QoS(フラグメンテーション、トラフィック シェーピング、LLQ/IP RTP プライオリティ)が備わった VoIP over Frame Relay
内容
概要
このドキュメントでは、Quality of Service(QoS)を使用した Voice over IP(VoIP)over Frame Relay ネットワークの設定例を紹介しています。 このドキュメントには、機能の設定、設計ガイドライン、基本的な検証とトラブルシューティングの方法についての技術的な背景情報が記載されています。
このドキュメントの設定例では、フレームリレー ネットワークに接続された 2 台のボイス ルータを使用しています。ただし、音声対応ルータは任意の場所に配置できます。通常、ボイス ルータは LAN 接続経由により、WAN に接続されている他のルータに接続します。ボイス ルータがフレームリレー ネットワークに直接接続されていない場合は、このドキュメントの設定例に示されているすべての WAN 関連の設定コマンドを、ボイス ルータではなく WAN に接続されているルータに設定する必要がある点に注意してください。
前提条件
要件
このドキュメントに特有の要件はありません。
使用するコンポーネント
このドキュメントの情報は、次のソフトウェアとハードウェアのバージョンに基づいています。
-
Cisco IOS®ソフトウェアリリース12.2.6a(Enterprise Plus)が稼働するCisco 3640ルータ
-
Cisco IOS ソフトウェア リリース 12.2.6a(Enterprise Plus)が稼働している Cisco 2621 ルータ
-
フレームリレー Permanent Virtual Circuit(PVC; 相手先固定接続)上の Low Latency Queueing(LLQ; 低遅延キューイング) (この機能は Cisco IOS ソフトウェア リリース 12.1.(2)T で導入されました)
-
Cisco IOS ソフトウェア リリース 12.0(7)T で導入されたフレームリレー IP Real-time Transport Protocol(RTP)プライオリティ
-
Cisco IOS ソフトウェア リリース 12.0(4)T で導入された Frame Relay Forum(FRF; フレームリレー フォーラム).12 フラグメンテーション
-
12.0.5T よりも新しい Cisco IOS ソフトウェア リリースでは、compressed RTP(cRTP; 圧縮 RTP)のパフォーマンスが大幅に改善されています。
このドキュメントの情報は、特定のラボ環境にあるデバイスに基づいて作成されました。このドキュメントで使用するすべてのデバイスは、初期(デフォルト)設定の状態から起動しています。対象のネットワークが実稼働中である場合には、どのようなコマンドについても、その潜在的な影響について確実に理解しておく必要があります。
表記法
ドキュメント表記の詳細は、「シスコ テクニカル ティップスの表記法」を参照してください。
VoIP over Frame Relay の QoS 設計ガイドライン
良好な音声品質を得るためには、次の 2 つの基本的な要件があります。
-
最小のエンドツーエンド遅延とジッタ回避(遅延変動)。
-
リンク帯域幅要件の最適化と適切な設計
上記の要件を満たすには、次のガイドラインに従います。
音声トラフィックの完全優先(LLQ または IP RTP プライオリティ)
ボイス トラフィックに完全な優先権を設定する方法には、主に次の 2 種類があります。
-
IP RTP プライオリティ(Priority Queue / Weighted Fair Queuing(PQ/WFQ; プライオリティ キュー/重み付け均等化キューイング)とも呼ばれる)
-
LLQ(PQ / Class Based Weighted Fair Queuing(PQ/CBWFQ; PQ/クラスベース重み付け均等化キューイング)とも呼ばれる)
IP RTP プライオリティ
フレームリレー IP RTP プライオリティでは、特定の範囲の User Datagram Protocol(UDP; ユーザ データグラム プロトコル)宛先ポートに属する RTP パケット フローのために、フレームリレー PVC 上に完全 Priority Queue(PQ; プライオリティ キュー)が作成されます。実際に使用されるポート番号はエンド デバイスまたはゲートウェイの間で動的にネゴシエートされますが、Cisco VoIP 製品はすべて同じ UDP ポート範囲(16384 ~ 32767)を利用します。 ルータは VoIP トラフィックを認識すると、そのトラフィックを完全 PQ に入れます。PQ が空の場合は、標準的な WFQ に基づいて、他のキューが処理されます。IP RTP プライオリティは、インターフェイスで輻輳が発生しない限りアクティブにはなりません。次の図は IP RTP プライオリティの動作の仕組みを示しています。
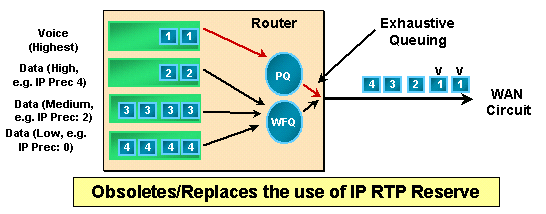
注: IP RTPプライオリティでは、デフォルトキュー(WFQ)に使用可能な帯域幅がある場合にPQをバーストできます。 ただし、インターフェイスで輻輳が発生している場合は、PQ の内容に対して厳密なポリシングが行われます。
LLQ
LLQ は CBWFQ に完全 PQ を提供する機能です。LLQ を使用すると、クラス レベルの CBWFQ 内に完全 PQ が 1 つ作成されます。LLQ では、(PQ 内にある)遅延に影響されやすいデータが最初に取り出され、送信されます。LLQ 実装を備えた VoIP では、音声トラフィックが完全 PQ に入れられます。
PQ は均等化キューが帯域幅不足に陥らないようにポリシングされます。PQ を設定するときには、その PQ で使用できる帯域幅の最大値を Kbps で指定します。インターフェイスで輻輳が発生すると、負荷が priority コマンドで設定された Kbps 値に達するまで PQ の処理は続けられます。下位の PQ が帯域幅不足となる従来のシスコのプライオリティ グループ機能の問題を回避するために、設定した帯域幅を超過したトラフィックは廃棄されます。
注:フレームリレーのLLQでは、キューはPVCごとに設定されます。各 PVC は 1 つの PQ と、設定された数の均等化キューを備えています。
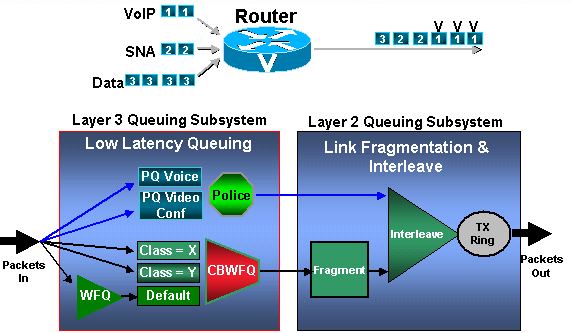
この方法は IP RTP プライオリティよりも複雑ですが、より柔軟な制御が可能です。どちらの方法を選択するかは、実際のネットワークでのトラフィック パターンと個々のニーズに基づきます。
LLQ と IP RTP プライオリティ
次の表は LLQ と IP RTP プライオリティの主な違いをまとめたもので、どのような場合にそれぞれの方法を使用すればよいかを示すガイドラインとなります。
| LLQ | IP RTP プライオリティ |
|---|---|
次に基づきボイス トラフィックを照合。
|
