Configuración del Ruteo InterVLAN Mediante un Router Interno (Tarjeta Capa 3) en Switches Catalyst 5500/5000 y 6500/6000 que Ejecutan CatOS System Software
Contenido
Introducción
Este documento proporciona información básica sobre cómo configurar el ruteo interVLAN en un switch Catalyst (en el que se ejecute el software del sistema Catalyst OS [CatOS]) usando un router interno (módulo/tarjeta capa 3 [L3]). El router interno del término hace referencia a estos módulos/tarjetas de los switches Catalyst 5500/5000 y 6500/6000:
-
Tarjeta de función de switch multicapa (MSFC) en los switches Catalyst serie 6500/6000
-
MSFC2 en los Catalyst 6500/6000 Series Switches
-
Tarjeta de función del switch de ruta (RSFC) en los switches Catalyst de la serie 5500/5000
-
Módulo de switch de ruta (RSM) en los switches Catalyst serie 5500/5000
Cualquier switch Catalyst de la serie 5500/5000 o Catalyst 6500/6000 que ejecute CatOS con una tarjeta L3 soportada podría haberse utilizado en este documento para obtener los mismos resultados.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Quienes lean este documento deben tener conocimiento de los siguientes temas:
Nota: Este documento no explica cómo configurar el ruteo interVLAN en los switches Catalyst 4500/4000 usando el módulo de servicios L3 (WS-X4232-L3). Para obtener estos detalles, consulte estos documentos:
-
Sección Configuración del Módulo para el Ruteo InterVLAN de Nota de Instalación y Configuración para el Módulo de Servicios de Capa 3 Catalyst 4000
Componentes Utilizados
La información que contiene este documento se basa en las siguientes versiones de software y hardware.
-
Switch Catalyst 5500 con RSM
-
Módulo de motor supervisor (WS-X5530) que ejecuta el software CatOS 6.1(1)
-
RSM (WS-X5302) que ejecuta Cisco IOS® Software Release 12.0(5)W5(12)
Se eliminaron las configuraciones de todos los dispositivos con los comandos clear config all y write erase para asegurar que tuvieran una configuración predeterminada.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Convenciones
For more information on document conventions, refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions.
Diagrama de la red
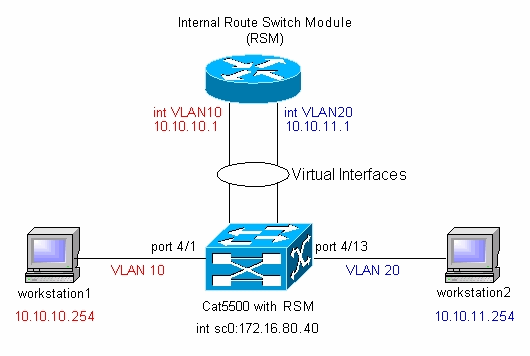
Nota: No conecte la estación de trabajo1 y la estación de trabajo2 a menos que se le pida que lo haga en este documento. Este documento señala un problema común que los clientes informan cuando configuran el ruteo interVLAN o interfaces VLAN múltiples en el módulo del router. Vea el problema común: La interfaz VLAN muestra la sección down/down para obtener más detalles.
Tareas de configuración generales
Esta sección proporciona un resumen de las principales tareas de configuración que se realizan en este documento:
-
Configure el switch para la administración
-
Creación de VLAN en el switch
-
Agregar puertos a las VLAN configuradas
-
Configuración del router interno para la administración
-
Configuración del Ruteo InterVLAN
-
Verifique la Configuración
Configuración del Ruteo InterVLAN
Complete estos pasos para configurar el ruteo interVLAN en el switch Catalyst:
-
Acceda al puerto de la consola en el motor supervisor.
Si tiene dificultades para acceder a la consola, consulte estos documentos:
-
Para los Catalyst 5500/5000 Series Switches: Conexión de un Terminal al Puerto de la Consola en los Catalyst Switches.
-
Para los Catalyst 6500/6000 Series Switches, sección Conexión de un Terminal de Conexión de un Terminal al Puerto de la Consola en los Catalyst Switches y sección Conexión de un Módem de Conexión de un Módem al Puerto de la Consola en los Catalyst Switches
-
-
Configure el switch para una administración básica.
