QoS を実装した PPP リンク上での VoIP(LLQ / IP RTP プライオリティ、LFI、cRTP)
内容
概要
この設定例では、低帯域幅の専用回線構成での Point to Point Protocol(PPP)による VoIP について説明します。このドキュメントには、機能の設定、設計ガイドライン、基本的な検証とトラブルシューティングの方法についての技術的な背景情報が記載されています。
注:次の設定では、2台のルータが専用回線を介してバックツーバックで接続されていることに注意してください。ただし、ほとんどのトポロジでは、音声対応ルータを任意の場所に配置できます。通常、音声ルータは LAN 接続を使用して、WAN に接続されている他のルータに接続します(すなわち、PPP 専用回線)。 音声ルータが専用回線上での PPP を介して直接接続されていない場合は、下記の設定に示されているように、すべての WAN 設定コマンドを、音声ルータではなく WAN に接続されているルータに設定する必要があるため、この点が重要となります。
前提条件
要件
このドキュメントに特有の要件はありません。
使用するコンポーネント
このドキュメントに記載されている設定は、次の機器でテストされています。
-
Cisco IOS(R) ソフトウェア リリース 12.2.6a(IP Plus)が動作している Cisco 3640 ルータ 2 台
-
IP RTP プライオリティは、Cisco IOS リリース 12.0(5)T で導入されています。
-
LLQ は、Cisco IOS リリース 12.0(7)T で導入されています。
-
LFI は、Cisco IOS リリース 11.3 で導入されています。
-
Cisco IOS リリース 12.0.5T 以降では cRTP の大幅なパフォーマンス改善がなされました。
表記法
ドキュメント表記の詳細は、「シスコ テクニカル ティップスの表記法」を参照してください。
PPP リンクでの VoIP に関する QoS の設計ガイドライン
このセクションでは、PPP専用回線でVoIPを設定するための設計ガイドラインを示します(低速リンクを強調します)。 良好な音声品質を得るためには、次の 2 つの基本的な要件があります。
-
最小のエンドツーエンド遅延とジッタ回避(遅延変動)。
-
リンク帯域幅要件の最適化と適切な設計
上記の要件を保証するために、従うべき重要なガイドラインがいくつかあります。
| ガイドライン | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 音声トラフィックの完全な優先権(IP RTP プライオリティまたは LLQ) | 音声トラフィックに完全な優先権を与える方法 |
| Link Fragmentation and Interleaving(LFI; リンク断片化およびインターリービング) | 低速の回線にはたいていの場合必須。 |
| RTP 圧縮 | 良好な音声品質を得るためには不要ですが、コールによる帯域幅の消費を抑制できます。RTP 圧縮に関する一般的なアドバイスとして、RTP 圧縮は、良好な音声品質が得られる動作状態が整った後で適用するようにします(トラブルシューティングを簡単にするため)。 |
| コール アドミッション制御(CAC) | この文書では説明していません。CAC は、リンク上で確立可能なコール数を制御するために使用します。たとえば、2 つのゲートウェイ間の WAN リンクで VoIP コールを 2 回だけ伝送できる場合、3 回目のコールを許可すると、3 コールすべての音声品質が低下する可能性があります。詳細については、次のドキュメントを参照してください。VoIP のコール アドミッション制御 |
要するに、音声トラフィックを唯一のソースとしてみた場合、ルータまたはゲートウェイを備えた低速の PPP 回線を使用するには、次の 2 つの機能が必須になります。
-
音声トラフィックに対する完全な優先権
-
Link Fragmentation and Interleaving(LFI; リンク断片化およびインターリービング)
音声トラフィックの完全な優先権(IP RTP プライオリティまたは LLQ)
Cisco IOSソフトウェアリリース12.2では、音声トラフィックに完全優先を提供する主な方法が2つあります。
-
IP RTP プライオリティ(別名 PQ/WFQ:Priority Queue / Weighted Fair Queuing)
-
低遅延キューイング(別名PQ/CBWFQ:プライオリティ キュー/クラスベース均等化キューイング)。
IP RTP プライオリティ
IP RTPプライオリティは、ユーザデータグラムプロトコル(UDP)宛先ポートの範囲に属する一連のRTPパケットフローに対して、完全優先キューを作成します。実際に使用されるポートはエンドデバイスまたはゲートウェイの間でダイナミックにネゴシエートされますが、Cisco VoIP 製品はすべて同じ UDP ポート範囲(16384~32767)を利用します。 ルータが VoIP トラフィックを認識すると、そのトラフィックを完全プライオリティ キューに入れます。プライオリティ キューが空のときは、標準の Weighted Fair Queuing(WFQ; 均等化キューイング)に従って他のキューが処理されます。IP RTP プライオリティは、インターフェイスで輻輳が発生しない限りアクティブにはなりません。次の図は IP RTP プライオリティの動作の仕組みを示しています。
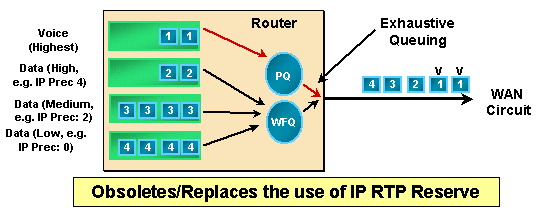
注:IP RTPプライオリティでは、デフォルトキュー(WFQ)に使用可能な帯域幅がある場合はプライオリティキュー(PQ)のバーストが許可されますが、インターフェイスに輻輳がある場合はプライオリティキューの内容を厳密にポリシングします。
低遅延キューイング
LLQは、クラスベース重み付け均等化キューイング(CBWFQ)に対して完全PQを提供する機能です。LLQ を使用すると、クラス レベルの CBWFQ 内に完全 PQ が 1 つ作成されます。LLQ では、(PQ 内にある)遅延に影響されやすいデータが最初に取り出され、送信されます。LLQ 実装を備えた VoIP では、音声トラフィックが完全 PQ に入れられます。
