IKEv2 de Android strongSwan a Cisco IOS con EAP y autenticación RSA
Contenido
Introducción
Este documento describe cómo configurar la versión móvil de strongSwan para acceder a un Cisco IOS® Software VPN gateway a través del protocolo Internet Key Exchange Version 2 (IKEv2) .
Se presentan tres ejemplos:
- Teléfono Android con strongSwan que se conecta al gateway VPN del software Cisco IOS con autenticación de protocolo de autenticación extensible - resumen de mensajes 5 (EAP-MD5).
- Teléfono Android con strongSwan que se conecta al gateway VPN del software Cisco IOS con autenticación de certificados (RSA).
- Teléfono Android con strongSwan que se conecta al gateway VPN del software Cisco IOS detrás de la traducción de direcciones de red (NAT). Hay un requisito para tener dos extensiones x509 Subject Alternative Name en el certificado de gateway VPN.
También se incluyen el software Cisco IOS y las limitaciones de strongSwan.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recomienda que tenga conocimiento sobre estos temas:
- Conocimiento básico de la configuración de OpenSSL
- Conocimiento básico de la configuración de la interfaz de línea de comandos (CLI) del software Cisco IOS
- Conocimiento básico de IKEv2
Componentes Utilizados
La información que contiene este documento se basa en las siguientes versiones de software y hardware.
- Android 4.0 o posterior con strongSwan
- Versión 15.3T o posterior del software del IOS de Cisco
- Software Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE), versión 1.1.4 y posteriores
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Configurar
Diagrama de la red

Android strongSwan establece un túnel IKEv2 con una gateway de software Cisco IOS para acceder a las redes internas de forma segura.
Inscripción de certificados
Los certificados son un prerrequisito para la autenticación basada en EAP y en RSA.
En el escenario de autenticación EAP, sólo se necesita un certificado en el gateway VPN. El cliente se conecta al software Cisco IOS solamente cuando el software presenta un certificado firmado por una Autoridad de Certificación (CA) que es de confianza en Android. A continuación, se inicia una sesión EAP para que el cliente se autentique con el software Cisco IOS.
Para la autenticación basada en RSA, ambos extremos deben tener un certificado correcto.
Cuando una dirección IP se utiliza como ID de peer, hay requisitos adicionales para el certificado. Android strongSwan verifica si la dirección IP del gateway VPN se incluye en la extensión x509 Subject Alternative Name. Si no, Android descarta la conexión; esta es una buena práctica, así como una recomendación de RFC 6125.
OpenSSL se utiliza como una CA porque el software Cisco IOS tiene una limitación: no puede generar certificados con una extensión que incluya una dirección IP. Todos los certificados son generados por OpenSSL e importados a Android y al software Cisco IOS.
En el Cisco IOS Software, el comando subject-alt-name se puede utilizar para crear una extensión que incluya una dirección IP, pero el comando funciona solamente con certificados autofirmados. El Id. de error de Cisco CSCui44783, "Capacidad PKI ENH de IOS para generar CSR con extensión subject-alt-name", es una solicitud de mejora para permitir que el software Cisco IOS genere la extensión para todos los tipos de inscripciones.
Este es un ejemplo de los comandos que generan una CA:
#generate key
openssl genrsa -des3 -out ca.key 2048
#generate CSR
openssl req -new -key ca.key -out ca.csr
#remove protection
cp ca.key ca.key.org
openssl rsa -in ca.key.org -out ca.key
#self sign certificate
openssl x509 -req -days 365 -in ca.csr -signkey ca.key -out ca.crt
-extensions v3_req -extfile conf_global.crt
conf_global.crt es un archivo de configuración. La extensión CA debe establecerse en TRUE:
[ req ]
default_bits = 1024 # Size of keys
default_md = md5 # message digest algorithm
string_mask = nombstr # permitted characters
#string_mask = pkix # permitted characters
distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name
req_extensions = v3_req
[ v3_req ]
basicConstraints = CA:TRUE
subjectKeyIdentifier = hash
Los comandos que generan un certificado son muy similares para Cisco IOS Software y Android. Este ejemplo asume que ya hay una CA utilizada para firmar el certificado:
#generate key
openssl genrsa -des3 -out server.key 2048
#generate CSR
openssl req -new -key server.key -out server.csr
#remove protection
cp server.key server.key.org
openssl rsa -in server.key.org -out server.key
#sign the cert and add Alternate Subject Name extension from
conf_global_cert.crt file with configuration
openssl x509 -req -in server.csr -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key -CAcreateserial
-out server.crt -days 365 -extensions v3_req -extfile conf_global_cert.crt
#create pfx file containig CA cert and server cert
openssl pkcs12 -export -out server.pfx -inkey server.key -in server.crt
-certfile ca.crt
conf_global_cert.crt es un archivo de configuración. La extensión Nombre de asunto alternativo es un valor de clave. En este ejemplo, la extensión CA se establece en FALSE:
[ req ]
default_bits = 1024 # Size of keys
default_md = md5 # message digest algorithm
string_mask = nombstr # permitted characters
#string_mask = pkix # permitted characters
distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name
req_extensions = v3_req
[ v3_req ]
basicConstraints = CA:FALSE
subjectKeyIdentifier = hash
subjectAltName = @alt_names
[alt_names]
IP.1 = 10.48.64.15
Se debe generar un certificado tanto para el Cisco IOS Software como para Android.