Utilice este conjunto de comandos para configurar el switch Catalyst para la administración:
Console> enable) set system name Cat5500 !--- Configure the system name. System name set. Cat5500> (enable) set interface sc0 172.16.80.40 255.255.255.0 !--- Configure the IP address. Interface sc0 IP address and netmask set. Cat5500> (enable) set ip route 0.0.0.0 172.16.80.1 !--- Configure the default gateway.
Nota: Si desea administrar un switch que se encuentra en el otro lado de un router, debe configurar un gateway predeterminado en el switch, ya que el switch no participa en el ruteo IP y, por lo tanto, no tiene conocimiento de la topología L3 de la red. También puede usar el comando set ip route default 172.16.80.1 para configurar el gateway predeterminado, en vez de usar el comando set ip route 0.0.0.0 172.16.80.1.
-
Configure el número requerido de VLAN en el switch.
Según el Diagrama de red, debe configurar dos nuevas VLAN (VLAN 10 y VLAN 20) en el switch.
Para poder crear una nueva VLAN, el switch debe estar en modo de servidor de protocolo de enlace troncal de VLAN (VTP) o en modo transparente de VTP. Si el switch es un servidor VTP, debe definir un nombre de dominio VTP antes de agregar VLAN. Esto debe definirse independientemente del número de switches en la red (uno o varios), e independientemente de si utiliza VTP para propagar VLAN a otros switches en la red. Para obtener más información sobre VTP, consulte este documento:
La configuración VTP predeterminada en el switch es:
Cat5500> (enable) show vtp domain Domain Name Domain Index VTP Version Local Mode Password -------------------------------- ------------ ----------- ----------- ---------- 1 2 server - Vlan-count Max-vlan-storage Config Revision Notifications ---------- ---------------- --------------- ------------- 5 1023 0 disabled Last Updater V2 Mode Pruning PruneEligible on Vlans --------------- -------- -------- ------------------------- 0.0.0.0 disabled disabled 2-1000Use el comando set vtp para configurar el nombre de dominio y el modo:
Cat5500> (enable) set vtp domain mode transparent VTP domain modified !--- Set the VTP mode. Cat5500> (enable) set vtp domain cisco VTP domain cisco modified !--- Set the VTP domain name.
Nota: En el ejemplo, el modo VTP se establece en transparente. De acuerdo con su red, configure el modo VTP de manera adecuada. Se eligió el modo transparente para evitar verse afectado por otros switches y evitar afectar a los otros switches del laboratorio.
-
Verifique la configuración VTP ejecutando el comando show vtp domain:
Cat5500> (enable) show vtp domain Domain Name Domain Index VTP Version Local Mode Password -------------------------------- ------------ ----------- ----------- ---------- cisco 1 2 Transparent - Vlan-count Max-vlan-storage Config Revision Notifications ---------- ---------------- --------------- ------------- 5 1023 0 disabled Last Updater V2 Mode Pruning PruneEligible on Vlans --------------- -------- -------- ------------------------- 0.0.0.0 disabled disabled 2-1000
-
Cree VLAN en el switch.
De forma predeterminada, sólo hay una VLAN en el switch, denominada VLAN 1. La VLAN 1 también se denomina VLAN predeterminada. Todos los puertos pertenecen a esta VLAN de forma predeterminada. No es posible eliminar ni cambiar el nombre de la VLAN.
