Ejemplo de configuración de uso de OSPFv3
Opciones de descarga
Lenguaje no discriminatorio
El conjunto de documentos para este producto aspira al uso de un lenguaje no discriminatorio. A los fines de esta documentación, "no discriminatorio" se refiere al lenguaje que no implica discriminación por motivos de edad, discapacidad, género, identidad de raza, identidad étnica, orientación sexual, nivel socioeconómico e interseccionalidad. Puede haber excepciones en la documentación debido al lenguaje que se encuentra ya en las interfaces de usuario del software del producto, el lenguaje utilizado en función de la documentación de la RFP o el lenguaje utilizado por un producto de terceros al que se hace referencia. Obtenga más información sobre cómo Cisco utiliza el lenguaje inclusivo.
Acerca de esta traducción
Cisco ha traducido este documento combinando la traducción automática y los recursos humanos a fin de ofrecer a nuestros usuarios en todo el mundo contenido en su propio idioma. Tenga en cuenta que incluso la mejor traducción automática podría no ser tan precisa como la proporcionada por un traductor profesional. Cisco Systems, Inc. no asume ninguna responsabilidad por la precisión de estas traducciones y recomienda remitirse siempre al documento original escrito en inglés (insertar vínculo URL).
Introducción
En este documento se describe cómo habilitar Abrir primero la ruta más corta (OSPF), versión 3, para IPv6 en una interfaz.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Antes de habilitar OSPF para IPv6 en una interfaz, debe:
-
Complete la estrategia y la planificación de la red OSPF para su red IPv6. Por ejemplo, decida si son necesarias varias áreas.
-
Habilite el routing IPv6 de unidifusión.
-
Habilite IPv6 en la interfaz.
-
Configure la interfaz de programa de aplicación de socket seguro (IP) de seguridad IP (IPsec) en OSPF para IPv6 para habilitar la autenticación y el cifrado.
Componentes Utilizados
Este documento no tiene restricciones específicas en cuanto a versiones de software y de hardware.
La información que contiene este documento se creó a partir de los dispositivos en un ambiente de laboratorio específico. Todos los dispositivos que se utilizan en este documento se pusieron en funcionamiento con una configuración verificada (predeterminada). Si tiene una red en vivo, asegúrese de entender el posible impacto de cualquier comando.
Convenciones
Antecedentes
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) es un protocolo de ruteo para IP. Es un protocolo de estado de enlace, a diferencia de un protocolo de vector de distancia.
Un protocolo de estado de enlace toma decisiones de routing según los estados de los enlaces que conectan las máquinas de origen y de destino.
El estado de un link es una descripción de esa interfaz y la relación con sus dispositivos de red vecinos.
La información de la interfaz incluye el prefijo IPv6 de la interfaz, la máscara de red, el tipo de red a la que se conecta, los routers conectados a esa red, y así sucesivamente.
Esta información se propaga en varios tipos de anuncios de estado de link (LSA). OSPF versión 3, que se describe en RFC 2740, admite IPv6.
Configurar
En esta sección encontrará la información para configurar las funciones descritas en este documento.
Nota: Utilice Command Lookup Tool /a> para obtener más información sobre los comandos utilizados en este documento.
Nota: Solo los usuarios registrados de Cisco tienen acceso a la información y las herramientas internas de Cisco.
Diagrama de la red
En este documento, se utiliza esta configuración de red:
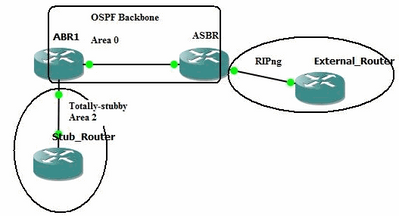 Diagrama de la red
Diagrama de la red
Configuración
Esta es la configuración de OSPFv3 para los routers que se muestran en el diagrama:
| Router de conexión única |
|---|
ipv6 unicast-routing ipv6 cef ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 no ip address ipv6 address FD01:ABAB::/64 eui-64 |
| Router ABR1 |
|---|
ipv6 unicast-routing ipv6 cef ! interface GigabitEthernet1 no ip address speed auto ipv6 address FD03::1/124 ipv6 enable ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 ! interface GigabitEthernet2 no ip address ipv6 address FD02:ABAB::/64 eui-64 ipv6 enable ipv6 ospf 1 area 2 |
| Router ASBR |
|---|
ipv6 unicast-routing ipv6 cef ! interface GigabitEthernet1 no ip address ipv6 address FD03::2/124 ipv6 enable ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 ! interface GigabitEthernet2 no ip address ipv6 address FD03::1:1/124 ipv6 enable ipv6 rip EXT enable ! ipv6 router ospf 1 router-id 10.2.2.2 default-metric 25 redistribute rip EXT metric-type 1 include-connected ! ipv6 router rip EXT redistribute ospf 1 match internal external 1 external 2 include-connected ! |
| Router externo |
|---|
ipv6 unicast-routing |
Verificación
Use esta sección para confirmar que su configuración funciona correctamente.
