New and Changed Information
The following table provides an overview of the significant changes up to this current release. The table does not provide an exhaustive list of all changes or of the new features up to this release.
|
Release Version |
Feature |
Description |
|
NDFC release 12.2.2 |
ePBR Support |
Beginning with NDFC release 12.2.2, support is available for enhanced policy-based redirect (ePBR), which is used for Layer 4 to Layer 7 service load balancing, and for single-site traffic steering and redirection. |
|
NDFC release 12.2.2 |
Updated workflow and terminology |
Beginning with NDFC release 12.2.2, the workflow for configuring Layer 4 to Layer 7 services has been enhanced. In addition, the following terms that were used in previous releases has been changed:
|
Layer 4 to Layer 7 Services Configuration
Cisco Nexus Dashboard Fabric Controller introduces the ability to insert Layer 4-Layer 7 (L4-L7) service devices in a data center fabric and to selectively redirect traffic to these L4-L7 service devices. You can add a L4-L7 service cluster, create service function between the L4-L7 service cluster and the L4-L7 service leaf switch, and then selectively redirect traffic to these L4-L7 service clusters.
Layer 4 to Layer 7 Services
To navigate to the Layer 4 to Layer 7 Services window:
-
Choose Manage > Fabrics.
-
Double-click on the appropriate Data Center VXLAN EVPN fabric to bring up the Fabric Overview window for that fabric.
-
Click the Services tab in that fabric.
You can also bring up the Services information specific to a switch by navigating to:
Manage > Inventory > Switches > Switches Overview > Services
NDFC release 12.2.2 provides a unified Layer 4 to Layer 7 services flow that includes the following use cases:
-
Redirect to Service Chain
-
Service as Default Gateway
-
Perimeter Service
-
Legacy Service Redirection
The switch configurations are generated with corresponding feature CLIs depending on the attached use case.
Service Clusters
In NDFC release 12.2.2, the service node resides in the same VXLAN EVPN fabric as the service switch, and you do not have to create the external fabric for the service cluster. Nexus Dashboard Fabric Controller does not auto-detect or discover any service cluster. You also have to specify the service cluster name, type, and form factor. The name of the service cluster has to be unique within a fabric. The service cluster is attached to a leaf, border leaf, border spine, border super spine, or a vPC border gateway. Nexus Dashboard Fabric Controller does not define a new switch role for a service switch.
Nexus Dashboard Fabric Controller manages the switches that are attached to a service cluster. Nexus Dashboard Fabric Controller also manages the interfaces of these attached switches. Ensure that the interfaces that the service cluster is attached to are in trunk mode and do not belong to any interface group. The Layer 4 to Layer 7 service will not change its mode. In case the attached switches are forming a vPC pair, the name of the attached switch is a combination of both switches.
MSD Support
This feature supports member fabrics in Multi-Site Domains (MSDs). You can choose the MSD member fabric as attached fabric during service cluster creation, create a service cluster (for example, firewall, or load balancer), attach the service cluster to the switch in the selected MSD member fabric, define the service function and service insertions, and deploy relevant configurations on the selected MSD member fabric. For more information on the procedure to configure service, see Configuring Layer 4 to Layer 7 Services.
RBAC Support
The Layer 4 to Layer 7 service supports Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) along with fabric access mode.
The admin, stager, and operator, are pre-defined roles in Nexus Dashboard Fabric Controller. The table below lists the various operations that each role can perform.
| Service Operation | Service Insertion | Service Function | Service Cluster | Service Chain |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Create/Update/Delete |
admin, stager |
admin, stager |
admin |
admin, stager |
|
List |
admin, stager, operator |
admin, stager, operator |
admin, stager, operator |
admin, stager, operator |
|
Attach/Detach |
admin, stager |
NA |
NA |
NA |
Traffic Redirect Support on WAN Interfaces of Border Switches
In the use cases of Redirect to Service Chain and Legacy Service Redirection, you can specify an arbitrary network that has not been defined in the top-down configuration as a source or destination network in the service insertion. This helps in streamlining policy enforcement for north-south traffic. The Nexus Dashboard Fabric Controller UI lists out routed Layer 3 interfaces of all border switches, standalone or vPC, that have a VRF association. You can then choose the required interface that has to be associated with the defined policy. The border switches include border leaf, border spine, border super spine and border gateway. There can be multiple interface associations. For example, multiple Layer 3 interfaces, subinterfaces, and port-channels can be selected for one border switch. You can also select multiple border switches for interface association. For more information, see the Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS Unicast Routing Configuration Guide.
Depending on the policy direction, the border switch and interface association for 'any' or arbitrary network may not be needed. For example, for a forwarding policy, the border switch and interface input or route-map association is not needed for 'any' or arbitrary destination network. For a reversed policy, the border switch and interface or route-map association is not needed for 'any' or arbitrary source network.
When the policy with 'any' or arbitrary network is attached, the policy related CLIs are generated and associated with the selected Layer 3 routed interfaces of the border switches. The deployment of that policy pushes the CLIs to the selected border switches. The service insertion stats diagram includes the PBR or ePBR related policy stats data, depending on the use case.
ePBR Support
Beginning with NDFC release 12.2.2, support is available for enhanced policy-based redirect (ePBR), which is used for Layer 4 to Layer 7 service load balancing, and for single-site traffic steering and redirection.
ePBR leverages the policy-based redirect solution to steer traffic and to enable application-based routing. ePBR also allows you to enable service chaining within the same fabric or across fabrics. ePBR services flows are similar to the PBR services flows, as described in the preceding section, consisting of service cluster, service function, and service insertion functions.
The service insertion in an ePBR services flow supports service chaining in the same fabric in NDFC release 12.2.2. The service cluster in the service chaining can be any combination of different service cluster types, and can also have different failure actions defined. You can associate multiple source and destination networks with the service insertion, and you can define multiple ACLs, and multiple ACEs in one ACL, for an easier application of the service insertion.
Static Route
The Layer 4 to Layer 7 service pushes static routes on all VTEPs, including service leaf switches, where the VRF being referenced in the static route is attached. This expedites service cluster failover with static routes.
Beginning with NDFC release 12.1.3, you can also enable an optional Export Gateway IP flag to export the gateway IP (service cluster IP) address as the next-hop, which will trigger the static routes to be deployed only on the service switches (the switches where the service clusters are attached).
Guidelines and Limitations for Layer 4 to Layer 7 Services
-
Layer 4 to Layer 7 Service in Nexus Dashboard Fabric Controller does not manage or provision service clusters, such as firewall, load balancer, and Virtual Network Function.
-
The Layer 4 to Layer 7 Service feature is supported only on the VXLAN BGP EVPN fabrics with the Data Center VXLAN EVPN template.
