Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine 6.0 Release Notes
This document provides information about Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine, including product overview, new features and functionality, compatibility information, and known issues and limitations.
Product Overview
Network operators are facing challenges to support the exponential growth of network traffic while addressing the pressure to efficiently run network operations. They need a toolset to help automate bandwidth optimization and efficiently steer traffic with little operator intervention. Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine fulfills this need by providing real-time network optimization capabilities that allow operators to effectively maximize network utility as well as increase service velocity.
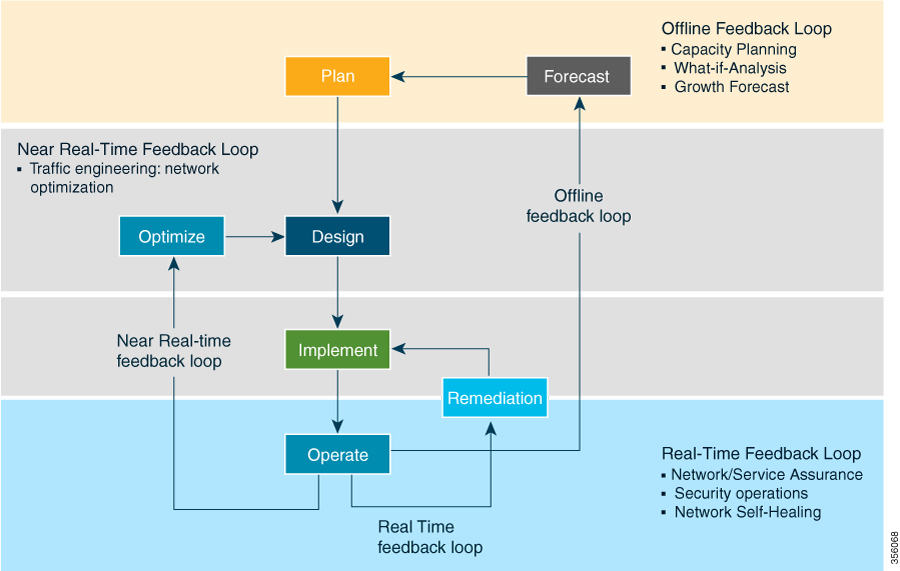
Looking at the following figure, Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine is built to fulfill the need for a closed-loop optimization loop as described under “Near Real-Time Feedback Loop”. Through Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine, the operator is able to define the optimization intent, implement the intent, and continuously monitor, track, and react to maintain the original intent.
Real-time Visibility
To run their network effectively, end-to-end visibility is important to any network operator. Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine not only provides this visibility, but also the ability to visualize the network across different layers and the relationship between each layer. Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine leverages IETF-standard BGP-LS protocol to discover IP network automatically, including the following features:
-
Real-time visibility: Provides the network operator with a true representation of the actual topology
-
Hierarchical topology view: Enables operators to define the different levels of granularity in the topology visualization
Simplified SR-TE Policy and RSVP-TE Tunnel Lifecycle Management
Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine also provides an easy to use UI and API to manage and monitor the TE tunnel lifecycle. The UI and API enables the network operator to perform the following tasks:
-
Visualize SR-TE (SR-MPLS and SRv6) policies and RSVP-TE tunnels.
-
Create, modify, and remove SR-MPLS policies and RSVP-TE tunnels using an intuitive workflow
-
Continuously track SR-MPLS policies and RSVP-TE tunnels and use dynamic path computations to maintain SLA objectives
-
Preview an SR-MPLS policy or RSVP-TE tunnel before deploying it to the network
Extensibility through Feature Packs
Crosswork Optimization Engine feature packs to help tackle bandwidth management, network congestions, and prevent over capacity utilization. A user defines the bandwidth optimization intent and the tools implement the intent, and continuously monitor, track, and react to maintain the original intent. A user can also define network congestion thresholds and configure whether to have the tool automatically remediate congestion or provide mitigation suggestions the operator can choose to act upon. The following feature packs are available with appropriate licensing. For licensing and ordering information, work with your Cisco Partner or Cisco Sales representative.
Bandwidth on Demand
As the name suggests, Bandwidth on Demand allows an operator/user to provision a Segment Routing Traffic Engineering (SR-TE)–based policy with a requested bandwidth between a specific set of devices. It is a soft bandwidth guarantee and can include a secondary optimization objective such as latency/TE/IGP.
