New and Changed Information
The following table provides an overview of the significant changes to this document.
|
Cisco NDB Release Version |
Feature |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
3.10 |
ERSPAN Termination from Production Switches. |
This document has details of how to implement ERSPAN termination for traffic from production switches. |
ERSPAN Termination
Encapsulated Remote SPAN (ERSPAN) transports mirrored traffic over an IP network and provides remote monitoring of multiple switches across the network. The traffic is encapsulated at the source device and is transferred across the network and decapsulated at the destination device and then sent to the destination interface. ERSPAN is a Cisco proprietary tunnelling protocol and used with generic routing encapsulation (GRE) .
ERSPAN brings GRE for all the packets and allows it to travel across layer 3 networks/domains. To transport data from one network to another network safely this encapsulation mechanism is widely used. In the NDB framework, ERPSAN termination is typically used for remote packets travelling from production switch(es) across multiple networks, reaching the NDB network.
|
Nexus Switches |
NDB Version |
NX-OS Version |
|---|---|---|
|
9300-EX, 9300-FX, 9300-FX2 and 9500 EoR chassis with -EX and -FX line cards |
3.8 and later |
9.3(1) and later |
|
9300-GX |
3.10 and later |
9.3(5) and later |
Guidelines and Limitations
Guidelines and Limitations for ERSPAN termination:
-
For proper tunnel terminations, ensure ERSPAN IDs and version (in some cases) should match on both ERSPAN source and destination sessions.
-
There should be a physical loopback port (physical recirculation on front panel ports) connected between session destination interface & remote source edge span. For each active ERSPAN destination session, one pair of physical loopback ports should be available on the NDB switches.
-
A maximum of four active ERSPAN terminations are supported per NDB switch.
Topology for One ERSPAN Tunnel Termination
Ensure to advertise/install the route in the production switch and NDB switch via static/dynamic routing for proper tunnel termination.
ERSPAN production traffic terminated on remote source interface is handled by session destination to decapsulate. Decapsulated packets are given to Edge-Span/Tap port via physical loopback connection. Edge-Span/Tap port match the packets based on the filters and redirect to the respective Monitor Tool(s).


 Note |
Route should be advertised/installed in the production switch and NDB switch via static/dynamic routing for proper tunnel termination on the loopback interface IP. |
Topology for one ERSPAN tunnel termination.
-
Remote Source port (1/30) is the Layer3 interface on which the ERSPAN traffic is terminated from the production switch.
-
Session Destination port (1/1) is the port which decapsulates the ERSPAN header and egresses the traffic.
-
Edge-Span port (1/ 2) is the input port on which the inside packets are available for applying Tap Aggregation policy for filtering and redirection.
-
Monitoring Tool port (1/5) is the port though which the filtered egress traffic reaches the monitoring tool(s).
-
(applicable only for topology with loopback interface) ERSPAN source tunnel is destined to the Loopback IP address of the NDB switch but the tunnel is physically terminated on the Layer3 interface.
Topology for Multiple ERSPAN Tunnel Terminations
Ensure to advertise/install the route(s) in the production switch and NDB switch via static/dynamic routing for proper tunnel termination.
ERSPAN Production traffic terminated on Remote source interface is handled by session destination session to decapsulate. Decapsulated packets are given to Edge-Span/Tap port via physical loopback connection. Edge-Span/Tap port match the packets based on the filters and redirect the traffic to the respective Monitor Tool(s).

Multiple ERSPAN tunnels can be terminated, but all the ERSPAN source session packets should have a destination IP address as Remote Source Layer3 interface.
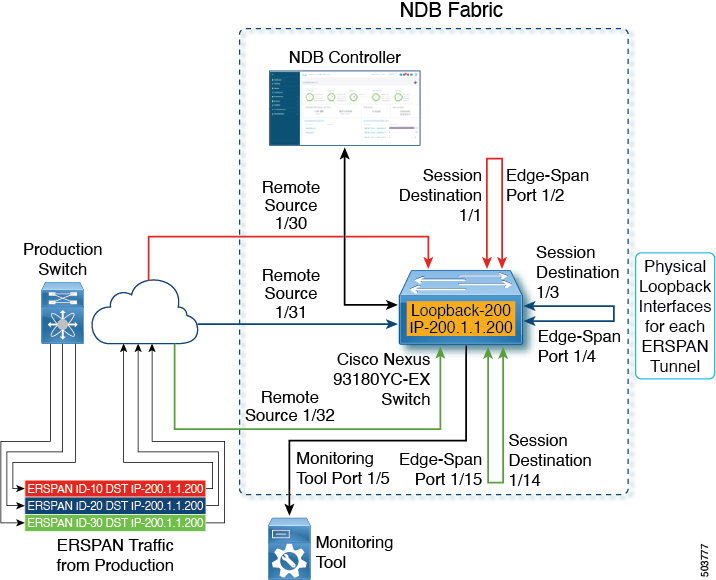
Multiple ERSPAN tunnels can be terminated but destined to the same Loopback Interface. Here, 3 ERSPAN source tunnels from production switch are terminated on 3 different layer3 NDB interfaces, but destined to a common loopback IP.