-
The service insertions defined in this feature leverage policy-based routing (PBR) and, beginning with NDFC release 12.2.2, enhanced policy-based routing (ePBR). See the following documents for more information:
-
Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS ePBR Configuration Guide for PBR related configurations and constraints
-
Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS ePBR Configuration Guide for ePBR related configurations and constraints
-
-
Active/standby, scale-up, and scale-out clustered deployments are supported with the ePBR feature.
-
This feature supports Cisco Cloud Scale platform switches as leaf, border leaf, border spine, border super spine, and border gateway switches.
-
ePBR support is for VTEPs with NX-OS release 10.2(5) and above.
-
Layer 4 to Layer 7 Service REST APIs are accessible via Nexus Dashboard Fabric Controller packaged REST API documentation. For more information, see the Cisco Nexus Dashboard Fabric Controller REST API Reference Guide.
-
Load sharing is not supported.
-
IPv6 is supported for Layer 4 to Layer 7 Services. See the Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS VXLAN Configuration Guide for PBR on VXLAN with IPv6 in the Underlay constraints.
-
This feature creates, updates, and deletes the service network, as required. Service networks cannot be created or deleted from the Manage > Fabrics > Networks window.
-
Layer 4 to Layer 7 services in NDFC release 12.2.2 does not support change control.
-
You must run
Recalculate and Deployat the fabric level after service insertion is attached or detached to generate the complete pending configurations.
Types of Service Devices
The L4-L7 Service in Cisco Nexus Dashboard Fabric Controller supports any vendors service cluster attachments. Typical service cluster types that are deployed in a data center are Firewalls, Load Balancers, and other Layer-4 to Layer-7 products.
Examples of supported Firewall vendors are Cisco Systems, Palo Alto Networks, Fortinet, Check Point Software Technologies, and others.
Examples of supported Load Balancer vendors are F5 Networks, Citrix Systems, A10 Networks, and others.
Note that these example lists are meant to serve as examples and not intended to be exhaustive lists. The L4-L7 service attachment is generic and applies to any vendors service cluster.
Configuring Fabric Settings for Layer 4 to Layer 7 Service
You must configure certain fabric settings to enable Layer 4 to Layer 7 Service functionality.
To configure these settings:
-
Navigate to the Overview page for the VXLAN EVPN fabric where you want to enable Layer 4 to Layer 7 Service functionality.
-
If you are creating a new VXLAN EVPN fabric:
-
Navigate to Manage > Fabrics, then click Actions > Create Fabric.
The Create Fabric window is displayed.
-
Provide a fabric name, then choose the Data Center VXLAN EVPN template.
-
-
If you are editing an existing VXLAN EVPN fabric:
-
Navigate to Manage > Fabrics, then double-click on that VXLAN fabric.
-
Click Actions > Edit Fabric.
-
-
-
Click the Advanced tab for this VXLAN EVPN fabric and make the following configurations:
-
In the Enable L4-L7 Services Re-direction field, check the checkbox to enable routing of packets based on the specified policy.
-
-
Click the Resources tab and make the following configurations:
-
Specify a VLAN range in the Service Network VLAN Range field.
This is a per switch overlay service network VLAN range. The minimum allowed value is 2 and the maximum allowed value is 4094.
-
Specify a value for the Route Map Sequence Number Range field.
The minimum allowed value is 1 and the maximum allowed value is 65534.
-
If the ePBR service endpoint probe is needed, enable the Per VRF Per VTEP Loopback Auto-Provisioning options and specify Per VRF Per VTEP IP Pool for Loopbacks range for IPv4 and/or IPv6.
-
-
Click Save to save the updated configuration.
Configuring Layer 4 to Layer 7 Services
To launch the Layer 4 to Layer 7 Services, or the Elastic Service, on the Cisco Nexus Dashboard Fabric Controller Web UI, navigate to Manage > Fabrics > Fabric Overview > Services.
You can also bring up the Services window specific to a switch by navigating to:
Manage > Inventory > Switches > Switches Overview > Services
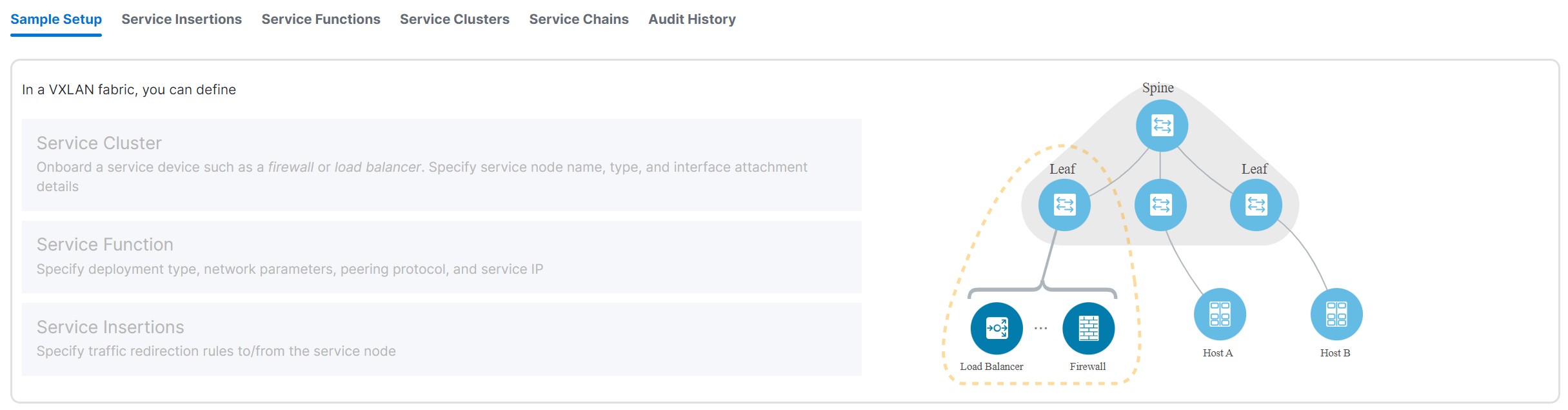
The following tabs are shown in the Services window:
-
Sample Setup: Shows an example Layer 4 to Layer 7 services setup.
-
Service Insertions: Shows the Layer 4 to Layer 7 service insertions that you have configured in your NDFC.
-
Service Functions: Shows the Layer 4 to Layer 7 service functions that you have configured in your NDFC.
-
Service Clusters: Shows the Layer 4 to Layer 7 service clusters that you have configured in your NDFC.
-
Service Chains: Shows the Layer 4 to Layer 7 service chains that you have configured in your NDFC.
-
Audit History: Allows you to view audit history of Layer 4 to Layer 7 services related actions and details that are involved in the selected service insertion or service function.
Add a Service Insertion
To add a service insertion:
-
Navigate to the Service Insertions tab.