Local Congestion Mitigation
Local Congestion Mitigation resolves congestion issues at the local interface level. This is done by rerouting traffic via tactical SR-TE policies only between devices on either side of the congested link. This way, the mitigation is localized to the congested interface and the end-to-end policy is not rerouted. This feature allows for operators to regain some control of the network by introducing a human in the loop. Upon congestion detection, mitigation recommendations are provided to the user and applied to the network only upon user confirmation. It can also be used as a monitoring tool to understand long-term congestion and failure patterns in the network, which will enable operators to augment capacity or perform maintenance in the identified parts of the network.
SR Circuit Style Manager
Segment Routing Circuit-Style (SR Circuit-Style) is a new way to provide a predictable way to transport circuit-like services (Optical circuits, TDM) over a Segment Routing network. To do so, SR Circuit-Style provides a bandwidth management mechanism that will guarantee that a given service will get the necessary bandwidth along its path (and along its backup path). The SR policy itself is supposed to follow some strict rules when provisioned: explicit path only, co-routed, bi-directional (guaranteed latency), bandwidth guaranteed, fault protected and diversity.
What's New
This section lists new features and changes delivered in Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine 6.0.
|
Feature |
What's New |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Local Congestion Mitigation (LCM) feature pack |
|
||||
|
SR Circuit Style Manager (CSM) feature pack |
|
||||
|
Bandwidth on Demand feature pack |
|
||||
|
Flexible Algorithm |
|
||||
|
Tree-SID |
PCE warnings and path compute elements are displayed in Tree-SID policy details: 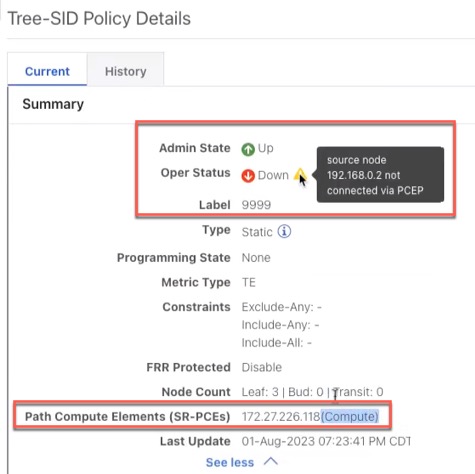 |
||||
|
Performance Metrics of TE policies |
When Service Health is installed and SR-PM collection is enabled, you can view KPI metrics (Delay, Jitter, and Liveness) from the Traffic Engineering table or from the TE tunnel details. To view the KPI metrics for the policy:
SR-MPLS policies KPI metrics contain Delay, Delay Variance (Jitter) or Liveness (Boolean value) along with traffic utilization. For example: 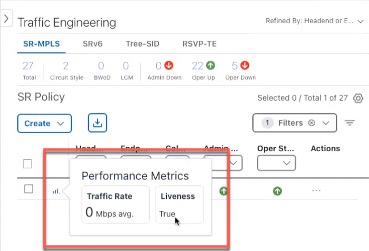 RSVP-TE Tunnel KPI metrics include Delay and Delay Variance (Jitter) along with Utilization. For example: 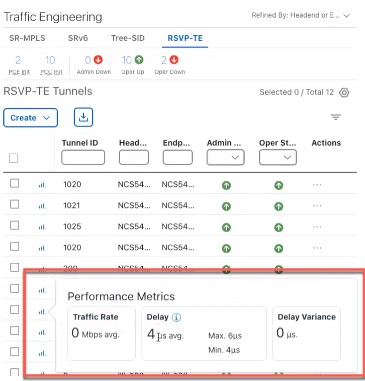 |
||||
|
Asymmetric delay for links |
In previous releases, only one side of the link delay value for an interface was considered during computation. When you configure delays on both remote and local nodes, the calculation of each delay on each interface is now taken into consideration when computing a path.
|
||||
|
Unique TE tunnel and device detail URLs |
TE tunnel or device details are now assigned unique URLs that can be shared. The URL sends the user to the Policy or Device Details page after logging in. To get to the unique URL:
 |
||||
|
Increased performance and memory footprint |
Major improvement in topology discovery time, network model building, and processing cache, bandwidth, metric, and TE tunnel type information. |
 Note |
Cisco Crosswork Infrastructure is a microservices-based platform and is the foundation required for running Crosswork Optimization Engine. For a list of new Cisco Crosswork Infrastructure features, see Cisco Crosswork Network Controller 6.0.x Release Notes. |
Compatibility Information
The following table details Crosswork Optimization Engine support for IOS Versions, SR-PCE, and Cisco devices. A later table indicates compatibility with Cisco Crosswork applications, NSO Function Packs, and browsers.
