PIX/ASA 7.x: Ejemplo de Configuración de Multicast en las Plataformas PIX/ASA con el Remitente en el Exterior
Contenido
Introducción
Este documento proporciona una configuración de ejemplo de multicast en Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) y/o PIX Security Appliance que ejecuta la versión 7.x. En este ejemplo, el remitente multicast se encuentra en el exterior del dispositivo de seguridad y los hosts del interior están intentando recibir el tráfico multicast. Los hosts envían informes IGMP para notificar la pertenencia al grupo, y el firewall utiliza el modo disperso del Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) como el protocolo de ruteo multicast dinámico al router ascendente, detrás del cual reside el origen del flujo.
Nota: FWSM/ASA no admite subred 232.x.x.x/8 como número de grupo, ya que está reservado para ASA SSM. Por lo tanto, FWSM/ASA no permite que esta subred se utilice o atraviese y no se crea mroute. Sin embargo, todavía puede pasar este tráfico multicast a través de ASA/FWSM si lo encapsula en el túnel GRE.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Un Cisco PIX o ASA Security Appliance que ejecuta la versión de software 7.0, 7.1 ó 7.2.
Componentes Utilizados
La información de este documento se basa en un Cisco PIX o Cisco ASA Firewall que ejecuta la versión 7.x.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Convenciones
Consulte Convenciones de Consejos Técnicos de Cisco para obtener más información sobre las convenciones sobre documentos.
Antecedentes
PIX/ASA 7.x introduce el modo disperso PIM completo y soporte bidireccional para el ruteo multicast dinámico a través del firewall. No se admite el modo denso PIM. El software 7.x aún soporta el 'modo stub' multicast heredado en el cual el firewall es simplemente un proxy IGMP entre interfaces como fue soportado en la versión 6.x de PIX.
Estas afirmaciones son verdaderas para el tráfico multicast a través del firewall:
-
Si se aplica una lista de acceso a la interfaz en la que se recibe el tráfico de multidifusión, la lista de control de acceso (ACL) debe permitir explícitamente el tráfico. Si no se aplica ninguna lista de acceso a la interfaz, la entrada ACL explícita que permite el tráfico multicast no es necesaria.
-
Los paquetes de datos multicast siempre están sujetos a la verificación Reverse Path Forwarding del firewall, independientemente de si el comando reverse-path forward check está configurado en la interfaz. Por lo tanto, si no hay ninguna ruta en la interfaz en la que se recibió el paquete al origen del paquete multicast, entonces el paquete se descarta.
-
Si no hay ninguna ruta en la interfaz de regreso al origen de los paquetes multicast, utilice el comando mroute para indicar al firewall que no descarte los paquetes.
Configurar
En esta sección encontrará la información para configurar las funciones descritas en este documento.
Nota: Utilice la herramienta Command Lookup (sólo para clientes registrados) para obtener más información sobre los comandos utilizados en esta sección.
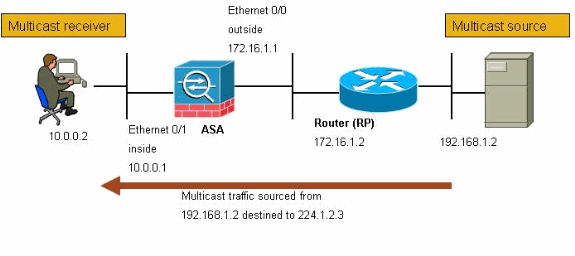
Diagrama de la red
Este documento utiliza esta configuración de red:
El tráfico multicast se origina desde 192.168.1.2 y utiliza paquetes UDP en el puerto 1234 destinado al grupo 224.1.2.3.
