Configuración del Protocolo de tunelización de la capa 2 (L2TP) por IPSec.
Contenido
Introducción
Los protocolos de tunelización Layer 2, como L2TP, no proporcionan mecanismos de cifrado para el tráfico que tunelizan. En su lugar, se basan en otros protocolos de seguridad, como IPSec, para cifrar sus datos. Utilice esta configuración de ejemplo para cifrar el tráfico L2TP usando IPSec para los usuarios que marquen.
El túnel L2TP se establece entre el L2TP Access Concentrator (LAC) y el L2TP Network Server (LNS). También se establece un túnel IPSec entre estos dispositivos y todo el tráfico del túnel L2TP se cifra mediante IPSec.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Este documento requiere una comprensión básica del protocolo IPSec Si desea más información sobre IPSec, consulte Introducción al encripción de seguridad IP (IPSec).
Componentes Utilizados
La información que contiene este documento se basa en estas versiones de software y hardware.
-
Software Cisco IOS® versión 12.2(24a)
-
Cisco 2500 Series Routers
La información que se presenta en este documento se originó a partir de dispositivos dentro de un ambiente de laboratorio específico. Todos los dispositivos que se utilizan en este documento se pusieron en funcionamiento con una configuración verificada (predeterminada). Si la red está funcionando, asegúrese de haber comprendido el impacto que puede tener un comando antes de ejecutarlo.
Convenciones
Para obtener más información sobre las convenciones del documento, consulte Convenciones de Consejos Técnicos de Cisco.
Configurar
En esta sección encontrará la información para configurar las funciones descritas en este documento.
Nota: Para encontrar información adicional sobre los comandos utilizados en este documento, utilice la Command Lookup Tool (sólo para clientes registrados) .
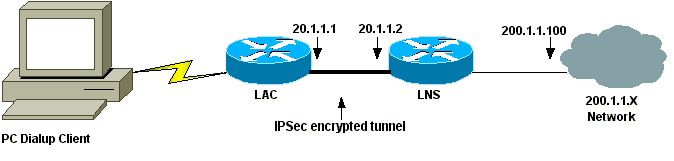
Diagrama de la red
Este documento utiliza la configuración de red que se muestra en el siguiente diagrama. El usuario de marcación manual inicia una sesión PPP con un LAC sobre el sistema de telefonía analógica. Después de autenticar al usuario, el LAC inicia un túnel L2TP al LNS. Los puntos finales del túnel, LAC y LNS, se autentican entre sí antes de crear el túnel. Una vez establecido el túnel, se crea una sesión L2TP para el usuario de marcación manual. Para cifrar todo el tráfico L2TP entre LAC y LNS, el tráfico L2TP se define como el tráfico interesante (el tráfico a cifrar) para IPSec.
Configuraciones
Este documento usa estas configuraciones.
| Configuración LAC |
|---|
Current configuration: ! version 12.2 service timestamps debug datetime msec localtime show-timezone service timestamps log datetime msec localtime show-timezone service password-encryption ! hostname LAC ! enable password 7 094F471A1A0A ! !--- Usernames and passwords are used !--- for L2TP tunnel authentication. username LAC password 7 0107130A550E0A1F205F5D username LNS password 7 001006080A5E07160E325F !--- Username and password used for authenticating !--- the dial up user. username dialupuser password 7 14131B0A00142B3837 ip subnet-zero ! !--- Enable VDPN. vpdn enable vpdn search-order domain ! !--- Configure vpdn group 1 to request dialin to the LNS, !--- define L2TP as the protocol, and initiate a tunnel to the LNS 20.1.1.2. !--- If the user belongs to the domain cisco.com, !--- use the local name LAC as the tunnel name. vpdn-group 1 request-dialin protocol l2tp domain cisco.com initiate-to ip 20.1.1.2 local name LAC ! !--- Create Internet Key Exchange (IKE) policy 1, !--- which is given highest priority if there are additional !--- IKE policies. Specify the policy using pre-shared key !--- for authentication, Diffie-Hellman group 2, lifetime !--- and peer address. crypto isakmp policy 1 authentication pre-share group 2 lifetime 3600 crypto isakmp key cisco address 20.1.1.2 ! !--- Create an IPSec transform set named "testtrans" !--- with the DES for ESP with transport mode. !--- Note: AH is not used. crypto ipsec transform-set testtrans esp-des ! !--- Create crypto map l2tpmap (assigned to Serial 0), using IKE for !--- Security Associations with map-number 10 !--- and using "testrans" transform-set as a template. !--- Set the peer and specify access list 101, which is used !--- to determine which traffic (L2TP) is to be protected by IPSec. crypto map l2tpmap 10 ipsec-isakmp set peer 20.1.1.2 set transform-set testtrans match address 101 ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 10.31.1.6 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast ! interface Serial0 ip address 20.