Cisco IOS Support
We recommend that the SR-PCE version you use be equal to or higher than the PCC software version. PCC 7.11.1 is recommended and has been validated to work with Crosswork Optimization Engine 6.0 features. Other listed PCC versions are supported, but may not support all Crosswork Optimization Engine features because of PCC version limitations.
 Note |
Software Maintenance Updates (SMUs) are required for both PCC/Headend and SR-PCE versions indicated in the table. To download the Cisco IOS XR versions and updates, see the IOS XR Software Maintenance Updates (SMUs) document. The correct SMUs to download will have "Optima" or the bug ID appended to the filename. For example: asr9k-x64-7.3.2.Optima.tar or xrv9k-7.3.2.CSCvy63506.tar. |
|
Cisco IOS XR |
Cisco ASR 9901 (64-bit) |
Cisco XRv 90001 | Cisco 8000 series | Cisco NCS 5500 series |
Cisco NCS 540 series2 |
Cisco NCS 560 series |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
7.3.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.3.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.4.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.4.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.5.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.6.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.7.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.7.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.8.1 + SMU (CSCwc93705) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.8.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.9.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.9.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.10.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.11.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS XE Version |
Cisco ASR 920 |
Cisco ASR 903 RSP 3 |
|---|---|---|
|
17.4.13 |
|
|
|
17.5.1 |
|
|
|
17.6.3 |
|
|
|
17.7.1 |
|
|
|
17.8.1 |
|
|
|
17.9.1 |
|
|
|
17.12.1 |
|
|
 Note |
|
Cisco Crosswork Application, NSO Function Pack, and Browser Support
The following table lists software versions that have been tested and are known to be compatible with Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine. For complete installation requirements, see the Cisco Crosswork Network Controller 6.0 Installation Guide.
| Hardware/Software | Supported Version |
|---|---|
|
Cisco Crosswork Infrastructure |
Version 6.0 |
|
Crosswork Data Gateway |
Version 6.0 |
|
Browsers |
|
Networking Technology Support
The following is the networking support information for SR-PCE 7.11.1.
| Category |
Description |
Notes / Details |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR |
SR-MPLS PCE initiated policies |
Policies that are provisioned or discovered by Cisco Crosswork. |
||
|
SR |
PCC initiated policies and ODN policies |
Policies that are discovered by Cisco Crosswork. |
||
|
SR |
Explicit path SR-TE policies |
Policies that are PCC initiated (SID list with labeled SID list with addresses), PCE reported, PCE initiated. Includes SRv6 TE discovery of PCC initiated policies. |
||
|
SR |
Dynamic path SR-TE policies |
PCC computed, PCE reported, PCE delegated |
||
|
SR |
Single consistent Segment Routing Global Block (SRGB) configured on routers throughout domain covered by Cisco Crosswork |
— |
||
|
SR |
Egress Peer Engineering (EPE) PeerAdjacency SIDs, PeerNode SIDs |
|
||
|
SR |
Prefix SID |
Regular/Strict Node SIDs + FA. Includes SRv6 Locators. |
||
|
SR |
Adjacency SID |
B-flag (protected/unprotected), P-flag (Persistent). Includes SRv6 Locators. |
||
|
SR |
SR policy optimization objective min-metric (IGP, TE, and Latency) |
PCE initiated provisioning and PCC initiated discovery |
||
