Comprendre le flux CWA sur un client
Options de téléchargement
-
ePub (1.6 MB)
Consulter à l’aide de différentes applications sur iPhone, iPad, Android ou Windows Phone -
Mobi (Kindle) (1.0 MB)
Consulter sur un appareil Kindle ou à l’aide d’une application Kindle sur plusieurs appareils
Langage exempt de préjugés
Dans le cadre de la documentation associée à ce produit, nous nous efforçons d’utiliser un langage exempt de préjugés. Dans cet ensemble de documents, le langage exempt de discrimination renvoie à une langue qui exclut la discrimination en fonction de l’âge, des handicaps, du genre, de l’appartenance raciale de l’identité ethnique, de l’orientation sexuelle, de la situation socio-économique et de l’intersectionnalité. Des exceptions peuvent s’appliquer dans les documents si le langage est codé en dur dans les interfaces utilisateurs du produit logiciel, si le langage utilisé est basé sur la documentation RFP ou si le langage utilisé provient d’un produit tiers référencé. Découvrez comment Cisco utilise le langage inclusif.
À propos de cette traduction
Cisco a traduit ce document en traduction automatisée vérifiée par une personne dans le cadre d’un service mondial permettant à nos utilisateurs d’obtenir le contenu d’assistance dans leur propre langue. Il convient cependant de noter que même la meilleure traduction automatisée ne sera pas aussi précise que celle fournie par un traducteur professionnel.
Table des matières
Introduction
Ce document décrit le flux du client final lors de la connexion à un WLAN CWA.
Conditions préalables
Exigences
Cisco vous recommande d'avoir des connaissances de base sur :
- Contrôleur LAN sans fil Cisco (WLC) série 9800
- Compréhension générale de l'authentification Web centrale (CWA) et de sa configuration sur Identity Services Engine (ISE)
Composants utilisés
Les informations contenues dans ce document sont basées sur les versions logicielles et matérielles suivantes :
- WLC 9800-CL
- Cisco AP 3802
- 9800 WLC Cisco IOS® XE v17.3.6
- Identity Service Engine (ISE) v3.1
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. Si votre réseau est en ligne, assurez-vous de bien comprendre l’incidence possible des commandes.
Informations générales
CWA est un type d'authentification SSID qui peut être configuré sur le WLC où le client final essayant de se connecter est invité à entrer son nom d'utilisateur et son mot de passe sur un portail Web qui lui est présenté. En bref, le flux du client final lors de la connexion au WLAN est le suivant :
- Le client final se connecte au SSID affiché sur son périphérique
- Le client final est redirigé vers le portail Web pour entrer ses informations d'identification
- Le client final est authentifié par ISE avec les informations d'identification entrées
- ISE répond au WLC en disant que le client final a été authentifié. ISE peut transmettre certains attributs supplémentaires que le client doit respecter lors de l'accès au réseau (tels que des listes de contrôle d'accès spécifiques)
- Le client final est ré-associé et ré-authentifié, puis accède au réseau

Remarque : il est important de noter que le client final authentifié deux fois est transparent pour le client final
Le processus sous-jacent par lequel le client doit passer est divisé en deux : une connexion du client au serveur ISE et, une fois authentifié, une autre connexion du client au réseau lui-même. Le contrôleur et ISE communiquent toujours entre eux via le protocole RADIUS. Ci-dessous, une analyse approfondie d'une trace radioactive (RA) et d'une capture de paquets intégrée (EPC).
Flux CWA - Suivi radioactif (RA)
Une trace RA est un ensemble de journaux capturés pour un client spécifique. Elle montre l'ensemble du processus que le client est en train de suivre lors de la connexion à un WLAN. Pour plus d'informations sur ce qu'ils sont et comment récupérer des traces RA, veuillez visiter Comprendre les débogages sans fil et la collection de journaux sur les contrôleurs LAN sans fil Catalyst 9800.
Première connexion : client vers serveur ISE
Le WLC n'autorise pas une connexion au réseau si le client n'a pas été autorisé par ISE auparavant.
Association au WLAN
Le WLC détecte que le client veut s'associer au WLAN « cwa », qui est lié au profil de politique « cwa-policy-profile » et se connecte au point d'accès « BC-3802 »
[client-orch-sm] [17558]: (note): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Association received. BSSID dc8c.37d0.83af, WLAN cwa, Slot 1 AP dc8c.37d0.83a0, BC-3802
[client-orch-sm] [17558]: (debug): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Received Dot11 association request. Processing started,SSID: cwa, Policy profile: cwa-policy-profile, AP Name: BC-3802, Ap Mac Address: dc8c.37d0.83a0 BSSID MAC0000.0000.0000 wlan ID: 1RSSI: -46, SNR: 40
[client-orch-state] [17558]: (note): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Client state transition: S_CO_INIT -> S_CO_ASSOCIATING
[dot11-validate] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 WiFi direct: Dot11 validate P2P IE. P2P IE not present.
Filtrage MAC
Tester la connectivité du serveur ISE
Une fois que le WLC a reçu la demande d'association du client, la première étape consiste à effectuer le filtrage MAC (également connu sous le nom de MAB). Le filtrage MAC est une méthode de sécurité dans laquelle l'adresse MAC du client est comparée à une base de données pour vérifier si ces derniers sont autorisés à se connecter au réseau ou non.
[dot11] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 DOT11 state transition: S_DOT11_INIT -> S_DOT11_MAB_PENDING <-- The WLC is waiting for ISE to authenticate the user. It does not send an "Association Response" until the client is accepted by ISE.
[client-orch-state] [17558]: (note): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Client state transition: S_CO_ASSOCIATING -> S_CO_MACAUTH_IN_PROGRESS
[client-auth] [17558]: (note): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 MAB Authentication initiated. Policy VLAN 0, AAA override = 1, NAC = 1 <-- no VLAN is assigned as ISE can do that
[sanet-shim-translate] [17558]: (ERR): 4203.9522.e682 wlan_profile Not Found : Device information attributes not populated
[auth-mgr] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] Session Start event called from SANET-SHIM with conn_hdl 14, vlan: 0
[auth-mgr] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] Wireless session sequence, create context with method MAB
[auth-mgr-feat_wireless] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] - authc_list: cwa_authz <-- Authentication method list used
[auth-mgr-feat_wireless] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] - authz_list: Not present under wlan configuration
[client-auth] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Client auth-interface state transition: S_AUTHIF_INIT -> S_AUTHIF_AWAIT_MAB_AUTH_START_RESP
[auth-mgr] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:unknown] auth mgr attr change notification is received for attr (952)
[auth-mgr] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] auth mgr attr change notification is received for attr (1263)
[auth-mgr] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] auth mgr attr change notification is received for attr (220)
[auth-mgr] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] auth mgr attr change notification is received for attr (952)
[auth-mgr] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] Retrieved Client IIF ID 0x530002f1
[auth-mgr] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] Allocated audit session id 0E1E140A0000000C8E2DA642
[auth-mgr] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] Applying policy for WlanId: 1, bssid : dc8c.37d0.83af, slotid: 1 bssid hdl : 12364632849490379189
[auth-mgr] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] Wlan vlan-id from bssid hdl 0
[auth-mgr] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] SM Reauth Plugin: Received valid timeout = 1800
[mab] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] MAB authentication started for 4203.9522.e682
[client-auth] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Client auth-interface state transition: S_AUTHIF_AWAIT_MAB_AUTH_START_RESP -> S_AUTHIF_MAB_AUTH_PENDING
[ewlc-infra-evq] [17558]: (note): Authentication Success. Resolved Policy bitmap:11 for client 4203.9522.e682
[client-auth] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Client auth-interface state transition: S_AUTHIF_MAB_AUTH_PENDING -> S_AUTHIF_MAB_AUTH_PENDING
[mab] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] Received event 'MAB_CONTINUE' on handle 0x8A000002 <-- ISE server connectivity has been tested, the WLC is about to send the MAC address to ISE
[caaa-author] [17558]: (info): [CAAA:AUTHOR:92000002] DEBUG: mlist=cwa_authz for type=1
WLC envoie une requête à ISE
Le WLC envoie un paquet de demande d'accès RADIUS à ISE contenant l'adresse MAC du client qui veut s'authentifier auprès du WLAN.