次に基づきボイス トラフィックを照合。
|
ガイドライン:
|
|
音声の FRTS
FRTS にはネットワーク トラフィックの輻輳の管理に役立つパラメータがあります。FRTS は、中央サイトへの高速接続とブランチ サイトへの低速接続を使用したフレームリレー ネットワーク内のボトルネックを解消します。レート強制値を設定すると、中央サイトの Virtual Circuit(VC; 仮想回線)から送信されるデータの転送速度を制限できます。
ここでは、FRTS に関連する用語について説明しています。
-
Committed Information Rate(CIR; 認定情報レート):フレームリレー プロバイダーが保証するデータ転送レート(bps)。CIR 値はフレームリレー サービス プロバイダーによって設定され、ユーザがルータ上で設定します。
注:ポート/インターフェイスのアクセスレートはCIRよりも高い場合があります。このレートは、Committed Rate Measurement Interval(Tc;認定レート測定間隔)の期間で平均化されます。
-
Committed Burst(Bc; 認定バースト):フレームリレー ネットワークが Tc の間に転送する最大の認定ビット数。Tc = Bc / CIR。
-
Excess Burst(Be; 超過バースト):フレームリレー スイッチが Tc 上で CIR を超過して転送を試みる最大の非認定ビット数。
-
Committed Rate Measurement Interval(Tc; 認定レート測定間隔):Bc または(Bc + Be)ビットが転送される時間間隔。Tcは、Tc = Bc / CIRとして計算されます。Tc値は、Ciscoルータでは直接設定されません。この値は、Bc 値と CIR 値を設定すると自動的に計算されます。Tc が 125 ミリ秒を超えることはありません。
-
Backwards Explicit Congestion Notification(BECN; 逆方向明示的輻輳通知):ネットワークの輻輳を示す、フレームリレー ヘッダー内のビット。フレームリレー スイッチは輻輳を検出すると、送信元ルータ向けのフレームに BECN ビットを設定して、転送レートを下げるようにルータに指示します。
音声トラフィックの FRTS の設定は、データ トラフィックのみを対象とするトラフィック シェーピングの設定とは異なります。ボイス品質用の FRTS を設定すると、データ トラフィック パラメータとの間で調整が行われます。これらの制限の詳細は、このドキュメントの「フラグメンテーション(FRF.12)」セクションを参照してください。
フラグメンテーション(FRF.12)
ボイスデータ統合における大きな課題は、ボイス(音声)などの時間の影響を受けやすいトラフィックで生じる、一方向のエンドツーエンドの最大遅延を制御することです。良好な音声品質を得るには、この遅延が150 ms未満である必要があります。この遅延の重要な部分は、インターフェイスでのシリアル化遅延です。この値は10ミリ秒に設定し、20ミリ秒を超えないことを推奨します。シリアライゼーションディレイとは、ビットをインターフェイス上に実際に配置するときにかかる時間です。
Serialization Delay = frame size (bits) / link bandwidth (bps)
たとえば、1500 バイトのパケットがルータから 56 Kbps の回線に送出されるためには 214 ミリ秒かかります。1500 バイトの非リアルタイム データ パケットが送信されている場合、リアルタイム(ボイス)データ パケットは、その大きなデータ パケットが伝送されるまでキューイングされています。この遅延は、音声トラフィックでは許容できません。非リアルタイム データ パケットがより小さいフレームに分割されていれば、リアルタイム(ボイス)データ フレームをそれらの分割されたパケットの間に埋め込む(インターリーブ)ことができます。この方法を使用すれば、リアルタイム ボイス トラフィックに過度の遅延が引き起こされることなく、ボイス フレームとデータ フレームの両方を低速リンクにのせて伝送することが可能となります。
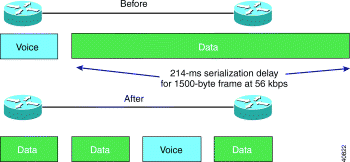
フラグメンテーションについての詳細は、「ボイスのフレーム リレー フラグメンテーション」を参照してください。
注:専用のハーフT1接続(768 kbps)がある場合は、フラグメンテーション機能は必要ありません。しかし、それでも QoS メカニズム(このケースでは IP RTP プライオリティまたは LLQ)は必要です。 ハーフ T1 またはそれよりも高速な回線では、推奨されるシリアル化遅延(送出遅延)の範囲(10 ミリ秒。最大限度 20 ミリ秒)内でボイス パケットをキューに出し入れするのに十分な帯域幅が提供されます。 フル T1 の場合は、IP RTP ヘッダーを圧縮して帯域幅を節約する cRTP も必要ありません。
帯域幅の削減
cRTP
RFC 2508 に基づき、IP/UDP/RTP パケット ヘッダーは cRTP 機能により 40 バイトから 2 バイトまたは 4 バイトに圧縮されます。 ![]() これにより、不要な帯域幅の使用が軽減されます。これはホップバイホップ圧縮方式です。そのため、パッシブ オプションが設定されていない場合は、リンクの両端で cRTP を設定する必要があります。
これにより、不要な帯域幅の使用が軽減されます。これはホップバイホップ圧縮方式です。そのため、パッシブ オプションが設定されていない場合は、リンクの両端で cRTP を設定する必要があります。
注:良好な音声品質を確保するためにcRTPは必要ありません。これは帯域幅の使用量を削減するための機能です。cRTP は、他の条件がすべて満たされていて、音声品質が良好な場合に設定してください。こうすると、cRTP の問題を切り離すことが可能になるので、トラブルシューティングに要する時間を短縮できます。
ルータの CPU 使用率を監視する必要があります。使用率が 75 % を超えた場合は cRTP を無効にしてください。回線速度が高速な場合は、cRTP による帯域幅の節約よりも CPU への負荷が問題になることがあります。ルータの CPU 使用率が高い場合を除き、768 Kbps よりも低速のリンクでは cRTP を使用することを推奨いたします。
注:標準がない場合、フレームリレー用のcRTPはシスコ独自のカプセル化で開発されました。そのため、cRTP はフレームリレーの Internet Engineering Task Force(IETF)カプセル化方式では動作しません。最近、IETF カプセル化方式で RTP ヘッダー圧縮を可能にする FRF.20 が標準化されました。ただし、この文書の最終更新時点(2002 年 5 月)では、シスコルータはFRF.20 をサポートしていません。
詳細は、『圧縮リアルタイム転送プロトコル』を参照してください。
コーダ/デコーダ(コーデック)の選択