Configuración
Este documento usa esta configuración:
| Cisco PIX o ASA Firewall que ejecuta la versión 7.x |
|---|
maui-soho-01#show running-config SA Version 7.1(2) ! hostname ciscoasa enable password 8Ry2YjIyt7RRXU24 encrypted !--- The multicast-routing command enables IGMP and PIM !--- on all interfaces of the firewall. multicast-routing names ! interface Ethernet0/0 nameif outside security-level 0 ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0/1 nameif inside security-level 100 ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0/2 no nameif no security-level no ip address ! interface Ethernet0/3 shutdown no nameif no security-level no ip address ! interface Management0/0 shutdown no nameif no security-level no ip address ! passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted !--- The rendezvous point address must be defined in the !--- configuration in order for PIM to function correctly. pim rp-address 172.16.1.2 boot system disk0:/asa712-k8.bin ftp mode passive !--- It is necessary to permit the multicast traffic with an !--- access-list entry. access-list outside_access_inbound extended permit ip any host 224.1.2.3 pager lines 24 logging enable logging buffered debugging mtu outside 1500 mtu inside 1500 no failover !--- The access-list that permits the multicast traffic is applied !--- inbound on the outside interface. access-group outside_access_inbound in interface outside !--- This mroute entry specifies that the multicast sender !--- 192.168.1.2 is off the outside interface. In this example !--- the mroute entry is necessary since the firewall has no route to !--- the 192.168.1.2 host on the outside interface. Otherwise, this !--- entry is not necessary. mroute 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.255 outside icmp permit any outside asdm image disk0:/asdm521.bin no asdm history enable arp timeout 14400 timeout xlate 3:00:00 timeout conn 1:00:00 half-closed 0:10:00 udp 0:02:00 icmp 0:00:02 timeout sunrpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00 h225 1:00:00 mgcp 0:05:00 timeout mgcp-pat 0:05:00 sip 0:30:00 sip_media 0:02:00 timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute no snmp-server location no snmp-server contact snmp-server enable traps snmp authentication linkup linkdown coldstart telnet timeout 5 ssh timeout 5 console timeout 0 ! class-map inspection_default match default-inspection-traffic ! ! policy-map global_policy class inspection_default inspect ftp inspect h323 h225 inspect h323 ras inspect rsh inspect rtsp inspect esmtp inspect sqlnet inspect skinny inspect sunrpc inspect xdmcp inspect sip inspect netbios inspect tftp ! service-policy global_policy global ! end |
Verificación
Use esta sección para confirmar que su configuración funciona correctamente.
La herramienta Output Interpreter Tool (clientes registrados solamente) (OIT) soporta ciertos comandos show. Utilice la OIT para ver un análisis del resultado del comando show.
-
show mroute—Muestra la tabla de ruteo multicast IPv4.
ciscoasa#show mroute Multicast Routing Table Flags: D - Dense, S - Sparse, B - Bidir Group, s - SSM Group, C - Connected, L - Local, I - Received Source Specific Host Report, P - Pruned, R - RP-bit set, F - Register flag, T - SPT-bit set, J - Join SPT Timers: Uptime/Expires Interface state: Interface, State !--- Here you see the mroute entry for the shared tree. Notice that the !--- incoming interface specifies outside and that the outgoing interface !--- list specifies inside. (*, 224.1.2.3), 00:00:12/never, RP 172.16.1.2, flags: SCJ Incoming interface: outside RPF nbr: 172.16.1.2 Outgoing interface list: inside, Forward, 00:00:12/never !--- Here is the source specific tree for the mroute entry. (192.168.1.2, 224.1.2.3), 00:00:12/00:03:17, flags: SJ Incoming interface: outside RPF nbr: 0.0.0.0 Immediate Outgoing interface list: Null -
show conn: muestra el estado de conexión del tipo de conexión designado.
!--- A connection is built through the firewall for the multicast stream. !--- In this case the stream is sourced from the sender IP and destined !--- to the multicast group. ciscoasa#show conn 10 in use, 12 most used UDP out 192.168.1.2:51882 in 224.1.2.3:1234 idle 0:00:00 flags - ciscoasa#
-
show pim neighbor: muestra las entradas de la tabla de vecinos PIM.
!--- When you use PIM, the neighbor devices should be seen with the !--- show pim neighbor command. ciscoasa#show pim neighbor Neighbor Address Interface Uptime Expires DR pri Bidir 172.16.1.2 outside 04:06:37 00:01:27 1 (DR)
Troubleshoot
En esta sección encontrará información que puede utilizar para solucionar problemas de configuración.
Procedimiento de Troubleshooting
Siga estas instrucciones para resolver problemas de configuración.
La herramienta Output Interpreter Tool (clientes registrados solamente) (OIT) soporta ciertos comandos show. Utilice la OIT para ver un análisis del resultado del comando show.
Nota: Consulte Información Importante sobre Comandos Debug antes de utilizar los comandos debug.
-
Si los receptores multicast están conectados directamente al interior del firewall, envían informes IGMP para recibir el flujo multicast. Utilice el comando show igmp traffic para verificar que recibe informes IGMP desde el interior.
ciscoasa#show igmp traffic IGMP Traffic Counters Elapsed time since counters cleared: 04:11:08 Received Sent Valid IGMP Packets 413 244 Queries 128 244 Reports 159 0 Leaves 0 0 Mtrace packets 0 0 DVMRP packets 0 0 PIM packets 126 0 Errors: Malformed Packets 0 Martian source 0 Bad Checksums 0 ciscoasa# -
El firewall puede mostrar información más detallada sobre los datos IGMP mediante el comando debug igmp.
En este caso, las depuraciones se habilitan y el host 10.0.0.2 envía un informe IGMP para el grupo 224.1.2.3.