 Note |
Route should be advertised/installed in Production switch and NDB switch via Static/Dynamic routing for proper tunnel termination on the Loopback interface IP. |
The topology described below is for multiple ERSPAN tunnel terminations.
-
Physical loopback connection between Session Destination and Edge-Span port is per ERSPAN tunnel termination(s). In this case we have 3 ERSPAN tunnels terminated, so 3 physical loopback connections should be established (total 6 ports burnt for 3 ERSPAN tunnels).
-
Remote Source port(1/30) is the Layer3 interface on which the ERSPAN traffic is terminated from the production switch.
-
Session Destination ( 1/1, 1/3, 1/14) is the port which decapsulates the ERSPAN header and egresses the traffic.
-
Edge-Span Port (1/ 4, 1/15, 1/ 2) is the input port on which the inside packets are available for applying Tap Aggregation policy for filtering and redirection.
-
Monitoring Tool port (1/5) egresses the filtered traffic to respective monitoring tool(s).
-
(applicable only for topology with loopback interface) ERSPAN source tunnels are destined to the Loopback IP address of the NDB device but the tunnels are physically terminated on the Layer3 interfaces.
Workflow of Tasks
The following table lists the tasks for the workflow. Complete the tasks in the order as indicated in the table. For a detailed procedure, click the hyperlink of each procedure.
|
Procedure |
Description |
Result of the Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Creates a remote source interface, which is the input port for the NDB device. |
Run the show running-config command: Sample output for one ERSPAN tunnel (without loopback): |
|
|
Create a monitoring port, through which the traffic egresses to the monitoring tool. |
Run the show running-config command: Sample output for one ERSPAN tunnel (without loopback): |
|
|
Defines the connection between the input port and the monitoring tool port. |
Run the show access-lists command: Sample output for one ERSPAN tunnel (without loopback): |
Creating a Remote Source Interface
Use this procedure to create a remote source interface which is the input port for the NDB device.
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Navigate to Components > Input Ports > Actions > Add Input Port. The Add Input Port window is displayed. |
||
| Step 2 |
Select the Device and a Port on the device which is to be configured as the remote source. |
||
| Step 3 |
Select Remote Source Edge-SPAN from the Port Type drop-down list. Enter the following details:
|
||
| Step 4 |
Click Add Input Port. Repeat the above steps (Step 1 to Step 4) for terminating multiple ERSPAN tunnels. |
What to do next
Use the show running-config command to verify the configurations on the input port, session destination port, and remote source port.
Creating a Monitoring Port
Use this procedure to create a monitoring port, through which the traffic egresses to the monitoring tool.
This procedure is for terminating the ERSPAN tunnel on a front panel Layer 3 port or loopback interface, either for one tunnel or multiple tunnels.
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Navigate to Components > Monitoring Tools > Actions > Add Monitoring Tool. The Add Monitoring Tool window is displayed. |
| Step 2 |
Enter the Monitoring Tool Name. |
| Step 3 |
Select the Device and Port, that will be configured as the monitoring tool port. |
| Step 4 |
Add a Port Description. The other optional fields of the screen can be left as-is. |
| Step 5 |
Click Add Monitoring Tool. |
What to do next
Use the show running-config command, to verify the configuration of the monitoring tool port.
Creating a Connection
Use this procedure to create a connection using the default match-all filter.
This procedure is for terminating the ERSPAN tunnel on a front panel Layer 3 port or loopback interface, either for one tunnel or multiple tunnels.
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Navigate to Connections > Actions > Add Connection. The Add Connection window is displayed. |
| Step 2 |
Enter a Connection Name. The other optional fields of the screen can be left as-is. |
| Step 3 |
Under Connection Topology, select the Input Port, Filter and Monitoring Tool to establish the connection sequence using these parameters. |
| Step 4 |
Click Install Connection to add and deploy the connection on the NDB device. |
What to do next
Use the show access-lists command, to verify the connection details on the NDB device.
 Feedback
Feedback