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Send Access-Request to <ise-ip-addr>:1812 id 0/28, len 415 <-- The packet is traveling via RADIUS port 1812. The "28" is the session ID and it is unique for every connection attempt
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: authenticator e7 85 1b 08 31 58 ee 91 - 17 46 82 79 7d 3b c4 30
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: User-Name [1] 14 "42039522e682" <-- MAC address that is attempting to authenticate
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: User-Password [2] 18 *
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 25 "service-type=Call Check" <-- This indicates a MAC filtering process
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Framed-MTU [12] 6 1485
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Message-Authenticator[80] 18 ...
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: EAP-Key-Name [102] 2 *
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 43 "audit-session-id=0E1E140A0000000C8E2DA642"
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 12 "method=mab" <-- Controller sends an AVpair with MAB method
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 26 "client-iif-id=1392509681"
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 14 "vlan-id=1000"
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: NAS-IP-Address [4] 6 <wmi-ip-addr> <-- WLC WMI IP address
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: NAS-Port-Id [87] 17 "capwap_90000005"
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: NAS-Port-Type [61] 6 802.11 wireless [19]
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 30 "cisco-wlan-ssid=cwa" <-- SSID and WLAN the client is attempting to connect
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 32 "wlan-profile-name=cwa"
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Called-Station-Id [30] 32 "dc-8c-37-d0-83-a0:cwa"
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Calling-Station-Id [31] 19 "42-03-95-22-e6-82"
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Airespace-WLAN-ID [1] 6 1
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Nas-Identifier [32] 9 "BC-9800"
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Started 5 sec timeout

Remarque : une paire AV est « Attribute-Value » utilisée par ISE. Il s'agit d'une structure Key-Value d'informations prédéfinies qui peuvent être envoyées au WLC. Ces valeurs sont appliquées à ce client spécifique pour cette session spécifique.
Exemples de paires AV :
- Nom ACL
- URL de redirection
- Attribution de VLAN
- Temporisation de session
- Minuteurs de réauthentification
ISE répond à la requête WLC
Si l'adresse MAC envoyée par le WLC est acceptée par ISE, alors ISE envoie un paquet Access-Accept RADIUS. En fonction de la configuration ISE, s'il s'agit d'une adresse MAC inconnue, ISE doit l'accepter et poursuivre le flux. Si vous voyez un Access-Reject, alors il y a quelque chose de mal configuré sur ISE qui doit être vérifié.
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Received from id 1812/28 <ise-ip-addr>:0, Access-Accept, len 334 <-- The packet is traveling via RADIUS port 1812 and is has a session ID of 28 (as a response to the above packet)
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: authenticator 14 0a 6c f7 01 b2 77 6a - 3d ba f0 ed 92 54 9b d6
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: User-Name [1] 19 "42-03-95-22-E6-82" <-- MAC address of the client that was authorized by ISE
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Class [25] 51 ...
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Message-Authenticator[80] 18 ...
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 31 "url-redirect-acl=cwa-acl" <-- ACL to be applied to the client
[radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 183 "url-redirect=https://<ise-ip-addr>:8443/portal/[...]" <-- Redirection URL for the client
[radius] [17558]: (info): Valid Response Packet, Free the identifier
[eap-auth] [17558]: (info): SUCCESS for EAP method name: Identity on handle 0xB0000039
[mab] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] MAB received an Access-Accept for 0x8A000002
[mab] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] Received event 'MAB_RESULT' on handle 0x8A000002
[auth-mgr] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] Authc success from MAB, Auth event success
Processus WLC des informations reçues d'ISE
Le WLC traite toutes les informations reçues d'ISE. Avec elle, il applique le profil utilisateur qu'il avait créé à l'origine avec celui des données envoyées par ISE. Le WLC attribue une nouvelle liste de contrôle d'accès à l'utilisateur, par exemple. Si AAA Override n'est pas activé sur le WLAN, ce traitement par le WLC ne se produit pas.
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info):
<< username 0 "42-03-95-22-E6-82">> <-- Processing username received from ISE
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info):
<< class 0 43 41 43 53 3a 30 45 31 45 31 34 30 41 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 43 38 45 32 44 41 36 34 32 3a 62 63 2d 69 73 65 2f 34 33 36 37 33 31 34 32 37 2f 33 38 >>
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info):
<<Message-Authenticator 0 <hidden>>>
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info):
<< url-redirect-acl 0 "cwa-acl">> <-- Processing ACL redirection received from ISE
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info):
<< url-redirect 0 "https://<ise-ip-addr>:8443/portal/[...]">> <-- Processing URL redirection received from ISE
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info):
<< dnis 0 "DC-8C-37-D0-83-A0">>
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info):
<< formatted-clid 0 "42-03-95-22-E6-82">>
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info):
<< audit-session-id 0 "0E1E140A0000000C8E2DA642">>
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info):
<< method 0 2 [mab]>>
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info):
<< clid-mac-addr 0 42 03 95 22 e6 82 >>
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info):
<< intf-id 0 2415919109 (0x90000005)>>
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [auth-mgr] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] auth mgr attr change notification is received for attr (450)
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [auth-mgr] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] Received User-Name 42-03-95-22-E6-82 for client 4203.9522.e682
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [auth-mgr] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] User profile is to be applied. Authz mlist is not present, Authc mlist cwa_authz ,session push flag is unset
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [webauth-dev] [17558]: (info): Central Webauth URL Redirect, Received a request to create a CWA session for a mac [42:03:95:22:e6:82]
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [auth-mgr-feat_wireless] [17558]: (info): [0000.0000.0000:unknown] Retrieved zone id 0x0 for bssid 12364632849490379189
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [webauth-dev] [17558]: (info): No parameter map is associated with mac 4203.9522.e682
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [epm-redirect] [17558]: (info): [0000.0000.0000:unknown] URL-Redirect-ACL = cwa-acl
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [epm-redirect] [17558]: (info): [0000.0000.0000:unknown] URL-Redirect = https://<ise-ip-addr>:8443/portal/[...]
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [auth-mgr] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] User Profile applied successfully for 0x92000002 - REPLACE <-- WLC replaces the user profile it had originally created
Authentification MAB terminée
Une fois que le profil utilisateur du client a été modifié avec succès, le WLC termine l'authentification de l'adresse MAC du client. Si la liste de contrôle d'accès reçue d'ISE n'existe pas sur le WLC, le WLC ne sait pas quoi faire avec ces informations, et par conséquent l'action REPLACE échoue complètement provoquant l'échec de l'authentification MAB aussi bien. Le client ne peut pas s'authentifier.
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [mm-client] [17558]: (debug): MAC: 0000.0000.0000 Sending pmk_update of XID (0) to (MobilityD[0])
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-auth] [17558]: (note): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 MAB Authentication success.
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-auth] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Client auth-interface state transition: S_AUTHIF_MAB_AUTH_PENDING -> S_AUTHIF_MAB_AUTH_DONE
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-orch-sm] [17558]: (debug): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Processing MAB authentication result status: 0, CO_AUTH_STATUS_SUCCESS
WLC envoie une réponse d'association au client
Maintenant que le client a été authentifié par ISE et que la liste de contrôle d'accès correcte a été appliquée, le WLC envoie finalement une réponse d'association au client. L'utilisateur peut à présent continuer à se connecter au réseau.
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-orch-state] [17558]: (note): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Client state transition: S_CO_MACAUTH_IN_PROGRESS -> S_CO_ASSOCIATING
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [dot11] [17558]: (debug): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 dot11 send association response. Sending association response with resp_status_code: 0
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [dot11] [17558]: (debug): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dot11 Capability info byte1 1, byte2: 11
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [dot11-frame] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 WiFi direct: skip build Assoc Resp with P2P IE: Wifi direct policy disabled
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [dot11] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 dot11 send association response. Sending assoc response of length: 137 with resp_status_code: 0, DOT11_STATUS: DOT11_STATUS_SUCCESS
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [dot11] [17558]: (note): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Association success. AID 1, Roaming = False, WGB = False, 11r = False, 11w = False
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [dot11] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 DOT11 state transition: S_DOT11_MAB_PENDING -> S_DOT11_ASSOCIATED
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-orch-sm] [17558]: (debug): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Station Dot11 association is successful.