VoIP コール レッグでは、低ビット レートのコーデックを使用してください。VoIP ダイヤルピアのデフォルト コーデックは G.729(8 Kbps)です。
注:デュアルトーン多重周波数(DTMF)は、通常、高ビットレートの音声コーデック(G.711など)を使用する場合は正確に転送されますが、低ビットレートのコーデック(G.729やG.723.1)は音声パターンに対して高度ににに最適化され、歪がされます。そのため、このアプローチを使用すると Interactive Voice Response(IVR; 対話式音声自動応答)システムへのアクセス時に問題が生じるおそれがあります。dtmf relay コマンドを使用すると、DTMF の歪みの問題が解消されます。DTMF トーンはアウトオブバンドで転送されるか、符号化されたボイス ストリームから切り離されて転送されます。低ビットレートのコーデック(G.729、G.723)を使用している場合は、VoIP ダイヤルピアで dtmf relay コマンドを有効にしてください。
Voice Activity Detection(VAD; ボイス アクティビティ検出)の有効化
標準的な会話には、35 ~ 50 % の無音部分が含まれています。VAD を使用すると、無音時にパケットの送出が抑制されます。VoIP の帯域幅を計画するときは、VAD によって帯域幅が 35 % 削減されるものと仮定してください。VoIP ダイヤルピアでは VAD がデフォルトで設定されています。
設定
このセクションでは、このドキュメントで説明する機能を設定するために必要な情報を提供しています。
注:この文書で使用されているコマンドの詳細を調べるには、「Command Lookup ツール」を使用してください(登録ユーザのみ)。
LLQ
LLQ を設定するには、次の手順に従います。
-
VoIP トラフィック用のクラス マップを作成し、照合基準を定義します。
この作業を行うには、次のコマンドを使用します。
maui-voip-sj(config)#class-map ? WORD class-map name match-all Logical-AND all matching statements under this classmap match-any Logical-OR all matching statements under this classmap maui-voip-sj(config)#class-map match-all voice-traffic !--- Choose a descriptive class_name. maui-voip-sj(config-cmap)#match ? access-group Access group any Any packets class-map Class map cos IEEE 802.1Q/ISL class of service/user priority values destination-address Destination address input-interface Select an input interface to match ip IP specific values mpls Multi Protocol Label Switching specific values not Negate this match result protocol Protocol qos-group Qos-group source-address Source address !--- In this example the access-group matching !--- option is used for its flexibility (it uses an access-list). maui-voip-sj(config-cmap)#match access-group ? <1-2699> Access list index name Named Access List maui-voip-sj(config-cmap)#match access-group 102 !--- Create the access-list to match the class-map access-group: maui-voip-sj(config)#access-list 102 permit udp any any range 16384 32767 !--- The safest and easiest way is to match with UDP port range 16384-32767. !--- This is the port range Cisco IOS H.323 products utilize to transmit !--- VoIP packets.match access-group コマンドでボイス トラフィックを照合するには、次のアクセスリストも使用します。
access-list 102 permit udp any any precedence critical !--- This list filters traffic based on the IP packet TOS: Precedence field. !--- Note: Ensure that the other non-voice traffic does not use the !--- same precedence value. access-list 102 permit udp any any dscp ef !--- In order for this list to work, ensure that VoIP packets are tagged !--- with the dscp ef code before they exit on the LLQ WAN interface. !--- For more information on DSCP, refer to !--- Implementing Quality of Service Policies with DSCP. !--- Note: If endpoints are not trusted on their packet marking, !--- mark incoming traffic by applying an inbound service policy on an !--- inbound interface. This procedure is out of the scope !--- of this document. access-list 102 permit udp host 192.10.1.1 host 192.20.1.1 !--- This access-list can be used in cases where the VoIP !--- devices cannot do precedence or DSCP marking and you !--- cannot determine the VoIP UDP port range.