-
Navigate to:
Manage > Fabrics
-
Double-click the appropriate Data Center VXLAN EVPN fabric.
The Overview window for that fabric appears.
-
Click the Services tab.
-
Click the Service Insertions subtab.
A list of configured service insertions is displayed.
-
-
Click Actions > Add Service Insertion.
The Add Service Insertion window is displayed.
-
Enter a name for the service insertion in the Service Insertion Name field.
The name can have alphanumeric, underscore, or dash characters.
-
In the Use Case field, choose from the following types of service insertion use cases:
-
Redirect to Service Chain: Selective traffic redirection, load-balancing and service chaining with health monitoring
-
Service as Default Gateway: Intra-VRF or intra-tenant redirection with the service as the default gateway
-
Perimeter Service: Inter-VRF or inter-tenant service redirection
-
Legacy Service Redirection: Selective traffic redirection with legacy PBR workflow (no health monitoring)
-
Redirect to Service Chain
This service insertion use case configures selective traffic redirection, load-balancing and service chaining with health monitoring.
-
Enter the necessary information to configure service insertion with this use case:
Field
Description
Traffic Source VRF
Choose an existing traffic source VRF to associate with this service insertion use case, or click Create VRF to create a new VRF. Refer to the section "VRFs" in About Fabric Overview for LAN Operational Mode Setups for more information.
Traffic Destination VRF
Choose an existing traffic destination VRF to associate with this service insertion use case, or click Create VRF to create a new VRF. Refer to the section "VRFs" in About Fabric Overview for LAN Operational Mode Setups for more information.
Detach/Attach
Toggle the switch to detach or attach.
Direction
Choose the direction for this service insertion use case. Options are:
-
Bidirectional
-
Forward
-
Reverse
Enable Statistics
Check the check box to enable statistics for this service insertion use case.
-
-
In the Traffic Flow Redirects area, click Add Traffic Flow Redirect and enter the necessary information:
Field
Description
Match ACL Name
Choose an already-configured access control list (ACL) from the drop-down list, or click Create ACL to create a new access control list. See ACL Templates for more information.
Match Action
Select the appropriate ACL match action. Options are:
-
Redirect
-
Drop
-
Exclude
You can have only one Drop and one Exclude in the service insertion for a service chain.
Service Chain Name
Choose an already-configured service chain from the drop-down list, or click Create Service Chain to create a new service chain. See Add a Service Chain for more information.
Details
Provides details of the traffic flow redirect that you configured. If additional details are configured but are not shown in the Details area, click the pencil icon (edit), then click View Details under the Service Chain Name entry.
-
-
When you have completed the configuration for this traffic flow redirect, click the check mark at the end of the row to accept the values that you entered.
Repeat these steps to configure additional traffic flow redirects.
-
In the Networks area, click Add Row and enter the necessary information:
Field
Description
Source Network
The source and destination network fields are auto-populated based on the ACL entries in the selected or newly created ACL. You can override the system auto-populated source and/or destination network.
If you want to override the system auto-populated source and/or destination network, choose an already-configured source and/or destination network from the drop-down list, or click Create Network to create a new network. Refer to the section "Networks" in About Fabric Overview for LAN Operational Mode Setups for more information.
The source and destination network cannot be the same for the Redirect to Service Chain use case.
Destination Network
Source Switch(Interfaces)
Choose the source switch interfaces, if necessary.
Destination Switch(Interfaces)
Choose the destination switch interfaces, if necessary.
-
When you have completed the configuration for this network, click the check mark at the end of the row to accept the values that you entered.
Repeat these steps to configure additional networks.
-
Click Save after you have entered the necessary information to add a service insertion with this use case.
You are returned to the Fabric Overview page, with Services > Service Insertions selected.
In the list of configured service insertions that is displayed, perform any of the following actions:
-
Click the down arrow at the upper right corner of the area for a service insertion to see additional information on that service insertion.
-
Select a service insertion and click Actions > Edit to edit that service insertion configuration.
-
Select a service insertion and click Actions > Attach to attach that service insertion configuration.
-
Select a service insertion and click Actions > Detach to detach that service insertion configuration.
-
Select a service insertion and click Actions > Delete to delete that service insertion.
-
Click View Details in the Statistics/Probe Details area to view the statistics for that service insertion. See View Service Insertion Stats Details for more details.
Service as Default Gateway
This service insertion use case configures intra-VRF or intra-tenant redirection with the service as the default gateway.
-
Enter the necessary information to configure service insertion with this use case:
Field
Description
Outside VRF Name
Choose an existing outside VRF to associate with this service insertion use case, or click Create VRF to create a new VRF. Refer to the section "VRFs" in About Fabric Overview for LAN Operational Mode Setups for more information.
Detach/Attach
Toggle the switch to detach or attach.
Service Function
The service function pull-down list is pre-populated with service functions that have an N Arms connectivity mode and have a matched outside VRF. Choose an existing service function to associate with this service insertion use case, or click Create Service Function to create a new service function. See Add a Service Function for more information.
-
In the Inside L2 Network area, click Add L2 Network, then choose an existing Layer 2 network to associate with this service insertion use case, or click Create Network to create a new Layer 2 network. Refer to the section "Networks" in About Fabric Overview for LAN Operational Mode Setups for more information.
-
When you have completed the configuration for inside L2 network, click the check mark at the end of the row to accept the values that you entered.
Repeat these steps to configure additional inside L2 networks, if necessary.
-
Click Save after you have entered the necessary information to add a service insertion with this use case.
You are returned to the Fabric Overview page, with Services > Service Insertions selected.
In the list of configured service insertions that is displayed, perform any of the following actions:
-
Click the down arrow at the upper right corner of the area for a service insertion to see additional information on that service insertion.
-
Select a service insertion and click Actions > Edit to edit that service insertion configuration.
-
Select a service insertion and click Actions > Attach to attach that service insertion configuration.
-
Select a service insertion and click Actions > Detach to detach that service insertion configuration.
-
Select a service insertion and click Actions > Delete to delete that service insertion.
-
Click View Details in the Statistics/Probe Details area to view the statistics for that service insertion. See View Service Insertion Stats Details for more details.
Perimeter Service
This service insertion use case configures inter-VRF or inter-tenant service redirection.
-
Enter the necessary information to configure service insertion with this use case:
Field
Description
Outside VRF Name
Choose an existing outside VRF to associate with this service insertion use case, or click Create VRF to create a new VRF. Refer to the section "VRFs" in About Fabric Overview for LAN Operational Mode Setups for more information.
Inside VRF Name
Choose an existing inside VRF to associate with this service insertion use case, or click Create VRF to create a new VRF. Refer to the section "VRFs" in About Fabric Overview for LAN Operational Mode Setups for more information.
Detach/Attach
Toggle the switch to detach or attach.