Authentification L2
Selon le processus qu’un client doit suivre lorsqu’il s’associe à un WLAN, l’authentification L2 « démarre ». Cependant, en réalité, l'authentification L2 a déjà été effectuée en raison de l'authentification MAB effectuée auparavant. Le client termine immédiatement l'authentification L2.
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-orch-sm] [17558]: (debug): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Starting L2 authentication. Bssid in state machine:dc8c.37d0.83af Bssid in request is:dc8c.37d0.83af
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-orch-state] [17558]: (note): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Client state transition: S_CO_ASSOCIATING -> S_CO_L2_AUTH_IN_PROGRESS
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-auth] [17558]: (note): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 L2 WEBAUTH Authentication Successful
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-auth] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Client auth-interface state transition: S_AUTHIF_MAB_AUTH_DONE -> S_AUTHIF_L2_WEBAUTH_DONE
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-orch-sm] [17558]: (debug): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 L2 Authentication of station is successful., L3 Authentication : 1
Plomb de données
Le WLC attribue des ressources au client qui se connecte afin que le trafic puisse circuler à travers le réseau.
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-orch-sm] [17558]: (note): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Mobility discovery triggered. Client mode: Local
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-orch-state] [17558]: (note): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Client state transition: S_CO_L2_AUTH_IN_PROGRESS -> S_CO_MOBILITY_DISCOVERY_IN_PROGRESS
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [mm-transition] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 MMIF FSM transition: S_MA_INIT -> S_MA_MOBILITY_DISCOVERY_PROCESSED_TR on E_MA_MOBILITY_DISCOVERY
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [mm-client] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Invalid transmitter ip in build client context
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [mm-client] [17558]: (debug): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Sending mobile_announce of XID (0) to (MobilityD[0])
{mobilityd_R0-0}{1}: [mm-client] [18482]: (debug): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Received mobile_announce, sub type: 0 of XID (0) from (WNCD[0])
{mobilityd_R0-0}{1}: [mm-transition] [18482]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 MMFSM transition: S_MC_INIT -> S_MC_ANNOUNCE_PROCESSED_NEW_CLIENT_TR on E_MC_ANNOUNCE_RCVD from WNCD[0]
{mobilityd_R0-0}{1}: [mm-client] [18482]: (debug): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Add MCC by tdl mac: client_ifid 0xa0000001 is assigned to client
{mobilityd_R0-0}{1}: [mm-client] [18482]: (debug): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Sending capwap_msg_unknown (100) of XID (5) to (WNCD[0])
{mobilityd_R0-0}{1}: [mm-client] [18482]: (debug): MAC: 0000.0000.0000 Sending mobile_announce_nak of XID (5) to (WNCD[0])
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [mm-client] [17558]: (debug): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Received mobile_announce_nak, sub type: 1 of XID (5) from (MobilityD[0])
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [mm-transition] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 MMIF FSM transition: S_MA_INIT_WAIT_ANNOUNCE_RSP -> S_MA_NAK_PROCESSED_TR on E_MA_NAK_RCVD
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [mm-client] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Roam type changed - None -> None
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [mm-client] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Mobility role changed - Unassoc -> Local
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [mm-client] [17558]: (note): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Mobility Successful. Roam Type None, Sub Roam Type MM_SUB_ROAM_TYPE_NONE, Client IFID: 0xa0000001, Client Role: Local PoA: 0x90000005 PoP: 0x0
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-orch-sm] [17558]: (debug): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Processing mobility response from MMIF. Client ifid: 0xa0000001, roam type: None, client role: Local
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [ewlc-qos-client] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Client QoS add mobile cb
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [ewlc-qos-client] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 No QoS PM Name or QoS Level received from SANet for pm_dir:0. Check client is fastlane, otherwise set pm name to none
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [ewlc-qos-client] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 No QoS PM Name or QoS Level received from SANet for pm_dir:1. Check client is fastlane, otherwise set pm name to none
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-auth] [17558]: (note): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ADD MOBILE sent. Client state flags: 0x72 BSSID: MAC: dc8c.37d0.83af capwap IFID: 0x90000005
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-orch-state] [17558]: (note): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Client state transition: S_CO_MOBILITY_DISCOVERY_IN_PROGRESS -> S_CO_DPATH_PLUMB_IN_PROGRESS
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [dot11] [17558]: (note): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Client datapath entry params - ssid:training_cwa,slot_id:1 bssid ifid: 0x0, radio_ifid: 0x90000003, wlan_ifid: 0xf0400001
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [ewlc-qos-client] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Client QoS dpath create params
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [ewlc-qos-client] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 No QoS PM Name or QoS Level received from SANet for pm_dir:0. Check client is fastlane, otherwise set pm name to none
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [ewlc-qos-client] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 No QoS PM Name or QoS Level received from SANet for pm_dir:1. Check client is fastlane, otherwise set pm name to none
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [avc-afc] [17558]: (debug): AVC enabled for client 4203.9522.e682
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [dpath_svc] [17558]: (note): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Client datapath entry created for ifid 0xa0000001
Une adresse IP est attribuée à l'utilisateur
L’utilisateur final a besoin d’une adresse IP pour naviguer sur le réseau. Il est soumis au processus DHCP. Si l'utilisateur était déjà connecté et qu'il se souvient de son adresse IP, le processus DHCP est ignoré. Si l'utilisateur ne peut pas recevoir d'adresse IP, l'utilisateur final ne peut pas afficher le portail Web. Sinon, il passe par les étapes suivantes :
- Un paquet DISCOVER est envoyé par le client qui se connecte en tant que diffusion pour rechercher les serveurs DHCP disponibles
- Si un serveur DHCP est disponible, le serveur DHCP répond par une OFFRE. L'offre contient des informations telles que l'adresse IP à attribuer au client qui se connecte, la durée du bail, etc. De nombreuses OFFRES peuvent être reçues de divers serveurs DHCP
- Le client accepte une OFFRE de l'un des serveurs et répond par une REQUÊTE pour l'adresse IP qu'il a sélectionnée
- Enfin, le serveur DHCP envoie un paquet ACKNOWLEDGMENT au client avec sa nouvelle adresse IP attribuée
Le WLC enregistre la méthode utilisée par le client pour recevoir son adresse IP.