La dirección IP 10.48.64.15 pertenece al gateway del software Cisco IOS. Cuando genere un certificado para el Cisco IOS Software, asegúrese de que subjectAltName esté establecido en 10.48.64.15. Android valida el certificado recibido del software Cisco IOS e intenta encontrar su dirección IP en subjectAltName.
Cisco IOS Software
El software Cisco IOS necesita tener instalado un certificado correcto para la autenticación basada en RSA y en EAP.
El archivo pfx (que es un contenedor pkcs12) para el software Cisco IOS se puede importar:
BSAN-2900-1(config)# crypto pki import TP pkcs12
http://10.10.10.1/server.pfx password 123456
% Importing pkcs12...
Source filename [server.pfx]?
CRYPTO_PKI: Imported PKCS12 file successfully.
Utilice el comando show crypto pki certificates verbose para verificar que la importación se realizó correctamente:
BSAN-2900-1# show crypto pki certificates verbose
Certificate
Status: Available
Version: 3
Certificate Serial Number (hex): 00A003C5DCDEFA146C
Certificate Usage: General Purpose
Issuer:
cn=Cisco
ou=Cisco TAC
o=Cisco
l=Krakow
st=Malopolskie
c=PL
Subject:
Name: IOS
IP Address: 10.48.64.15
cn=IOS
ou=TAC
o=Cisco
l=Krakow
st=Malopolska
c=PL
Validity Date:
start date: 18:04:09 UTC Aug 1 2013
end date: 18:04:09 UTC Aug 1 2014
Subject Key Info:
Public Key Algorithm: rsaEncryption
RSA Public Key: (2048 bit)
Signature Algorithm: SHA1 with RSA Encryption
Fingerprint MD5: 2C45BF10 0BACB98D 444F5804 1DC27ECF
Fingerprint SHA1: 26B66A66 DF5E7D6F 498DD653 A2C164D7 4C7A7F8F
X509v3 extensions:
X509v3 Subject Key ID: AD598A9B 8AB6893B AB3CB8B9 28B2039C 78441E72
X509v3 Basic Constraints:
CA: FALSE
X509v3 Subject Alternative Name:
10.48.64.15
Authority Info Access:
Associated Trustpoints: TP
Storage: nvram:Cisco#146C.cer
Key Label: TP
Key storage device: private config
CA Certificate
Status: Available
Version: 3
Certificate Serial Number (hex): 00DC8EAD98723DF56A
Certificate Usage: General Purpose
Issuer:
cn=Cisco
ou=Cisco TAC
o=Cisco
l=Krakow
st=Malopolskie
c=PL
Subject:
cn=Cisco
ou=Cisco TAC
o=Cisco
l=Krakow
st=Malopolskie
c=PL
Validity Date:
start date: 16:39:55 UTC Jul 23 2013
end date: 16:39:55 UTC Jul 23 2014
Subject Key Info:
Public Key Algorithm: rsaEncryption
RSA Public Key: (2048 bit)
Signature Algorithm: SHA1 with RSA Encryption
Fingerprint MD5: 0A2432DC 33F0DC46 AAB23E26 ED474B7E
Fingerprint SHA1: A50E3892 ED5C4542 FA7FF584 DE07B6E0 654A62D0
X509v3 extensions:
X509v3 Subject Key ID: 786F263C 0F5A1963 D6AD18F8 86DCE7C9 0185911E
X509v3 Basic Constraints:
CA: TRUE
Authority Info Access:
Associated Trustpoints: TP
Storage: nvram:Cisco#F56ACA.cer
BSAN-2900-1#show ip int brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0 10.48.64.15 YES NVRAM up up
Android
Para la autenticación basada en EAP, Andorid necesita tener instalado sólo el certificado de CA correcto.
Para la autenticación basada en RSA, Andorid necesita tener instalado tanto el certificado de CA como su propio certificado.
Este procedimiento describe cómo instalar ambos certificados:
- Envíe el archivo pfx por correo electrónico y ábralo.
- Proporcione la contraseña que se utilizó cuando se generó el archivo pfx.

- Introduzca el nombre del certificado importado.

- Navegue hasta Configuraciones > Seguridad > Credenciales de Confianza para verificar la instalación del certificado. El nuevo certificado debe aparecer en el almacén de usuarios:

En este momento, se instalan un certificado de usuario y un certificado de CA. El archivo pfx es un contenedor pkcs12 con el certificado de usuario y el certificado CA.