PQ は均等化キューが帯域幅不足に陥らないようにポリシングされます。PQ を設定するときには、その PQ で使用できる帯域幅の最大量を Kbps で指定します。インターフェイスで輻輳が発生すると、負荷が priority コマンドで設定された Kbps 値に達するまで PQ の処理は続けられます。下位のプライオリティ キューが処理されなくなるという、シスコの従来のプライオリティ グループ機能の問題を避けるために、超過トラフィックは廃棄されます。
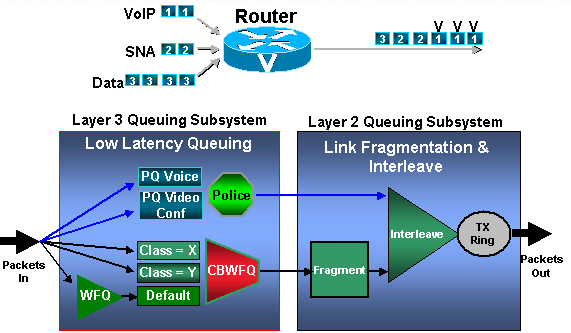
この方法は IP RTP プライオリティよりも複雑ですが、より柔軟な制御が可能です。どちらの方法を選択するかは、実際のネットワークでのトラフィック パターンと実際のニーズに基づきます。
LLQ と IP RTP プライオリティ
次の表は、LLQとIP RTPプライオリティの主な違いをまとめたもので、それぞれの方法を使用する場合のガイドラインを示しています。
| 低遅延キューイング(LLQ) | IP RTP プライオリティ |
|---|---|
次に基づきボイス トラフィックを照合。
|
次に基づきボイス トラフィックを照合。
|
ガイドライン
|
|
キューイング方式の相関と違いについての詳細は、『輻輳管理の概要』を参照してください。
LLQ 設定のガイドライン
LLQ の設定は、次のガイドラインに従います。
-
VoIP トラフィックのためのクラス マップを作成し、照合規準を定義します。
この作業を行うには、次のコマンドを使用します。
maui-voip-sj(config)#class-map ? WORD class-map name match-all Logical-AND all matching statements under this classmap match-any Logical-OR all matching statements under this classmap maui-voip-sj(config)#class-map match-all voice-traffic !-- Choose a descriptive class_name. maui-voip-sj(config-cmap)#match ? access-group Access group any Any packets class-map Class map cos IEEE 802.1Q/ISL class of service/user priority values destination-address Destination address input-interface Select an input interface to match ip IP specific values mpls Multi Protocol Label Switching specific values not Negate this match result protocol Protocol qos-group Qos-group source-address Source address !-- In this example, the access-group matching option is used for its !-- flexibility (it uses an access-list) maui-voip-sj(config-cmap)#match access-group ? <1-2699> Access list index name Named Access List maui-voip-sj(config-cmap)#match access-group 102 !-- Now, create the access-list to match the class-map access-group: maui-voip-sj(config)#access-list 102 permit udp any any range 16384 32776 !-- Safest and easiest way is to match with UDP port range 16384-32767 !-- This is the port range Cisco IOS H.323 products utilize to transmit !-- VoIP packets.これらのアクセスリストは、match access-groupコマンドを使用して音声トラフィックを照合する場合にも使用できます。
access-list 102 permit udp any any precedence critical !-- This list filters traffic based on the IP packet TOS: Precedence field. !-- Note: Ensure that other non-voice traffic does NOT uses the !-- same precedence value. access-list 102 permit udp any any dscp ef !-- In order for this list to work, ensure that VoIP packets are tagged with !-- the dscp ef code before they exit on the LLQ WAN interface. !-- For more information on DSCP refer to: !-- Implementing Quality of Service Policies with DSCP !-- Note: If endpoints are not trusted on their packet marking, you can mark !-- incoming traffic by applying an inbound service policy on an inbound !-- interface. This procedure is out of the scope of this doc. Access-list 102 permit udp host 192.10.1.1 host 192.20.1.1 !-- This access-list can be used in cases where the VoIP devices cannot !-- do precedence or dscp marking and you cannot determine the !-- VoIP UDP port range.