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-orch-state] [17558]: (note): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Client state transition: S_CO_DPATH_PLUMB_IN_PROGRESS -> S_CO_IP_LEARN_IN_PROGRESS
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-iplearn] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 IP-learn state transition: S_IPLEARN_INIT -> S_IPLEARN_IN_PROGRESS
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-auth] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Client auth-interface state transition: S_AUTHIF_L2_WEBAUTH_DONE -> S_AUTHIF_L2_WEBAUTH_DONE
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [auth-mgr-feat_dsensor] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] Skipping DHCP TLVs for further processing. DHCP based classification isn't enabled
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (info): RX: DHCPv4 from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Src MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dst MAC: ffff.ffff.ffff src_ip: 0.0.0.0, dst_ip: 255.255.255.255, BOOTPREQUEST, SISF_DHCPDISCOVER, giaddr: 0.0.0.0, yiaddr: 0.0.0.0, CMAC: 4203.9522.e682
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (info): TX: DHCPv4 from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Src MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dst MAC: ffff.ffff.ffff src_ip: 0.0.0.0, dst_ip: 255.255.255.255, BOOTPREQUEST, SISF_DHCPDISCOVER, giaddr: 0.0.0.0, yiaddr: 0.0.0.0, CMAC: 4203.9522.e682
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [auth-mgr-feat_dsensor] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] Skipping DHCP TLVs for further processing. DHCP based classification isn't enabled
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (info): RX: DHCPv4 from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Src MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dst MAC: ffff.ffff.ffff src_ip: 0.0.0.0, dst_ip: 255.255.255.255, BOOTPREQUEST, SISF_DHCPDISCOVER, giaddr: 0.0.0.0, yiaddr: 0.0.0.0, CMAC: 4203.9522.e682
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (info): TX: DHCPv4 from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Src MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dst MAC: ffff.ffff.ffff src_ip: 0.0.0.0, dst_ip: 255.255.255.255, BOOTPREQUEST, SISF_DHCPDISCOVER, giaddr: 0.0.0.0, yiaddr: 0.0.0.0, CMAC: 4203.9522.e682
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (info): RX: DHCPv4 from interface Tw0/0/0 on vlan 1000 Src MAC: dca6.32d2.e93f Dst MAC: 4203.9522.e682 src_ip: <dhcp-server-ip-addr>, dst_ip: <end-user-ip-addr>, BOOTPREPLY, SISF_DHCPOFFER, giaddr: 0.0.0.0, yiaddr: <end-user-ip-addr>, CMAC: 4203.9522.e682
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (info): TX: DHCPv4 from interface Tw0/0/0 on vlan 1000 Src MAC: dca6.32d2.e93f Dst MAC: 4203.9522.e682 src_ip: <dhcp-server-ip-addr>, dst_ip: <end-user-ip-addr>, BOOTPREPLY, SISF_DHCPOFFER, giaddr: 0.0.0.0, yiaddr: <end-user-ip-addr>, CMAC: 4203.9522.e682
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (info): RX: DHCPv4 from interface Tw0/0/0 on vlan 1000 Src MAC: dca6.32d2.e93f Dst MAC: 4203.9522.e682 src_ip: <dhcp-server-ip-addr>, dst_ip: <end-user-ip-addr>, BOOTPREPLY, SISF_DHCPOFFER, giaddr: 0.0.0.0, yiaddr: <end-user-ip-addr>, CMAC: 4203.9522.e682
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (info): TX: DHCPv4 from interface Tw0/0/0 on vlan 1000 Src MAC: dca6.32d2.e93f Dst MAC: 4203.9522.e682 src_ip: <dhcp-server-ip-addr>, dst_ip: <end-user-ip-addr>, BOOTPREPLY, SISF_DHCPOFFER, giaddr: 0.0.0.0, yiaddr: <end-user-ip-addr>, CMAC: 4203.9522.e682
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [auth-mgr-feat_dsensor] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] Skipping DHCP TLVs for further processing. DHCP based classification isn't enabled
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (info): RX: DHCPv4 from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Src MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dst MAC: ffff.ffff.ffff src_ip: 0.0.0.0, dst_ip: 255.255.255.255, BOOTPREQUEST, SISF_DHCPREQUEST, giaddr: 0.0.0.0, yiaddr: 0.0.0.0, CMAC: 4203.9522.e682
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (info): TX: DHCPv4 from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Src MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dst MAC: ffff.ffff.ffff src_ip: 0.0.0.0, dst_ip: 255.255.255.255, BOOTPREQUEST, SISF_DHCPREQUEST, giaddr: 0.0.0.0, yiaddr: 0.0.0.0, CMAC: 4203.9522.e682
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (info): RX: DHCPv4 from interface Tw0/0/0 on vlan 1000 Src MAC: dca6.32d2.e93f Dst MAC: 4203.9522.e682 src_ip: <dhcp-server-ip-addr>, dst_ip: <end-user-ip-addr>, BOOTPREPLY, SISF_DHCPACK, giaddr: 0.0.0.0, yiaddr: <end-user-ip-addr>, CMAC: 4203.9522.e682
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (info): TX: DHCPv4 from interface Tw0/0/0 on vlan 1000 Src MAC: dca6.32d2.e93f Dst MAC: 4203.9522.e682 src_ip: <dhcp-server-ip-addr>, dst_ip: <end-user-ip-addr>, BOOTPREPLY, SISF_DHCPACK, giaddr: 0.0.0.0, yiaddr: <end-user-ip-addr>, CMAC: 4203.9522.e682
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-iplearn] [17558]: (note): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Client IP learn successful. Method: DHCP IP: <end-user-ip-addr>
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [epm] [17558]: (info): [0000.0000.0000:unknown] HDL = 0x0 vlan 1000 fail count 0 dirty_counter 0 is_dirty 0
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [auth-mgr] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] auth mgr attr change notification is received for attr (8)
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-iplearn] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 IP-learn state transition: S_IPLEARN_IN_PROGRESS -> S_IPLEARN_COMPLETE
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-orch-sm] [17558]: (debug): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Received ip learn response. method: IPLEARN_METHOD_DHCP
L'authentification C3 démarre
Maintenant que l'utilisateur final a reçu une adresse IP, l'authentification de couche 3 commence par CWA détecté comme méthode d'authentification souhaitée.
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-orch-sm] [17558]: (debug): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Triggered L3 authentication. status = 0x0, Success
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-orch-state] [17558]: (note): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Client state transition: S_CO_IP_LEARN_IN_PROGRESS -> S_CO_L3_AUTH_IN_PROGRESS
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-auth] [17558]: (note): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 L3 Authentication initiated. CWA
Tests d'adresses IP saines
Pour poursuivre la connexion, le client doit exécuter deux requêtes ARP :
1. Vérifiez que personne d'autre n'a son adresse IP. S'il existe une réponse ARP pour l'adresse IP de l'utilisateur final, elle est une adresse IP dupliquée
2. Validez l'accessibilité à la passerelle. Cela permet de s’assurer que le client peut quitter le réseau. La réponse ARP doit provenir de la passerelle
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-auth] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Client auth-interface state transition: S_AUTHIF_L2_WEBAUTH_DONE -> S_AUTHIF_WEBAUTH_PENDING
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): RX: ARP from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dest MAC: ffff.ffff.ffff ARP REQUEST, ARP sender MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP target MAC: 0000.0000.0000 ARP sender IP: 0.0.0.0, ARP target IP: <end-user-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): TX: ARP from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dest MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP REQUEST, ARP sender MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP target MAC: 0000.0000.0000 ARP sender IP: 0.0.0.0, ARP target IP: <end-user-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): RX: ARP from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dest MAC: ffff.ffff.ffff ARP REQUEST, ARP sender MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP target MAC: 0000.0000.0000 ARP sender IP: 0.0.0.0, ARP target IP: <end-user-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): TX: ARP from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dest MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP REQUEST, ARP sender MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP target MAC: 0000.0000.0000 ARP sender IP: 0.0.0.0, ARP target IP: <end-user-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): RX: ARP from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dest MAC: ffff.ffff.ffff ARP REQUEST, ARP sender MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP target MAC: 0000.0000.0000 ARP sender IP: 0.0.0.0, ARP target IP: <end-user-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): TX: ARP from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dest MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP REQUEST, ARP sender MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP target MAC: 0000.0000.0000 ARP sender IP: 0.0.0.0, ARP target IP: <end-user-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): RX: ARP from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dest MAC: ffff.ffff.ffff ARP REQUEST, ARP sender MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP target MAC: 0000.0000.0000 ARP sender IP: <end-user-ip-addr>, ARP target IP: <end-user-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): TX: ARP from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dest MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP REQUEST, ARP sender MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP target MAC: 0000.0000.0000 ARP sender IP: <end-user-ip-addr>, ARP target IP: <end-user-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): RX: ARP from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dest MAC: ffff.ffff.ffff ARP REQUEST, ARP sender MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP target MAC: 0000.0000.0000 ARP sender IP: <end-user-ip-addr>, ARP target IP: <end-user-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): TX: ARP from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dest MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP REQUEST, ARP sender MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP target MAC: 0000.0000.0000 