Configuration de clés pré-partagées IKE en utilisant un serveur RADIUS pour Cisco Secure VPN Client
Contenu
Introduction
Ce document décrit comment configurer le secret partagé par Échange de clés Internet (IKE) utilisant un serveur de RAYON. L'IKE a partagé la caractéristique secrète qui utilise une consultation principale d'enables de serveur d'Authentification, autorisation et comptabilité (AAA) du serveur d'AAA. Les clés pré-partagées ne mesurent pas bien quand vous déployez un système du à grande échelle VPN sans autorité de certification (CA). En utilisant l'adressage IP dynamique tel que des compositions sur cadran du protocole DHCP (DHCP) ou du Protocole point à point (PPP), l'adresse IP changeante peut rendre la consultation principale difficile ou impossible à moins qu'une clé pré-partagée de masque soit utilisée. Dans l'IKE partagé la caractéristique secrète qui utilise un serveur d'AAA, le secret partagé est accédée à pendant le mode agressif de la négociation d'IKE par le serveur d'AAA. L'ID de l'échange est utilisé comme nom d'utilisateur pour questionner l'AAA si aucune clé locale ne peut être trouvée sur le routeur de Cisco IOS® auquel l'utilisateur essaye de se connecter. Ceci a été introduit dans la version du logiciel Cisco IOS 12.1.T. Vous devez avoir le mode agressif activé sur le client vpn utiliser cette caractéristique.
Conditions préalables
Conditions requises
Vous devez avoir le mode agressif activé sur le client VPN, et vous devez être la version du logiciel Cisco IOS courante 12.1.T ou plus tard le routeur.
Composants utilisés
Les informations contenues dans ce document sont basées sur les versions de matériel et de logiciel suivantes :
-
Cisco Secure ACS pour Windows
-
Version du logiciel Cisco IOS 12.2.8T
-
Routeur de Cisco 1700
Les informations présentées dans ce document ont été créées à partir de périphériques dans un environnement de laboratoire spécifique. Tous les périphériques utilisés dans ce document ont démarré avec une configuration effacée (par défaut). Si vous travaillez dans un réseau opérationnel, assurez-vous de bien comprendre l'impact potentiel de toute commande avant de l'utiliser.
Conventions
Pour plus d'informations sur les conventions utilisées dans ce document, reportez-vous aux Conventions relatives aux conseils techniques Cisco.
Configurez
Ce document utilise les configurations présentées ci-dessous.
Remarque: Pour obtenir des informations supplémentaires sur les commandes utilisées dans ce document, utilisez l'Outil de recherche de commande (clients enregistrés seulement).
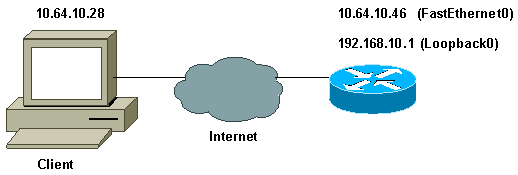
Diagramme du réseau
Ce document utilise la configuration réseau suivante :
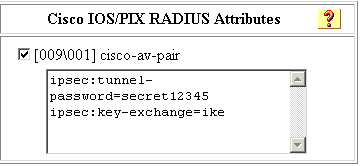
Création d'un profil Cisco Secure
Ce profil a été créé avec l'UNIX, mais un profil semblable peut être créé sur le Cisco Secure ACS pour Windows.
# ./ViewProfile -p 9900 -u haseeb User Profile Information !--- The user name is sent by the VPN Client; !--- look at the client configuration. user = haseeb{ radius=Cisco12.05 { check_items= { !--- This should always be "cisco." 2=cisco } reply_attributes= { 6=5 64=9 65=1 !--- Pre-shared key. 9,1="ipsec:tunnel-password=secret12345" 9,1="ipsec:key-exchange=ike" } } }
Cette sortie affiche le script qui est utilisé pour ajouter un profil utilisateur dans le Cisco Secure ACS pour l'UNIX.
#!/bin/sh
./DeleteProfile -p 9900 -u haseeb
./AddProfile -p 9900 -u haseeb -a 'radius=Cisco12.05
{ \n check_items = { \n 2="cisco" \n } \n
reply_attributes = { \n 6=5 \n 64=9 \n 65=1 \n
9,1="ipsec:tunnel-password=cisco" \n
9,1="ipsec:key-exchange=ike" \n } \n }'
Suivez ces étapes pour utiliser le GUI pour configurer le profil utilisateur sur le Cisco Secure ACS pour Windows 2.6.
-
Définissez le nom d'utilisateur, avec « Cisco » comme mot de passe.

-
Définissez l'échange clé comme IKE et la clé pré-partagée sous les poids du commerce-paires de Cisco.