Para crear VLAN, utilice el comando set vlan:
Cat5500> (enable) set vlan Usage: set vlan <mod/port> (An example of mod/port is 1/1,2/1-12,3/1-2,4/1-12) set vlan [name ] [type ] [state ] [said ] [mtu ] [ring ] [decring ] [bridge ] [parent ] [mode ] [stp ] [translation ] [backupcrf <off/on> [aremaxhop ] [stemaxhop ] (name = 1..32 characters, state = (active, suspend) type = (ethernet, fddi, fddinet, trcrf, trbrf) said = 1..4294967294, mtu = 576..18190 hex_ring_number = 0x1..0xfff, decimal_ring_number = 1..4095 bridge_number = 0x1..0xf, parent = 2..1005, mode = (srt, srb) stp = (ieee, ibm, auto), translation = 1..1005 hopcount = 1..13) Set vlan commands: ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- set vlan Set vlan information set vlan mapping Map an 802.1Q vlan to an Ethernet vlan set vlan Vlan number(s)Cat5500> (enable) set vlan 10 !--- Create VLAN 10. VTP advertisements transmitting temporarily stopped and will resume after the command finishes. Vlan 10 configuration successful Cat5500> (enable) set vlan 20 !--- Create VLAN 20. VTP advertisements transmitting temporarily stopped and will resume after the command finishes. Vlan 20 configuration successful Cat5500> (enable) set vlan 10 4/1-12 !--- Add ports to VLAN 10. VLAN 10 modified. VLAN 1 modified. VLAN Mod/Ports ---- ----------------------- 10 4/1-12 Cat5500> (enable) set vlan 20 4/13-20 !--- Add ports to VLAN 20. VLAN 20 modified. VLAN 1 modified. VLAN Mod/Ports ---- ----------------------- 20 4/13-20 Cat5500> (enable) show vlan VLAN Name Status IfIndex Mod/Ports, Vlans ---- -------------------------------- --------- ------- ------------------------ 1 default active 443 1/1-2 3/1-3 4/21-24 11/1-48 12/1-2 10 VLAN0010 active 448 4/1-12 20 VLAN0020 active 449 4/13-20 1002 fddi-default active 444 1003 token-ring-default active 447 1004 fddinet-default active 445 1005 trnet-default active 446 VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BrdgNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2 ---- ----- ---------- ----- ------ ------ ------ ---- -------- ------ ------ 1 enet 100001 1500 - - - - - 0 0 10 enet 100010 1500 - - - - - 0 0 20 enet 100020 1500 - - - - - 0 0 1002 fddi 101002 1500 - - - - - 0 0 1003 trcrf 101003 1500 - - - - - 0 0 1004 fdnet 101004 1500 - - - - - 0 0 1005 trbrf 101005 1500 - - - ibm - 0 0 !--- Output suppressed. -
Configure el protocolo de árbol de extensión (STP) PortFast en los puertos que se conectan a las estaciones de trabajo o los servidores.
Ejecute el siguiente comando para habilitar la función STP PortFast:
Cat5500> (enable) set spantree portfast 4/1-20 enable Warning: Spantree port fast start should only be enabled on ports connected to a single host. Connecting hubs, concentrators, switches, bridges, etc. to a fast start port can cause temporary spanning tree loops. Use with caution. Spantree ports 4/1-20 fast start enabled.
Nota: Este paso es opcional, pero es una buena práctica habilitar STP PortFast en los puertos que se conectan a estaciones de trabajo o servidores regulares. Para obtener más información sobre por qué habilitar PortFast, consulte este documento:
-
Configure una interfaz VLAN en el módulo del router para cada una de las VLAN entre las cuales desea rutear el tráfico.
Acceda al módulo del router ejecutando el comando session module# , donde module# es la ranura en la que se encuentra el módulo del router. En el ejemplo, el RSM se encuentra en el slot 7, como se muestra aquí:
Cat5500> (enable) show module 7 Mod Slot Ports Module-Type Model Sub Status --- ---- ----- ------------------------- ------------------- --- -------- 7 7 1 Route Switch WS-X5302 no ok Mod Module-Name Serial-Num --- ------------------- -------------------- 7 00006591991 Mod MAC-Address(es) Hw Fw Sw --- -------------------------------------- ------ ---------- ----------------- 7 00-e0-1e-91-b5-08 to 00-e0-1e-91-b5-09 4.5 20.20 12.0(5)W5(12) Cat5500> (enable) session 7 Trying Router-7... Connected to Router-7. Escape character is '^]'. Router>
-
Configure la habilitación y la contraseña Telnet en el módulo del router.
De nuevo, este paso es opcional, pero la contraseña de Telnet es necesaria si intenta acceder al módulo del router directamente con Telnet y no a través de Supervisor Engine. Utilice este conjunto de comandos para configurar las contraseñas en el módulo del router:
Router> enable Router# configure terminal !--- Enter the global configuration mode. Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)# enable password cisco !--- Set enable password. Router(config)# line vty 0 4 Router(config-line)# login Router(config-line)# password cisco !--- Set Telnet password. Router(config-line)# end Router# 05:22:40: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by vty0 (127.0.0.2) Router#
-
Cree dos interfaces VLAN, asigne direcciones IP a esas interfaces VLAN y habilite el ruteo en el módulo.
Nota: Este paso es clave para configurar el ruteo interVLAN.