access-groupsの代わりに使用できるその他の照合方法を次に示します。
-
Cisco IOS リリース 12.1.2.T 以降では、LLQ に対する IP RTP プライオリティ機能が実装されています。この機能では、設定されている UDP ポートに基づいてプライオリティ クラスの内容が照合されますが、PQ 内の偶数ポートしか処理されないという制限があります。
class-map voice match ip rtp 16384 16383
-
これらの2つの方法は、発信LLQ動作を適用する前に、発信元ホストでVoIPパケットがマーキングされているか、ルータで照合およびマーキングされていることを前提として動作します。
class-map voice match ip precedence 5
または
class-map voice match ip dscp ef
注:IOSリリース12.2.2T以降では、VoIPダイヤルピアはLLQ動作の前に音声ベアラとシグナリングパケットをマーキングできます。これにより、LLQ 用の DSCP コード値を介して VoIP パケットのマーキングと照合を行うというスケーラブルな方法が可能になります。
-
-
VoIP シグナリング用のクラス マップを作成し、照合基準を定義します(オプション)。
この作業を行うには、次のコマンドを使用します。
class-map voice-signaling match access-group 103 ! access-list 103 permit tcp any eq 1720 any access-list 103 permit tcp any any eq 1720
注:VoIPコールは、H.323、SIP、MGCP、またはSkinny(Cisco Call Managerで使用される独自のプロトコル)を使用して確立できます。 上記の例では H.323 Fast Connect を想定しています。次のリストは、VoIPシグナリング/制御チャネルで使用されるポートのリファレンスとして機能します。
-
H.323/H.225 = TCP 1720
-
H.323/H.245 = TCP 11xxx(Standard Connect)
-
H.323/H.245 = TCP 1720(Fast Connect)
-
H.323/H.225 RAS = TCP 1719
-
ICCP = TCP 8001~8002(CM Encore)
-
ICCP = TCP 8001 ~ 8002(CM Encore)
-
MGCP = UDP 2427、TCP 2428(CM Encore)
-
SIP= UDP 5060、TCP 5060(設定可能)
-
-
ポリシー マップを作成し、VoIP クラス マップに関連付けます。
ポリシー マップの目的は、リンク リソースがどのように共有されるか、または各種マップ クラスにどのように割り当てられるかを定義することです。この作業を行うには、次のコマンドを使用します。
maui-voip-sj(config)#policy-map VOICE-POLICY !-- Choose a descriptive policy_map_name. maui-voip-sj(config-pmap)#class voice-traffic maui-voip-sj(config-pmap-c)#priority ? <8-2000000> Kilo Bits per second !-- Configure the voice-traffic class to the strict priority !-- Queue (priority command) and assign the bandwidth. maui-voip-sj(config-pmap)#class voice-signaling maui-voip-sj(config-pmap-c)#bandwidth 8 !-- Assign 8 Kbps to the voice-signaling class maui-voip-sj(config-pmap)#class class-default maui-voip-sj(config-pmap-c)#fair-queue !-- The remaining data traffic is treated as Weighted Fair Queue
注:さまざまな種類のリアルタイムトラフィックをPQにキューイングすることは可能ですが、音声トラフィックだけをPQに送ることをお勧めします。ビデオなどのリアルタイムトラフィックでは、遅延に変動が生じる可能性があります(PQはFIFO - First In First Out(FIFO;先入れ先出し)キューです)。 ボイス トラフィックでは、ジッタを避けるために遅延を一定にする必要があります。
注:priority文とbandwidth文の値の合計は、リンク帯域幅の75 %以下である必要があります。これを超えると、service-policy をリンクに割り当てることができなくなります(エラー メッセージを表示するには、コンソール アクセスの場合には logging console が、telnet アクセスの場合には terminal monitor が使用可能であることを確認してください)。
注:64 Kbpsリンク上で2つの音声コールをサポートするようにVoIPを設定する場合は、通常、リンク帯域幅の75 %(48 Kbps)以上をPQに割り当てます。このような場合、コマンドmax-reserved-bandwidth 80を使用して使用可能な帯域幅を80 %(51 Kbps)に増やすことができます。
bandwidth コマンドと priority コマンドの詳細は、『QOS サービス ポリシーの bandwidth コマンドと priority コマンドの比較』を参照してください。
-
LLQ をイネーブルにします。ポリシー マップを発信 WAN インターフェイスに適用します。
この作業を行うには、次のコマンドを使用します。
maui-voip-sj(config)#interface multilink 1 maui-voip-sj(config-if)#service-policy output VOICE-POLICY !-- In this scenario (MLPPP LFI), the service policy is applied to !-- the Multilink interface.
IP RTP プライオリティ設定のガイドライン
IP RTPプライオリティを設定するには、次のガイドラインを使用します。
-
Router(config-if)#ip rtp priority starting-rtp-port-#port-#-rangebandwidthコマンド 説明 starting-rtp-port-number
UDP ポートの下限。これはパケットが送信される最小のポート番号です。VoIP では、この値を 16384 に設定します。 port-number-range
UDP 宛先ポートの範囲。starting-rtp-port-number にこの数値を加えた値が最大の UDP ポート番号になります。VoIP の場合は、この値を 16383 に設定します(32767 - 16384 = 16383)。 bandwidth
プライオリティ キューで許可される最大の帯域幅(kbps)。この番号は、システムがサポートする同時コールの数に応じて設定します。 設定例:
interface Multilink1 !--- Some output omitted bandwidth 64 ip address 172.22.130.2 255.255.255.252 ip tcp header-compression fair-queue no cdp enable ppp multilink ppp multilink fragment-delay 10 ppp multilink interleave multilink-group 1 ip rtp header-compression iphc-format ip rtp priority 16384 16383 45
リンク・フラグメンテーション・アンド・インターリービング(LFI):マルチリンク PPP
データ パケットの通常の大きさは 1500 バイトですが、一般的な VoIP パケット(G.729 音声フレームを搬送するもの)は、約 66 バイト(ペイロードに 20 バイト、レイヤ 2 ヘッダに 6 バイト、RTP および UDP ヘッダーに 20 バイト、IP ヘッダーに 20 バイト)です。