Configurer le routeur
| Cisco 1751 avec IOS 12.2.8T |
|---|
version 12.2 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! hostname 1751-vpn ! !--- Enable AAA. aaa new-model ! ! aaa authentication login default none !--- Configure authorization. aaa authorization network vpn_users group radius aaa session-id common ! memory-size iomem 15 mmi polling-interval 60 no mmi auto-configure no mmi pvc mmi snmp-timeout 180 ip subnet-zero ! no ip domain-lookup ! !--- Define IKE policy for phase 1 negotiations of the VPN Clients. crypto isakmp policy 10 hash md5 authentication pre-share crypto isakmp client configuration address-pool local mypool ! !--- Define IPSec policies - Phase 2 Policy for actual data encryption. crypto ipsec transform-set myset esp-des esp-md5-hmac ! !--- Create dynamic crypto map. crypto dynamic-map dynmap 10 set transform-set myset ! !--- Configure IKE shared secret using AAA server on this router. crypto map intmap isakmp authorization list vpn_users !--- IKE Mode Configuration - the router will attempt !--- to set IP addresses for each peer. crypto map intmap client configuration address initiate !--- IKE Mode Configuration - the router will accept !--- requests for IP addresses from any requesting peer. crypto map intmap client configuration address respond crypto map intmap 10 ipsec-isakmp dynamic dynmap ! interface Loopback0 ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Loopback1 no ip address ! interface Ethernet0/0 no ip address half-duplex ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 10.64.10.46 255.255.255.224 speed auto !--- Assign crypto map to interface. crypto map intmap ! !--- Configure a local pool of IP addresses to be used when a !--- remote peer connects to a point-to-point interface. ip local pool mypool 10.1.2.1 10.1.2.254 ip classless ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.64.10.33 no ip http server ip pim bidir-enable ! !--- Specify the security server protocol and defines security !--- server host IP address and UDP port number. radius-server host 10.64.10.7 auth-port 1645 acct-port 1646 key cisco123 radius-server retransmit 3 ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 ! end |
Configurer le client
Suivez ces étapes pour configurer le client.
-
Dans l'éditeur de stratégie de sécurité, allez à la stratégie de sécurité réseau > rtrtest. Sélectionnez le type d'ID comme adresse électronique et mettez dans un nom d'utilisateur à configurer sur le serveur de RAYON. Si cette configuration est laissée en tant que « adresse IP, » alors le nom d'utilisateur envoyé au serveur de RAYON serait l'adresse IP du PC client.
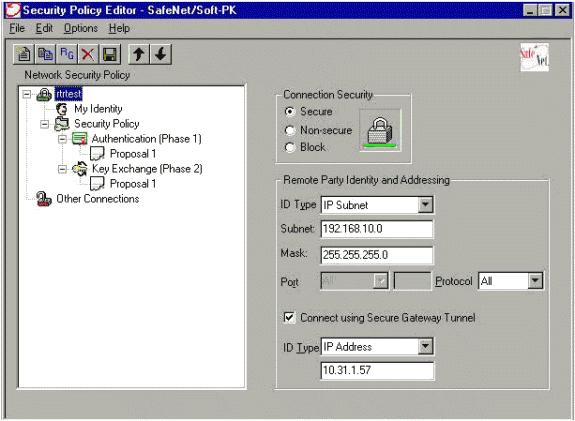
-
Allez à la stratégie de sécurité réseau > rtrtest > mon identité et sélectionnez le mode agressif. L'installation ne fonctionnera pas si ce mode n'est pas sélectionné.
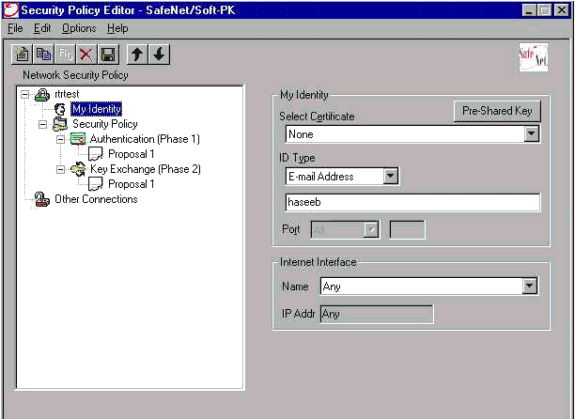
Vérifiez
Aucune procédure de vérification n'est disponible pour cette configuration.
Dépannez
Cette section fournit des informations que vous pouvez utiliser pour dépanner votre configuration.