Nota: En el módulo del router, las interfaces VLAN son interfaces virtuales, pero se configuran como interfaces físicas.
Ejecute este conjunto de comandos desde el modo exec privilegiado:
Router# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. !--- Configure interface VLAN 1 and assign it an IP address. !--- An interface VLAN 1 is configured for management purposes only !--- so that you can establish a Telnet session or ping the switch !--- from the workstation. Router(config)# interface vlan 1 Router(config-if)# no shutdown Router(config-if)# ip address 172.16.80.79 255.255.255.0 Router(config-if)# exit !--- Configure interface VLAN 10 and assign it an IP address. Router(config)# interface vlan 10 Router(config-if)# no shutdown Router(config-if)# ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0 Router(config-if)# exit !--- Configure interface VLAN 20 and assign it an IP address. Router(config)# interface vlan 20 Router(config-if)# ip address 10.10.11.1 255.255.255.0 Router(config-if)# no shutdown Router(config)# ip routing !--- Enable routing protocol on the module. !--- The following two commands are optional; !--- they are only used if you have multiple routers in your network. !--- Depending on your network, you may want to use a different routing protocol. Router(config)# router rip Router(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0 Router(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0 Router(config-router)# Ctrl-Z Router# 07:05:17: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by vty0 (127.0.0.2) Router# write memory !--- Save the configuration. Building configuration... Router#
En este punto, según el Diagrama de red, la configuración interVLAN está completa.
-
Vuelva al módulo Supervisor Engine ejecutando el comando exit en el mensaje Router#:
Router# exit Cat5500> (enable
Problema común: La interfaz VLAN muestra down/down
Esta sección explica un problema común que los clientes encuentran cuando intentan configurar las interfaces VLAN en los módulos de router Catalyst 5500/5000 o Catalyst 6500/6000 Series (RSM, MSFC, RSFC).
Los clientes informan de que no pueden hacer ping con algunas o todas las interfaces VLAN configuradas en el módulo del router. Además, su estado no se muestra como activo/activo cuando ejecutan el comando show interface vlan vlan#. Se han asegurado de que no han configurado apagado en esas interfaces. La única interfaz VLAN que se muestra como up/up es VLAN 1.
En esta situación, si algunas o todas sus interfaces VLAN no aparecen/no, lo primero que debe verificar es si hay puertos activos en el switch para las VLAN en cuestión.
Nota importante: Una interfaz VLAN en el módulo del router sólo se activa/activa si hay al menos un puerto asignado a esa VLAN en el switch (que no sea la interfaz del router) y ese puerto está conectado. Un puerto configurado como trunk también satisface este requisito de VLAN up/up. Si no se cumple esta condición, la interfaz del router no se activa.
En la sección Diagrama de red, se le advierte que no conecte las estaciones de trabajo al switch Catalyst 5500. En este punto, si ejecuta este conjunto de comandos, se da cuenta de que sólo la interfaz VLAN 1 se muestra up/up, y las otras dos están inactivas:
Router# show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol Vlan1 172.16.80.79 YES manual up up Vlan10 10.10.10.1 YES manual down down Vlan20 10.10.11.1 YES manual down down Router# show interface vlan 1 Vlan1 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is Cat5k Virtual Ethernet, address is 0010.f6a9.9800 (bia 0010.f6a9.9800) Internet address is 172.16.80.79/24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input 00:00:00, output 00:00:02, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 1 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec !--- Output suppressed. Router# show interface vlan 10 Vlan10 is down, line protocol is down Hardware is Cat5k Virtual Ethernet, address is 0010.f6a9.9800 (bia 0010.f6a9.9800) Internet address is 10.10.10.1/24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input 00:00:01, output 00:25:48, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec !--- Output suppressed. Router# show interface vlan 20 Vlan20 is down, line protocol is down Hardware is Cat5k Virtual Ethernet, address is 0010.f6a9.9800 (bia 0010.f6a9.9800) Internet address is 10.10.11.1/24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input 00:00:01, output 00:01:04, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops 5 minute input rate 2000 bits/sec, 2 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 1000 bits/sec, 2 packets/sec !--- Output suppressed. Router#