ここで、音声トラフィックとデータ トラフィックが共存している 56Kbps の専用回線リンクを想像してみてください。データ パケットがリンク上への伝送され始めた時点で音声パケットがシリアル化されようとすると、問題が生じます。遅延の影響を受けやすい音声パケットは、送信されるまで214ミリ秒を待機する必要があります(56Kbpsリンクで1500バイトのパケットをシリアル化するには214ミリ秒を要する)。
このように、大きなデータ パケットが小さな音声パケットの配送を遅延させ、会話の品質を低下させます。このような大きなデータ パケットを小さなものにフラグメントし、この間に音声パケットを挿入(インターリービング)すれば、ジッタや遅延を減らすことができます。Cisco IOS の リンク フラグメンテーション アンド インターリービング(LFI) 機能は、VoIP のリアルタイム配送の要件を満たすのに役立ちます。次の図は、LFIの動作を示しています。
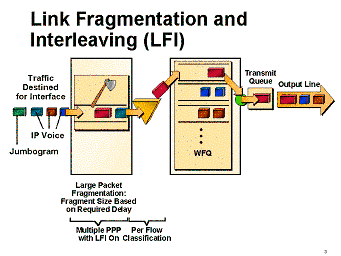
表 1 に示すように、単方向のエンドツーエンドの遅延は 150 ミリ秒を超えてはならないという目標を考慮すると、シリアル化による遅延(ビットをインターフェイス上に実際に送り出すためにかかる時間)によって低速の WAN リンクにもたらされる影響が重大なものになる場合があります。(ITU-T G.114勧告では、一方向エンドツーエンドで最大150ミリ秒を指定します)。
表1.低速リンクの各種フレームサイズのシリアライゼーション遅延シリアライゼーション遅延=フレームサイズ(ビット)/リンク帯域幅(bps)| 1 バイト | 64 バイト | 128 バイト | 256 バイト | 512 バイト | 1024 バイト | 1500 バイト | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 56 kbps | 143 マイクロ秒 | 9 ミリ秒 | 18 ミリ秒 | 36 ミリ秒 | 72 ミリ秒 | 144 ミリ秒 | 214 ミリ秒 |
| 64 Kbps | 125 マイクロ秒 | 8 ms | 16 ミリ秒 | 32 ミリ秒 | 64 ミリ秒 | 126 ミリ秒 | 187 ミリ秒 |
| 128 kbps | 62.5 マイクロ秒 | 4 ミリ秒 | 8 ms | 16 ミリ秒 | 32 ミリ秒 | 64 ミリ秒 | 93 ミリ秒 |
| 256 kbps | 31 マイクロ秒 | 2 ミリ秒 | 4 ミリ秒 | 8 ms | 16 ミリ秒 | 32 ミリ秒 | 46 ミリ秒 |
| 512 kbps | 15.5 マイクロ秒 | 1 ミリ秒 | 2 ミリ秒 | 4 ミリ秒 | 8 ms | 16 ミリ秒 | 32 ミリ秒 |
| 768 kbps | 10 マイクロ秒 | 640 マイクロ秒 | 1.28 ミリ秒 | 2.56 ミリ秒 | 5.12 ミリ秒 | 10.24 ミリ秒 | 15 ミリ秒 |
| 1536 kbps | 5 マイクロ秒 | 320 マイクロ秒 | 640 マイクロ秒 | 1.28 ミリ秒 | 2.56 ミリ秒 | 5.12 ミリ秒 | 7.5 ミリ秒 |
注:音声アプリケーションでは、推奨されるシリアル化遅延(ホップ単位)は10ミリ秒であり、20ミリ秒を超えることはできません。
リンクのフラグメント サイズは、ppp multilink fragment-delay コマンドを使用してミリ秒(msec)の時間単位で設定できます。LFI では、ppp multilink を、ppp multilink interleave が有効になるよう設定することが必要です。LFIの設定の詳細については、このドキュメントのセクションを参照してください。
注:専用のハーフT1接続(768 Kbps)を超える場合は、フラグメンテーション機能は必要ありません。(ただし、LLQやIP RTPプライオリティなどのQoSメカニズムは必要です)。 ハーフ T1 では、音声パケットのキューへの出し入れを、遅延を発生させずに行えるだけの十分な帯域幅が供給されます。また、ハーフ T1 のケースでは、Compression for Real-time Protocol(cRTP; 圧縮リアルタイム プロトコル)(IP RTP ヘッダーを圧縮して帯域幅を節約する機能)も不要の場合があります。
圧縮リアルタイム プロトコル(cRTP)
注:良好な音声品質を確保するためにcRTPは必要ありません。これは帯域幅の使用量を削減するための機能です。cRTP は、他の条件がすべて満たされていて、音声品質が良好な場合に設定してください。こうすれば、可能性のある cRTP の問題が切り離されるため、トラブルシューティング時間を節約できます。
RFC 2508 で規定されている RTP ヘッダー圧縮機能は、IP/UDP/RTP パケットのヘッダーを 40 バイトから 2 または 4 バイトに圧縮し、無駄な帯域幅の使用を減らします。これはホップ単位の圧縮方式です。(passive オプションが設定されていない限り)cRTP はリンクの両端で設定する必要があります。 cRTPを設定するには、インターフェイスレベルで次のコマンドを使用します。
-
Router(config-if)#ip rtp header-compression [passive]
圧縮プロセスは CPU に高い負荷をかけるため、RTP ヘッダー圧縮は、IOS リリース 12.0.(7)T から高速のスイッチングおよび CEF スイッチング パスに実装されます。これらの実装が壊れている場合があり、その後で唯一の方法がスイッチド処理されます。シスコでは、ルータの CPU 使用率が低い場合を除き、768 Kbps よりも低速のリンクで cRTP を使用することを推奨しています。ルータの CPU 使用率を監視し、使用率が 75 % を超えた場合は cRTP を無効にしてください。
注:コマンドip rtp header-compressionを設定すると、ルータはデフォルトでコマンドip tcp header-compressionを設定に追加します。これは、ヘッダーのTCP/IPパケットを圧縮するために使用されます。ヘッダー圧縮は、多数の Telnet 接続をサポートしているなど、小さなパケットが大きな比率を占めるネットワークで特に有効です。TCP ヘッダー圧縮技術は、RFC 1144 で完全に説明されており、HDLC または PPP カプセル化を使用して、シリアル回線上でサポートされています。
cRTPを有効にせずにTCPヘッダーを圧縮するには、次のコマンドを使用します。
-
Router(config-if)#ip tcp header-compression [passive]
詳細は、「VoIP のデバッグ コマンド」を参照してください。圧縮リアルタイム転送プロトコル
その他の帯域幅削減に関するヒント
-
VoIPコールレッグで低ビットレートコーダ/デコーダ(コーデック)を使用します。G.729(8 Kbps)が推奨されます。(これは VoIP ダイヤルピアでのデフォルトのコーデックです)。 異なるコーデックを設定するには、router(config-dial-peer)#codecコマンドをvoipダイヤルピアの下で使用します。
-
G.711 のような高ビットレートの音声コーデックを使用すると、通常 dual tone multifrequency(DTMF)は正確に転送されますが、低ビットレートのコーデック(G.729 および G.723.1)は音声パターンに高度に最適化され、DTMF トーンを歪ませる傾向があります。そのため、このアプローチを使用すると Interactive Voice Response(IVR; 対話式音声自動応答)システムへのアクセス時に問題が生じるおそれがあります。dtmf relay コマンドを使用すれば、DTMF トーンが「帯域外」で転送されるか、または符号化された音声ストリームから切り離されて転送されるため、DTMF の歪みの問題は解決します。低ビットレートコーデック(G.729、G.723)を使用する場合は、VoIPダイヤルピアでdtmf relayをオンにします。
-
標準的な会話には 35~50 % の無音部分があります。Voice Activity Detection(VAD)を使用すると、無音パケットが抑制されます。VoIP帯域幅計画では、VADによって帯域幅が35 %削減されると仮定します。VoIP ダイヤルピアでは VAD がデフォルトで設定されています。VADを有効または無効にするには、目的のVoIPダイヤルピアの下でrouter(config-dial-peer)#vadおよびrouter(config-dial-peer)# no vadコマンドを使用します。
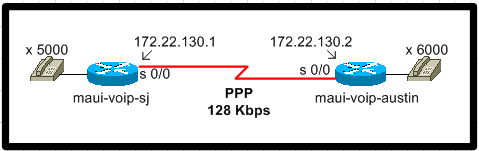
ネットワーク図
設定
| maui-voip-sj(Cisco 3640) |
|---|
version 12.2service timestamps debug datetime msec