|
SR |
SR policy path constraints (affinity and disjointness, protected segments) |
|
||
|
SR |
Binding SID for explicit or dynamic policies |
Discovered for PCC initiated and PCE initiated policies. It is configurable for PCE initiated policies. |
||
|
SR |
Profile ID (Discovered and configurable for PCE-init) |
Parameter used for applying features on PCC to PCE initiated policies. |
||
|
SR |
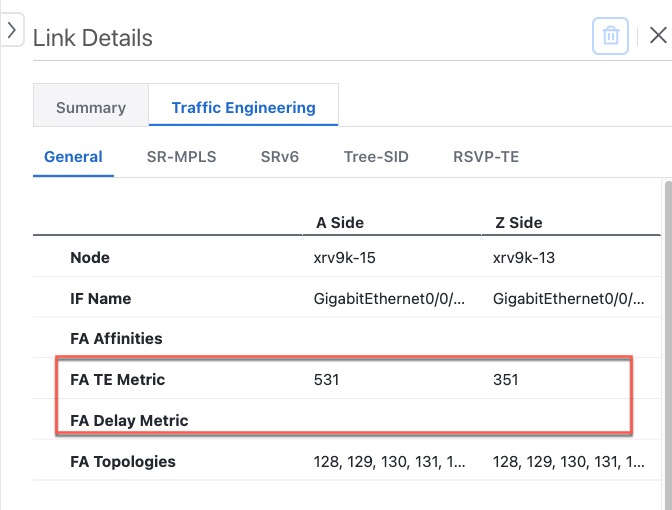
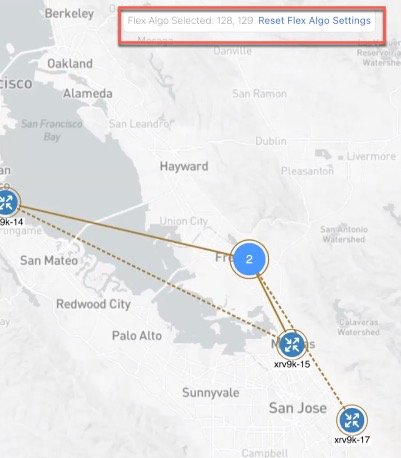
Flexible Algorithm (Flex Algo) for SR-MPLS and SRv6 policies |
|
||
|
SR |
Discovery and visualization of multiple candidate paths |
— |
||
|
SR |
Binding SIDs as Segment List Hops for SR policies |
Discovery and visualization of PCC initiated policies. |
||
|
SR |
Tree-SID |
Visualization and provisioning of PCE initiated policies. |
||
|
SR |
SR policies with Loopback IPs (Prefixes) other than TE router ID for headend/endpoint and prefix SIDs in segment list |
Prefix (node) SIDs associated with specific IGP domain / area. |
||
|
SR |
Maximum SID Depth (MSD) |
|
||
|
SR |
Global Max Latency |
Configured on PCE and applied to all PCE delegated SRTE policies with a latency metric. |
||
|
SR |
Inter-domain SRTE policies (inter-IGP domain, inter-AS) |
PCE delegated and Bandwidth on Demand policies. |
||
|
SR |
Node SID reuse across different IGP domains |
Recommended to not reuse node SIDs in adjacent IP domains. Inter domain explicit path policies with a label-only hop that is a node SID used in adjacent domains may be unresolvable if hop after ABR hop. |
||
|
SR-IGP |
Application-Specific Link Attribute (ASLA) Delay / TE metric |
Crosswork collects and uses ASLA delay and TE metric in Flex Algo topology computations and SRTE policy IGP paths. |
||
|
SR-IGP |
Visualizing native SR-IGP path |
Path Query OAM feature to use traceroute on device to report actual SR-IGP multi-paths to destination node (SR-MPLS only) |
||
|
SR |
Dynamic Circuit Style |
Path computation and bandwidth reservation through the Circuit Style feature pack. |
||
|
RSVP |
PCE initiated tunnels (provisioned by or discovered by Cisco Crosswork), PCC initiated tunnels discovered by Cisco Crosswork |
— |
||
|
RSVP |
ERO strict hops, ERO loose hops (PCC initiated only) |
— |
||
|
RSVP |
FRR protection on Cisco Crosswork provisioned tunnels |
— |
||
|
RSVP |
Path optimization objective min-metric (IGP|TE|Latency) |
— |
||
|
RSVP |
Path constraints (affinity, disjointness) |
Only 2 RSVP tunnels per disjoint group or sub-id | ||
|
RSVP |
Binding Label (explicit | dynamic) |
— |
||
|
RSVP |
Signaled Bandwidth |
— |
||
|
RSVP |
Setup and Hold Priority |
— |
||
|
RSVP |
Path Protection (partial support) |
Paths discovered as independent tunnels if multiple paths are up. Cisco XR only reports active path. Other vendors may report all active paths. |
||
|
PCEP |
PCEP Session discovery |
Each PCEP session a PCC has with a PCE along with its details is displayed as part of node details |
||
|
IPv4/IPv6 |
Dual Stack IPv4 or IPv6 |
Nodes can be IPv4, IPv6 or IPv4/IPv6 capable |
||
|
IPv4 |
Unnumbered Interfaces (partial) |
Topology discovery, SR policies with unnumbered IF hops discovery/provisioning, LCM policy support |
||
|
IPv6 |
IPv6 Link Local Interfaces |
Discovery of IPv6 link local interfaces as part of topology and as a hop in an SRv6 TE policy |
||
|
IPv6 |
IPv6 Router ID |
Nodes with IPv6 and IPv6 Router ID only with support for SRv6 only |
|
Category |
Description |
Notes / Details |
|---|---|---|
|
SR |
Provisioning multiple candidate paths via Cisco Crosswork |
— |
|
SR |
Per-Flow Policies (PFP) |