access-group コマンドの代わりに使用できる他の照合方法を次に示します。
-
Cisco IOS ソフトウェア リリース 12.1.2.T 以降では、LLQ 向けに IP RTP プライオリティ機能が実装されています。この機能では、設定されている UDP ポートに基づいてプライオリティ クラスの内容が照合されます。ただし、PQ 内の偶数ポートだけが処理されるという制限があります。
class-map voice match ip rtp 16384 16383
-
次の 2 つの方法は、発信元ホストで VoIP パケットにマークが設定されているか、または発信 LLQ 処理が行われる前にルータで VoIP パケットが照合およびマーキングされるという前提のもとで使用できます。
class-map voice match ip precedence 5
または
class-map voice match ip dscp ef
注:Cisco IOSソフトウェアリリース12.2.2T以降では、VoIPダイヤルピアは、LLQ操作の前に音声ベアラとシグナリングパケットをマーキングできます。これにより、LLQ 用の DSCP コード値を通じて VoIP パケットのマーキングと照合を行うというスケーラブルな方法が可能になります。詳細は、「QoS のための DSCP による VoIP シグナリングとメディアの分類」を参照してください。
Router(config-dial-peer)#ip qos dscp ?
-
-
VoIP シグナリング用のクラス マップを作成し、照合基準を定義します(オプション)。
この作業を完了するには、次のコマンドを使用します。
class-map voice-signaling match access-group 103 ! access-list 103 permit tcp any eq 1720 any access-list 103 permit tcp any any eq 1720
注:VoIPコールは、H.323、セッション開始プロトコル(SIP)、メディアゲートウェイコントロールプロトコル(MGCP)、またはSkinny Call Control Protocol(SCCP)(Cisco Call Managerで使用される独自のプロトコル)を使用して確立できます。上記の例では H.323 Fast Connect を想定しています。次のリストは、VoIP シグナリングおよび制御チャネルで使用されるポート番号を示しています。
-
H.323/H.225 = TCP 1720
-
H.323/H.245 = TCP 11xxx(Standard Connect)
-
H.323/H.245 = TCP 1720(Fast Connect)
-
H.323/H.225 RAS = UDP 1718(ゲートキーパーへ)
-
SCCP = TCP 2000 ~ 2002(CM Encore)
-
ICCP = TCP 8001 ~ 8002(CM Encore)
-
MGCP = UDP 2427、TCP 2428(CM Encore)
-
SIP= UDP 5060、TCP 5060(設定可能)
-
-
ポリシー マップを作成して、VoIP クラス マップに関連付けます。
ポリシー マップの目的は、リンク リソースがどのように共有されるか、または各種マップ クラスにどのように割り当てられるかを定義することです。この作業を完了するには、次のコマンドを使用します。
maui-voip-sj(config)#policy-map VOICE-POLICY !--- Choose a descriptive policy_map_name. maui-voip-sj(config-pmap)#class voice-traffic maui-voip-sj(config-pmap-c)#priority ? <8-2000000> Kilo Bits per second !--- Configure the voice-traffic class to the strict PQ !--- (priority command) and assign the bandwidth. maui-voip-sj(config-pmap)#class voice-signaling maui-voip-sj(config-pmap-c)#bandwidth 8 !--- Assign 8 Kbps to the voice-signaling class. maui-voip-sj(config-pmap)#class class-default maui-voip-sj(config-pmap-c)#fair-queue !--- The remaining data traffic is treated as WFQ.
注:PQには、さまざまなタイプのリアルタイムトラフィックをキューイングできますが、音声トラフィックのみをキューイングすることをお勧めします。ビデオなどのリアルタイム トラフィックを PQ に入れると、パケットの揺らぎが生じる可能性があります(PQ は First In, First Out(FIFO)キューであるため)。 ボイス トラフィックでは、ジッタを避けるために遅延を一定にする必要があります。
注:priority文とbandwidth文の値の合計は、PVCのminCIR以下である必要があります。そうしないと、service-policy コマンドをリンクに割り当てることができません。minCIR はデフォルトでは CIR の半分の値になっています。エラー メッセージを表示するには、logging console コマンドが console アクセスで有効になっており、terminal monitor コマンドが Telnet アクセスで有効になっていることを確認してください。
bandwidth コマンドと priority コマンドの詳細は、『QOS サービス ポリシーの bandwidth コマンドと priority コマンドの比較』を参照してください。
-
ポリシー マップを発信側の WAN インターフェイスに適用して、LLQ を有効にします。
LLQ を有効にするには、次のコマンドを使用します。
maui-voip-sj(config)#map-class frame-relay VoIPovFR maui-voip-sj(config-if)#service-policy output VOICE-POLICY !--- The service-policy is applied to the PVC !--- indirectly by configuring !--- it under the map-class associated to the PVC.