La interfaz VLAN 1 está activa/activa, aunque en el switch no tiene ningún puerto conectado y activo en la VLAN 1. Tiene un puerto/interfaz activo en la VLAN 1, la interfaz sc0 en el Módulo Supervisor. De forma predeterminada, la interfaz sc0 es un miembro de VLAN 1. Ejecute este comando en el switch (Supervisor Engine) para verificar la configuración de la interfaz sc0:
Cat5500> (enable) show interface
sl0: flags=51 <UP ,POINTOPOINT ,RUNNING>
slip 0.0.0.0 dest 0.0.0.0
sc0: flags=63 <UP ,BROADCAST ,RUNNING>
vlan 1 inet 172.16.80.40 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 172.16.80.255
Cat5500> (enable)
En este punto, conecte la estación de trabajo 1 en el puerto 4/1 y la estación de trabajo 2 en el puerto 4/13. Ejecute el comando show port 4/1 y show port 4/13 en el switch para asegurarse de que estos puertos muestren el estado como conectados:
Cat5500> (enable) show port 4/1 Port Name Status Vlan Level Duplex Speed Type ----- ------------------ ---------- ---------- ------ ------ ----- ------------ 4/1 connected 10 normal a-half a-10 10/100BaseTX !--- Output suppressed. Cat5500> (enable) show port 4/13 Port Name Status Vlan Level Duplex Speed Type ----- ------------------ ---------- ---------- ------ ------ ----- ------------ 4/13 connected 20 normal a-full a-100 10/100BaseTX !--- Output suppressed. Cat5500> (enable)
Ahora, inicie sesión en el módulo del router y verifique el estado de las interfaces VLAN 10 y VLAN 20. Debería verlos como up/up. Ejecute este conjunto de comandos para verificar el estado de las interfaces VLAN en el módulo del router:
Cat5500> (enable) session 7 Trying Router-7... Connected to Router-7. Escape character is '^]'. User Access Verification Password: !--- Enter the password; in this case, it is cisco. Router> enable Password: !--- Enter the password; in this case, it is cisco. Router# show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol Vlan1 172.16.80.79 YES manual up up Vlan10 10.10.10.1 YES manual up up Vlan20 10.10.11.1 YES manual up up Router# show interface vlan 10 Vlan10 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is Cat5k Virtual Ethernet, address is 0010.f6a9.9800 (bia 0010.f6a9.9800) Internet address is 10.10.10.1/24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input 00:00:01, output 00:46:14, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec !--- Output suppressed. Router# show interface vlan 20 Vlan20 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is Cat5k Virtual Ethernet, address is 0010.f6a9.9800 (bia 0010.f6a9.9800) Internet address is 10.10.11.1/24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input 00:00:00, output 00:00:56, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops 5 minute input rate 2000 bits/sec, 5 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 2000 bits/sec, 2 packets/sec !--- Output suppressed. Router# exit Cat5500> (enable)
Verifique la Configuración
Se pueden realizar varias pruebas de ping para verificar la configuración que se explica en este documento. En esta sección, utiliza la estación de trabajo2 para hacer ping a la estación de trabajo1, la interfaz sc0 en el switch y las interfaces VLAN en el módulo del router.
Nota: Asegúrese de haber establecido las gateways predeterminadas en sus estaciones de trabajo como interfaces VLAN en el módulo del router. Según el Diagrama de red, el gateway predeterminado en la estación de trabajo1 se establece como 10.10.1, y como 10.10.11.1 para la estación de trabajo2.
Prueba 1: Ping de Workstation2 a Workstation1
C:\> ipconfig
!--- This command is used to check the IP configuration on the !--- Windows 2000 workstation. Use the appropriate commands on the workstations !--- that you use.
