Conexión troncal 802.1Q entre switches Catalyst que ejecutan CatOS y el software del sistema Cisco IOS
Contenido
Introducción
Este documento proporciona configuraciones de ejemplo para el enlace troncal IEEE 802.1Q entre switches Catalyst que ejecutan el software del sistema Catalyst OS (CatOS) y switches modulares de capa 3 (L3) que ejecutan el software del sistema Cisco IOS®. Los switches que ejecutan CatOS incluyen los Catalyst 4500/4000, 5500/5000 y 6500/6000 Series Switches. Los switches L3 modulares que ejecutan el software Cisco IOS incluyen los switches serie Catalyst 4500/4000 y Catalyst 6500/6000. Las configuraciones de ejemplo utilizan un Catalyst 4000 (CatOS) y un Catalyst 6500 (Cisco IOS Software), pero cualquiera de los switches mencionados podría haberse utilizado para lograr los mismos resultados.
Trunking es una forma de llevar el tráfico de varias VLAN a través de un link punto a punto entre dos dispositivos. Las dos formas de implementar los troncales Ethernet son:
-
Protocolo de link entre switches (ISL) (protocolo propietario de Cisco)
-
802.1q (norma IEEE)
Prerequisites
Requirements
Para conocer los requisitos del sistema, las pautas y las restricciones relacionadas con 802.1Q e ISL en switches Catalyst, consulte: Requisitos del sistema para implementar el enlace troncal
Componentes Utilizados
Para crear los ejemplos en este documento, se utilizaron estos switches:
-
Catalyst 4000 switch con Supervisor Engine II (WS-X4013) ejecutan el software CatOS versión 8.1.3
-
Catalyst 6509 con Supervisor Engine 2/Tarjeta de características de switch multicapa 2 (MSFC2) que ejecuta la versión 12.1(20)E2 del software Cisco IOS en Supervisor Engine y MSFC2
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Convenciones
Para obtener más información sobre las convenciones del documento, consulte Convenciones de Consejos Técnicos de Cisco.
Teoría Precedente
Este documento sólo incluye los archivos de configuración de los switches y los resultados de los comandos show de muestra relacionados. Para obtener detalles sobre cómo configurar un tronco 802.1Q entre switches Catalyst, consulte las páginas de soporte de productos LAN.
En la conexión troncal 802.1Q, todos los paquetes VLAN tienen etiquetas en el link troncal, salvo en la VLAN nativa. Los paquetes VLAN nativos se envían sin etiquetas en el link de troncal. En consecuencia, la VLAN original debe ser la misma en ambos switches configurados para conexión troncal. De esta manera, puede deducir a qué VLAN pertenece una trama cuando recibe una trama sin etiqueta. Por defecto, VLAN1 es la VLAN nativa de todos los switches.
-
En CatOS, la VLAN puede modificarse mediante el comando set vlan vlan-id mod/port, donde mod/port es el puerto troncal.
-
En el software Cisco IOS, se puede cambiar la VLAN nativa al ejecutar el comando switchport trunk native vlan vlan-id interface que está configurado en el puerto de troncal.
Configurar
En esta sección encontrará la información para configurar las funciones descritas en este documento.
Las configuraciones de este documento fueron implementadas en un entorno aislado de laboratorio. Asegúrese de comprender el posible efecto que tendrá cualquier configuración o comando sobre la red antes de usarlo. Se eliminaron las configuraciones de todos los dispositivos con los comandos clear config all y write erase para asegurar que tuvieran una configuración predeterminada.
Nota: Para encontrar información adicional sobre los comandos usados en este documento, utilice la Command Lookup Tool ![]() (sólo clientes registrados).
(sólo clientes registrados).
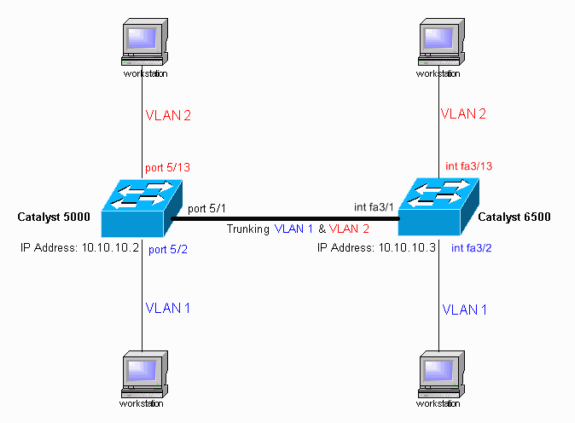
Diagrama de la red
En este documento, se utiliza esta configuración de red:
Configuraciones
En este documento, se utilizan estas configuraciones:
Nota: Los comentarios y las explicaciones se muestran en cursiva azul.