ARP sender IP: <end-user-ip-addr>, ARP target IP: <end-user-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): RX: ARP from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dest MAC: ffff.ffff.ffff ARP REQUEST, ARP sender MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP target MAC: 0000.0000.0000 ARP sender IP: <end-user-ip-addr>, ARP target IP: <end-user-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): TX: ARP from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dest MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP REQUEST, ARP sender MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP target MAC: 0000.0000.0000 ARP sender IP: <end-user-ip-addr>, ARP target IP: <end-user-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): RX: ARP from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dest MAC: ffff.ffff.ffff ARP REQUEST, ARP sender MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP target MAC: 0000.0000.0000 ARP sender IP: <end-user-ip-addr>, ARP target IP: <default-gateway-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): TX: ARP from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dest MAC: ffff.ffff.ffff ARP REQUEST, ARP sender MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP target MAC: 0000.0000.0000 ARP sender IP: <end-user-ip-addr>, ARP target IP: <default-gateway-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): RX: ARP from interface Tw0/0/0 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 64cc.2284.ae10 Dest MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP REPLY, ARP sender MAC: 64cc.2284.ae10 ARP target MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP sender IP: <default-gateway-ip-addr>, ARP target IP: <end-user-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): TX: ARP from interface Tw0/0/0 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 64cc.2284.ae10 Dest MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP REPLY, ARP sender MAC: 64cc.2284.ae10 ARP target MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP sender IP: <default-gateway-ip-addr>, ARP target IP: <end-user-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): RX: ARP from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dest MAC: ffff.ffff.ffff ARP REQUEST, ARP sender MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP target MAC: 0000.0000.0000 ARP sender IP: <end-user-ip-addr>, ARP target IP: <dhcp-server-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): TX: ARP from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dest MAC: ffff.ffff.ffff ARP REQUEST, ARP sender MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP target MAC: 0000.0000.0000 ARP sender IP: <end-user-ip-addr>, ARP target IP: <dhcp-server-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): RX: ARP from interface Tw0/0/0 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: dca6.32d2.e93f Dest MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP REPLY, ARP sender MAC: dca6.32d2.e93f ARP target MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP sender IP: <dhcp-server-ip-addr>, ARP target IP: <end-user-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): TX: ARP from interface Tw0/0/0 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: dca6.32d2.e93f Dest MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP REPLY, ARP sender MAC: dca6.32d2.e93f ARP target MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP sender IP: <dhcp-server-ip-addr>, ARP target IP: <end-user-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): RX: ARP from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dest MAC: ffff.ffff.ffff ARP REQUEST, ARP sender MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP target MAC: 0000.0000.0000 ARP sender IP: <end-user-ip-addr>, ARP target IP: <default-gateway-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): TX: ARP from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dest MAC: ffff.ffff.ffff ARP REQUEST, ARP sender MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP target MAC: 0000.0000.0000 ARP sender IP: <end-user-ip-addr>, ARP target IP: <default-gateway-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): RX: ARP from interface Tw0/0/0 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 64cc.2284.ae10 Dest MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP REPLY, ARP sender MAC: 64cc.2284.ae10 ARP target MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP sender IP: <default-gateway-ip-addr>, ARP target IP: <end-user-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): TX: ARP from interface Tw0/0/0 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 64cc.2284.ae10 Dest MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP REPLY, ARP sender MAC: 64cc.2284.ae10 ARP target MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP sender IP: <default-gateway-ip-addr>, ARP target IP: <end-user-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): RX: ARP from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dest MAC: ffff.ffff.ffff ARP REQUEST, ARP sender MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP target MAC: 0000.0000.0000 ARP sender IP: <end-user-ip-addr>, ARP target IP: 10.20.30.17,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): TX: ARP from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dest MAC: ffff.ffff.ffff ARP REQUEST, ARP sender MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP target MAC: 0000.0000.0000 ARP sender IP: <end-user-ip-addr>, ARP target IP: 10.20.30.17,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): RX: ARP from interface Tw0/0/0 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 000c.290e.1c37 Dest MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP REPLY, ARP sender MAC: 000c.290e.1c37 ARP target MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP sender IP: 10.20.30.17, ARP target IP: <end-user-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): TX: ARP from interface Tw0/0/0 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 000c.290e.1c37 Dest MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP REPLY, ARP sender MAC: 000c.290e.1c37 ARP target MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP sender IP: 10.20.30.17, ARP target IP: <end-user-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): RX: ARP from interface Tw0/0/0 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: dca6.32d2.e93f Dest MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP REQUEST, ARP sender MAC: dca6.32d2.e93f ARP target MAC: 0000.0000.0000 ARP sender IP: <dhcp-server-ip-addr>, ARP target IP: <end-user-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): TX: ARP from interface Tw0/0/0 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: dca6.32d2.e93f Dest MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP REQUEST, ARP sender MAC: dca6.32d2.e93f ARP target MAC: 0000.0000.0000 ARP sender IP: <dhcp-server-ip-addr>, ARP target IP: <end-user-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): RX: ARP from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dest MAC: dca6.32d2.e93f ARP REPLY, ARP sender MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP target MAC: dca6.32d2.e93f ARP sender IP: <end-user-ip-addr>, ARP target IP: <dhcp-server-ip-addr>,
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [17558]: (debug): TX: ARP from interface capwap_90000005 on vlan 1000 Source MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Dest MAC: dca6.32d2.e93f ARP REPLY, ARP sender MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ARP target MAC: dca6.32d2.e93f ARP sender IP: <end-user-ip-addr>, ARP target IP: <dhcp-server-ip-addr>,
Deuxième connexion : du client au réseau
À ce stade, l'utilisateur final a été authentifié auprès d'ISE via son adresse MAC, mais il n'a pas encore été entièrement autorisé. Le WLC doit à nouveau se référer à ISE pour autoriser le client à se connecter au réseau. À ce stade, le portail est présenté à l'utilisateur dans lequel le nom d'utilisateur doit entrer son nom d'utilisateur et son mot de passe. Sur le WLC, l'utilisateur final est vu dans l'état « Authentification Web en attente ».
Changement d'autorisation (CoA)
C'est ici que la prise en charge de CoA dans la configuration du WLC prend effet. Jusqu’à présent, la liste de contrôle d’accès était utilisée. Une fois que le client final a vu le portail, la liste de contrôle d’accès n’est plus utilisée, car tout ce qu’il a fait était de rediriger le client vers le portail. À ce stade, le client entre ses informations d'identification pour se connecter afin de démarrer le processus CoA et de réauthentifier le client. Le WLC prépare le paquet à envoyer et le transmet à ISE

Conseil : CoA utilise le port 1700. Assurez-vous qu'il n'est pas bloqué par le pare-feu.
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [caaa-ch] [17558]: (info): [CAAA:COMMAND HANDLER:92000002] Processing CoA request under CH-ctx. <-- ISE requests the client to reauthenticate
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [caaa-ch] [17558]: (info): [CAAA:COMMAND HANDLER:92000002] Reauthenticate request (0x55de3f898b88)
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [mab] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] MAB re-authentication started for 2315255810 (4203.9522.e682) <-- ISE requests the WLC to reauthenciate the CoA
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-coa] [17558]: (info): radius coa proxy relay coa resp(wncd)
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-coa] [17558]: (info): CoA Response Details
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info): << ssg-command-code 0 32 >>
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info): << formatted-clid 0 "4203.9522.e682">>
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info): << error-cause 0 1 [Success]>> <-- The WLC responds with a sucess after processing the packet to be sent to ISE
[aaa-coa] [17558]: (info): server:10.20.30.14 cfg_saddr:10.20.30.14 udpport:64016 sport:0, tableid:0iden:30 rad_code:43 msg_auth_rcvd:TRUE coa_resp:ACK
[caaa-ch] [17558]: (info): [CAAA:COMMAND HANDLER] CoA response sent <-- The WLC sends the CoA response to ISE
Deuxième authentification à ISE
La deuxième authentification ne commence pas à zéro. C'est la puissance de CoA. De nouvelles règles et/ou paris AV peuvent être appliqués à l'utilisateur. La liste de contrôle d'accès et l'URL de redirection reçues sur le premier Access-Accept ne sont plus transmises à l'utilisateur final.