Cette sortie affiche que bon met au point pour cette configuration :
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:0): received packet from 10.64.10.28 (N) NEW SA
23:43:41: ISAKMP: local port 500, remote port 500
23:43:41: ISAKMP: Locking CONFIG struct 0x8180BEF4 from
crypto_ikmp_config_initialize_sa, count 2
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): processing SA payload. message ID = 0
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): processing ID payload. message ID = 0
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): processing vendor id payload
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): vendor ID seems Unity/DPD but bad major
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): vendor ID is XAUTH
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): Checking ISAKMP transform 1 against priority 10 policy
23:43:41: ISAKMP: encryption DES-CBC
23:43:41: ISAKMP: hash MD5
23:43:41: ISAKMP: default group 1
23:43:41: ISAKMP: auth pre-share
!--- ISAKMP policy proposed by VPN Client !--- matched the configured ISAKMP policy.
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): atts are acceptable. Next payload is 0
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): processing KE payload. message ID = 0
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): processing NONCE payload. message ID = 0
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): SKEYID state generated
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): processing vendor id payload
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): vendor ID seems Unity/DPD but bad major
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): vendor ID is XAUTH
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): SA is doing pre-shared key authentication
using id type ID_IPV4_ADDR
23:43:41: ISAKMP (3): ID payload
next-payload : 10
type : 1
protocol : 17
port : 500
length : 8
23:43:41: ISAKMP (3): Total payload length: 12
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): sending packet to 10.64.10.28 (R) AG_INIT_EXCH
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): Input = IKE_MESG_FROM_PEER, IKE_AM_EXCH
Old State = IKE_READY New State = IKE_R_AM2
23:43:42: ISAKMP (0:3): received packet from 10.64.10.28 (R) AG_INIT_EXCH
23:43:42: ISAKMP (0:3): processing HASH payload. message ID = 0
23:43:42: ISAKMP (0:3): SA has been authenticated with 10.64.10.28
23:43:42: ISAKMP (0:3): Input = IKE_MESG_FROM_PEER, IKE_AM_EXCH
Old State = IKE_R_AM2 New State = IKE_P1_COMPLETE
23:43:43: ISAKMP (0:3): received packet from 10.64.10.28 (R) QM_IDLE
23:43:43: ISAKMP (0:3): Need config/address
23:43:43: ISAKMP (0:3): Need config/address
23:43:43: ISAKMP: Sending private address: 10.1.2.2
23:43:43: ISAKMP (0:3): initiating peer config to 10.64.10.28.
ID = -1082015193
23:43:43: ISAKMP (0:3): sending packet to 10.64.10.28 (R) CONF_ADDR
23:43:43: ISAKMP (0:3): Input = IKE_MESG_INTERNAL, IKE_PHASE1_COMPLETE
Old State = IKE_P1_COMPLETE New State = IKE_CONFIG_MODE_SET_SENT
23:43:43: ISAKMP (0:3): received packet from 10.64.10.28 (R) CONF_ADDR
23:43:43: ISAKMP (0:3): processing transaction payload from 10.64.10.28.
message ID = -1082015193
23:43:43: ISAKMP: Config payload ACK
23:43:43: ISAKMP (0:3): peer accepted the address!
23:43:43: ISAKMP (0:3): deleting node -1082015193 error FALSE
reason "done with transaction"
23:43:43: ISAKMP (0:3): Input = IKE_MESG_FROM_PEER, IKE_CFG_ACK
Old State = IKE_CONFIG_MODE_SET_SENT New State = IKE_P1_COMPLETE
23:43:43: ISAKMP (0:3): Delaying response to QM request.
23:43:43: ISAKMP (0:3): Input = IKE_MESG_INTERNAL, IKE_PHASE1_COMPLETE
Old State = IKE_P1_COMPLETE New State = IKE_P1_COMPLETE
23:43:44: ISAKMP (0:3): received packet from 10.64.10.28 (R) QM_IDLE
23:43:44: ISAKMP (0:3): processing HASH payload. message ID = -920829332
23:43:44: ISAKMP (0:3): processing SA payload. message ID = -920829332
23:43:44: ISAKMP (0:3): Checking IPSec proposal 1
23:43:44: ISAKMP: transform 1, ESP_DES
23:43:44: ISAKMP: attributes in transform:
23:43:44: ISAKMP: authenticator is HMAC-MD5
23:43:44: ISAKMP: encaps is 1
!--- Proposed Phase 2 transform set !--- matched configured IPSec transform set.
23:43:44: ISAKMP (0:3): atts are acceptable.