!--- Enable IGMP debugging. ciscoasa#debug igmp IGMP debugging is on ciscoasa# IGMP: Received v2 Report on inside from 10.0.0.2 for 224.1.2.3 IGMP: group_db: add new group 224.1.2.3 on inside IGMP: MRIB updated (*,224.1.2.3) : Success IGMP: Switching to EXCLUDE mode for 224.1.2.3 on inside IGMP: Updating EXCLUDE group timer for 224.1.2.3 ciscoasa# !--- Disable IGMP debugging ciscoasa#un all
-
Verifique que el firewall tenga vecinos PIM válidos y que el firewall envíe y reciba información de unión/separación.
ciscoasa#show pim neigh Neighbor Address Interface Uptime Expires DR pri Bidir 172.16.1.2 outside 04:26:58 00:01:20 1 (DR) ciscoasa#show pim traffic PIM Traffic Counters Elapsed time since counters cleared: 04:27:11 Received Sent Valid PIM Packets 543 1144 Hello 543 1079 Join-Prune 0 65 Register 0 0 Register Stop 0 0 Assert 0 0 Bidir DF Election 0 0 Errors: Malformed Packets 0 Bad Checksums 0 Send Errors 0 Packet Sent on Loopback Errors 0 Packets Received on PIM-disabled Interface 0 Packets Received with Unknown PIM Version 0 Packets Received with Incorrect Addressing 0 ciscoasa# -
Utilice el comando capture para verificar que la interfaz externa reciba los paquetes multicast para el grupo.
ciscoasa#configure terminal !--- Create an access-list that is only used !--- to flag the packets to capture. ciscoasa(config)#access-list captureacl permit ip any host 224.1.2.3 !--- Define the capture named capout, bind it to the outside interface, and !--- specify to only capture packets that match the access-list captureacl. ciscoasa(config)#capture capout interface outside access-list captureacl !--- Repeat for the inside interface. ciscoasa(config)#capture capin interface inside access-list captureacl !--- View the contents of the capture on the outside. This verifies that the !--- packets are seen on the outside interface ciscoasa(config)#show capture capout 138 packets captured 1: 02:38:07.639798 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 2: 02:38:07.696024 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 3: 02:38:07.752295 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 4: 02:38:07.808582 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 5: 02:38:07.864823 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 6: 02:38:07.921110 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 7: 02:38:07.977366 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 8: 02:38:08.033689 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 9: 02:38:08.089961 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 10: 02:38:08.146247 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 11: 02:38:08.202504 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 12: 02:38:08.258760 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 13: 02:38:08.315047 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 14: 02:38:08.371303 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 15: 02:38:08.427574 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 16: 02:38:08.483846 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 17: 02:38:08.540117 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 18: 02:38:08.596374 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 19: 02:38:08.652691 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 20: 02:38:08.708932 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 21: 02:38:08.765188 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 22: 02:38:08.821460 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 23: 02:38:08.877746 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 24: 02:38:08.934018 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 !--- Here you see the packets forwarded out the inside !--- interface towards the clients. ciscoasa(config)#show capture capin 89 packets captured 1: 02:38:12.873123 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 2: 02:38:12.929380 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 3: 02:38:12.985621 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 4: 02:38:13.041898 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 5: 02:38:13.098169 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 6: 02:38:13.154471 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 7: 02:38:13.210743 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 8: 02:38:13.266999 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 9: 02:38:13.323255 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 10: 02:38:13.379542 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 11: 02:38:13.435768 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 12: 02:38:13.492070 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 13: 02:38:13.548342 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 14: 02:38:13.604598 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 15: 02:38:13.660900 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 16: 02:38:13.717141 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 17: 02:38:13.773489 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 18: 02:38:13.829699 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 19: 02:38:13.885986 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 20: 02:38:13.942227 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 21: 02:38:13.998483 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 22: 02:38:14.054852 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 23: 02:38:14.111108 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 24: 02:38:14.167365 192.168.1.2.52292 > 224.1.2.3.1234: udp 1316 ciscoasa(config)# !--- Remove the capture from the memory of the firewall. ciscoasa(config)#no capture capout
Error de funcionamiento conocido
Id. de error de Cisco CSCse81633 (sólo clientes registrados): los puertos Gig ASA 4GE-SSM descartan silenciosamente las uniones IGMP.
-
Síntoma: cuando se instala un módulo 4GE-SSM en un ASA y se configura el ruteo multicast junto con el IGMP en las interfaces, las uniones IGMP se descartan en las interfaces del módulo 4GE-SSM.
-
Condiciones: las uniones IGMP no se descartan en las interfaces Gig integradas del ASA.
-
Solución alternativa: para el ruteo multicast, utilice los puertos de interfaz Gig integrados.
-
Fijado en versiones—7.0(6), 7.1(2)18, 7.2(1)11
Información Relacionada
Historial de revisiones
| Revisión | Fecha de publicación | Comentarios |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
26-Sep-2008 |
Versión inicial |
Contacte a Cisco
- Abrir un caso de soporte

- (Requiere un Cisco Service Contract)
 Comentarios
Comentarios