Service Function
The service function pull-list is pre-populated with service functions that have a matched outside and inside VRF. Choose an existing service function to associate with this service insertion use case, or click Create Service Function to create a new service function. See Add a Service Function for more information.
Enter different loopback IP addresses for the outside and inside VRFs if you selected manual loopback, and your firewall connects to the inside or outside VRF using a common VRF.
-
Click Save after you have entered the necessary information to add a service insertion with this use case.
You are returned to the Fabric Overview page, with Services > Service Insertions selected.
In the list of configured service insertions that is displayed, perform any of the following actions:
-
Click the down arrow at the upper right corner of the area for a service insertion to see additional information on that service insertion.
-
Select a service insertion and click Actions > Edit to edit that service insertion configuration.
-
Select a service insertion and click Actions > Attach to attach that service insertion configuration.
-
Select a service insertion and click Actions > Detach to detach that service insertion configuration.
-
Select a service insertion and click Actions > Delete to delete that service insertion.
-
Click View Details in the Statistics/Probe Details area to view the statistics for that service insertion. See View Service Insertion Stats Details for more details.
Legacy Service Redirection
This service insertion use case configures selective traffic redirection with legacy PBR workflow. Health monitoring is not configured with this use case.
-
Enter the necessary information to configure service insertion with this use case:
Field
Description
VRF Name
Choose an VRF to associate with this service insertion use case, or click Create VRF to create a new VRF. Refer to the section "VRFs" in About Fabric Overview for LAN Operational Mode Setups for more information.
Detach/Attach
Toggle the switch to detach or attach.
Direction
Choose the direction for this service insertion use case. Options are:
-
Bidirectional
-
Forward
-
Reverse
Enable Statistics
Check the check box to enable statistics for this service insertion use case.
Matched ACL Name
Choose an already-configured access control list (ACL) from the drop-down list, or click Create ACL to create a new access control list. See ACL Templates for more information.
Service Function
The Service Function pull-down list is pre-populated with service functions that have a matched VRF and do not have a probe defined. Choose an existing service function to associate with this service insertion use case, or click Create Service Function to create a new service function. See Add a Service Function for more information.
Single Service Redirect Template
Select the service_pbr service redirect template. See Service Insertion Template for more information.
-
-
Click the General Parameters tab and enter the necessary information.
Field
Description
Route Map Action
Select an action from the drop-down list. The options are permit or deny. If you select permit, the matched traffic is redirected based on the next-hop option and the defined policy. If you select deny, the traffic is routed based on the routing table rules.
Next Hop Option
Specify an option for the next-hop. The options are none, drop-on-fail, and drop. If you select none, the matched traffic is redirected based on the defined PBR rules. If you select drop-on-fail, the matched traffic is dropped if the specified next hop is not reachable. If you select drop, the matched traffic is dropped.
-
Click the Advanced tab and enter the necessary information.
All values in the Advanced tab are automatically generated unless otherwise specified.
Field
Description
ACL Name
Specify a name for the generated access control list (ACL). If not specified, this is auto-generated.
ACL Name for reversed traffic
Specify a name for the ACL that is generated for reversed traffic. If not specified, this is auto-generated.
Route map match number
Specify a route map match number. A valid value ranges from 1 to 65535. If not specified, a route map match sequence number will be retrieved from the predefined resource pool. This number is associated with the name of the ACL.
Route map match number for reversed traffic
Specify a route map match number for reversed traffic. A valid value ranges from 1 to 65535. If not specified, a route map match sequence number will be retrieved from the predefined resource pool. This number is associated with the name of the ACL that has been generated for reversed traffic.
-
In the Networks area, click Add Row and enter the necessary information:
Field
Description
Source Network
Choose an already-configured source network from the drop-down list, or click Create Network to create a new network. Refer to the section "Networks" in About Fabric Overview for LAN Operational Mode Setups for more information.
Destination Network
Choose an already-configured destination network from the drop-down list, or click Create Network to create a new network. Refer to the section "Networks" in About Fabric Overview for LAN Operational Mode Setups for more information.
Source Switch(Interfaces)
Choose the source switch interfaces, if necessary.
Destination Switch(Interfaces)
Choose the destination switch interfaces, if necessary.
-
When you have completed the configuration for this network, click the check mark at the end of the row to accept the values that you entered.
Repeat these steps to configure additional networks.
-
Click Save after you have entered the necessary information to add a service insertion with this use case.
You are returned to the Fabric Overview page, with Services > Service Insertions selected.
In the list of configured service insertions that is displayed, perform any of the following actions:
-
Click the down arrow at the upper right corner of the area for a service insertion to see additional information on that service insertion.
-
Select a service insertion and click Actions > Edit to edit that service insertion configuration.
-
Select a service insertion and click Actions > Attach to attach that service insertion configuration.
-
Select a service insertion and click Actions > Detach to detach that service insertion configuration.
-
Select a service insertion and click Actions > Delete to delete that service insertion.
-
Click View Details in the Statistics/Probe Details area to view the statistics for that service insertion. See View Service Insertion Stats Details for more details.
View Service Insertion Stats Details
After you have completed the configurations for a service insertion, you can view the statistics by clicking View Details in the Statistics/Probe Details area for that service insertion.
-
Click in the Select Date area to change the date range for the statistics.
-
Click in the Switch area to change the switch that you will use for the statistics.
-
Click Clear Stats to clear the statistics.
Add a Service Function
To add a service function:
-
Navigate to the Service Functions tab.
-
Navigate to:
Manage > Fabrics
-
Double-click the appropriate Data Center VXLAN EVPN fabric.
The Overview window for that fabric appears.
-
Click the Services tab.
-
Click the Service Functions subtab.
A list of configured service functions is displayed.
-
-
Click Actions > Add Service Function.
The Add Service Function window is displayed.
-
Enter the necessary information to add a service function.
Field
Description
Type
Choose from the following types of service clusters:
-
Firewall
-
Load Balancer
-
Virtual Networking Function
-
Other
Service Function Name
Enter a name for the service cluster. The name can have alphanumeric, underscore, or dash characters.
Connectivity Mode
Choose the connectivity mode:
-
One Arm
-
Two Arm
-
N Arms
Service VRF
Displayed in the following situations:
-
Type: Firewall, Load Balancer, Virtual Networking Function, and Other
-
Connectivity Mode: One Arm
Choose an existing VRF to associate with this service function, or click +Create VRF to create a new VRF. Refer to the section "VRFs" in About Fabric Overview for LAN Operational Mode Setups for more information.
First Arm VRF
Displayed in the following situations:
-
Type: Load Balancer, Virtual Networking Function
-
Connectivity Mode: Two Arm, N Arms
Choose an existing VRF to associate with this service function, or click +Create VRF to create a new VRF. Refer to the section "VRFs" in About Fabric Overview for LAN Operational Mode Setups for more information.