PFP (ODN or manually configured) not supported in PCEP. This PFP is the mapping of forward class to PDP with matching color and EP. Underlying PDP is reported as normal. |
|
SR |
Multiple segment lists per candidate path |
This configuration is not supported in Crosswork. These segment lists will not be discovered if configured on a PCC. High level requirements:
|
|
SR |
Anycast SIDs |
— |
|
SR |
SR policy provisioned (SR-PCE initiated) with IPv6 endpoints or hops |
— |
|
SR |
SR-MPLS policy optimization objective min-metric with margin |
Not supported for policies provisioned by Cisco Crosswork. Margin is not discovered for PCC initiated policies. |
|
SR |
SR-MPLS policy constraints (resource exclusion or metric bound) |
Not supported for policies provisioned by Cisco Crosswork. Constraints are not discovered for PCC initiated policies. |
|
SR |
Heterogeneous SRGBs |
Different SRGBs configured on nodes are not supported. SRGB must be configured to ensure proper discovery and visualization of SR policy paths. |
|
SR |
Egress Peer Engineering (EPE) Peer Set SIDs |
No discovery |
|
SR |
Routers that are not SR-capable |
All nodes assumed SR capable when computing SR policy IGP paths. LCM and BWoD SR policy path computation will not exclude non-SR capable nodes in IGP path. |
|
SRv6 |
PCE initiated provisioning of SRv6 policies is not supported. |
— |
|
SRv6 |
Traffic collection on SRv6 policies is not currently supported. |
Requires telemetry (gNMI) for policy counters (no SNMP support) |
|
IGP |
ISIS Overload bit |
Affects IGP paths for all policies and PCE path computation (BWoD, LCM). PCE reports but does not process. |
|
IGP |
OSPF MADJ Interfaces |
No support for discovering OSPF Multi-area adjacencies |
|
IGP |
Multiple IGP instances on same interface |
Single interface that participates in multiple IGP instances are not supported. |
|
IGP |
Cisco Crosswork supports L1 or L2 adjacencies on links but not both on the same link. |
— |
|
RSVP |
Configuring loose hop Explicit Route Object (ERO) in Crosswork |
Only strict hops can be configured. If strict hops are not configured for every hop along the path and those hops are not remote interface IPs or loopbacks, unexpected behavior may occur |
|
RSVP |
Named tunnels configured on PCCs |
Required for Juniper RSVP HEs |
|
RSVP |
Tunnels with Loopback IPs other than TE router ID for headend/endpoint and path hops |
— |
|
RSVP |
Display of active FRR protected path in UI |
Cisco Crosswork will discover FRR tunnels which are displayed in UI but will not associate an actively protected tunnel with the FRR tunnel. Path in UI will not include FRR protected path when protection is active. |
|
RSVP |
P2MP tunnels |
— |
|
RSVP |
Path protected RSVP LSPs |
No association between paths discovered. |
|
LDP |
Local Congestion Mitigation (LCM) in Mixed SR/LDP networks |
LCM will not work in a mixed SR/LDP network with PEs that are LDP only. LDP traffic destined to the LDP-only egress PE attempted to be steered into Autoroute LCM tactical polices will be blackholed |
|
IPv4 |
IPv4 Unnumbered Interfaces |
BWoD, Circuit Style Support, and RSVP |
|
IPv4/IPv6 |
Secondary IP addresses for interfaces |
Not supported. Unpredictable behavior if discovered. |
|
IPv4/IPv6 |
Overlapping IP addresses in different IGP domains |
IP addresses for IGP interfaces and nodes (router-ids) are assumed to be unique across all domains |
|
IPv6 |
IPv6 Router ID |
SR and RSVP not supported (SRv6 only) |
Installation Notes
Cisco Crosswork Infrastructure (Cisco Crosswork) is a microservices-based platform that must be installed prior to installing Crosswork Optimization Engine. For complete installation steps, see the Cisco Crosswork Network Controller 6.0 Installation Guide.