| Catalyst 4000 Switch |
|---|
#version 8.1(3) ! ! #system web interface version(s) ! #system set system name cat4000 ! #frame distribution method set port channel all distribution mac both ! #vtp set vtp domain cisco !--- In this example, the VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) domain name is the same !--- on both sides. This is required for the autonegotiation of the trunk !--- by the Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP). set vtp mode client vlan !--- In this example, the VTP mode is set to client. !--- Set the VTP mode according to your network requirements. !--- For more details, refer to !--- Understanding and Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP). ! #ip set interface sc0 1 10.10.10.2/255.255.255.0 10.10.10.255 !--- This is the IP address used for management. !--- Output suppressed. ! #module 1 : 2-port 1000BaseX Supervisor ! #module 2 empty ! #module 3 empty ! #module 4 empty ! #module 5 : 48-port Inline Power Module set vlan 2 5/13-24 !--- Ports 5/13-24 have been assigned to VLAN 2. set trunk 5/1 desirable dot1q 1-1005,1025-4094 !--- The trunking mode is set to desirable mode, which means !--- the port automatically tries to form a trunk with a !--- neighboring port set to desirable, auto, or on mode. !--- For recommended trunk mode settings, refer to !--- the Dynamic Trunking Protocol section of !--- Best Practices for Catalyst 4500/4000, 5500/5000, and 6500/6000 Series Switches Running CatOS Configuration and Management. !--- Output suppressed. set spantree portfast 5/2-24 enable set port channel 5/2-24 mode off !--- The macro command set port host 5/2-24 was used to do three things: !--- disable trunking, disable port channeling, and enable spantree portfast. !--- For details on using the set port host command, refer to !--- Using Portfast and Other Commands to Fix Workstation Startup Connectivity Delays. ! #module 6 empty end |
| Catalyst 6500 Switch |
|---|
Current configuration : 4408 bytes ! version 12.1 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! hostname cat6500 ! boot system flash sup-bootflash:c6sup22-jsv-mz.121-20.E2 enable password mysecret !--- This is the privileged mode password used in the example. ! ip subnet-zero ! ! ! mls flow ip destination mls flow ipx destination ! redundancy mode rpr-plus main-cpu auto-sync running-config auto-sync standard ! ! ! interface GigabitEthernet2/1 no ip address shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet2/2 no ip address shutdown ! interface fastethernet3/1 switchport !--- The switchport command must be entered once, !--- without any keywords, to configure the interface as a Layer 2 port. !--- The interface is now automatically configured with the default command !--- switchport mode dynamic desirable. !--- This means the interface is ready to autonegotiate trunking !--- encapsulation and form a trunk link (using DTP) with a neighbor port !--- in desirable, auto, or on mode. !--- For recommended trunk mode settings, refer to !--- the "Dynamic Trunking Protocol" section of !--- Best Practices for Catalyst 6500/6000 Series and Catalyst 4500/4000 Series Switches Running Cisco IOS Software. ! interface FastEthernet3/2 switchport switchport mode access spanning-tree portfast !--- The interface range fastethernet mod/beginport - endport !--- command is used to configure interfaces 3/2 - 24 at once. !--- Next, the switchport command is issued (if this has not been done already). switchport mode access spanning-tree portfast !--- Next, issue the macro command switchport host 3/2 - 24 to automatically !--- configure these ports as access ports and to enable spantree portfast. !--- For details on using the switchport host command, refer to !--- Using Portfast and Other Commands to Fix Workstation Startup Connectivity Delays. ! interface FastEthernet3/13 switchport switchport access vlan 2 !--- Interfaces 3/13 - 24 are placed in VLAN 2 !--- using the switchport access vlan 2 command. switchport mode access spanning-tree portfast !--- Output suppressed. ! interface FastEthernet3/24 shutdown switchport switchport access vlan 2 switchport mode access spanning-tree portfast !--- Output suppressed. ! interface FastEthernet3/48 no ip address shutdown ! interface vlan 1 ip address 10.10.10.3 255.255.255.0 !--- This is the IP address used for management. ! ip classless no ip http server ! ! ! line con 0 line vty 0 4 password mysecret !--- This is the Telnet password used in the example. login transport input lat pad mop telnet rlogin udptn nasi ! ! end cat6500# |
Verificación
En esta sección encontrará información que puede utilizar para confirmar que su configuración esté funcionando correctamente.