La herramienta Output Interpreter Tool soporta ciertos comandos show. Utilice la OIT para ver un análisis del resultado del comando show.
El comando show ipv6 ospf database muestra la base de datos de estado de enlace (LSDB) del router.
Nota: solo los usuarios registrados de Cisco pueden acceder a la información y las herramientas internas de Cisco.
Stub_Router#show ipv6 ospf database OSPFv3 Router with ID (10.3.3.3) (Process ID 1) Router Link States (Area 2) ADV Router Age Seq# Fragment ID Link count Bits 10.1.1.1 5 0x8000000F 0 1 B 10.3.3.3 38 0x8000000E 0 1 None Inter Area Prefix Link States (Area 2) ADV Router Age Seq# Prefix 10.1.1.1 5 0x80000002 ::/0 Link (Type-8) Link States (Area 2) ADV Router Age Seq# Link ID Interface 10.1.1.1 5 0x8000000A 8 Gi0/0 10.3.3.3 292 0x80000005 2 Gi0/0 Intra Area Prefix Link States (Area 2) ADV Router Age Seq# Link ID Ref-lstype Ref-LSID 10.1.1.1 5 0x8000000B 0 0x2001 0 10.3.3.3 548 0x80000002 0 0x2001 0
El comando show ipv6 ospf database router muestra los LSA del router donde el router se origina y recibe. Los LSA del router no llevan información de dirección o prefijo.
Stub_Router#show ipv6 ospf database router OSPFv3 Router with ID (10.3.3.3) (Process ID 1) Router Link States (Area 2) Routing Bit Set on this LSA LS age: 141 Options: (V6-Bit, R-Bit, DC-Bit) LS Type: Router Links Link State ID: 0 Advertising Router: 10.1.1.1 LS Seq Number: 8000000F Checksum: 0x9C2C Length: 40 Area Border Router Number of Links: 1 Link connected to: another Router (point-to-point) Link Metric: 1 Local Interface ID: 8 Neighbor Interface ID: 2 Neighbor Router ID: 10.3.3.3 LS age: 174 Options: (V6-Bit, R-Bit, DC-Bit) LS Type: Router Links Link State ID: 0 Advertising Router: 10.3.3.3 LS Seq Number: 8000000E Checksum: 0xBBF Length: 40 Number of Links: 1 Link connected to: another Router (point-to-point) Link Metric: 1 Local Interface ID: 2 Neighbor Interface ID: 8 Neighbor Router ID: 10.1.1.1
Los LSA llevan un campo Opciones que tiene estos bits:
-
Bit V6: indica si el router/link se debe utilizar en el cálculo de ruteo.
-
Bit R: este es el "bit del router". Indica si el originador es un router activo.
-
Bit DC: indica el manejo del router del circuito de demanda.
El comando show ipv6 ospf database link self-originate muestra que los LSA de enlace llevan direcciones específicas de enlace.
Stub_Router#show ipv6 ospf database link self-originate OSPFv3 Router with ID (10.3.3.3) (Process ID 1) Link (Type-8) Link States (Area 2) LS age: 650 Options: (V6-Bit, R-Bit, DC-Bit) LS Type: Link-LSA (Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0) Link State ID: 2 (Interface ID) Advertising Router: 10.3.3.3 LS Seq Number: 80000005 Checksum: 0x8578 Length: 56 Router Priority: 1 Link Local Address: FE80::5054:FF:FE00:3A Number of Prefixes: 1 Prefix Address: FD01:ABAB:: Prefix Length: 64, Options: None
Dado que el router de rutas internas pertenece a un área de rutas internas totales, el router ABR1 envía solo la ruta predeterminada al router de rutas internas.