WLC envoie une requête à ISE
Le WLC envoie un nouveau paquet RADIUSAccess-Requestpacket à ISE avec la combinaison nom d'utilisateur/mot de passe entrée. Cela déclenche une nouvelle authentification MAB, et comme ISE connaît déjà le client, un nouvel ensemble de stratégies doit être appliqué (par exemple, Accès accordé).
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [mab] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] Received event 'MAB_REAUTHENTICATE' on handle 0x8A000002
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [caaa-author] [17558]: (info): [CAAA:AUTHOR:92000002] DEBUG: mlist=cwa_authz for type=1
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Send Access-Request to <ise-ip-addr>:1812 id 0/29, len 421 <-- The packet is traveling via RADIUS port 1812. The "29" is the session ID and it is unique for every connection attempt
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: authenticator c6 ae ab d5 55 c9 65 e2 - 4d 28 01 75 65 54 df 4d
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: User-Name [1] 14 "42039522e682" <-- MAC address that is attempting to authenticate
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: User-Password [2] 18 *
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 25 "service-type=Call Check" <-- This indicates a MAC filtering process
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Framed-MTU [12] 6 1485
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Message-Authenticator[80] 18 ...
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: EAP-Key-Name [102] 2 *
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 43 "audit-session-id=0E1E140A0000000C8E2DA642"
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 12 "method=mab" <-- Controller sends an AVpair with MAB method
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 26 "client-iif-id=1392509681"
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 14 "vlan-id=200"
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: NAS-IP-Address [4] 6 <wmi-ip-addr> <-- WLC WMI IP address
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: NAS-Port-Id [87] 17 "capwap_90000005"
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: NAS-Port-Type [61] 6 802.11 wireless [19]
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 30 "cisco-wlan-ssid=cwa" <-- SSID and WLAN the client is attempting to connect
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 32 "wlan-profile-name=cwa"
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Called-Station-Id [30] 32 "dc-8c-37-d0-83-a0:cwa"
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Calling-Station-Id [31] 19 "42-03-95-22-e6-82"
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Airespace-WLAN-ID [1] 6 1
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Nas-Identifier [32] 9 "BC-9800"
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Started 5 sec timeout
ISE répond à la requête WLC
ISE effectue une recherche de sa stratégie, et si le nom d'utilisateur reçu correspond au profil de stratégie, alors ISE répond au WLC une fois de plus, acceptant la connexion du client au WLAN. Elle renvoie le nom d'utilisateur de l'utilisateur final. Si elles sont configurées sur ISE, des règles supplémentaires et/ou des paires AV peuvent être appliquées à l'utilisateur et elles sont visibles sur Access-Accept.
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Received from id 1812/29 <ise-ip-addr>:0, Access-Accept, len 131 <-- The packet is traveling via RADIUS port 1812 and is has a session ID of 29 (as a response to the above packet)
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: authenticator a3 b0 45 d6 e5 1e 38 4a - be 15 fa 6b f4 67 62 8a
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: User-Name [1] 14 "cwa-username" <-- Username entered by the end client on the portal that was shown
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Class [25] 51 ...
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Message-Authenticator[80] 18 ...
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 22 "profile-name=Unknown"
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [radius] [17558]: (info): Valid Response Packet, Free the identifier
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [eap-auth] [17558]: (info): SUCCESS for EAP method name: Identity on handle 0xEE00003B
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [mab] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] MAB received an Access-Accept for 0x8A000002
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [mab] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] Received event 'MAB_RESULT' on handle 0x8A000002
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [auth-mgr] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] Authc success from MAB, Auth event success
Processus WLC des informations reçues d'ISE
Une fois de plus, le WLC traite les informations reçues par ISE. Il exécute une autre action REPLACE sur l'utilisateur avec les nouvelles valeurs reçues d'ISE.
[aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info):
<< username 0 "cwa-username">> <-- Processing username received from ISE
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info):
<< class 0 43 41 43 53 3a 30 45 31 45 31 34 30 41 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 43 38 45 32 44 41 36 34 32 3a 62 63 2d 69 73 65 2f 34 33 36 37 33 31 34 32 37 2f 34 30 >>
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info):
<<Message-Authenticator 0 <hidden>>>
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info):
<< dnis 0 "DC-8C-37-D0-83-A0">>
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info):
<< formatted-clid 0 "42-03-95-22-E6-82">>
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info):
<< audit-session-id 0 "0E1E140A0000000C8E2DA642">>
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info):
<< method 0 2 [mab]>>
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info):
<< clid-mac-addr 0 42 03 95 22 e6 82 >>
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info):
<< intf-id 0 2415919109 (0x90000005)>>
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [auth-mgr] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] auth mgr attr change notification is received for attr (450)
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [auth-mgr] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] auth mgr attr change notification is received for attr (450)
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [auth-mgr] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] Received User-Name cwa-username for client 4203.9522.e682
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [auth-mgr] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] User profile is to be applied. Authz mlist is not present, Authc mlist cwa_authz ,session push flag is unset
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [auth-mgr] [17558]: (info): [4203.9522.e682:capwap_90000005] User Profile applied successfully for 0x92000002 - REPLACE <-- WLC replaces the user profile it had originally created
L'authentification L3 se termine
L'utilisateur final a été authentifié avec les données fournies. L'authentification L3 (authentification Web) est terminée.
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-auth] [17558]: (note): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 L3 Authentication Successful. ACL:[]
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-auth] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Client auth-interface state transition: S_AUTHIF_WEBAUTH_PENDING -> S_AUTHIF_WEBAUTH_DONE
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [ewlc-qos-client] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Client QoS add mobile cb
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [ewlc-qos-client] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 No QoS PM Name or QoS Level received from SANet for pm_dir:0. Check client is fastlane, otherwise set pm name to none
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [ewlc-qos-client] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 No QoS PM Name or QoS Level received from SANet for pm_dir:1. Check client is fastlane, otherwise set pm name to none
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-auth] [17558]: (note): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 ADD MOBILE sent. Client state flags: 0x78 BSSID: MAC: dc8c.37d0.83af capwap IFID: 0x90000005
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [errmsg] [17558]: (info): %CLIENT_ORCH_LOG-6-CLIENT_ADDED_TO_RUN_STATE: Username entry (cwa-username) joined with ssid (cwa) for device with MAC: 4203.9522.e682 <-- End user "cwa-username" has joined the WLAN "cwa"
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info): [ Applied attribute : username 0 "cwa-username" ]
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info): [ Applied attribute : class 0 43 41 43 53 3a 30 45 31 45 31 34 30 41 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 43 38 45 32 44 41 36 34 32 3a 62 63 2d 69 73 65 2f 34 33 36 37 33 31 34 32 37 2f 34 30 ]
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info): [ Applied attribute :bsn-vlan-interface-name 0 "MGMT" ]
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [aaa-attr-inf] [17558]: (info): [ Applied attribute : timeout 0 1800 (0x708) ]
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [ewlc-qos-client] [17558]: (info): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Client QoS run state handler
L'utilisateur final atteint l'état d'exécution sur le WLC
Enfin, l'utilisateur est authentifié et associé au WLAN.
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [rog-proxy-capwap] [17558]: (debug): Managed client RUN state notification: 4203.9522.e682
{wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [client-orch-state] [17558]: (note): MAC: 4203.9522.e682 Client state transition: S_CO_L3_AUTH_IN_PROGRESS -> S_CO_RUN
Flux CWA - Capture de paquets intégrée (EPC)
Un EPC est une capture de paquets qui peut être récupérée directement à partir du WLC en affichant tous les paquets qui traversent le WLC ou qui en proviennent. Pour plus d'informations sur ce qu'ils sont et comment les récupérer, s'il vous plaît visitez Comprendre les débogages sans fil et la collecte de journaux sur les contrôleurs LAN sans fil Catalyst 9800.