!-- < Some output omitted >
!
hostname maui-voip-sj
!
ip subnet-zero
!
no ip domain-lookup
!
!-- Definition of the voice signaling and traffic class maps !-- "voice-traffic" class uses access-list 102 for its matching criteria. !-- "voice-signaling" class uses access-list 103 for its matching criteria.
Class-map match-all voice-signaling
match access-group 103
class-map match-all voice-traffic
match access-group 102
!
!-- The policy-map defines how the link resources are assigned !-- to the different map classes. In this configuration, strict priority !-- queue is assigned to "voice-traffic" class with (based on ACL in !-- class voice) with max bandwidth = 45 Kbps.
policy-map VOICE-POLICY
class voice-traffic
priority 48
class voice-signaling
bandwidth 8
!-- Assigns a queue for "voice-signaling" traffic that ensures 8 Kbps. !-- Note that this is optional and has nothing to do with good voice !-- quality, but rather a way to secure signaling.
class class-default
fair-queue
!-- The class-default class is used to classify traffic that does !-- not fall into one of the defined classes. !-- The fair-queue command associates the default class WFQ queueing.
!
call rsvp-sync
!
!-- Note that MLPPP is strictly an LFI mechanism. It does not !-- bundle multiple serial interfaces to the same virtual interface as !-- the name stands (This bundling is done for data and NOT recommended !-- for voice). The end result may manifest itself as jitter and no audio.
interface Multilink1
ip address 172.22.130.1 255.255.255.252
ip tcp header-compression iphc-format
service-policy output VOICE-POLICY
!-- LLQ is an outbound operation and applied to the outbound WAN !-- interface.
no cdp enable
ppp multilink
ppp multilink fragment-delay 10
!-- The configured value of 10 sets the fragment size such that !-- all fragments have a 10 ms maximum serialization delay.
ppp multilink interleave
multilink-group 1
ip rtp header-compression iphc-format
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 172.22.113.3 255.255.255.0
no keepalive
half-duplex
!
interface Serial0/0
bandwidth 128
!-- the bandwidth command needs to be set correctly for the !-- right fragment size to be calculated.
no ip address
encapsulation ppp
clockrate 128000
ppp multilink
multilink-group 1
!-- This command links the multilink interface to the physical !-- serial interface.
!
router eigrp 69
network 172.22.0.0
auto-summary
no eigrp log-neighbor-changes
!
!-- access-list 102 matches VoIP traffic based on the UDP port range. !-- Both odd and even ports are put into the PQ. !-- access-list 103 is used to match VoIP signaling protocol. In this !-- case, H.323 V2 with fast start feature is used.
access-list 102 permit udp any any range 16384 32767
access-list 103 permit tcp any eq 1720 any
access-list 103 permit tcp any any eq 1720
!
voice-port 1/0/0
!
voice-port 1/0/1
!
voice-port 1/1/0
!
voice-port 1/1/1
!
dial-peer cor custom
!
dial-peer voice 1 pots
destination-pattern 5000
port 1/0/0
!
dial-peer voice 2 voip
destination-pattern 6000
session target ipv4:172.22.130.2
|
| maui-voip-austin(Cisco 3640) |
|---|
version 12.2
service timestamps debug datetime msec
!
hostname maui-voip-austin
!
boot system flash slot1:c3640-is-mz.122-6a.bin
!
ip subnet-zero
!
class-map match-all voice-signaling
match access-group 103
class-map match-all voice-traffic
match access-group 102
!
policy-map voice-policy
class voice-signaling
bandwidth 8
class voice-traffic
priority 48
class class-default
fair-queue
!
interface Multilink1
bandwidth 128
ip address 172.22.130.2 255.255.255.252
ip tcp header-compression iphc-format
service-policy output voice-policy
no cdp enable
ppp multilink
ppp multilink fragment-delay 10
ppp multilink interleave
multilink-group 1
ip rtp header-compression iphc-format
!-- Configure cRTP after you have a working configuration. !-- This helps isolate potential cRTP issues.
