 19:00:48.277: %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Serial0/0, changed state to administratively down *May 23 12:00:51.255: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0, changed state to down R1#show ip bgp BGP table version is 12, local router ID is 192.168.31.1 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *>i0.0.0.0 192.168.21.2 150 0 400 i !--- The best default path is now through the R2-ISP(B) link.
* i10.10.10.0/24 192.168.21.2 0 100 0 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* i10.10.20.0/24 192.168.21.2 0 100 0 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*>i10.40.40.0/24 192.168.21.2 0 150 0 400 i
R2#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 14, local router ID is 192.168.42.2 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 0.0.0.0 192.168.42.4 150 0 400 i !--- The best default route is now through ISP(B) with a local preference of 150.
* i10.10.10.0/24 192.168.21.1 0 100 0 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* i10.10.20.0/24 192.168.21.1 0 100 0 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 10.40.40.0/24 192.168.42.4 0 150 0 400 i
Bekijk de route voor netwerk 10.10.10.0/24 in router 6:
R6#show ip bgp BGP table version is 14, local router ID is 192.168.64.6 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 10.10.10.0/24 192.168.64.4 0 400 100 100 i !--- Network 10.10.10.0 is reachable through ISP(B), which announced the network with AS path prepend.
*> 10.10.20.0/24 192.168.64.4 0 400 100 i
*> 10.30.30.0/24 192.168.63.3 0 0 300 i
*> 10.40.40.0/24 192.168.64.4 0 0 400 i
Problemen oplossen
Er is momenteel geen specifieke informatie beschikbaar om deze configuratie problemen op te lossen.
Gerelateerde informatie
- BGP multi-homing: ontwerp en probleemoplossing - video van live webcast
- BGP Multi-homing: Ontwerp en Problemen oplossen - Vragen en antwoorden via live Webcast
- Hoe werkt taakverdeling?
- Monsterconfiguratie voor BGP met twee verschillende serviceproviders (Multihoming)
- Hoe BGP-routers de Multi-Exit Discriminator gebruiken voor de beste padselectie
- Ondersteuning van IP-routingtechnologie
- Technische ondersteuning en documentatie – Cisco Systems
Revisiegeschiedenis
| Revisie | Publicatiedatum | Opmerkingen |
|---|---|---|
3.0 |
30-Aug-2023 |
Bijgewerkte Titel, Achtergrond Informatie, Stijlvereisten en het Opmaken. |
2.0 |
21-Jul-2022 |
Hercertificering |
1.0 |
10-Dec-2001 |
Eerste vrijgave |
Bijgedragen door Cisco-engineers
- Julio JimenezCisco Project Manager
Contact Cisco
- Een ondersteuningscase openen

- (Vereist een Cisco-servicecontract)
 Feedback
Feedback