IP RTP プライオリティ
LLQ を使用しない場合は、次のガイドラインに従います。
Router(config-map-class)#frame-relay ip rtp priority starting-rtp-port port-range bandwidth
-
starting-rtp-port:最初の UDP ポート番号です。これはパケットが送信される最小のポート番号です。VoIP では、この値を 16384 に設定します。
-
port-range:UDP 宛先ポートの範囲です。starting-rtp-port にこの数値を加えた値が最大の UDP ポート番号になります。VoIP では、この値を 16383 に設定します。
-
bandwidth:優先キューに割り当てられる最大の帯域幅を kbps で表します。この数値は、同時コール数と、システムでサポートされる各コールの帯域幅に基づいて設定します。
設定例:
map-class frame-relay VoIPovFR frame-relay cir 64000 frame-relay BC 600 no frame-relay adaptive-shaping frame-relay fair-queue frame-relay fragment 80 frame-relay ip rtp priority 16384 16383 45
ボイスのためのトラフィック シェーピング
ボイスのトラフィック シェーピングを設定する場合は、次のガイドラインに従います。
-
PVC の CIR 値を超えないようにする。
-
フレームリレーのアダプティブ シェーピングを無効にする。
-
Tc(シェーピング間隔)が 10 ミリ秒になるように Bc を低い値に設定する(Tc = Bc/CIR)。 目的の Tc 値が確実に得られるように Bc 値を設定する。
-
Be 値を 0 に設定する。
このガイドラインの詳細は、『VoIP および VoFR 用のフレームリレー トラフィック シェーピング』を参照してください。
注:一部のお客様は、データと音声に個別のPVCを使用しています。2 つの PVC がある場合、データ側 PVC でバースト伝送を行おうとすると、ボイス側 PVC が Committed Information Rate(CIR; 認定情報レート)を超えない状態であっても、ボイス品質に悪影響が及ぶ可能性があります。これは、両方の PVC が同じ物理インターフェイスを使用しているためです。このような場合は、ルータだけでなく、フレームリレー プロバイダーでもボイス PVC に優先順位を設定する必要があります。後者の方法は、Cisco IOS ソフトウェア リリース 12.1(1)T では、PVC Interface Priority Queueing(PIPQ)で利用可能です。
フラグメンテーション(FRF.12)
低速リンク(768 kbps 以下)ではフラグメンテーションを有効にします。 音声パケットがフラグメント化されず、20ミリ秒を超えるシリアル化遅延が発生しないように、フラグメントサイズを設定します。フラグメンテーションサイズは、ルータ間で最も低速側の回線速度を基準として設定します。たとえば、ハブ & スポーク型のフレームリレー トポロジで、ハブ ルータの速度が T1、リモート ルータのポート速度が 64 K の場合、フラグメンテーション サイズはどちらのルータでも 64 K の速度を基準に設定する必要があります。同じ物理インターフェイスを共有する PVC があれば、それらの PVC には必ずボイス PVC で使用されているのと同じフラグメンテーション サイズを設定するようにします。フラグメンテーション サイズの値を決める際は、次の表に従ってください。
| パス内の最も遅いリンク速度 | 推奨されるフラグメンテーション サイズ(シリアル化遅延が 10 ミリ秒の場合) |
|---|---|
| 56 Kbps | 70 バイト |
| 64 Kbps | 80 バイト |
| 128 Kbps | 160 バイト |
| 256 Kbps | 320 バイト |
| 512 Kbps | 640 バイト |
| 768 Kbps | 1000 バイト |
| 1536 Kbps | 1600 バイト |
設定例:
map-class frame-relay VoIPovFR !--- Some output is omitted. frame-relay fragment 80
注:1536 Kbpsの場合、技術的にフラグメンテーションは必要ありません。ただし、デュアル FIFO キューイング システムを有効にしてボイス品質を確保する場合は、フラグメンテーションが必要になります。フラグメント サイズを 1600 バイトにすると、デュアル FIFO が有効になります。ただし、1600 バイトは標準シリアル インターフェイスの Maximum Transmission Unit(MTU; 最大伝送ユニット)を超えているため、大きなデータ パケットは分割されません。
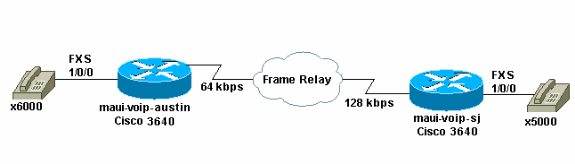
ネットワーク図
このドキュメントでは、次の図に示すネットワーク設定を使用します。
設定
このドキュメントで使用する設定を次に示します。
-
maui-voip-sj(Cisco 3640)
-
maui-voip-austin(Cisco 3640)
| maui-voip-sj(Cisco 3640) |
|---|
version 12.2 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption ! hostname maui-voip-sj ! logging buffered 10000 debugging enable secret 5 $1$MYS3$TZ6bwrhWB25b2cVpEVgBo1 ! ip subnet-zero ! !--- Definition of the voice signaling and traffic class maps. !--- "voice-traffic" class uses access-list 102 for its matching criteria. !--- "voice-signaling" class uses access-list 103 for its matching criteria. class-map match-all voice-signaling match access-group 103 class-map match-all voice-traffic match access-group 102 ! !--- The policy map defines how the link resources are assigned !--- to the different map classes. In this configuration, strict PQ !--- is assigned to the voice-traffic class !--- with a maximum bandwidth of 45 Kbps. policy-map VOICE-POLICY class voice-traffic priority 45 class voice-signaling bandwidth 8 !--- Assigns a queue for voice-signaling traffic that ensures 8 Kbps. !--- Note that this is optional and has nothing to do with good voice !--- quality. Instead, it is a way to secure signaling. class class-default fair-queue !--- The class-default class is used to classify traffic that does !--- not fall into one of the defined classes. !--- The fair-queue command associates the default class WFQ queueing. ! interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 172.22.113.3 255.255.255.0 half-duplex ! interface Serial0/0 bandwidth 128 no ip address encapsulation frame-relay no fair-queue frame-relay traffic-shaping frame-relay ip rtp header-compression !--- Turns on traffic shaping and cRTP. If traffic-shaping is not !--- enabled, then map-class does not start and FRF.12 and LLQ does !--- not work. ! interface Serial0/0.1 point-to-point bandwidth 128 ip address 192.168.10.2 255.255.255.252 frame-relay interface-dlci 300 class VOIPovFR !--- This command links the subinterface to a VoIPovFR map-class. !--- See the map-class frame-relay VoIPovFR command here: !--- Note: The word VoIPovFR is selected by the user. ! ip classless ip route 172.22.112.