Première connexion : client vers serveur ISE

Avertissement : les adresses IP sur les images de la capture de paquets ont été supprimées. Ils sont affichés comme et
Association au WLAN et requête envoyée au serveur ISE
 Premiers paquets
Premiers paquets
Requête d'association du WLC au client
En regardant le premier paquet « Association Request », vous pouvez voir les adresses MAC des périphériques qui sont impliqués dans ce processus.
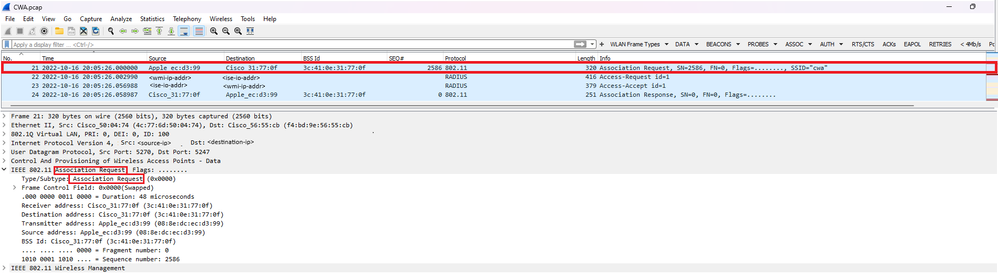 Demande D'Association
Demande D'Association
Paquet de demande d'accès envoyé du WLC à ISE
Une fois que la demande d'association a été traitée par le WLC, le WLC envoie un paquet de demande d'accès au serveur ISE.
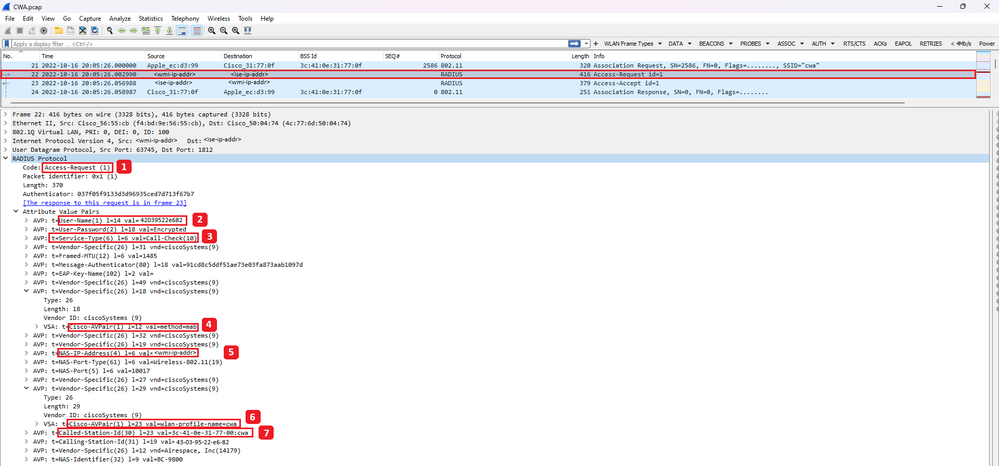 Analyse du paquet de demande d'accès
Analyse du paquet de demande d'accès
- Nom du paquet.
- Adresse MAC qui tente de s'authentifier.
- Cela indique un filtrage MAC.
- Paire AV envoyée par le contrôleur à ISE pour indiquer un processus de filtrage MAC.
- Adresse IP WMI du WLC.
- SSID auquel le client tente de se connecter.
- Nom du réseau local sans fil auquel le client tente de se connecter.
Paquet d'acceptation d'accès envoyé du WLC à ISE
Une fois qu'ISE a traité le paquet d'acceptation d'accès, il répond par un paquet d'acceptation d'accès s'il réussit ou par un paquet de refus d'accès s'il échoue.
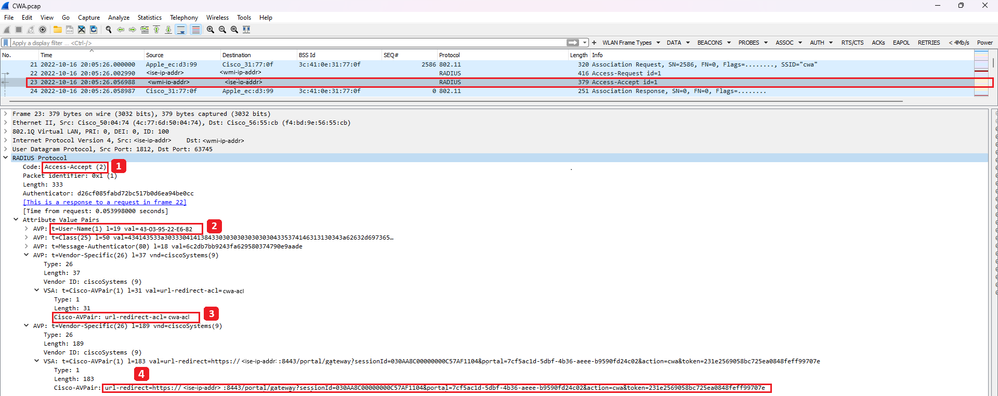 Analyse du paquet d'acceptation d'accès
Analyse du paquet d'acceptation d'accès
- Nom du paquet.
- Adresse MAC authentifiée.
- La liste de contrôle d'accès à appliquer.
- URL vers laquelle rediriger l'utilisateur.
Réponse d'association du WLC au client
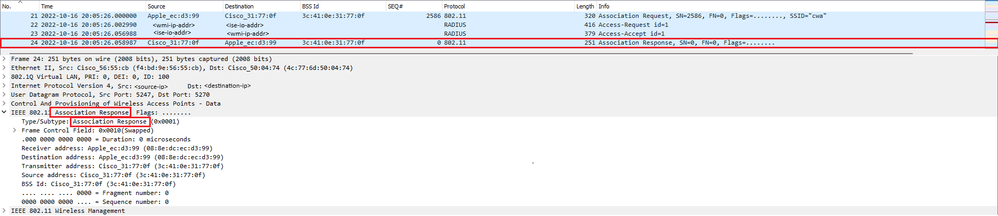 Réponse d'association
Réponse d'association
Processus DHCP
 Processus DHCP
Processus DHCP

Remarque : désormais, les paquets sont vus en double, mais c'est seulement parce que l'un est encapsulé CAPWAP et l'autre ne l'est pas
ARP
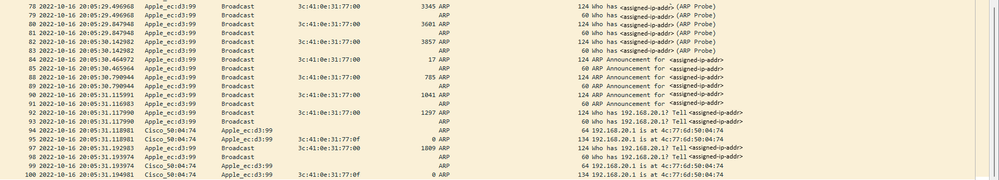 Client ARPing pour sa propre adresse IP et pour le modem routeur
Client ARPing pour sa propre adresse IP et pour le modem routeur
Test de connectivité
Une fois le processus ARP terminé, le périphérique qui tente de se connecter effectue une vérification pour vérifier si un portail est déclenché, également appelée « sondage ». Si le périphérique indique qu'il n'y a pas de connexion Internet, cela signifie que le processus ARP a échoué (par exemple, la passerelle n'a jamais répondu) ou que le périphérique n'a pas pu effectuer l'analyse.
Cette analyse n'est pas visible sur les traces RA, seule l'EPC est en mesure de fournir ces informations. La requête de sondage dépend de l'appareil qui tente une connexion. Dans cet exemple, l'appareil de test était un appareil Apple. Le sondage a donc été effectué directement vers le portail captif d'Apple.
Comme la recherche est effectuée à l'aide d'une URL, DNS est requis pour résoudre cette URL. Par conséquent, si le serveur DNS ne peut pas répondre aux requêtes du client, celui-ci continue à demander l'URL et le portail n'est jamais vu. À ce stade, si l'adresse IP du serveur ISE est entrée dans le navigateur Web du périphérique final, le portail doit être visible. Si c'est le cas, il y a un problème avec le serveur DNS.