Android tiene requisitos precisos cuando se importan certificados. Por ejemplo, para que un certificado de CA se importe correctamente, Android requiere que la extensión x509v3 Basic Constraint CA se establezca en TRUE. Por lo tanto, cuando genera una CA o utiliza su propia CA, es importante verificar que tenga la extensión correcta:
pluton custom_ca # openssl x509 -in ca.crt -text
Certificate:
Data:
Version: 3 (0x2)
Serial Number:
dc:8e:ad:98:72:3d:f5:6a
Signature Algorithm: sha1WithRSAEncryption
Issuer: C=PL, ST=Malopolskie, L=Krakow, O=Cisco, OU=Cisco TAC, CN=Cisco
<.....output omitted>
X509v3 Basic Constraints:
CA:TRUE
<.....output omitted>
Autenticación EAP
Configuración de Cisco IOS Software para la Autenticación EAP
IKEv2 permite el uso de una pila de protocolo EAP para realizar la autenticación de usuario. El gateway VPN se presenta con el certificado. Una vez que el cliente confía en ese certificado, el cliente responde a la identidad de solicitud EAP desde el gateway. El software Cisco IOS utiliza esa identidad y envía un mensaje de solicitud de radio al servidor de autenticación, autorización y contabilidad (AAA), y se establece una sesión EAP-MD5 entre el suplicante (Android) y el servidor de autenticación (Access Control Server [ACS] o ISE).
Después de una autenticación EAP-MD5 exitosa, como indica un mensaje Radius-Accept, el software Cisco IOS utiliza el modo de configuración para enviar la dirección IP al cliente y continuar con la negociación del selector de tráfico.
Observe que Android ha enviado IKEID=cisco (tal y como está configurado). Este IKEID recibido en el Cisco IOS Software coincide con 'ikev2 profile PROF'.
aaa new-model
aaa authentication login eap-list-radius group radius
aaa authorization network IKE2_AUTHOR_LOCAL local
crypto pki trustpoint TP
revocation-check none
crypto ikev2 authorization policy IKE2_AUTHOR_POLICY
pool POOL
!
crypto ikev2 proposal ikev2-proposal
encryption aes-cbc-128
integrity sha1
group 14
!
crypto ikev2 policy ikev2-policy
proposal ikev2-proposal
!
!
crypto ikev2 profile PROF
match identity remote key-id cisco
authentication remote eap query-identity
authentication local rsa-sig
pki trustpoint TP
aaa authentication eap eap-list-radius
aaa authorization group eap list IKE2_AUTHOR_LOCAL IKE2_AUTHOR_POLICY
aaa authorization user eap cached
virtual-template 1
crypto ipsec transform-set 3DES-MD5 esp-aes esp-sha-hmac
mode tunnel
!
crypto ipsec profile PROF
set transform-set 3DES-MD5
set ikev2-profile PROF
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 10.48.64.15 255.255.255.128
interface Virtual-Template1 type tunnel
ip unnumbered GigabitEthernet0/0
tunnel mode ipsec ipv4
tunnel protection ipsec profile PROF
ip local pool POOL 192.168.0.1 192.168.0.10
radius-server host 10.48.66.185 key cisco
Configuración de Android para la Autenticación EAP
Android strongSwan debe tener EAP configurado:
- Inhabilitar la selección automática de certificados; de lo contrario, se envían 100 o más CERT_REQ en el tercer paquete.
- Elija un certificado específico (CA) que se importó en el paso anterior; el nombre de usuario y la contraseña deben ser los mismos que en el servidor AAA.