!
Interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 172.22.112.3 255.255.255.0
no keepalive
half-duplex
!
interface Serial0/0
bandwidth 128
no ip address
encapsulation ppp
no ip mroute-cache
ppp multilink
multilink-group 1
!
router eigrp 69
network 172.22.0.0
auto-summary
no eigrp log-neighbor-changes
!
access-list 102 permit udp any any range 16384 32767
access-list 103 permit tcp any eq 1720 any
access-list 103 permit tcp any any eq 1720
!
voice-port 1/0/0
!
voice-port 1/0/1
!
voice-port 1/1/0
!
voice-port 1/1/1
!
dial-peer cor custom
!
dial-peer voice 1 pots
destination-pattern 6000
port 1/0/0
!
dial-peer voice 2 voip
destination-pattern 5000
session target ipv4:172.22.130.1
|
検証とトラブルシューティングに関するコマンド
debugコマンドを使用する前に、『debugコマンドの重要な情報』を参照してください。ここにリストされているコマンドの詳細については、このドキュメントの「showおよびdebugの出力例」のセクションを参照してください。
インターフェイス コマンド
-
show interface [serial | multilink]:シリアルインターフェイスのステータスを確認します。シリアルおよびマルチリンクのインターフェイスが、アップおよびオープンの状態であることを確認してください。
LFI コマンド:
-
show ppp multilink:このコマンドは、マルチリンクPPPバンドルのバンドル情報を表示します。
-
debug ppp multilink fragments:このdebugコマンドは、個々のマルチリンクフラグメントおよびインターリービングイベントに関する情報を表示します。このコマンドの出力では、パケットのシーケンス番号とフラグメント サイズも分かります。
LLQ/IP RTPプライオリティコマンド:
-
show policy-map interface multilink interface# :このコマンドは、LLQの動作を確認したり、PQでのドロップを確認したりするのに非常に便利です。このコマンドのさまざまなフィールドの詳細は、『show policy-map interface 出力内のパケット カウンタについて』を参照してください。
-
show policy-map policy_map_name:このコマンドは、ポリシーマップの設定に関する情報を表示します。
-
show queue interface-type interface-number:このコマンドは、特定のインターフェイスの均等化キューイング設定と統計情報をリストします。
-
Debug priority:このdebugコマンドは、プライオリティキューイングイベントを表示し、このキューで廃棄が発生しているかどうかを表示します。プライオリティキューイングによる出力ドロップのトラブルシューティングも参照してください。
-
show class-map class_name:このコマンドは、クラスマップ設定に関する情報を表示します。
-
show call active voice:このコマンドは、DSPレベルで損失パケットをチェックするのに便利です。
その他のコマンド/リファレンス:
-
show ip rtp header-compression:このコマンドは、RTPヘッダー圧縮の統計情報を表示します。
既知の問題:
-
CSCds43465:「LLQ、ポリサー、シェーパーがCRTP圧縮フィードバックを受け取る必要がある」リリースノートを参照するには、Bug ToolKit(登録ユーザ専用)を参照してください。
ガイドライン:
PPPリンクがアップ状態で実行された後の基本的なトラブルシューティング手順(MLPPP、フラグメンテーション、インターリービング)を次に示します。
-
show call active voice:DSPレベルで損失パケットをチェックするために使用します。
-
show interface:一般的なシリアル回線またはインターフェイスの問題を確認します。このインターフェイスでのパケットの廃棄は、必ずしも問題があるとは言えませんが、パケットの廃棄は、低いプライオリティのキューがインターフェイス キューに到達する前に行う方が好ましいと言えます。
-
show policy-map interface:LLQドロップとキューイングの設定を確認するために使用します。ポリシーに違反する廃棄は報告する必要がありません。
-
show ip rtp header-compression:cRTP固有の問題を確認するために使用します。
show および debug の出力例
!----------------------------------------------- !----------------------------------------------- !---- To capture sections of this output, the LLQ PQ bandwidth !---- was lowered and large data traffic was placed !---- on the link to force some packets drops. !----------------------------------------------- !----------------------------------------------- !---- Packet Drop Verification (During an Active Call) !--- Assuming your ppp link is up and running, the first step of voice !--- quality problems verification is to check for lost packets !--- at the DSP. Note: Use the show call active voice command !--- NOT show call active voice brief
maui-voip-austin#show call active voice
Total call-legs: 2
!--- Indicates that the connection is established and both legs exist
GENERIC:
SetupTime=155218260 ms
Index=1
PeerAddress=5000
PeerSubAddress=
PeerId=2
PeerIfIndex=13
LogicalIfIndex=0
ConnectTime=155218364
CallDuration=00:00:27
CallState=4
!--- indicates that it is the active call !--- (#define D_callActiveCallState_active 4).
CallOrigin=2
ChargedUnits=0
InfoType=2
TransmitPackets=365
TransmitBytes=7300
ReceivePackets=229
ReceiveBytes=4580
VOIP:
!--- For this call, this was the terminating gateway. !--- At this gateway, the call started at the VoIP leg.
ConnectionId[0x18872BEB 0x1A8911CC 0x808CBE60 0x6D946FC6]
IncomingConnectionId[0x18872BEB 0x1A8911CC 0x808CBE60 0x6D946FC6]
RemoteIPAddress=172.22.130.1
!--- Indicates from which IP address the RTP stream is originating.