Comandos show
Ciertos comandos show son soportados por la herramienta Output Interpreter ![]() (sólo para clientes registrados), que le permite ver un análisis del resultado del comando show.
(sólo para clientes registrados), que le permite ver un análisis del resultado del comando show.
En switches Catalyst que ejecutan CatOS, use estos comandos:
-
show port capabilities module/port
-
show port module/port
-
show trunk module/port
-
show vtp domain
Utilice los siguientes comandos en los switches Catalyst 6000 que ejecutan el software del IOS de Cisco:
-
show interfaces interface-type module/port trunk
-
show vlan
Ejemplo de Resultado del Comando show
Catalyst 4000 Switch
El comando show port capabilities módulo/puerto se usa para verificar si el puerto puede realizar la conexión troncal.
cat4000> (enable) show port capabilities 5/1 Model WS-X4148-RJ45V Port 5/1 Type 10/100BaseTX Speed auto,10,100 Duplex half,full Trunk encap type 802.1Q Trunk mode on,off,desirable,auto,nonegotiate Channel 5/1-48 Flow control no Security yes Dot1x yes Membership static,dynamic Fast start yes QOS scheduling rx-(none),tx-(2q1t) CoS rewrite no ToS rewrite no Rewrite no UDLD yes Inline power auto,off,static AuxiliaryVlan 1..1000,1025..4094,untagged,none SPAN source,destination,reflector Link debounce timer yes IGMPFilter yes Dot1q-all-tagged no cat4000> (enable)
El comando show port module/port muestra el estado de un puerto determinado y si está realizando conexiones troncales o no.
cat4000> (enable) show port status 5/1 Port Name Status Vlan Level Duplex Speed Type ----- ------------------ ---------- ---------- ------ ------ ----- ------------ 5/1 connected trunk normal a-full a-100 10/100BaseTX cat4000> (enable)
El comando show trunk se usa para verificar el estado y la configuración del enlace troncal.
cat4000> (enable) show trunk * - indicates vtp domain mismatch # - indicates dot1q-all-tagged enabled on the port Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan -------- ----------- ------------- ------------ ----------- 5/1 desirable dot1q trunking 1 Port Vlans allowed on trunk -------- --------------------------------------------------------------------- 5/1 1-1005,1025-4094 Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain -------- --------------------------------------------------------------------- 5/1 1-2 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned -------- --------------------------------------------------------------------- 5/1 1-2 cat4000> (enable)
El comando show vtp domain se utiliza para verificar la información de VTP.
cat4000> (enable) show vtp domain Version : running VTP1 (VTP3 capable) Domain Name : cisco Password : not configured Notifications: disabled Updater ID: 10.10.10.3 Feature Mode Revision -------------- -------------- ----------- VLAN Client 21 Pruning : disabled VLANs prune eligible: 2-1000
Catalyst 6500 Switch
El comando show interfaces interface-type module/port trunk indica si el puerto está realizando una conexión troncal.
cat6500# show interfaces fastethernet 3/1 trunk Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Fa3/1 desirable n-802.1q trunking 1 Port Vlans allowed on trunk Fa3/1 1-4094 Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain Fa3/1 1-2 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Fa3/1 1-2 cat6500#
El comando show vlan brinda información sobre las VLAN y los puertos que pertenecen a una VLAN determinada.
cat6500# show vlan
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
1 default active Fa3/2, Fa3/3, Fa3/4, Fa3/5
Fa3/6, Fa3/7, Fa3/8, Fa3/9
Fa3/10, Fa3/11, Fa3/12
2 VLAN0002 active Fa3/13, Fa3/14, Fa3/15, Fa3/16
Fa3/17, Fa3/18, Fa3/19, Fa3/20
Fa3/21, Fa3/22, Fa3/23, Fa3/24
1002 fddi-default act/unsup
1003 token-ring-default act/unsup
1004 fddinet-default act/unsup
1005 trnet-default act/unsup
!--- Output suppressed.
cat6500#
Nota: Sólo se muestran los puertos configurados como puertos no troncales de Capa 2.
Troubleshoot
Actualmente, no hay información específica de troubleshooting disponible para esta configuración.
Información Relacionada
Contacte a Cisco
- Abrir un caso de soporte

- (Requiere un Cisco Service Contract)
 Comentarios
Comentarios