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 no ip directed-broadcast no ip route-cache no ip mroute-cache no fair-queue !--- Assign crypto map l2tpmap to the interface. crypto map l2tpmap ! interface Async1 ip unnumbered Ethernet0 no ip directed-broadcast encapsulation ppp no ip route-cache no ip mroute-cache async mode dedicated peer default ip address pool my_pool ppp authentication chap ! !--- Create an IP Pool named "my_pool" and !--- specify the IP range. ip local pool my_pool 10.31.1.100 10.31.1.110 ip classless ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Serial0 !--- Specify L2TP traffic as interesting to use with IPSec. access-list 101 permit udp host 20.1.1.1 eq 1701 host 20.1.1.2 eq 1701 ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 transport input none line 1 autoselect during-login autoselect ppp modem InOut transport input all speed 38400 flowcontrol hardware line aux 0 line vty 0 4 password |
| Configuración de LNS |
|---|
Current configuration: ! version 12.2 service timestamps debug datetime msec localtime show-timezone service timestamps log datetime msec localtime show-timezone service password-encryption ! hostname LNS ! enable password 7 0822455D0A16 !--- Usernames and passwords are used for !--- L2TP tunnel authentication. username LAC password 7 0107130A550E0A1F205F5D username LNS password 7 120D10191C0E00142B3837 !--- Username and password used to authenticate !--- the dial up user. username dialupuser@cisco.com password 7 104A0018090713181F ! ip subnet-zero ! !--- Enable VDPN. vpdn enable ! !--- Configure VPDN group 1 to accept !--- an open tunnel request from LAC, !--- define L2TP as the protocol, and identify virtual-template 1 !--- to use for cloning virtual access interfaces. vpdn-group 1 accept-dialin protocol l2tp virtual-template 1 terminate-from hostname LAC local name LNS ! !--- Create IKE policy 1, which is !--- given the highest priority if there are additional IKE policies. !--- Specify the policy using the pre-shared key for authentication, !--- Diffie-Hellman group 2, lifetime and peer address. crypto isakmp policy 1 authentication pre-share group 2 lifetime 3600 crypto isakmp key cisco address 20.1.1.1 ! ! !--- Create an IPSec transform set named "testtrans" !--- using DES for ESP with transport mode. !--- Note: AH is not used. crypto ipsec transform-set testtrans esp-des ! !--- Create crypto map l2tpmap !--- (assigned to Serial 0), using IKE for !--- Security Associations with map-number 10 !--- and using "testrans" transform-set as a template. !--- Set the peer and specify access list 101, which is used !--- to determine which traffic (L2TP) is to be protected by IPSec. crypto map l2tpmap 10 ipsec-isakmp set peer 20.1.1.1 set transform-set testtrans match address 101 ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 200.1.1.100 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast no keepalive ! !--- Create a virtual-template interface !--- used for "cloning" !--- virtual-access interfaces using address pool "mypool" !--- with Challenge Authentication Protocol (CHAP) authentication. interface Virtual-Template1 ip unnumbered Ethernet0 no ip directed-broadcast no ip route-cache peer default ip address pool mypool ppp authentication chap ! interface Serial0 ip address 20.1.1.2 255.255.255.252 no ip directed-broadcast no ip route-cache no ip mroute-cache no fair-queue clockrate 1300000 !--- Assign crypto map l2tpmap to the interface. crypto map l2tpmap ! !--- Create an IP Pool named "mypool" and !--- specify the IP range. ip local pool mypool 200.1.1.1 200.1.1.10 ip classless ! !--- Specify L2TP traffic as interesting to use with IPSec. access-list 101 permit udp host 20.1.1.2 eq 1701 host 20.1.1.1 eq 1701 ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 transport input none line aux 0 line vty 0 4 password login ! end |
Verificación
En esta sección encontrará información que puede utilizar para confirmar que su configuración esté funcionando correctamente.
La herramienta Output Interpreter (sólo para clientes registrados) permite utilizar algunos comandos “show” y ver un análisis del resultado de estos comandos.
Utilice estos comandos show para verificar la configuración.
-
show crypto isakmp sa : muestra todas las asociaciones de seguridad actuales IKE (SA) en un par.