Stub_Router#show ipv6 route IPv6 Routing Table - default - 5 entries Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, U - Per-user Static route B - BGP, HA - Home Agent, MR - Mobile Router, R - RIP H - NHRP, I1 - ISIS L1, I2 - ISIS L2, IA - ISIS interarea IS - ISIS summary, D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, NM - NEMO ND - ND Default, NDp - ND Prefix, DCE - Destination, NDr - Redirect RL - RPL, O - OSPF Intra, OI - OSPF Inter, OE1 - OSPF ext 1 OE2 - OSPF ext 2, ON1 - OSPF NSSA ext 1, ON2 - OSPF NSSA ext 2 la - LISP alt, lr - LISP site-registrations, ld - LISP dyn-eid lA - LISP away, a - Application OI ::/0 [110/2] via FE80::5054:FF:FE00:15, GigabitEthernet0/0 C FD01:ABAB::/64 [0/0] via GigabitEthernet0/0, directly connected L FD01:ABAB::5054:FF:FE00:3A/128 [0/0] via GigabitEthernet0/0, receive O FD02:ABAB::/64 [110/2] via FE80::5054:FF:FE00:15, GigabitEthernet0/0 L FF00::/8 [0/0] via Null0, receive
El router ABR1 es el router de borde de área.
ABR1#show ipv6 ospf Routing Process "ospfv3 1" with ID 10.1.1.1 Supports NSSA (compatible with RFC 3101) Supports Database Exchange Summary List Optimization (RFC 5243) Event-log enabled, Maximum number of events: 1000, Mode: cyclic It is an area border router Router is not originating router-LSAs with maximum metric Initial SPF schedule delay 50 msecs Minimum hold time between two consecutive SPFs 200 msecs Maximum wait time between two consecutive SPFs 5000 msecs Initial LSA throttle delay 50 msecs Minimum hold time for LSA throttle 200 msecs Maximum wait time for LSA throttle 5000 msecs Minimum LSA arrival 100 msecs LSA group pacing timer 240 secs Interface flood pacing timer 33 msecs Retransmission pacing timer 66 msecs Retransmission limit dc 24 non-dc 24 EXCHANGE/LOADING adjacency limit: initial 300, process maximum 300 Number of external LSA 2. Checksum Sum 0x011699 Number of areas in this router is 2. 1 normal 1 stub 0 nssa Graceful restart helper support enabled Reference bandwidth unit is 100 mbps RFC1583 compatibility enabled Area BACKBONE(0) Number of interfaces in this area is 1 SPF algorithm executed 17 times Number of LSA 8. Checksum Sum 0x05579B Number of DCbitless LSA 0 Number of indication LSA 0 Number of DoNotAge LSA 0 Flood list length 0 Area 2 Number of interfaces in this area is 1 It is a stub area, no summary LSA in this area Generates stub default route with cost 1 SPF algorithm executed 20 times Number of LSA 7. Checksum Sum 0x0380EA Number of DCbitless LSA 0 Number of indication LSA 0 Number of DoNotAge LSA 0 Flood list length 0
El router ABR1 recibe rutas externas (rutas RIP) del router ASBR.
ABR1#show ipv6 route IPv6 Routing Table - default - 8 entries Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, U - Per-user Static route B - BGP, R - RIP, H - NHRP, I1 - ISIS L1 I2 - ISIS L2, IA - ISIS interarea, IS - ISIS summary, D - EIGRP EX - EIGRP external, ND - ND Default, NDp - ND Prefix, DCE - Destination NDr - Redirect, RL - RPL, O - OSPF Intra, OI - OSPF Inter OE1 - OSPF ext 1, OE2 - OSPF ext 2, ON1 - OSPF NSSA ext 1 ON2 - OSPF NSSA ext 2, la - LISP alt, lr - LISP site-registrations ld - LISP dyn-eid, lA - LISP away, le - LISP extranet-policy lp - LISP publications, a - Application, m - OMP O FD01:ABAB::/64 [110/2] via FE80::5054:FF:FE00:3A, GigabitEthernet2 C FD02:ABAB::/64 [0/0] via GigabitEthernet2, directly connected L FD02:ABAB::5054:FF:FE00:15/128 [0/0] via GigabitEthernet2, receive C FD03::/124 [0/0] via GigabitEthernet1, directly connected L FD03::1/128 [0/0] via GigabitEthernet1, receive OE1 FD03::1:0/124 [110/26] via FE80::5054:FF:FE00:3E, GigabitEthernet1 OE1 FD04:ABAB::/64 [110/26] via FE80::5054:FF:FE00:3E, GigabitEthernet1 L FF00::/8 [0/0] via Null0, receive
El router ASBR es el router de borde del sistema autónomo para la red. Está conectado a la red RIP a través de la interfaz serial 0/0.