Prueba de autenticación EAP
En el software Cisco IOS, estos son los debugs más importantes para la autenticación EAP. La mayoría de los resultados se han omitido para mayor claridad:
debug crypto ikev2 error
debug crypto ikev2 internal
debug radius authentication
debug radius verbose
IKEv2:New ikev2 sa request admitted
IKEv2:(SA ID = 1):Searching policy based on peer's identity 'cisco' of type
'FQDN'
IKEv2:(1): Choosing IKE profile PROF
IKEv2:Sending certificates as X509 certificates
RADIUS(00000025): Send Access-Request to 10.48.66.185:1645 id 1645/4,len 110
RADIUS: Received from id 1645/4 10.48.66.185:1645, Access-Challenge, len 79
RADIUS(00000025): Send Access-Request to 10.48.66.185:1645 id 1645/5,len 141
RADIUS: Received from id 1645/5 10.48.66.185:1645, Access-Challenge, len 100
RADIUS(00000025): Send Access-Request to 10.48.66.185:1645 id 1645/6,len 155
RADIUS: Received from id 1645/6 10.48.66.185:1645, Access-Accept, len 76
IKEv2:(SA ID = 1):SM Trace-> SA: I_SPI=AABAB198FACAAEDE R_SPI=D61F37C4DC875001
(R) MsgID = 00000004 CurState: R_PROC_EAP_RESP Event: EV_RECV_EAP_SUCCESS
IKEv2:IKEv2 local AAA author request for 'IKE2_AUTHOR_POLICY'
IKEv2:Received group author attributes: ipv4-pool: POOL, route-accept any tag:1
distance:1
IKEv2:Allocated addr 192.168.0.2 from local pool POOL
IKEv2:(SA ID = 1):SM Trace-> SA: I_SPI=AABAB198FACAAEDE R_SPI=D61F37C4DC875001
(R) MsgID = 00000005 CurState: R_VERIFY_AUTH Event:
EV_OK_RECD_VERIFY_IPSEC_POLICY
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Virtual-Access1, changed state
to up
Los registros de Android indican:
00[DMN] Starting IKE charon daemon (strongSwan 5.1.0dr2,
Linux 3.4.0-perf-gf43c3d9, armv7l)
00[KNL] kernel-netlink plugin might require CAP_NET_ADMIN capability
00[LIB] loaded plugins: androidbridge charon android-log openssl fips-prf
random nonce pubkey pkcs1 pkcs8 pem xcbc hmac socket-default kernel-netlink
00[LIB] unable to load 9 plugin features (9 due to unmet dependencies)
00[JOB] spawning 16 worker threads
13[IKE] initiating IKE_SA android[1] to 10.48.64.15
13[ENC] generating IKE_SA_INIT request 0 [ SA KE No N(NATD_S_IP) N(NATD_D_IP) ]
13[NET] sending packet: from 10.147.24.153[45581] to 10.48.64.15[500]
(648 bytes)
11[NET] received packet: from 10.48.64.15[500] to 10.147.24.153[45581]
(497 bytes)
11[ENC] parsed IKE_SA_INIT response 0 [ SA KE No V V N(NATD_S_IP) N(NATD_D_IP)
CERTREQ N(HTTP_CERT_LOOK) ]
11[ENC] received unknown vendor ID:
43:49:53:43:4f:2d:44:45:4c:45:54:45:2d:52:45:41:53:4f:4e
11[ENC] received unknown vendor ID:
46:4c:45:58:56:50:4e:2d:53:55:50:50:4f:52:54:45:44
11[IKE] faking NAT situation to enforce UDP encapsulation
11[IKE] cert payload ANY not supported - ignored
11[IKE] sending cert request for "C=PL, ST=Malopolskie, L=Krakow, O=Cisco,
OU=Cisco TAC, CN=Cisco"
11[IKE] establishing CHILD_SA android
11[ENC] generating IKE_AUTH request 1 [ IDi N(INIT_CONTACT) CERTREQ
CP(ADDR ADDR6 DNS DNS6) N(ESP_TFC_PAD_N) SA TSi TSr N(MOBIKE_SUP)
11[NET] sending packet: from 10.147.24.153[35564] to 10.48.64.15[4500]
(508 bytes)
10[NET] received packet: from 10.48.64.15[4500] to 10.147.24.153[35564]
(1292 bytes)
10[ENC] parsed IKE_AUTH response 1 [ V IDr CERT AUTH EAP/REQ/ID ]
10[IKE] received end entity cert "C=PL, ST=Malopolska, L=Krakow, O=Cisco,
OU=TAC, CN=IOS"
10[CFG] using certificate "C=PL, ST=Malopolska, L=Krakow, O=Cisco, OU=TAC,
CN=IOS"
10[CFG] using trusted ca certificate "C=PL, ST=Malopolskie, L=Krakow, O=Cisco,
OU=Cisco TAC, CN=Cisco"
10[CFG] reached self-signed root ca with a path length of 0
10[IKE] authentication of '10.48.64.15' with RSA signature successful
10[IKE] server requested EAP_IDENTITY (id 0x3B), sending 'cisco'
10[ENC] generating IKE_AUTH request 2 [ EAP/RES/ID ]
10[NET] sending packet: from 10.147.24.153[35564] to 10.48.64.15[4500]
(76 bytes)
09[NET] received packet: from 10.48.64.15[4500] to 10.147.24.153[35564]
(76 bytes)