Windows 2000 IP Configuration
Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection:
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
IP Address. . . . . . . . . . . . : 10.10.11.254
Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . : 10.10.11.1
C:\> ping 10.10.10.254
Pinging 10.10.10.254 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 10.10.10.254: bytes=32 time=10ms TTL=31
Reply from 10.10.10.254: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=31
Reply from 10.10.10.254: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=31
Reply from 10.10.10.254: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=31
Ping statistics for 10.10.10.254:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 10ms, Average = 2ms
Prueba 2: Ping de Workstation2 a la Interfaz sc0 en Supervisor Engine
C:\> ping 172.16.80.40
Pinging 172.16.80.40 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 172.16.80.40: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=59
Reply from 172.16.80.40: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=59
Reply from 172.16.80.40: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=59
Reply from 172.16.80.40: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=59
Ping statistics for 172.16.80.40:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
Prueba 3: Ping de Workstation2 a Interface VLAN 1 en el Módulo del Router
C:\> ping 172.16.80.79
Pinging 172.16.80.79 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 172.16.80.79: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 172.16.80.79: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 172.16.80.79: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 172.16.80.79: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Ping statistics for 172.16.80.79:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
Prueba 4: Ping de Workstation2 a Interface VLAN 10 en el Módulo del Router
C:\> ping 10.10.10.1
Pinging 10.10.10.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 10.10.10.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 10.10.10.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 10.10.10.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 10.10.10.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Ping statistics for 10.10.10.1:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
Prueba 5: Ping de Workstation2 a Interface VLAN 20 en el Módulo del Router
C:\> ping 10.10.11.1
Pinging 10.10.11.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 10.10.11.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 10.10.11.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 10.10.11.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 10.10.11.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Ping statistics for 10.10.11.1:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
Appendix
Configuración del Módulo Supervisor Engine
Cat5500> (enable) show config This command shows non-default configurations only. Use show config all to show both default and non-default configurations. ... begin ! # ***** NON-DEFAULT CONFIGURATION ***** ! ! #time: Tue Apr 10 2001, 09:09:54 ! #version 6.1(1) ! set option fddi-user-pri enabled set password $2$lx7B$WipkVnLnbYIfrBSqD2SN9. set enablepass $2$6/eK$I3lDb2nnP7Fc9JKF3XwRW/ set prompt Cat5500> ! #errordetection set errordetection portcounter enable ! #system set system name Cat5500 ! #frame distribution method set port channel all distribution mac both ! #vtp set vtp domain cisco set vtp mode transparent set vlan 1 name default type ethernet mtu 1500 said 100001 state active set vlan 1002 name fddi-default type fddi mtu 1500 said 101002 state active set vlan 1004 name fddinet-default type fddinet mtu 1500 said 101004 state active stp ieee set vlan 1005 name trnet-default type trbrf mtu 1500 said 101005 state active stp ibm set vlan 10,20 set vlan 1003 name token-ring-default type trcrf mtu 1500 said 101003 state active mode srb aremaxhop 7 stemaxhop 7 backupcrf off ! #ip set interface sc0 1 172.16.80.40/255.255.255.0 172.16.80.255 set ip route 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0 172.16.80.79 ! #set boot command set boot config-register 0x2102 clear boot system all ! # default port status is enable ! ! #module 1 : 2-port 1000BaseSX Supervisor ! #module 2 : 4-port 10/100BaseTX Supervisor ! #module 3 : 3-port 1000BaseX Ethernet ! #module 4 : 24-port 10/100BaseTX Ethernet set vlan 10 4/1-12 set vlan 20 4/13-20 set spantree portfast 4/1-20 enable ! #module 5 : 2-port MM OC-3 Dual-Phy ATM ! #module 6 empty ! #module 7 : 1-port Route Switch ! #module 8 empty ! #module 9 empty ! #module 10 empty ! #module 11 : 48-port 10BaseT Ethernet ! #module 12 : 2-port MM MIC FDDI ! #module 13 empty end Cat5500> (enable)
Configuración de RSM
Router# show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration: ! version 12.0 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! hostname Router ! enable password cisco ! ip subnet-zero ip cef ! ! process-max-time 200 ! interface Vlan1 ip address 172.16.80.79 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast ! interface Vlan10 ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast ! interface Vlan20 ip address 10.10.11.1 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast ! ip classless ! ! line con 0 transport input none line aux 0 line vty 0 4 password cisco login ! end Router#
Información Relacionada
- Configuración y características generales del módulo del router para Catalyst 4000 Family (WS-X4232-L3)
- Uso de Portfast y otros comandos para solucionar retrasos al iniciar la conectividad de la estación de trabajo
- Páginas de Soporte de Productos de LAN
- Página de Soporte de LAN Switching
- Soporte Técnico - Cisco Systems
Historial de revisiones
| Revisión | Fecha de publicación | Comentarios |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
30-Aug-2005 |
Versión inicial |
Contacte a Cisco
- Abrir un caso de soporte

- (Requiere un Cisco Service Contract)
 Comentarios
Comentarios