23:43:44: IPSEC(validate_proposal_request): proposal part #1,
(key eng. msg.) INBOUND local= 10.64.10.46, remote= 10.64.10.28,
local_proxy= 192.168.10.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
remote_proxy= 10.1.2.2/255.255.255.255/0/0 (type=1),
protocol= ESP, transform= esp-des esp-md5-hmac ,
lifedur= 0s and 0kb,
spi= 0x0(0), conn_id= 0, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4
23:43:44: ISAKMP (0:3): processing NONCE payload. message ID = -920829332
23:43:44: ISAKMP (0:3): processing ID payload. message ID = -920829332
23:43:44: ISAKMP (0:3): processing ID payload. message ID = -920829332
23:43:44: ISAKMP (0:3): asking for 1 spis from ipsec
23:43:44: ISAKMP (0:3): Node -920829332,
Input = IKE_MESG_FROM_PEER, IKE_QM_EXCH
Old State = IKE_QM_READY New State = IKE_QM_SPI_STARVE
23:43:44: IPSEC(key_engine): got a queue event...
23:43:44: IPSEC(spi_response): getting spi 2940839732 for SA
from 10.64.10.46 to 10.64.10.28 for prot 3
23:43:44: ISAKMP: received ke message (2/1)
23:43:45: ISAKMP (0:3): sending packet to 10.64.10.28 (R) QM_IDLE
23:43:45: ISAKMP (0:3): Node -920829332,
Input = IKE_MESG_FROM_IPSEC, IKE_SPI_REPLY
Old State = IKE_QM_SPI_STARVE New State = IKE_QM_R_QM2
23:43:45: ISAKMP (0:3): received packet from 10.64.10.28 (R) QM_IDLE
23:43:45: ISAKMP (0:3): Creating IPSec SAs
23:43:45: inbound SA from 10.64.10.28 to 10.64.10.46
(proxy 10.1.2.2 to 192.168.10.0)
23:43:45: has spi 0xAF49A734 and conn_id 200 and flags 4
23:43:45: outbound SA from 10.64.10.46 to 10.64.10.28
(proxy 192.168.10.0 to 10.1.2.2 )
23:43:45: has spi 1531785085 and conn_id 201 and flags C
23:43:45: ISAKMP (0:3): deleting node 1961959105 error FALSE
reason "saved qm no longer needed"
23:43:45: ISAKMP (0:3): deleting node -920829332 error FALSE
reason "quick mode done (await()"
23:43:45: ISAKMP (0:3): Node -920829332,
Input = IKE_MESG_FROM_PEER, IKE_QM_EXCH
Old State = IKE_QM_R_QM2 New State = IKE_QM_PHASE2_COMPLETE
23:43:45: IPSEC(key_engine): got a queue event...
23:43:45: IPSEC(initialize_sas): ,
(key eng. msg.) INBOUND local= 10.64.10.46, remote= 10.64.10.28,
local_proxy= 192.168.10.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
remote_proxy= 10.1.2.2/0.0.0.0/0/0 (type=1),
protocol= ESP, transform= esp-des esp-md5-hmac ,
lifedur= 0s and 0kb,
spi= 0xAF49A734(2940839732), conn_id= 200, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4
23:43:45: IPSEC(initialize_sas): ,
(key eng. msg.) OUTBOUND local= 10.64.10.46, remote= 10.64.10.28,
local_proxy= 192.168.10.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
remote_proxy= 10.1.2.2/0.0.0.0/0/0 (type=1),
protocol= ESP, transform= esp-des esp-md5-hmac ,
lifedur= 0s and 0kb,
spi= 0x5B4D2F7D(1531785085), conn_id= 201, keysize= 0, flags= 0xC
!--- IPSec SAs created.
23:43:45: IPSEC(create_sa): sa created, (sa) sa_dest= 10.64.10.46,
sa_prot= 50, sa_spi= 0xAF49A734(2940839732),
sa_trans= esp-des esp-md5-hmac , sa_conn_id= 200
23:43:45: IPSEC(create_sa): sa created, (sa) sa_dest= 10.64.10.28,
sa_prot= 50, sa_spi= 0x5B4D2F7D(1531785085),
sa_trans= esp-des esp-md5-hmac , sa_conn_id= 201
23:43:45: ISAKMP: received ke message (4/1)
23:43:45: ISAKMP: Locking CONFIG struct 0x8180BEF4
for crypto_ikmp_config_handle_kei_mess, count 3
23:43:50: ISAKMP (0:2): purging node 618568216
23:43:50: ISAKMP (0:2): purging node -497663485
23:44:00: ISAKMP (0:2): purging SA., sa=816B5724, delme=816B5724
23:44:00: ISAKMP: Unlocking CONFIG struct 0x8180BEF4 on
return of attributes, count 2
Informations connexes
Contacter Cisco
- Ouvrir un dossier d’assistance

- (Un contrat de service de Cisco est requis)
 Commentaires
Commentaires