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.10.1 ! map-class frame-relay VOIPovFR no frame-relay adaptive-shaping !--- Disable Frame Relay BECNS. Note also that Be equals 0 by default. frame-relay cir 64000 frame-relay bc 640 !--- Tc = BC/CIR. In this case Tc is forced to its minimal !--- configurable value of 10 ms. frame-relay be 0 frame-relay mincir 64000 !--- Although adaptive shaping is disabled, make CIR equal minCIR !--- as a double safety. By default minCIR is half of CIR. service-policy output VOICE-POLICY !--- Enables LLQ on the PVC. frame-relay fragment 80 !--- Turns on FRF.12 fragmentation and sets the fragment size equal to 80 bytes. !--- This value is based on the port speed of the slowest path link. !--- This command also enables dual-FIFO. ! access-list 102 permit udp any any range 16384 32767 access-list 103 permit tcp any eq 1720 any access-list 103 permit tcp any any eq 1720 ! !--- access-list 102 matches VoIP traffic !--- based on the UDP port range. !--- Both odd and even ports are put into the PQ. !--- access-list 103 matches VoIP signaling protocol. In this !--- case, H.323 V2 is uesd with the fast start feature. ! voice-port 1/0/0 ! dial-peer voice 1 pots destination-pattern 5000 port 1/0/0 ! dial-peer voice 2 voip destination-pattern 6000 session target ipv4:192.168.10.1 dtmf-relay cisco-rtp ip precedence 5 |
| maui-voip-austin(Cisco 3640) |
|---|
version 12.2
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
service password-encryption
!
hostname maui-voip-austin
!
boot system flash slot1:c3640-is-mz.122-6a.bin
logging buffered 1000000 debugging
!
ip subnet-zero
!
class-map match-all voice-signaling
match access-group 103
class-map match-all voice-traffic
match access-group 102
!
policy-map voice-policy
class voice-signaling
bandwidth 8
class voice-traffic
priority 45
class class-default
fair-queue
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 172.22.112.3 255.255.255.0
no keepalive
half-duplex
!
interface Serial0/0
bandwidth 64
no ip address
encapsulation frame-relay
no ip mroute-cache
no fair-queue
frame-relay traffic-shaping
frame-relay ip rtp header-compression
!
interface Serial0/0.1 point-to-point
bandwidth 64
ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
frame-relay interface-dlci 400
class VOIPovFR
!
ip classless
ip route 172.22.113.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.10.2
!
map-class frame-relay VOIPovFR
no frame-relay adaptive-shaping
frame-relay cir 64000
frame-relay bc 640
frame-relay be 0
frame-relay mincir 64000
service-policy output voice-policy
frame-relay fragment 80
access-list 102 permit udp any any range 16384 32767
access-list 103 permit tcp any eq 1720 any
access-list 103 permit tcp any any eq 1720
!
voice-port 1/0/0
!
dial-peer voice 1 pots
destination-pattern 6000
port 1/0/0
!
dial-peer voice 2 voip
destination-pattern 5000
session target ipv4:192.168.10.2
dtmf-relay cisco-rtp
ip precedence 5 |
確認とトラブルシューティング
このセクションでは、設定が正常に動作しているかどうかを確認するための情報について説明しています。
一部の show コマンドが、アウトプット インタープリタ ツール(登録ユーザ専用)でサポートされています。 これを使用して、show コマンドの出力の解析を表示できます。
LLQ / IP RTP プライオリティのコマンド
次に示す show コマンドと debug コマンドを使用すると、LLQ および IP RTP プライオリティの設定を容易に検証できます。
-
show policy-map interface serial interface#:このコマンドは、LLQ の動作と PQ での廃棄を表示するのに便利です。このコマンドのさまざまなフィールドの詳細は、『show policy-map interface 出力内のパケット カウンタについて』を参照してください。
-
show policy-map policy_map_name:ポリシーマップ設定に関する情報を表示します。
-
show queue interface-type interface-number:特定のインターフェイスの均等化キューイング設定と統計情報を表示します。
-
debug priority:PQ イベントを表示して、このキューで廃棄が発生しているかどうかを示します。詳細は、『プライオリティ キューイングによる出力ドロップのトラブルシューティング』を参照してください。
-
show class-map class_name:クラスマップ設定に関する情報を表示します。
-
show call active voice:DSP レベルで損失パケットをチェックします。
-
show frame-relay ip rtp header-compression:RTP ヘッダー圧縮の統計情報を表示します。
フラグメンテーションのコマンド
フラグメンテーション設定の確認とトラブルシューティングを行うには、次の debug コマンドと show コマンドを使用します。
-
show frame-relay fragment:Cisco ルータで実行されているフレームリレー フラグメンテーションに関する情報を表示します。
-
debug frame-relay fragment—フレームリレー フラグメンテーションに関連するイベントまたはエラー メッセージを表示します。このデバッグは、選択したインターフェイスの PVC レベルでだけ有効になります。
フレームリレー / インターフェイスのコマンド
フレームリレー/インターフェイス設定の確認とトラブルシューティングを行うには、次の show コマンドを使用します。
-
show traffic-shape queue interface:VC Data-Link Connection Identifier(DLCI; データリンク接続識別子)レベルでキューイングされたエレメントに関する情報を表示します。これは、フレームリレー上での IP RTP プライオリティの動作を確認するときに使用します。リンクが輻輳している場合、ボイス フローは重み(weight)0 で識別されます。これはボイス フローが PQ を使用していることを示します。下記の出力例を参照してください。
-