 Test de connectivité du client - Requête DNS et réponse
Test de connectivité du client - Requête DNS et réponse
Adresse IP résolue par DNS
En examinant la réponse à la requête DNS, vous pouvez voir l'adresse IP qui a été résolue par le serveur DNS.
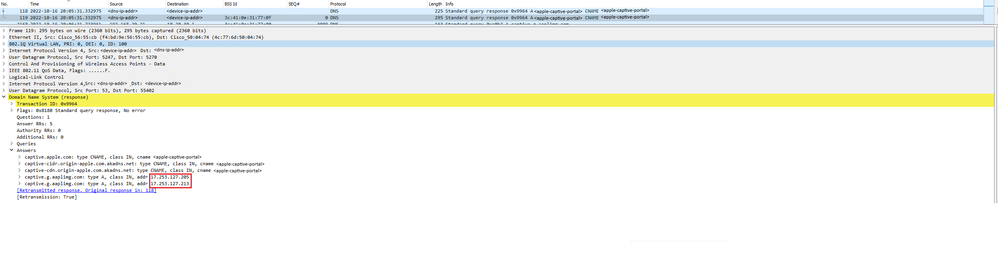 Adresse IP résolue par le serveur DNS
Adresse IP résolue par le serveur DNS
Établissement d'une connexion en trois étapes
Une fois l'adresse IP DNS résolue, une connexion TCP en trois étapes est établie entre le portail et le client. L'adresse IP utilisée est l'une des adresses IP résolues.
 Établissement D'Une Connexion En Trois Étapes
Établissement D'Une Connexion En Trois Étapes
GET Hotspot
Une fois la session TCP établie, le client effectue une recherche et tente d'accéder au portail.
 GET Hotspot
GET Hotspot
Paquet OK
Le paquet OK contient le portail ISE vers lequel le client doit être redirigé.
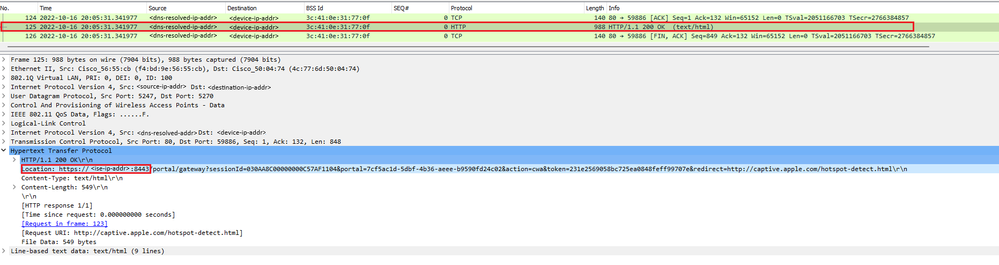 Paquet OK
Paquet OK

Remarque : la plupart des personnes ont une autre URL retournée dans le paquet OK. Par conséquent, une autre requête DNS doit être effectuée pour obtenir l'adresse IP finale.
Nouvelle session TCP établie
Maintenant que l'adresse IP du portail a été découverte, de nombreux paquets sont échangés, mais à la fin un paquet avec l'adresse IP de destination qui a été retourné dans le paquet OK (ou résolu par DNS) qui correspond à l'adresse IP d'ISE, montre une nouvelle session TCP en cours d'établissement sur le portail.
 Deuxième connexion et nouvelle session TCP vers le portail ISE
Deuxième connexion et nouvelle session TCP vers le portail ISE
Le portail s'affiche pour l'utilisateur
À ce stade, le portail d'ISE s'affiche enfin sur le navigateur du navigateur client. Comme précédemment, de nombreux paquets sont échangés entre ISE et le périphérique ; par exemple, un Hello client et un Hello serveur, etc. C'est ici qu'ISE demande au client le nom d'utilisateur et le mot de passe, accepte les conditions générales ou tout autre élément configuré sur le serveur ISE.
Demande CoA / Accusé de réception CoA
Une fois que l'utilisateur a entré toutes les données demandées, ISE envoie une requête CoA au contrôleur pour modifier l'autorisation de l'utilisateur. Si tout sur le WLC est configuré comme prévu, comme avoir l'état NAC, la prise en charge de CoA, et ainsi de suite, le WLC envoie un accusé de réception CoA (CoA ACK). Sinon, le WLC peut envoyer un CoA Non-Acknowledgement (CoA NACK) ou simplement il n'envoie même pas le CoA ACK.
 Demande et accusé de réception CoA
Demande et accusé de réception CoA
Deuxième connexion : du client au réseau
Nouvelle demande d'accès
Le WLC envoie un nouveau paquet de demande d'accès à ISE.
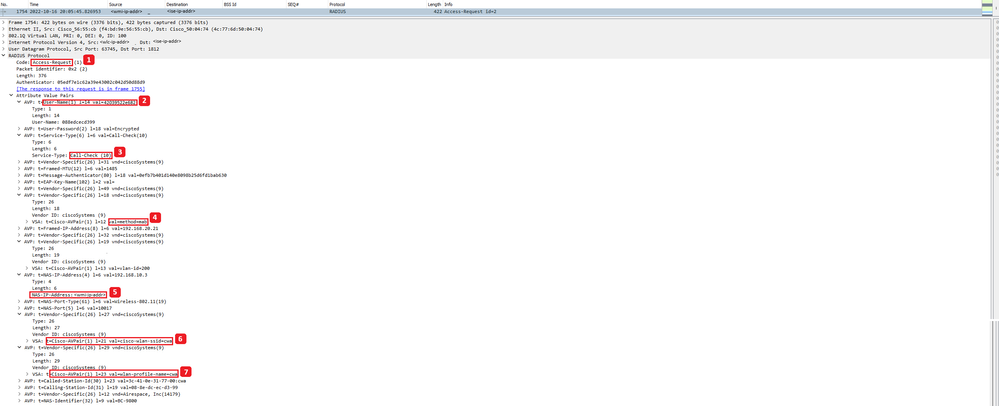 Analyse du nouveau paquet de demande d'accès
Analyse du nouveau paquet de demande d'accès
- Nom du paquet.
- Adresse MAC qui tente de s'authentifier.
- Cela indique un filtrage MAC.
- Paire AV envoyée par le contrôleur à ISE pour indiquer un processus de filtrage MAC.
- Adresse IP WMI du WLC.
- SSID auquel le client tente de se connecter.
- Nom du réseau local sans fil auquel le client tente de se connecter.
Nouvel accès - Acceptation
Le WLC envoie un nouveau paquet de demande d'accès à ISE.
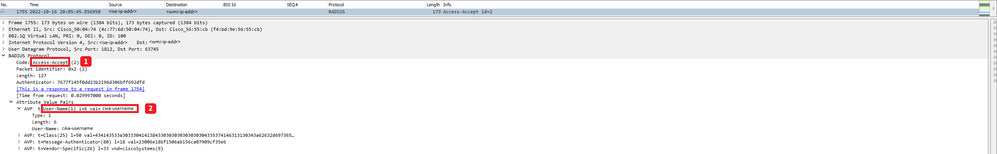 Analyse du nouveau paquet d'acceptation d'accès
Analyse du nouveau paquet d'acceptation d'accès
- Nom du paquet.
- Nom d'utilisateur entré par le client final sur le portail affiché.
Là encore, un nouveau test de connectivité de sondage est effectué à partir du client. Une fois que le client a confirmé qu'il dispose d'une connectivité Internet, le portail peut être fermé (il peut l'être automatiquement, en fonction du périphérique utilisé). Le client est maintenant connecté au réseau.
Historique de révision
| Révision | Date de publication | Commentaires |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
06-Oct-2023 |
Première publication |
Contribution d’experts de Cisco
- Daniela Vignau LeonIngénieur-conseil technique Cisco
Contacter Cisco
- Ouvrir un dossier d’assistance

- (Un contrat de service de Cisco est requis)
 Commentaires
Commentaires