09[ENC] parsed IKE_AUTH response 2 [ EAP/REQ/TLS ]
09[IKE] server requested EAP_TLS authentication (id 0x59)
09[IKE] EAP method not supported, sending EAP_NAK
09[ENC] generating IKE_AUTH request 3 [ EAP/RES/NAK ]
09[NET] sending packet: from 10.147.24.153[35564] to 10.48.64.15[4500]
(76 bytes)
08[NET] received packet: from 10.48.64.15[4500] to 10.147.24.153[35564]
(92 bytes)
08[ENC] parsed IKE_AUTH response 3 [ EAP/REQ/MD5 ]
08[IKE] server requested EAP_MD5 authentication (id 0x5A)
08[ENC] generating IKE_AUTH request 4 [ EAP/RES/MD5 ]
08[NET] sending packet: from 10.147.24.153[35564] to 10.48.64.15[4500]
(92 bytes)
07[NET] received packet: from 10.48.64.15[4500] to 10.147.24.153[35564]
(76 bytes)
07[ENC] parsed IKE_AUTH response 4 [ EAP/SUCC ]
07[IKE] EAP method EAP_MD5 succeeded, no MSK established
07[IKE] authentication of 'cisco' (myself) with EAP
07[ENC] generating IKE_AUTH request 5 [ AUTH ]
07[NET] sending packet: from 10.147.24.153[35564] to 10.48.64.15[4500]
(92 bytes)
06[NET] received packet: from 10.48.64.15[4500] to 10.147.24.153[35564]
(236 bytes)
06[ENC] parsed IKE_AUTH response 5 [ AUTH CP(ADDR) SA TSi TSr N(SET_WINSIZE)
N(ESP_TFC_PAD_N) N(NON_FIRST_FRAG) ]
06[IKE] authentication of '10.48.64.15' with EAP successful
06[IKE] IKE_SA android[1] established between
10.147.24.153[cisco]...10.48.64.15[10.48.64.15]
06[IKE] scheduling rekeying in 35421s
06[IKE] maximum IKE_SA lifetime 36021s
06[IKE] installing new virtual IP 192.168.0.1
06[IKE] received ESP_TFC_PADDING_NOT_SUPPORTED, not using ESPv3 TFC padding
06[IKE] CHILD_SA android{1} established with SPIs c776cb4f_i ea27f072_o and
TS 192.168.0.1/32 === 0.0.0.0/0
06[DMN] setting up TUN device for CHILD_SA android{1}
06[DMN] successfully created TUN device
Este ejemplo muestra cómo verificar el estado en el Cisco IOS Software:
BSAN-2900-1#show crypto session detail
Crypto session current status
Code: C - IKE Configuration mode, D - Dead Peer Detection
K - Keepalives, N - NAT-traversal, T - cTCP encapsulation
X - IKE Extended Authentication, F - IKE Fragmentation
Interface: Virtual-Access1
Uptime: 00:02:12
Session status: UP-ACTIVE
Peer: 10.147.24.153 port 60511 fvrf: (none) ivrf: (none)
Phase1_id: cisco
Desc: (none)
IKEv2 SA: local 10.48.64.15/4500 remote 10.147.24.153/60511 Active
Capabilities:NX connid:1 lifetime:23:57:48
IPSEC FLOW: permit ip 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0 host 192.168.0.2
Active SAs: 2, origin: crypto map
Inbound: #pkts dec'ed 40 drop 0 life (KB/Sec) 4351537/3468
Outbound: #pkts enc'ed 5 drop 0 life (KB/Sec) 4351542/3468
BSAN-2900-1#show crypto ikev2 sa detailed
IPv4 Crypto IKEv2 SA
Tunnel-id Local Remote fvrf/ivrf Status
1 10.48.64.15/4500 10.147.24.153/60511 none/none READY
Encr: AES-CBC, keysize: 128, Hash: SHA96, DH Grp:14, Auth sign: RSA,
Auth verify: EAP
Life/Active Time: 86400/137 sec
CE id: 1002, Session-id: 2
Status Description: Negotiation done
Local spi: D61F37C4DC875001 Remote spi: AABAB198FACAAEDE
Local id: 10.48.64.15
Remote id: cisco
Remote EAP id: cisco
Local req msg id: 0 Remote req msg id: 6
Local next msg id: 0 Remote next msg id: 6
Local req queued: 0 Remote req queued: 6
Local window: 5 Remote window: 1
DPD configured for 0 seconds, retry 0
Fragmentation not configured.
Extended Authentication configured.
NAT-T is detected outside
Cisco Trust Security SGT is disabled
Assigned host addr: 192.168.0.2
Initiator of SA : No
Estas cifras muestran cómo verificar el estado en Android:
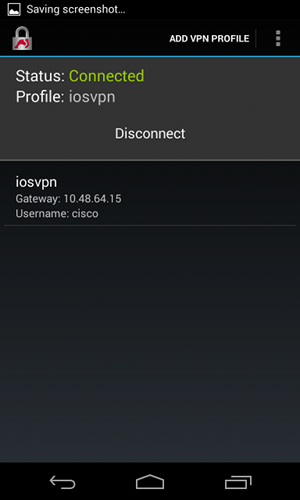
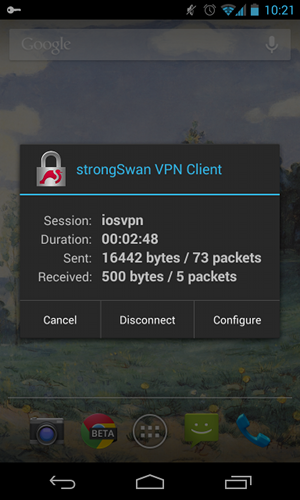
Autenticación RSA
Configuración de Cisco IOS Software para la Autenticación RSA
En la autenticación de Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA), Android envía el certificado para autenticarse en el software Cisco IOS. Es por eso que se necesita el mapa del certificado que enlaza ese tráfico a un perfil IKEv2 específico. No se requiere autenticación EAP de usuario.