ASBR#show ipv6 ospf Routing Process "ospfv3 1" with ID 10.2.2.2 Supports NSSA (compatible with RFC 3101) Supports Database Exchange Summary List Optimization (RFC 5243) Event-log enabled, Maximum number of events: 1000, Mode: cyclic It is an autonomous system boundary router Redistributing External Routes (with default metric 25) from, rip EXT with metric-type 1 include-connected Router is not originating router-LSAs with maximum metric Initial SPF schedule delay 50 msecs Minimum hold time between two consecutive SPFs 200 msecs Maximum wait time between two consecutive SPFs 5000 msecs Initial LSA throttle delay 50 msecs Minimum hold time for LSA throttle 200 msecs Maximum wait time for LSA throttle 5000 msecs Minimum LSA arrival 100 msecs LSA group pacing timer 240 secs Interface flood pacing timer 33 msecs Retransmission pacing timer 66 msecs Retransmission limit dc 24 non-dc 24 EXCHANGE/LOADING adjacency limit: initial 300, process maximum 300 Number of external LSA 2. Checksum Sum 0x011699 Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa Graceful restart helper support enabled Reference bandwidth unit is 100 mbps RFC1583 compatibility enabled Area BACKBONE(0) Number of interfaces in this area is 1 SPF algorithm executed 10 times Number of LSA 8. Checksum Sum 0x05579B Number of DCbitless LSA 0 Number of indication LSA 0 Number of DoNotAge LSA 0 Flood list length 0ASBR#show ipv6 rip RIP process "EXT", port 521, multicast-group FF02::9, pid 678 Administrative distance is 120. Maximum paths is 16 Updates every 30 seconds, expire after 180 Holddown lasts 0 seconds, garbage collect after 120 Split horizon is on; poison reverse is off Default routes are not generated Periodic updates 267, trigger updates 11 Full Advertisement 1, Delayed Events 0 Interfaces: GigabitEthernet2 Redistribution: Redistributing protocol ospf 1 with transparent metric (internal, external 1 & 2, ) include-connected
Troubleshoot
Use esta sección para resolver problemas de configuración.
Nota: Consulte Información Importante sobre Comandos de Debug antes de usar un comando debug.
debug ipv6
En cuanto OSPFv3 se habilita en el router de rutas internas, envía mensajes de saludo de tipo 1 de OSPFv3 a la dirección de multidifusión FF02 :: 5. Una vez que recibe los paquetes Hello del router ABR1, negocian la relación Primario/Secundario y luego comienzan a enviar paquetes DBD.
Stub_Router#debug ipv6 ospf events Stub_Router#debug ipv6 ospf packet
Stub_Router#debug ipv6 ospf adj*Mar 8 17:47:01.324: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 PAK : Gi0/0: OUT: FE80::5054:FF:FE00:3A->FF02::5: ver:3 type:1 len:36 rid:10.3.3.3 area:0.0.0.2 chksum:A0F9 inst:0 *Mar 8 17:47:03.307: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 PAK : Gi0/0: IN: FE80::5054:FF:FE00:15->FF02::5: ver:3 type:1 len:36 rid:10.1.1.1 area:0.0.0.2 chksum:A31C inst:0 *Mar 8 17:47:03.308: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 ADJ Gi0/0: Added 10.1.1.1 to nbr list *Mar 8 17:47:03.308: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 PAK : Gi0/0: OUT: FE80::5054:FF:FE00:3A->FE80::5054:FF:FE00:15: ver:3 type:1 len:40 rid:10.3.3.3 area:0.0.0.2 chksum:470D inst:0 *Mar 8 17:47:03.320: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 PAK : Gi0/0: IN: FE80::5054:FF:FE00:15->FE80::5054:FF:FE00:3A: ver:3 type:1 len:40 rid:10.1.1.1 area:0.0.0.2 chksum:4707 inst:0 *Mar 8 17:47:03.321: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 ADJ Gi0/0: 2 Way Communication to 10.1.1.1, state 2WAY *Mar 8 17:47:03.321: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 ADJ Gi0/0: Nbr 10.1.1.1: Prepare dbase exchange *Mar 8 17:47:03.322: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 ADJ Gi0/0: Send DBD to 10.1.1.1 seq 0x983C9C0 opt 0x11 flag 0x7 len 28 *Mar 8 17:47:03.322: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 PAK : Gi0/0: OUT: FE80::5054:FF:FE00:3A->FE80::5054:FF:FE00:15: ver:3 type:2 len:28 rid:10.3.3.3 area:0.0.0.2 chksum:7A33 inst:0 *Mar 8 17:47:03.328: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 PAK : Gi0/0: IN: FE80::5054:FF:FE00:15->FE80::5054:FF:FE00:3A: ver:3 type:2 len:148 rid:10.1.1.1 area:0.0.0.2 chksum:141A inst:0 *Mar 8 17:47:03.329: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 ADJ Gi0/0: Rcv DBD from 10.1.1.1 seq 0x983C9C0 opt 0x11 flag 0x2 len 148 mtu 1500 state EXSTART *Mar 8 17:47:03.330: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 ADJ Gi0/0: NBR Negotiation Done. We are the MASTER *Mar 8 17:47:03.330: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 ADJ Gi0/0: Nbr 10.1.1.1: Summary list built, size 7 *Mar 8 17:47:03.331: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 ADJ Gi0/0: Send DBD to 10.1.1.1 seq 0x983C9C1 opt 0x11 flag 0x1 len 128 *Mar 8 17:47:03.331: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 PAK : Gi0/0: OUT: FE80::5054:FF:FE00:3A->FE80::5054:FF:FE00:15: ver:3 type:2 len:128 rid:10.3.3.3 area:0.0.0.2 chksum:F771 inst:0 *Mar 8 17:47:03.334: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 PAK : Gi0/0: IN: FE80::5054:FF:FE00:15->FE80::5054:FF:FE00:3A: ver:3 type:3 len:64 rid:10.1.1.1 area:0.0.0.2 chksum:C6FA inst:0 *Mar 8 17:47:03.335: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 PAK : Gi0/0: IN: FE80::5054:FF:FE00:15->FE80::5054:FF:FE00:3A: ver:3 type:2 len:28 rid:10.1.1.1 area:0.0.0.2 chksum:7C3D inst:0
Una vez que se intercambian los paquetes DBD, los routers envían mensajes de solicitud de estado de enlace (LS REQ) y de actualización de estado de enlace (LS UPD) para crear su LSDB. Después de mensajes de LS REQ y LS UPD sucesivos, y cuando el estado llega a FULL, los routers continúan intercambiando paquetes de saludo.
Stub_Router#*Mar 8 17:47:03.337: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 ADJ Gi0/0: Rcv LS REQ from 10.1.1.1 length 64 LSA count 4 *Mar 8 17:47:03.337: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 ADJ Gi0/0: Send LS UPD to FE80::5054:FF:FE00:15 length 172 LSA count 4 *Mar 8 17:47:03.338: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 PAK : Gi0/0: OUT: FE80::5054:FF:FE00:3A->FE80::5054:FF:FE00:15: ver:3 type:4 len:172 rid:10.3.3.3 area:0.0.0.2 chksum:D2CE inst:0 *Mar 8 17:47:03.339: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 ADJ Gi0/0: Rcv DBD from 10.1.1.1 seq 0x983C9C1 opt 0x11 flag 0x0 len 28 mtu 1500 state EXCHANGE *Mar 8 17:47:03.339: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 ADJ Gi0/0: Exchange Done with 10.1.1.1*Mar 8 17:47:03.340: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 ADJ Gi0/0: Send LS REQ to 10.1.1.1 length 40 *Mar 8 17:47:03.340: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 PAK : Gi0/0: OUT: FE80::5054:FF:FE00:3A->FE80::5054:FF:FE00:15: ver:3 type:3 len:40 rid:10.3.3.3 area:0.0.0.2 chksum:FD46 inst:0 *Mar 8 17:47:03.343: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 PAK : Gi0/0: IN: FE80::5054:FF:FE00:15->FE80::5054:FF:FE00:3A: ver:3 type:4 len:72 rid:10.1.1.1 area:0.0.0.2 chksum:825E inst:0 *Mar 8 17:47:03.345: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 ADJ Gi0/0: Rcv LS UPD from Nbr ID 10.1.1.1 length 72 LSA count 2 *Mar 8 17:47:03.345: OSPFv3-1-IPv6 ADJ Gi0/0: Synchronized with 10.1.1.1, state FULL *Mar 8 17:47:03.346: %OSPFv3-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 10.1.1.1 on GigabitEthernet0/0 from LOADING to FULL, Loading Done
Información Relacionada
Historial de revisiones
| Revisión | Fecha de publicación | Comentarios |
|---|---|---|
3.0 |
09-Mar-2023 |
Se reemplazó todo el código de salida. Recertificación. |
1.0 |
10-Aug-2010 |
Versión inicial |
Con la colaboración de ingenieros de Cisco
- Julio JimenezCisco Project Manager
Contacte a Cisco
- Abrir un caso de soporte

- (Requiere un Cisco Service Contract)
 Comentarios
Comentarios