Second Arm VRF
Displayed in the following situations:
-
Type: Load Balancer, Virtual Networking Function
-
Connectivity Mode: Two Arm
Choose an existing VRF to associate with this service function, or click +Create VRF to create a new VRF. Refer to the section "VRFs" in About Fabric Overview for LAN Operational Mode Setups for more information.
Outside VRF
Displayed in the following situations:
-
Type: Firewall
-
Connectivity Mode: Two Arm, N Arms
Choose an existing VRF to associate with this service function, or click +Create VRF to create a new VRF. Refer to the section "VRFs" in About Fabric Overview for LAN Operational Mode Setups for more information.
Inside VRF
Displayed in the following situations:
-
Type: Firewall
-
Connectivity Mode: Two Arm
Choose an existing VRF to associate with this service function, or click +Create VRF to create a new VRF. Refer to the section "VRFs" in About Fabric Overview for LAN Operational Mode Setups for more information.
-
If you select the same VRF for both the Outside VRF and the Inside VRF, then an intra-tenant firewall will be configured.
-
If you select different VRFs for the Outside VRF and the Inside VRF, then an inter-tenant firewall will be configured.
-
-
Click + Add Service Cluster Logical Connectivity.
The Add Service Cluster Logical Connectivity window appears.
-
Enter the necessary information to add service cluster logical connectivity.
Field
Description
Service Cluster Name
Select an already-configured service cluster, or click Add Service Cluster to create a new one. See Add a Service Cluster for more information.
IPv4 and/or IPv6
Choose from the following options:
-
IPv4
-
IPv6
-
IPv4 and IPv6
The following fields vary, depending on the connectivity mode that you chose:
-
If you chose One Arm in the Connectivity Mode field, the following fields appear:
Field
Description
Service IPv4
Enter the IPv4 and/or IPv6 service addresses.
Service IPv6
Service Network
Choose an existing service network to associate with this service function, or click +Add Service Network to create a new service network. Refer to the section "Networks" in About Fabric Overview for LAN Operational Mode Setups for more information.
Probe
Probe does not apply to an inter-tenant firewall.
Choose an existing probe to associate with this service function, or click +Add Probe to create a new probe. See Probe Templates for more information.
Peering Option
Choose the appropriate peering option to associate with this service function. Note that some peering options might not be available, depending on the previous configurations that you made.
-
Static
-
eBGP
-
Connected: Select this peering option if you already have your routing in place. Intra-tenant firewall will only have Connected as the peering option.
Peering Configuration
Choose the appropriate peering configuration to associate with this service function, or click +Add Peering Configuration to create a new peering configuration. See [Service Function Templates] for more information.
-
-
If you chose Two Arm in the Connectivity Mode field, the following fields appear:
Inside and Outside appear as qualifiers for the service networks if you chose Firewall as the service function type, whereas First-Arm and Second-Arm appear as qualifiers for the service networks if you chose Load Balancer or Virtual Networking Function as the service function type.
Field
Description
Outside/First-Arm Service IPv4
Enter the IPv4 and/or IPv6 outside service addresses.
Outside/First-Arm Service IPv6
Outside/First-Arm Service Network
Choose an existing outside service network to associate with this service function, or click +Add Service Network to create a new outside service network.
Probe
Probe does not apply to an inter-tenant firewall.
Choose an existing probe to associate with this service function, or click +Add Probe to create a new probe. See Probe Templates for more information.
Peering Option
Choose the appropriate peering option to associate with this service function. Note that some peering options might not be available, depending on the previous configurations that you made.
-
Static
-
eBGP
-
Connected: Select this peering option if you already have your routing in place. Intra-tenant firewall will only have Connected as the peering option.
Peering Configuration
Choose the appropriate peering configuration to associate with this service function, or click +Add Peering Configuration to create a new peering configuration. See [Service Function Templates] for more information.
Inside/Second-Arm Service IPv4
Enter the IPv4 and/or IPv6 inside service addresses.
Inside/Second-Arm Service IPv6
Inside/Second-Arm Service Network
Choose an existing inside service network to associate with this service function, or click +Add Service Network to create a new inside service network. Refer to the section "Networks" in About Fabric Overview for LAN Operational Mode Setups for more information.
Probe
Probe does not apply to an inter-tenant firewall.
Choose an existing probe to associate with this service function, or click +Add Probe to create a new probe. See Probe Templates for more information.
Peering Option
Choose the appropriate peering option to associate with this service function. Note that some peering options might not be available, depending on the previous configurations that you made.
-
Static
-
eBGP
-
Connected: Select this peering option if you already have your routing in place. Intra-tenant firewall will only have Connected as the peering option.
Peering Configuration
Choose the appropriate peering configuration to associate with this service function, or click +Add Peering Configuration to create a new peering configuration. See [Service Function Templates] for more information.
-
-
If you chose N Arms in the Connectivity Mode field, the following fields appear:
Field
Description
Outside Service IPv4
Enter the IPv4 and/or IPv6 service addresses.
Service IPv6
Outside Service Network
Choose an existing outside service network to associate with this service function, or click +Add Service Network to create a new service network. Refer to the section "Networks" in About Fabric Overview for LAN Operational Mode Setups for more information.
Probe
Probe does not apply to an inter-tenant firewall.
Choose an existing probe to associate with this service function, or click +Add Probe to create a new probe. See Probe Templates for more information.
Peering Option
Choose the appropriate peering option to associate with this service function. Note that some peering options might not be available, depending on the previous configurations that you made.
-
Static
-
eBGP
-
Connected: Select this peering option if you already have your routing in place. Intra-tenant firewall will only have Connected as the peering option.
Peering Configuration
Choose the appropriate peering configuration to associate with this service function, or click +Add Peering Configuration to create a new peering configuration. See [Service Function Templates] for more information.
-
-
-
Click Save after you have entered the necessary information in the Add Service Cluster Logical Connectivity window.
You are returned to the Add Service Function window.
-
Repeat the previous steps to add additional service cluster logical connectivity entries, or click Save in the Add Service Function window to save the service function information.
You are returned to the Fabric Overview page, with Services > Service Functions selected.
In the list of configured service functions that is displayed, perform any of the following actions:
-
Click the down arrow at the upper right corner of the area for a service function to see additional information on that function.
-
Select a service function and click Actions > Edit to edit that service function configuration.
-
Select a service function and click Actions > Delete to delete that function cluster.
Remote Peering
Beginning with NDFC release 12.2.1,the remote peering feature is supported for all Layer 4 to Layer 7 service node types. This allows for the separation of a service cluster’s control plane peering from the physical port attachment.
As part of the process for configuring route peering for a service cluster, you will have the option to specify the eBGP dynamic peering with the remote leaf, border or border gateway switches rather than the default service switch. You will also be able to push remote peering-related configurations through updates to the eBGP template for Layer 4 to Layer 7 services.