Este es un ejemplo de cómo se configura la autenticación RSA para un peer remoto:
crypto pki certificate map CERT_MAP 10
subject-name co android
crypto ikev2 profile PROF
match certificate CERT_MAP
authentication remote rsa-sig
authentication local rsa-sig
pki trustpoint TP
aaa authorization group cert list IKE2_AUTHOR_LOCAL IKE2_AUTHOR_POLICY
virtual-template 1
Configuración de Android para la Autenticación RSA
Las credenciales de usuario se han reemplazado por el certificado de usuario:

Prueba de autenticación RSA
En el Cisco IOS Software, estos son los debugs más importantes para la autenticación RSA. La mayoría de los resultados se han omitido para mayor claridad:
debug crypto ikev2 error
debug crypto ikev2 internal
debug crypto pki transactions
debug crypto pki validation
debug crypto pki messages
IKEv2:New ikev2 sa request admitted
IKEv2:(SA ID = 1):Searching policy based on peer's identity 'cn=android,ou=TAC,
o=Cisco,l=Krakow,st=Malopolska,c=PL' of type 'DER ASN1 DN'
IKEv2:(1): Choosing IKE profile PROF
IKEv2:Sending certificates as X509 certificates
IKEv2:(SA ID = 1):Peer's authentication method is 'RSA'
IKEv2:Peer has sent X509 certificates
CRYPTO_PKI: Found a issuer match
CRYPTO_PKI: (9000B) Certificate is verified
CRYPTO_PKI: (9000B) Certificate validation succeeded
IKEv2:(SA ID = 1):[Crypto Engine -> IKEv2] Verification of signed
authentication data PASSED
IKEv2:IKEv2 local AAA author request for 'IKE2_AUTHOR_POLICY'
IKEv2:Received group author attributes: ipv4-pool: POOL, route-accept any tag:1
distance:1
IKEv2:Allocated addr 192.168.0.3 from local pool POOL
IKEv2:(SA ID = 1):SM Trace-> SA: I_SPI=E53A57E359A8437C R_SPI=A03D273FC75EEBD9
(R) MsgID = 00000001 CurState: R_VERIFY_AUTH Event:
EV_OK_RECD_VERIFY_IPSEC_POLICY
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Virtual-Access1, changed state
to up
Los registros de Android indican:
00[DMN] Starting IKE charon daemon (strongSwan 5.1.0dr2,
Linux 3.4.0-perf-gf43c3d9, armv7l)
00[KNL] kernel-netlink plugin might require CAP_NET_ADMIN capability
00[LIB] loaded plugins: androidbridge charon android-log openssl fips-prf
random nonce pubkey pkcs1 pkcs8 pem xcbc hmac socket-default
00[LIB] unable to load 9 plugin features (9 due to unmet dependencies)
00[JOB] spawning 16 worker threads
05[CFG] loaded user certificate 'C=PL, ST=Malopolska, L=Krakow, O=Cisco,
OU=TAC, CN=android' and private key
05[CFG] loaded CA certificate 'C=PL, ST=Malopolskie, L=Krakow, O=Cisco,
OU=Cisco TAC, CN=Cisco'
05[IKE] initiating IKE_SA android[4] to 10.48.64.15
05[ENC] generating IKE_SA_INIT request 0 [ SA KE No N(NATD_S_IP) N(NATD_D_IP) ]
05[NET] sending packet: from 10.147.24.153[34697] to 10.48.64.15[500]
(648 bytes)
10[NET] received packet: from 10.48.64.15[500] to 10.147.24.153[34697]
(497 bytes)
10[ENC] parsed IKE_SA_INIT response 0 [ SA KE No V V N(NATD_S_IP) N(NATD_D_IP)
CERTREQ N(HTTP_CERT_LOOK) ]
10[ENC] received unknown vendor ID:
43:49:53:43:4f:2d:44:45:4c:45:54:45:2d:52:45:41:53:4f:4e
10[ENC] received unknown vendor ID:
46:4c:45:58:56:50:4e:2d:53:55:50:50:4f:52:54:45:44
10[IKE] faking NAT situation to enforce UDP encapsulation
10[IKE] cert payload ANY not supported - ignored
10[IKE] sending cert request for "C=PL, ST=Malopolskie, L=Krakow, O=Cisco,