RemoteUDPPort=18778
RemoteSignallingIPAddress=172.22.130.1
!--- Indicates from which IP address signaling messages are coming.
RemoteSignallingPort=11010
RemoteMediaIPAddress=172.22.130.1
RemoteMediaPort=18778
RoundTripDelay=50 ms
SelectedQoS=best-effort
tx_DtmfRelay=inband-voice
FastConnect=TRUE
Separate H245 Connection=FALSE
H245 Tunneling=FALSE
SessionProtocol=cisco
SessionTarget=
OnTimeRvPlayout=4570
GapFillWithSilence=20 ms
GapFillWithPrediction=1840 ms
GapFillWithInterpolation=0 ms
GapFillWithRedundancy=0 ms
HiWaterPlayoutDelay=70 ms
LoWaterPlayoutDelay=51 ms
ReceiveDelay=51 ms
LostPackets=90
EarlyPackets=1
LatePackets=0
!--- Indicates the precense of jitter, lost packets, or !--- corrupted packets.
VAD = enabled
CoderTypeRate=g729r8
CodecBytes=20
GENERIC:
SetupTime=155218260 ms
Index=2
PeerAddress=6000
PeerSubAddress=
PeerId=1
PeerIfIndex=12
LogicalIfIndex=6
ConnectTime=155218364
CallDuration=00:00:34
CallState=4
CallOrigin=1
ChargedUnits=0
InfoType=2
TransmitPackets=229
TransmitBytes=4580
ReceivePackets=365
ReceiveBytes=7300
TELE:
ConnectionId=[0x18872BEB 0x1A8911CC 0x808CBE60 0x6D946FC6]
IncomingConnectionId=[0x18872BEB 0x1A8911CC 0x808CBE60 0x6D946FC6]
TxDuration=35360 ms
VoiceTxDuration=730 ms
FaxTxDuration=0 ms
CoderTypeRate=g729r8
NoiseLevel=-46
ACOMLevel=2
OutSignalLevel=-58
InSignalLevel=-42
InfoActivity=2
ERLLevel=7
SessionTarget=
ImgPages=0Total call-legs: 2
!---------------------------------------------------------- !--- Interface Verification !--- Make sure you see this: !--- LCP Open, multilink Open: Link control protocol (LCP) open statement !--- indicates that the connection is establish. !--- Open:IPCP. Indicates that IP traffic can be transmitted via the PPP link.
maui-voip-sj#show interface multilink 1
Multilink1 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is multilink group interface
Internet address is 172.22.130.1/30
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 128 Kbit, DLY 100000 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation PPP, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
DTR is pulsed for 2 seconds on reset
LCP Open, multilink Open
Open: IPCP
Last input 00:00:01, output never, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters 00:25:20
Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 91
Queueing strategy: weighted fair
Output queue: 0/1000/64/37/383 (size/max total/threshold/drops/interleaves)
Conversations 0/3/32 (active/max active/max total)
Reserved Conversations 1/1 (allocated/max allocated)
Available Bandwidth 38 kilobits/sec
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
8217 packets input, 967680 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort
13091 packets output, 1254194 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
0 carrier transitions
----------------------------------------------------------------
!-- Note: There are no drops at the interface level. !-- All traffic that is dropped due to policing, is !-- dropped before it gets to the interface queue.
maui-voip-austin#show interface
serial 0/0Serial0/0 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is QUICC Serial
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 128 Kbit, DLY 20000 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 49/255, rxload 47/255
Encapsulation PPP, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
LCP Open, multilink Open
Last input 00:00:00, output 00:00:00, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters 00:22:08
Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0
Queueing strategy: weighted fair [suspended, using FIFO]
FIFO output queue 0/40, 0 drops
5 minute input rate 24000 bits/sec, 20 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 25000 bits/sec, 20 packets/sec 4851 packets input, 668983 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort
4586 packets output, 657902 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
0 carrier transitions
DCD=up DSR=up DTR=up RTS=up CTS=up
!----------------------------------- !--- LLQ Verification
maui-voip-austin#show policy-map int multilink 1
Multilink1
Service-policy output: voice-policy
Class-map: voice-signaling (match-all)
!--- This is the class for the voice signaling traffic.
10 packets, 744 bytes
5 minute offered rate 0 BPS, drop rate 0 BPS
Match: access-group 103
Weighted Fair Queueing
Output Queue: Conversation 42
Bandwidth 8 (kbps) Max Threshold 64 (packets)
(pkts matched/bytes matched) 10/744
(depth/total drops/no-buffer drops) 0/0/0
Class-map: voice-traffic (match-all)
!--- This is PQ class for the voice traffic.
458 packets, 32064 bytes
5 minute offered rate 0 BPS, drop rate 0 BPS
Match: access-group 102
Weighted Fair Queueing
Strict Priority
Output Queue: Conversation 40
Bandwidth 15 (kbps) Burst 375 (Bytes)
!--- Notice that the PQ bandwidth was lowered to force packet drops.
(pkts matched/bytes matched) 458/29647
(total drops/bytes drops) 91/5890
!--- Some packets were dropped. In a well designed link,
!--- there should be no (or few) drops of the PQ class.