show traffic-shape:Tc、Bc、Be、CIR などの設定値情報を表示します。出力例を参照してください。
-
show frame-relay pvc dlci-#:トラフィック シェーピング パラメータ、フラグメンテーション値、廃棄パケットなどの情報を表示します。出力例を参照してください。『トラブルシューティング:フレーム リレー』も参照してください。
既知の問題
VC ごとの LLQ で不具合が確認されており、インターフェイス上で輻輳が発生していない場合でも、PQ で完全なポリシングが行われてしまいます。この不具合はすでに解決されており、現在では、非適合パケットが廃棄されるのは VC 上で輻輳が発生している場合だけです。これにより、VC ごとの LLQ の動作も、LLQ を使用する他のインターフェイスでの動作と同じになります。この動作の修正は、Cisco IOS ソフトウェア リリース 12.2(3) 以降に取り込まれています。
show コマンド と debug コマンドの出力例
確認とトラブルシューティングに使用される show コマンドと debug コマンドの出力例を次に示します。
!--- To capture sections of this output, the LLQ PQ bandwidth !--- is lowered and large data traffic is placed !--- on the link to force packets drops. !--- Priority queue bandwidth is lowered to 10 Kbps to force drops from the PQ. !--- Note: To reset counters, use the clear counters command.
maui-voip-sj#show policy-map inter ser 0/0.1
Serial0/0.1: DLCI 300 -
Service-policy output: VOICE-POLICY
Class-map: voice-traffic (match-all)
26831 packets, 1737712 bytes
5 minute offered rate 3000 bps, drop rate 2000 bps
Match: access-group 102
Weighted Fair Queueing
Strict Priority
Output Queue: Conversation 24
Bandwidth 10 (kbps) Burst 250 (Bytes)
(pkts matched/bytes matched) 26311/1704020
(total drops/bytes drops) 439/28964
Class-map: voice-signaling (match-all)
80 packets, 6239 bytes
5 minute offered rate 0 bps, drop rate 0 bps
Match: access-group 103
Weighted Fair Queueing
Output Queue: Conversation 25
Bandwidth 8 (kbps) Max Threshold 64 (packets)
(pkts matched/bytes matched) 62/4897
(depth/total drops/no-buffer drops) 0/0/0
Class-map: class-default (match-any)
14633 packets, 6174492 bytes
5 minute offered rate 10000 bps, drop rate 0 bps
Match: any
Weighted Fair Queueing
Flow Based Fair Queueing
Maximum Number of Hashed Queues 16
(total queued/total drops/no-buffer drops) 0/0/0
!--- These commands are useful to verify the LLQ configuration.
maui-voip-austin#show policy-map voice-policy
Policy Map voice-policy
Class voice-signaling
Weighted Fair Queueing
Bandwidth 8 (kbps) Max Threshold 64 (packets)
Class voice-traffic
Weighted Fair Queueing
Strict Priority
Bandwidth 45 (kbps) Burst 1125 (Bytes)
Class class-default
Weighted Fair Queueing
Flow based Fair Queueing Max Threshold 64 (packets)
maui-voip-austin#show class-map
Class Map match-all voice-signaling (id 2)
Match access-group 103
Class Map match-any class-default (id 0)
Match any
Class Map match-all voice-traffic (id 3)
Match access-group 102
!--- Frame Relay verification command output.
maui-voip-sj#show frame-relay fragment
interface dlci frag-type frag-size in-frag out-frag dropped-frag
Serial0/0.1 300 end-to-end 80 4 4 0
maui-voip-sj#show frame-relay pvc 300
PVC Statistics for interface Serial0/0 (Frame Relay DTE)
DLCI = 300, DLCI USAGE = LOCAL, PVC STATUS = ACTIVE, INTERFACE = Serial0/0.1
input pkts 7 output pkts 7 in bytes 926
out bytes 918 dropped pkts 0 in FECN pkts 0
in BECN pkts 0 out FECN pkts 0 out BECN pkts 0
in DE pkts 0 out DE pkts 0
out bcast pkts 2 out bcast bytes 598
pvc create time 1w2d, last time pvc status changed 1w2d
service policy VOICE-POLICY
Service-policy output: VOICE-POLICY
Class-map: voice-traffic (match-all)
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute offered rate 0 bps, drop rate 0 bps
Match: access-group 102
Weighted Fair Queueing
Strict Priority
Output Queue: Conversation 24
Bandwidth 45 (kbps) Burst 250 (Bytes)
(pkts matched/bytes matched) 0/0
(total drops/bytes drops) 0/0
Class-map: voice-signaling (match-all)
0 packets, 0 bytes
5 minute offered rate 0 bps, drop rate 0 bps
Match: access-group 103
Weighted Fair Queueing
Output Queue: Conversation 25
Bandwidth 8 (kbps) Max Threshold 64 (packets)
(pkts matched/bytes matched) 0/0
(depth/total drops/no-buffer drops) 0/0/0
Class-map: class-default (match-any)
7 packets, 918 bytes
5 minute offered rate 0 bps, drop rate 0 bps
Match: any
Weighted Fair Queueing
Flow Based Fair Queueing
Maximum Number of Hashed Queues 16
(total queued/total drops/no-buffer drops) 0/0/0
Output queue size 0/max total 600/drops 0
fragment type end-to-end fragment size 80
cir 64000 bc 640 be 0 limit 80 interval 10
mincir 64000 byte increment 80 BECN response no
frags 13 bytes 962 frags delayed 8 bytes delayed 642
shaping inactive
traffic shaping drops 0
!--- In this Frame Relay verification command !--- output, the PQ bandwidth is lowered and heavy traffic !--- is placed on the interface to force drops.