OU=Cisco TAC, CN=Cisco"
10[IKE] authentication of 'C=PL, ST=Malopolska, L=Krakow, O=Cisco, OU=TAC,
CN=android' (myself) with RSA signature successful
10[IKE] sending end entity cert "C=PL, ST=Malopolska, L=Krakow, O=Cisco,
OU=TAC, CN=android"
10[IKE] establishing CHILD_SA android
10[ENC] generating IKE_AUTH request 1 [ IDi CERT N(INIT_CONTACT) CERTREQ
AUTH CP(ADDR ADDR6 DNS DNS6) N(ESP_TFC_PAD_N) SA
10[NET] sending packet: from 10.147.24.153[44527] to 10.48.64.15[4500]
(1788 bytes)
12[NET] received packet: from 10.48.64.15[4500] to 10.147.24.153[44527]
(1420 bytes)
12[ENC] parsed IKE_AUTH response 1 [ V IDr CERT AUTH CP(ADDR) SA TSi TSr
N(SET_WINSIZE) N(ESP_TFC_PAD_N) N(NON_FIRST_FRAG)
12[IKE] received end entity cert "C=PL, ST=Malopolska, L=Krakow, O=Cisco,
OU=TAC, CN=IOS"
12[CFG] using certificate "C=PL, ST=Malopolska, L=Krakow, O=Cisco, OU=TAC,
CN=IOS"
12[CFG] using trusted ca certificate "C=PL, ST=Malopolskie, L=Krakow, O=Cisco,
OU=Cisco TAC, CN=Cisco"
12[CFG] reached self-signed root ca with a path length of 0
12[IKE] authentication of '10.48.64.15' with RSA signature successful
12[IKE] IKE_SA android[4] established between 10.147.24.153[C=PL,
ST=Malopolska, L=Krakow, O=Cisco, OU=TAC,
CN=android]...10.48.64.15[10.48.64.15]
12[IKE] scheduling rekeying in 35413s
12[IKE] maximum IKE_SA lifetime 36013s
12[IKE] installing new virtual IP 192.168.0.3
12[IKE] received ESP_TFC_PADDING_NOT_SUPPORTED, not using ESPv3 TFC padding
12[IKE] CHILD_SA android{4} established with SPIs ecb3af87_i b2279175_o and
TS 192.168.0.3/32 === 0.0.0.0/0
12[DMN] setting up TUN device for CHILD_SA android{4}
12[DMN] successfully created TUN device
En el software Cisco IOS, RSA se utiliza tanto para la firma como para la verificación; en el escenario anterior, se utilizó EAP para la verificación:
BSAN-2900-1#show crypto ikev2 sa detailed
IPv4 Crypto IKEv2 SA
Tunnel-id Local Remote fvrf/ivrf Status
1 10.48.64.15/4500 10.147.24.153/44527 none/none READY
Encr: AES-CBC, keysize: 128, Hash: SHA96, DH Grp:14, Auth sign: RSA,
Auth verify: RSA
Life/Active Time: 86400/16 sec
CE id: 1010, Session-id: 3
Status Description: Negotiation done
Local spi: A03D273FC75EEBD9 Remote spi: E53A57E359A8437C
Local id: 10.48.64.15
Remote id: cn=android,ou=TAC,o=Cisco,l=Krakow,st=Malopolska,c=PL
Local req msg id: 0 Remote req msg id: 2
Local next msg id: 0 Remote next msg id: 2
Local req queued: 0 Remote req queued: 2
Local window: 5 Remote window: 1
DPD configured for 0 seconds, retry 0
Fragmentation not configured.
Extended Authentication not configured.
NAT-T is detected outside
Cisco Trust Security SGT is disabled
Assigned host addr: 192.168.0.3
Initiator of SA : No
La verificación de estado en Android es similar a la del escenario anterior.
Puerta de enlace VPN detrás de NAT - Limitaciones de software de Cisco IOS y strongSwan
Este ejemplo explica una limitación de las verificaciones de certificados strongSwan.
Suponga que la dirección IP del gateway VPN del software Cisco IOS se traduce estáticamente de 172.16.1.1 a 10.147.25.80. Se utiliza la autenticación EAP.
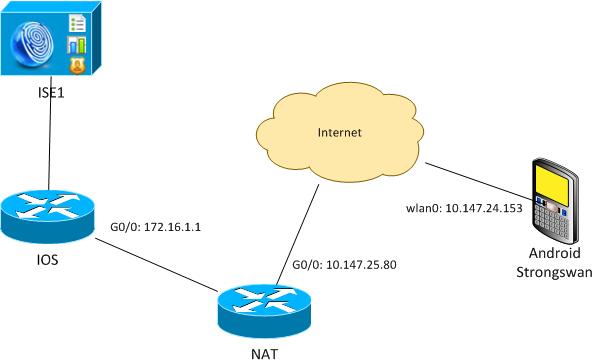
Suponga también que el certificado de software del IOS de Cisco tiene un nombre alternativo del sujeto para 172.16.1.1 y 10.147.25.80.