The remote peering feature allows service nodes to peer with multiple remote leaf, border or border gateway switches through eBGP dynamic peering. As part of the configuration process for remote peering, you can choose either local, or remote, or local and remote peering, and whether you want to export the gateway through the eBGP template for remote peering.
Guidelines and Limitations
-
The remote peering feature is supported only with eBGP dynamic peering.
Configuring Remote Peering
To configure remote peering for VNF service devices:
-
Configure the service insertion as you normally would, using the procedures provided in Add a Service Insertion.
-
Configure the route peering as you normally would, using the procedures in Add a Service Function, with the following settings specifically for the remote peering feature.
Make the following configurations to enable remote peering and to define dynamic peering with multiple remote switches:
-
In the Peering Option field, choose eBGP.
-
Click Add Remote Peering Configuration to specify the remote switches and corresponding peering configuration.
-
Enter the necessary information to add remote peering.
Field
Description
Switch Name
Choose the remote switch that will be used with remote peering.
Only the leaf, border, or border gateway switches that are not local to the service cluster are provided as options for this field.
-
If you see a single-switch option in the Switch Name field (for example, leaf1-v), that means that this is a single, standalone remote switch.
-
If you see a dual-switch option in this field (for example, bgw1-v ~ bgw2-v), that means that this is a vPC pair.
Peering Configuration
Choose an existing peering configuration, or click + Add Peering Configuration to create a new one.
If you click + Add Peering Configuration, the service_ebgp_route peering template appears. Complete the configurations using the information provided in [service_ebgp_route].
-
-
Click the checkmark to accept the changes in the Remote Peering Configurations area.
-
Repeat these steps to add additional remote peering configurations, or click Save in the Add Service Cluster Logical Connectivity window.
You are returned to the Edit Service Function window.
-
Repeat the previous steps to add additional service cluster logical connectivity configurations, or click Save in the Edit Service Function window.
You are returned to the Service Functions tab under Services.
-
Add a Service Cluster
A service cluster is a logical entity that has a single MAC IP address assigned to it, regardless of the number of service nodes that you have as part of that service cluster.
For example, when you create a service cluster with these procedures, if you choose Standalone in the Node Redundancy field, where you are adding a single node to the service cluster, then that service cluster, with that single node, has one MAC IP address. Similarly, if you choose Active/Standby Cluster in the Node Redundancy field, where you are adding two nodes to the service cluster, then that service cluster also has one MAC IP address, even though two nodes are part of that service cluster.
To add a service cluster:
-
Navigate to the Service Clusters tab.
-
Navigate to:
Manage > Fabrics
-
Double-click the appropriate Data Center VXLAN EVPN fabric.
The Overview window for that fabric appears.
-
Click the Services tab.
-
Click the Service Clusters subtab.
A list of configured service clusters is displayed.
-
-
Click Actions > Add Service Cluster.
The Add Service Cluster window is displayed.
-
Enter the necessary information to add a service cluster.
Field
Description
Type
Choose from the following types of service clusters:
-
Firewall
-
Load Balancer
-
Virtual Networking Function
-
Other
Service Cluster Name
Enter a name for the service cluster. The name can have alphanumeric, underscore, or dash characters.
Node Redundancy
Choose the node redundancy:
-
Standalone: Applicable if you are adding a single service node in the next step.
-
Active/Standby Cluster: Applicable if you are adding two service nodes in the next step.
-
Active/Active Cluster: Applicable if you are adding more than two service nodes in the next step.
Form Factor
Select Physical or Virtual.
-
-
Click + Add Service Node.
The Add Service Node window appears.
-
Enter a name for the service node in the Service Node Name field.
-
Click + Add Service Node Physical Connectivity.
The Add Service Node Physical Connectivity window appears.
-
Enter the necessary information in the Add Service Node Connectivity window.
Field
Description
Service Node Name
Automatically populated with the service node name that you entered in the previous step.
Service Node Interface
Enter the service node interface. The service node interface is used for visualization.
Service Node Interface Usage
Choose the service node interface usage. The displayed options vary depending on the service cluster type that you chose earlier in this procedure:
-
Firewall:
-
Outside
-
Inside
-
Inside-Outside: This link can be used for both inside and outside
-
-
Load Balancer, Virtual Networking Function, or Other:
-
First Arm
-
Second Arm
-
First-Second Arm: This link can be used for both first arm and second arm
-
Attached Switch
Select a switch or a switch pair from the list.
Switch Interface
Select the interface from the list.
-
If you selected a vPC pair in the Attached Switch list, the vPC channel will be shown in the Switch Interface list.
-
Otherwise, the port-channel and interfaces with trunk mode are shown in the Switch Interface list.
Link Template
Select the service_link_trunk, service_link_port_channel_trunk, or the service_link_vpc template from the drop-down list based on the specified attached switch interface type. For more information on template fields, see Templates.
-
-
Click Save after you have entered the necessary information in the Add Service Node Physical Connectivity window.
If you click Save, you are returned to the Add Service Node window.
-
Repeat the previous steps to add another service node interface, or click Save in the Add Service Node window to save the service node information.
You are returned to the Add Service Cluster window.
-
Repeat the previous steps to add another service node, or click Save in the Add Service Cluster window to save the service cluster information.
If you chose Standalone in the Node Redundancy field, the + Add Service Node option is grayed out and not selectable.
If you click Save, you are returned to the Fabric Overview page, with Services > Service Clusters selected.
In the list of configured service clusters that is displayed, perform any of the following actions:
-
Click the down arrow at the upper right corner of the area for a service cluster to see additional information on that cluster.
-
Select a service cluster and click Actions > Edit to edit that service cluster configuration.
-
Select a service cluster and click Actions > Delete to delete that service cluster.
Add a Service Chain
You will add a service chain to configure how traffic is redirected.
To add a service chain:
-
Navigate to the Service Chains tab.
-
Navigate to:
Manage > Fabrics
-
Double-click the appropriate Data Center VXLAN EVPN fabric.
The Overview window for that fabric appears.
-
Click the Services tab.
-
Click the Service Chains subtab.
A list of configured service chains is displayed.
-
-
Click Actions > Add Service Chain.
The Add Service Chain window is displayed.
-
Enter a name for the service chain in the Service Chain Name field.
-
Click + Add Service Chain Entries.
-
Enter the necessary information for the service chain entries.
Field
Description
Sequence Number
Enter the sequence number. The lower the number in the sequence, the higher the priority.
For example, if you have two service chain entries configured:
-
Firewall, with a sequence number of 10
-
Load balancer, with a sequence number of 20
Then the firewall, with a sequence number of 10, will be higher priority and will be trigger first in the sequence, followed by the load balancer with a sequence number of 20.