LAC#show crypto isakmp sa dst src state conn-id slot 20.1.1.2 20.1.1.1 QM_IDLE 1 0 LAC#
LAC#show crypto ipsec sa
interface: Serial0
Crypto map tag: l2tpmap, local addr. 20.1.1.1
local ident (addr/mask/prot/port): (20.1.1.1/255.255.255.255/0/0)
remote ident (addr/mask/prot/port): (20.1.1.2/255.255.255.255/0/0)
current_peer: 20.1.1.2
PERMIT, flags={transport_parent,}
#pkts encaps: 0, #pkts encrypt: 0, #pkts digest 0
#pkts decaps: 0, #pkts decrypt: 0, #pkts verify 0
#pkts compressed: 0, #pkts decompressed: 0
#pkts not compressed: 0, #pkts compr. failed: 0, #pkts decompress failed: 0
#send errors 0, #recv errors 0
local crypto endpt.: 20.1.1.1, remote crypto endpt.: 20.1.1.2
path mtu 1500, ip mtu 1500, ip mtu interface Serial0
current outbound spi: 0
inbound esp sas:
inbound ah sas:
inbound pcp sas:
outbound esp sas:
outbound ah sas:
outbound pcp sas:
local ident (addr/mask/prot/port): (20.1.1.1/255.255.255.255/17/1701)
remote ident (addr/mask/prot/port): (20.1.1.2/255.255.255.255/17/1701)
current_peer: 20.1.1.2
PERMIT, flags={origin_is_acl,reassembly_needed,parent_is_transport,}
#pkts encaps: 1803, #pkts encrypt: 1803, #pkts digest 0
#pkts decaps: 1762, #pkts decrypt: 1762, #pkts verify 0
#pkts compressed: 0, #pkts decompressed: 0
#pkts not compressed: 0, #pkts compr. failed: 0, #pkts decompress failed: 0
#send errors 5, #recv errors 0
local crypto endpt.: 20.1.1.1, remote crypto endpt.: 20.1.1.2
path mtu 1500, ip mtu 1500, ip mtu interface Serial0
current outbound spi: 43BE425B
inbound esp sas:
spi: 0xCB5483AD(3411313581)
transform: esp-des ,
in use settings ={Tunnel, }
slot: 0, conn id: 2000, flow_id: 1, crypto map: l2tpmap
sa timing: remaining key lifetime (k/sec): (4607760/1557)
IV size: 8 bytes
replay detection support: N
inbound ah sas:
inbound pcp sas:
outbound esp sas:
spi: 0x43BE425B(1136542299)
transform: esp-des ,
in use settings ={Tunnel, }
slot: 0, conn id: 2001, flow_id: 2, crypto map: l2tpmap
sa timing: remaining key lifetime (k/sec): (4607751/1557)
IV size: 8 bytes
replay detection support: N
outbound ah sas:
outbound pcp sas:
LAC#
LAC#show vpdn L2TP Tunnel and Session Information Total tunnels 1 sessions 1 LocID RemID Remote Name State Remote Address Port Sessions 26489 64014 LNS est 20.1.1.2 1701 1 LocID RemID TunID Intf Username State Last Chg Fastswitch 41 9 26489 As1 dialupuser@cisco.com est 00:12:21 enabled %No active L2F tunnels %No active PPTP tunnels %No active PPPoE tunnels LAC#
Troubleshoot
En esta sección encontrará información que puede utilizar para solucionar problemas de configuración.
Comandos para resolución de problemas
La herramienta Output Interpreter (sólo para clientes registrados) permite utilizar algunos comandos “show” y ver un análisis del resultado de estos comandos.
Nota: Antes de ejecutar los comandos debug, consulte Información Importante sobre Comandos Debug.
-
debug crypto ipsec—Muestra eventos de motor
-
debug crypto ipsec — Muestra eventos de IPSec.
-
debug crypto isakmp — Muestra mensajes acerca de eventos IKE.
-
debug ppp authentication: muestra mensajes del protocolo de autenticación, incluidos los intercambios de paquetes CHAP y los intercambios de protocolo de autenticación de contraseña (PAP).
-
debug vpdn event — Muestra mensajes relativos a eventos que forman parte del establecimiento o cierre normal del túnel.
-
debug vpdn error — Muestra errores que evitan que se establezca un túnel o errores que provocan que un túnel establecido se cierre.
-
debug ppp negotiation — Muestra los paquetes PPP transmitidos durante el inicio PPP, durante el cual se negocian las opciones PPP.
Información Relacionada
Historial de revisiones
| Revisión | Fecha de publicación | Comentarios |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
11-Dec-2001 |
Versión inicial |
Contacte a Cisco
- Abrir un caso de soporte

- (Requiere un Cisco Service Contract)
 Comentarios
Comentarios