Después de una autenticación EAP correcta, Android realiza la verificación e intenta encontrar la dirección IP del par que se utilizó en la configuración Android (10.147.25.80) en la extensión Subject Alternative Name. La verificación falla:
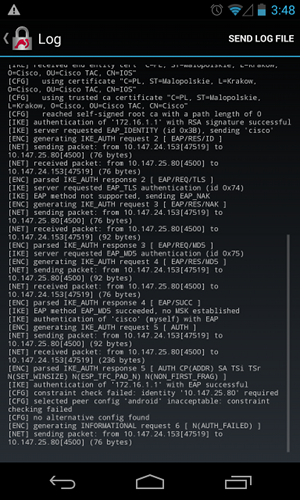
Los registros indican:
constraint check failed: identity '10.147.25.80' required
Se ha producido un error porque Android sólo puede leer la primera extensión de nombre alternativo del asunto (172.16.1.1).
Ahora, suponga que el certificado de software del IOS de Cisco tiene ambas direcciones en el nombre alternativo del sujeto pero en el orden inverso: 10.147.25.80 and 172.16.1.1. Android realiza la validación cuando recibe el IKEID, que es la dirección IP del gateway VPN (172.16.1.1), en el tercer paquete:
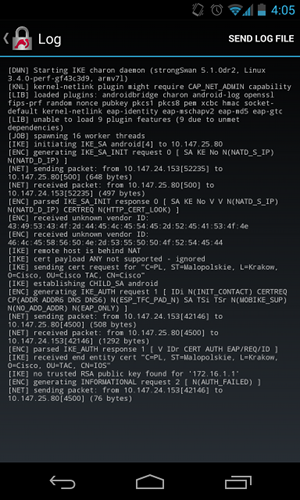
Ahora el registro muestra:
no trusted RSA public key found for '172.16.1.1'
Por lo tanto, cuando Android recibe el IKEID, necesita encontrar el IKEID en el nombre alternativo del asunto y puede utilizar solamente la primera dirección IP.
Verificación
Los procedimientos de verificación y prueba están disponibles en los ejemplos de configuración.
Troubleshoot
En esta sección encontrará información que puede utilizar para solucionar problemas de configuración.
strongSwan CA Multiple CERT_REQ
Cuando la configuración del certificado en strongSwan es Selección automática (el valor predeterminado), Android envía CERT_REQ para todos los certificados de confianza en el almacén local en el tercer paquete . El software Cisco IOS podría descartar la solicitud porque reconoce un gran número de solicitudes de certificado como un ataque de denegación de servicio:
*Jul 15 07:54:13: IKEv2:number of cert req exceeds the reasonable limit (100)
Fuente de túnel en DVTI
Aunque es bastante común establecer el origen del túnel en una interfaz de túnel virtual (VTI), no es necesario aquí. Suponga que el comando tunnel source se encuentra bajo un VTI dinámico (DVTI):
interface Virtual-Template1 type tunnel
ip unnumbered GigabitEthernet0/0
tunnel source GigabitEthernet0/0
tunnel mode ipsec ipv4
tunnel protection ipsec profile PROF
Después de la autenticación, si el software Cisco IOS intenta crear una interfaz de acceso virtual clonada a partir de una plantilla virtual, devuelve un error:
*Aug 1 13:34:22 IKEv2:Allocated addr 192.168.0.9 from local pool POOL
*Aug 1 13:34:22 IKEv2:(SA ID = 1):Set received config mode data
*Aug 1 13:34:22 IKEv2:% DVTI create request sent for profile PROF with PSH
index 1
*Aug 1 13:34:22 IKEv2:Failed to process KMI delete SA message with error 4
*Aug 1 13:34:24 IKEv2:Got a packet from dispatcher
*Aug 1 13:34:24 IKEv2:Processing an item off the pak queue
*Aug 1 13:34:24 IKEv2:Negotiation context locked currently in use
Dos segundos después de la falla, el software Cisco IOS recibe una IKE_AUTH retransmitida de Android. Ese paquete se descarta.
Errores y solicitudes de mejora del software del IOS de Cisco
- Id. de error de Cisco CSCui46418, "Dirección IP Ikev2 de IOS enviada como identidad para la autenticación RSA".
Este bug no es un problema, siempre y cuando strongSwan pueda ver un Subject Alternative Name correcto (la dirección IP) cuando busque el IKEID en el certificado para realizar la verificación. - El Id. de error de Cisco CSCui44976, "PKI de IOS visualiza incorrectamente el nombre alternativo de asunto de la extensión X509v3".
Este error ocurre solamente cuando hay varias direcciones IP en el nombre alternativo del sujeto. Sólo se muestra la última dirección IP, pero eso no afecta al uso del certificado. El certificado completo se envía y se procesa correctamente. - Id. de error de Cisco CSCui44783, "Capacidad de PKI ENH de IOS para generar CSR con extensión de nombre alternativo de asunto".
- Id. de error de Cisco CSCui44335, "Se muestran las extensiones x509 del certificado ASA ENH".
Información Relacionada
Contacte a Cisco
- Abrir un caso de soporte

- (Requiere un Cisco Service Contract)
 Comentarios
Comentarios