Service Cluster Type
Choose from the following types of service clusters:
-
Firewall
-
Load Balancer
-
Virtual Networking Function
-
Other
VRF
Choose an existing VRF to associate with this service chain, or click + Create VRF to create a new VRF.
Service Function
Choose an existing service function to associate with this service chain, or click + Add Service Function to add a new service function. See Add a Service Function for more information.
Probe Fail Action
Select the appropriate probe fail action. Options are:
-
Forward
-
Drop
-
Bypass
-
None
-
-
When you have completed the configuration for this service chain entry, click the check mark at the end of the row to accept the values that you entered.
Repeat these steps to configure additional service chain entries.
-
Click the down arrow next to Service Chain Template to expand that area, then make the necessary configurations in the Service Chain Template area.
See Service Chain Templates for more information.
-
Click Save after you have entered the necessary information in the Add Service Chain window.
You are returned to the Fabric Overview page, with Services > Service Chains selected.
In the list of configured service chains that is displayed, perform any of the following actions:
-
Select a service cluster and click Actions > Edit to edit that service chain configuration.
-
Select a service cluster and click Actions > Delete to delete that service chain.
View Audit History
To view the audit history of the switches and networks that are involved in the selected service insertion or service function, click the Audit History tab in the Services window. The Audit Logs table in the Audit History window displays information about all of the actions that have been performed, such as:
-
Creation of service clusters, service function, service insertions, service chains, probes, routes, and ACLs
-
Deletion of service clusters, service function, service insertions, service chains, probes, routes, and ACLs
-
Update of service clusters, service function, service insertions, service chains, probes, routes, and ACLs
-
Attachment and detachment of service insertions
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
User Name |
Specifies the user name of service cluster. |
|
User Role |
Specifies the user role name by whom latest action performed. |
|
Action Taken |
Specifies the latest action performed. |
|
Entity |
Specifies the name of the entity, such as |
|
Status |
Specifies the action status, such as |
|
Time |
Specifies the action time on that node. |
|
More Info |
Click More Info to view detailed information of a selected service cluster. |
To delete older audit reports, click Action > Purge Audit History, then specify the maximum retained dates and confirm deletion. Note that only users with the admin role can delete audit log entries.
Templates
-
ACL Templates: Used when adding a service insertion, as part of the Redirect to Service Chain and Legacy Service Redirection use cases.
-
Probe Templates: Used in the Add Service Cluster Logical Connectivity window when adding a service function.
-
Service Function Route Templates: Used in the Add Service Cluster Logical Connectivity window when adding a service function.
-
Service Chain Templates: Used when adding a service chain.
-
Service Node Link Templates: Used when adding a service cluster.
-
Service Insertion Template: Used when adding a service insertion, as part of the Legacy Service Redirection use case.
ACL Templates
The following ACL template is available beginning with NDFC release 12.2.2.
service_acl
IP ACL template for L4-L7 services.
|
Field |
Description |
|
Sequence Number |
Enter the sequence number for the ACL. Valid range: 1 - 4294967295. |
|
Protocol |
Specify the protocol to be used for the ACL. Options are:
|
|
Source IP |
Enter a source IP address for the ACL. This entry can be an IPv4 address, and IPv6 address, or any. |
|
Destination IP |
Enter a destination IP address for the ACL. This entry can be an IPv4 address, and IPv6 address, or any. |
|
Source Port |
Enter the source port number (for example, any or 443). The value in this field is ignored if you selected ip or icmp in the Protocol field. |
|
Destination Port |
Enter the destination port number (for example, any or 443). The value in this field is ignored if you selected ip or icmp in the Protocol field. |
Probe Templates
The following probe template is available beginning with NDFC release 12.2.2.
service_endpoint
ePBR service endpoint template for L4-L7 services.
|
Field |
Description |
|
General Parameters |
|
|
Enable Probe |
Check the box to enable the probe of the (reversed) next hop address. The probe uses loopback fabric-wide settings, as set in the Per VRF Per VTEP Loopback IPv4 Auto-Provisioning and Per VRF Per VTEP Loopback IPv6 Auto-Provisioning fields under Resources for that fabric. Refer to Data Center VXLAN EVPN for more information. |
|
Protocol |
Specify the protocol to be used for the probe. Options are:
|
|
Port Number |
Displayed for input only if the protocol is tcp or udp. Enter the port number for the probe. Valid ranges: 1 - 65535 (recommended range:1025-65534). |
|
User Input for HTTP Probe |
Displayed for input only if the protocol is http. Enter a user input text/filename for an HTTP probe (for example: http://192.168.50.254/index.html). Maximum size: 99. |
|
Advanced |
|
|
Threshold |
Enter the threshold value, in seconds. Valid range: 1 - 60. |
|
Frequency |
Enter the frequency value in seconds. Valid range: 1 - 604800. |
|
Delay Down Change Notification |
Enter the delay down change notification value, in seconds. Valid range: 1 - 180. |
|
Delay Up Change Notification |
Enter the delay up change notification value, in seconds. Valid range: 1 - 180. |
|
Timeout |
Enter the timeout value, in seconds. Valid range: 1 - 604800. |
Service Function Route Templates
service_static_route
|
Field |
Description |
|
Static Routes |
Enter the static routes in the Static Routes field. You can enter one static route per line. |
|
Export Gateway IP |
Click to export the gateway IP (the service node IP) address as the next-hop address. |
service_ebgp_route
|
Field |
Description |
|
General Parameters |
|
|
Service Node ASN |
Specify the service node ASN, with these minimum and maximum values:
|
|
Service Node IP Address |
Specify the IPv4 address or address with netmask (for example, 1.2.3.4 or 1.2.3.1/24). An IPv4 or IPv6 address is mandatory. |
|
Use Auto-Created Per VRF Per VTEP Loopback |
Check the box to use the automatically-created per VRF per VTEP loopback IP address. Only applicable when the Per VRF Per VTEP Loopback IPv4/IPv6 Auto-Provisioning option is enabled in the fabric setting. |
|
Loopback IP |
Specify the IPv4 address of the loopback on the switch. Loopback IPv4 or IPv6 address is mandatory. |
|
vPC Peer’s Loopback IP |
Specify the IPv4 address of the peer switch’s loopback. The switch with the smaller serial number will take this value. |
|
Export Gateway IP |
Click to export the gateway IP (the service node IP) address as the next-hop address. |
|
Advanced |
|
|
Service Node IPv6 Address |
Specify the IPv6 address of the neighbor. |
|
Loopback IPv6 |
Specify the IPv6 address of the loopback on the switch. |
|
vPC Peer’s Loopback IPv6 |
Specify the IPv6 address of the peer switch’s loopback. |
|
Route-Map TAG |
Specify the route-map tag that is associated with the interface IP. |
|
IPv4 Inbound Route-Map |
Specify the IPv4 inbound route map. No route map is used if this field is left blank. |
|
IPv4 Outbound Route-Map |