Class-map: class-default (match-any)
814 packets, 731341 bytes
5 minute offered rate 27000 BPS, drop rate 0 BPSMatch: any
Weighted Fair Queueing
Flow Based Fair Queueing
Maximum Number of Hashed Queues 32
(total queued/total drops/no-buffer drops) 0/0/0
!---------------------------------------------
!--- Verify the class-map configuration
maui-voip-austin#show class-map
Class Map match-all voice-signaling (id 2)
Match access-group 103
Class Map match-any class-default (id 0)
Match any
Class Map match-all voice-traffic(id 3)
Match access-group 102
!--- Verify the access-lists of the class-maps
maui-voip-austin#show access-lists
Extended IP access list 102
permit udp any any range 16384 32767 (34947 matches)
Extended IP access list 103
permit tcp any eq 1720 any (187 matches)
permit tcp any any eq 1720 (86 matches)
!--- Verify the policy-pap configuration
maui-voip-austin#show policy-map voice-policy
Policy Map voice-policy
Class voice-signaling
Weighted Fair Queueing
Bandwidth 8 (kbps) Max Threshold 64 (packets)
Class voice-traffic
Weighted Fair Queueing
Strict Priority
Bandwidth 50 (kbps) Burst 1250 (Bytes)
Class class-default
Weighted Fair Queueing
Flow based Fair Queueing Max Threshold 64 (packets)
---------------------------
!--- Debug priority command provides immediate feedback in case !--- of VoIP packet drops. !--- The output below shows the error message when VoIP packets !--- are being dropped from the strict priority queue.
maui-voip-sj#debug priority
priority output queueing debugging is on
maui-voip-sj#
Mar 17 19:47:09.947: WFQ: dropping a packet from the priority queue 0
Mar 17 19:47:09.967: WFQ: dropping a packet from the priority queue 0
Mar 17 19:47:09.987: WFQ: dropping a packet from the priority queue 0
-------------------------------------------------------------------
!--- Link Fragmentation and Interleaving (LFI) Verification
maui-voip-sj#show ppp multilink
!--- Verify the fragmentation size and multilink
Multilink1, bundle name is maui-voip-austin
Bundle up for 00:08:04
0 lost fragments, 0 reordered, 0 unassigned
0 discarded, 0 lost received, 1/255 load
0x6D received sequence, 0x6E sent sequence
Member links: 1 active, 0 inactive (max not set, min not set)
Serial0/0, since 00:08:09, last rcvd seq 00006C 160 weight
!--- Notice the fragmentation size is 160 Bytes. The link is configured with a !--- bandwidth of 128 kbps and a serialization delay of 10 msec. !--- Fragment Size (in bits) = bandwidth * serialization delay. !--- Note: There are 8 bits in one byte.
-------------------------------------------------------
!--- Link Fragmentation and Interleaving (LFI) Verification !--- Testing Multilink PPP Link LFI !--- This output displays fragmentation and interleaving information !--- when the the 128kbps PPP link is loaded with big data and VoIP packets.
maui-voip-sj#debug ppp multilink fragments
Multilink fragments debugging is on
1w3d: Se0/0 MLP: O frag 800004CF size 160
1w3d: Se0/0 MLP: O frag 000004D0 size 160
1w3d: Se0/0 MLP: I ppp IP (0021) size 64 direct
1w3d: Mu1 MLP: Packet interleaved from queue 40
1w3d: Se0/0 MLP: O ppp IP (0021) size 64
1w3d: Se0/0 MLP: I ppp IP (0021) size 64 direct
1w3d: Se0/0 MLP: O frag 400004D1 size 106
1w3d: Se0/0 MLP: O ppp IP (0021) size 64
1w3d: Se0/0 MLP: I ppp IP (0021) size 64 direct
1w3d: Se0/0 MLP: O ppp IP (0021) size 64 direct
1w3d: Se0/0 MLP: I frag 800004E0 size 160 direct
1w3d: Se0/0 MLP: I frag 000004E1 size 160 direct
1w3d: Se0/0 MLP: I ppp IP (0021) size 64 direct
-------------------------------------------------------------------
!--- Sample output of show ip rtp header-compression command
maui-voip-sj#show ip tcp header-compression
TCP/IP header compression statistics: Interface Multilink1:
Rcvd: 10 total, 6 compressed, 0 errors
0 dropped, 0 buffer copies, 0 buffer failures
Sent: 10 total, 7 compressed,
230 bytes saved, 99 bytes sent
3.32 efficiency improvement factor
Connect: 16 rx slots, 16 tx slots,
2 long searches, 1 misses 0 collisions, 0 negative cache hits
90% hit ratio, five minute miss rate 0 misses/sec, 0 max
----------------------------------------------------------------------
!--- This command displays information of the voip dial-peers command.
maui-voip-sj#show dial-peer voice 2
VoiceOverIpPeer2
information type = voice,
tag = 2, destination-pattern = `6000',
answer-address = `', preference=0,
group = 2, Admin state is up, Operation state is up,
incoming called-number = `', connections/maximum = 0/unlimited,
application associated:
type = voip, session-tMarget = `ipv4:172.22.130.2',
technology prefix:
ip precedence = 0, UDP checksum = disabled,
session-protocol = cisco, req-qos = best-effort,
acc-qos = best-effort,
fax-rate = voice, payload size = 20 bytes
codec = g729r8, payload size = 20 bytes,
Expect factor = 10, Icpif = 30,signaling-type = cas,
VAD = enabled, Poor QOV Trap = disabled,
Connect Time = 283, Charged Units = 0,
Successful Calls = 1, Failed Calls = 0,
Accepted Calls = 1, Refused Calls = 0,
Last Disconnect Cause is "10 ",
Last Disconnect Text is "normal call clearing.",
Last Setup Time = 93793451.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
!---The CPU utilization of the router should not exceed the 50-60 percent !--- during any five-minute interval.
maui-voip-austin#show processes cpu
CPU utilization for five seconds: 12%/8%; one minute: 11%; five minutes: 9%
PID Runtime(ms) Invoked uSecs 5Sec 1Min 5Min TTY Process
1 148 310794 0 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0 Load Meter
2 76 23 3304 0.81% 0.07% 0.01% 0 Exec
|
 フィードバック
フィードバック