maui-voip-sj#show frame-relay pvc 300
PVC Statistics for interface Serial0/0 (Frame Relay DTE)
DLCI = 300, DLCI USAGE = LOCAL, PVC STATUS = ACTIVE, INTERFACE = Serial0/0.1
input pkts 483 output pkts 445 in bytes 122731
out bytes 136833 dropped pkts 0 in FECN pkts 0
in BECN pkts 0 out FECN pkts 0 out BECN pkts 0
in DE pkts 0 out DE pkts 0
out bcast pkts 4 out bcast bytes 1196
pvc create time 1w2d, last time pvc status changed 1w2d
service policy VOICE-POLICY
Service-policy output: VOICE-POLICY
Class-map: voice-traffic (match-all)
352 packets, 22900 bytes
5 minute offered rate 2000 bps, drop rate 2000 bps
Match: access-group 102
Weighted Fair Queueing
Strict Priority
Output Queue: Conversation 24
Bandwidth 10 (kbps) Burst 250 (Bytes)
(pkts matched/bytes matched) 352/22900
(total drops/bytes drops) 169/11188
Class-map: voice-signaling (match-all)
7 packets, 789 bytes
5 minute offered rate 0 bps, drop rate 0 bps
Match: access-group 103
Weighted Fair Queueing
Output Queue: Conversation 25
Bandwidth 8 (kbps) Max Threshold 64 (packets)
(pkts matched/bytes matched) 7/789
(depth/total drops/no-buffer drops) 0/0/0
Class-map: class-default (match-any)
79 packets, 102996 bytes
5 minute offered rate 4000 bps, drop rate 0 bps
Match: any
Weighted Fair Queueing
Flow Based Fair Queueing
Maximum Number of Hashed Queues 16
(total queued/total drops/no-buffer drops) 5/0/0
Output queue size 5/max total 600/drops 169
fragment type end-to-end fragment size 80
cir 64000 bc 640 be 0 limit 80 interval 10
mincir 64000 byte increment 80 BECN response no
frags 2158 bytes 178145 frags delayed 1968 bytes delayed 166021
shaping active
traffic shaping drops 169
!--- Notice that the Tc interval equals 10 ms, !--- CIR equals 64000 BPS, and BC equals 640.
maui-voip-sj#show traffic-shape
Interface Se0/0.1
Access Target Byte Sustain Excess Interval Increment Adapt
VC List Rate Limit bits/int bits/int (ms) (bytes) Active
300 64000 80 640 0 10 80 -
!--- This output is captured on an isolated lab enviroment where !--- the routers are configured with IP RTP Priority instead of LLQ.
maui-voip-austin#show frame-relay PVC 100
PVC Statistics for interface Serial0/1 (Frame Relay DTE)
DLCI = 100, DLCI USAGE = LOCAL, PVC STATUS = ACTIVE, INTERFACE = Serial0/1.1
input pkts 336 output pkts 474 in bytes 61713
out bytes 78960 dropped pkts 0 in FECN pkts 0
in BECN pkts 0 out FECN pkts 0 out BECN pkts 0
in DE pkts 0 out DE pkts 0
out bcast pkts 0 out bcast bytes 0
PVC create time 1w0d, last time PVC status changed 1w0d
Current fair queue configuration:
Discard Dynamic Reserved
threshold queue count queue count
64 16 2
Output queue size 0/max total 600/drops 0
fragment type end-to-end fragment size 80
cir 64000 BC 640 be 0 limit 125 interval 10
mincir 32000 byte increment 125 BECN response no
frags 1091 bytes 82880 frags delayed 671 bytes delayed 56000
shaping inactive
traffic shaping drops 0
ip rtp priority parameters 16384 32767 45000
!--- This command displays information of the VoIP dial-peers.
maui-voip-austin#show dial-peer voice 2
VoiceOverIpPeer2
information type = voice,
tag = 2, destination-pattern = `5000',
answer-address = `', preference=0,
group = 2, Admin state is up, Operation state is up,
incoming called-number = `', connections/maximum = 0/unlimited,
application associated:
type = voip, session-target = `ipv4:192.168.10.2',
technology prefix:
ip precedence = 5, UDP checksum = disabled,
session-protocol = cisco, req-qos = best-effort,
acc-qos = best-effort,
dtmf-relay = cisco-rtp,
fax-rate = voice, payload size = 20 bytes
codec = g729r8, payload size = 20 bytes,
Expect factor = 10, Icpif = 30,signaling-type = cas,
VAD = enabled, Poor QOV Trap = disabled,
Connect Time = 165830, Charged Units = 0,
Successful Calls = 30, Failed Calls = 0,
Accepted Calls = 30, Refused Calls = 0,
Last Disconnect Cause is "10",
Last Disconnect Text is "normal call clearing.",
Last Setup Time = 69134010.
 フィードバック
フィードバック