Specify the IPv4 outbound route map. If this field is left blank, the system uses |
|
IPv6 Inbound Route-Map |
Specify the IPv6 inbound route map. No route map is used if this field is left blank. |
|
IPv6 Outbound Route-Map |
Specify the IPv6 outbound route map. If this field is left blank, the system uses |
|
Interface Description |
Enter a description for the interface. |
|
Local ASN |
Specify a local ASN to override the system ASN. |
|
Advertise Host Routes |
Select this option to enable advertisement of /32 and /128 routes to the edge routers. |
|
Enable eBGP Password |
Select this option to enable the eBGP password. Enabling this option automatically enables the following Inherit eBGP Password from Fabric Settings field. |
|
Inherit eBGP Password from Fabric Settings |
Select this option to inherit the eBGP password from the Fabric Settings. Enabling this option automatically disables the following eBGP Password and eBGP Authentication Key Encryption Type fields. |
|
eBGP Password |
Enabled if you did not enable the Inherit eBGP Password from Fabric Settings field above. If enabled, enter the encrypted eBGP Password hex string. |
|
eBGP Authentication Key Encryption Type |
Enabled if you did not enable the Inherit eBGP Password from Fabric Settings field above. If enabled, enter the BGP key encryption type:
|
|
Enable Interface |
Clear this option to disable the interface. By default, the interface is enabled. |
|
vPC |
|
|
Peering via vPC Peer-Link |
Check this box to configure per-VRF peering through the vPC peer-link. Normally, you might enable the vPC advertise-pip option at the fabric level. Use this Peering via vPC Peer-Link option if you don’t want to have the vPC advertise-pip setting for all of the vPC pairs in the fabric. This option is also needed if you have a shared border deployment with Layer 4 to Layer 7 devices. The remaining fields in this tab become available only if you enable the Peering via vPC Peer-Link option. |
|
Source IP Address/Netmask |
Specify the source IP address and netmask. For example, 192.168.10.1/30. |
|
Destination IP Address |
Specify the destination IP address. For example, 192.168.10.2. The switch with the smaller serial number will take this value. |
|
Source IPv6 Address/Prefix |
Specify the source IPv6 address and netmask. For example, 2001:db9::1/120. |
|
Destination IPv6 Address |
Specify the destination IPv6 address. For example, 2001:db9::10. The switch with the smaller serial number will take this value. |
|
VLAN for Peering Between vPC Peers |
Enter a value for the VLAN peering between vPCs (minimum: 2, maximum: 4094). If no value is specified in this field, the VLAN ID will be automatically assigned from the VLAN pool shown in the vPC Peer Link VLAN Range field on the vPC tab of fabric setting screen. |
Service Chain Templates
The following service chain template is available beginning with NDFC release 12.2.2.
service_epbr
Service chain policy template for L4-L7 services.
|
Field |
Description |
|
Hashing Method |
Choose the load balance method. Valid options are:
|
|
Hashing Bucket |
Enter the buckets for traffic distribution, in powers of 2. Max: 256. |
Service Node Link Templates
service_link_trunk
|
Field |
Description |
|
General Parameters |
|
|
MTU |
Specifies the MTU for the interface. By default, this is set to jumbo. |
|
SPEED |
Specifies the speed of the interface. By default, this is set to Auto. You can change it to different supported speeds as required. |
|
Trunk Allowed Vlans |
Specify 'none',' all', or VLAN ranges. By default, none is specified. |
|
Enable BPDU Guard |
Specify an option from the drop-down list. The available options are true, false, or no. By default, no is specified. |
|
Enable Port Type Fast |
Check this option to enable spanning tree edge port behavior. By default, this is enabled. |
|
Enable Interface |
Clear the check box to disable the interface. By default, the interface is enabled. |
|
Advanced |
|
|
Source Interface Description |
Enter a description for the source interface. |
|
Destination Interface Description |
Enter a description for the destination interface. |
|
Source Interface Freeform Config |
Enter any addition CLI for the source interface. |
|
Destination Interface Freeform Config |
Enter any addition CLI for the destination interface. |
service_link_port_channel_trunk
|
Field |
Description |
|
Port Channel Mode |
Select a port channel mode from the drop-down list. By default, active is specified. |
|
Enable BPDU Guard |
Specify an option from the drop-down list. The available options are true, false, or no. |
|
MTU |
Specifies the MTU for the interface. By default, this is set to jumbo. |
|
Trunk Allowed Vlans |
Specify 'none',' all', or VLAN ranges. By default, none is specified. |
|
Port Channel Description |
Enter a description for the port channel. |
|
Freeform Config |
Specify the required freeform configuration CLIs. |
|
Enable Port Type Fast |
Check this option to enable spanning tree edge port behavior. By default, this is enabled. |
|
Enable Port Channel |
Check this option to enable the port channel. By default, this is enabled. |
service_link_vpc
This template has no specifiable parameters.
Service Insertion Template
service_pbr
|
Field |
Description |
|
General Parameters |
|
|
Protocol |
Select a protocol from the drop-down list. The options are icmp, ip, tcp, and udp. |
|
Source Port |
Specify a source port number. If ip or icmp was selected in the Protocol field above, then the value in this Source Port field is ignored. |
|
Destination Port |
Specify a destination port number. If ip or icmp was selected in the Protocol field above, then the value in this Destination Port field is ignored. |
|
Advanced |
|
|
Route Map Action |
Select an action from the drop-down list. The options are permit or deny. If you select permit, the matched traffic is redirected based on the next-hop option and the defined policy. If you select deny, the traffic is routed based on the routing table rules. |
|
Next Hop Option |
Specify an option for the next-hop. The options are none, drop-on-fail, and drop.If you select none, the matched traffic is redirected based on the defined PBR rules. If you select drop-on-fail, the matched traffic is dropped if the specified next hop is not reachable. If you select drop, the matched traffic is dropped. |
|
ACL Name |
Specify a name for the generated access control list (ACL). If not specified, this is auto-generated. |
|
ACL Name for reversed traffic |
Specify a name for the ACL that is generated for reversed traffic. If not specified, this is auto-generated. |
|
Route map match number |
Specify a route map match number. A valid value ranges from 1 to 65535. If not specified, a route map match sequence number will be retrieved from the predefined resource pool. This number is associated with the name of the ACL. |
|
Route map match number for reversed traffic |
Specify a route map match number for reversed traffic. A valid value ranges from 1 to 65535. If not specified, a route map match sequence number will be retrieved from the predefined resource pool. This number is associated with the name of the ACL that has been generated for reversed traffic. |
You can also customize the templates based on specific requirements.
Copyright
THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS" WITH ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: https://www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
© 2017-2024 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.