 Note |
Download the Crosswork Optimization Engine Application tar.gz file to a directory on your machine. After Cisco Crosswork and Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway are installed, install Crosswork Optimization Engine using the Cisco Crosswork UI (Administration > Crosswork Manager > Application Management > Applications tab > Add File). For more information, see Step 2 in Install Crosswork Applications). |
Upgrade Crosswork Optimization Engine Feature Packs
If you have enabled feature packs (CSM, LCM, or BWoD) in Crosswork Optimization Engine 5.0 and want to upgrade to Crosswork Optimization Engine 6.0, you must perform the following tasks prior to upgrading:
LCM
-
From the LCM Configuration page:
-
Set the Delete Tactical SR Policies when Disabled option to False. This task must be done prior to disabling LCM so that tactical polices deployed by LCM remain in the network after the upgrade.
-
Set the Enable option to False. If LCM remains enabled, there is a chance that tactical policies may be deleted after the upgrade.
-
Note all options (Basic and Advanced) in the LCM Configuration page so that you can confirm the same configuration has been migrated after the upgrade.
-
-
Export the current list of interfaces managed by LCM (Traffic Engineering > Local Congestion Mitigation > Export icon). Confirm the interfaces are valid by reimporting the CSV file without errors. For more information, see "Add Individual Interface Thresholds".
-
After the upgrade, wait until the Traffic Engineering page shows all the nodes and links before enabling LCM
Note:
After the system is stable and before enabling domains for LCM, confirm that the migration of previously monitored interfaces has completed and that each domain has the expected configuration options.
-
Navigate to Administration > Alarms > All > Events and enter LCM to filter the Source column.
-
Look for the following event: "Migration complete. All migrated LCM interfaces and policies are mapped to their IGP domains". If this message does not appear wait for the Congestion Check Interval period (set in the LCM Configuration page), then restart LCM (Administration > Crosswork Manager > Optimization Engine > optima-lcm > ... > Restart).
-
Wait until the optima-lcm service changes from Degraded to Healthy state.
-
For each domain, navigate to the Configuration page and verify the options have been migrated successfully. If the domain configurations are incorrect, restart LCM (Administration > Crosswork Manager > Optimization Engine > optima-lcm > ... > Restart).
-
Check the Events page for the event mentioned above and the Configuration page to verify the options.
 Note |
|
CSM
-
Set the Enable option to False.
-
Note all options (Basic and Advanced) in the CSM Configuration page so that you can confirm the same configuration has been migrated after the upgrade.
-
After the upgrade, wait until the Traffic Engineering page shows all the nodes and links before enabling CSM.
-
Circuit Style SR-TE policies will go to operation down (Oper Down) state if CSM is not enabled within 8 hours after disabling.
BWoD
-
Set the Enable option to False. If BWoD remains enabled, there is a chance that tactical policies may be deleted after the upgrade
-
Note all options (Basic and Advanced) in the BWoD Configuration page so that you can confirm the same configuration has been migrated after the upgrade.
-
After the upgrade, wait until the Traffic Engineering page shows all the nodes and links before enabling BWoD.
Product Documentation
The following table lists the guides that Cisco provides for Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine.
Visit the Cisco Crosswork Network Controller Information Center to find direct links to topics within functional areas. You also can access all Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine end user documentation at https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/cloud-systems-management/crosswork-optimization-engine/model.html.
 Note |
We sometimes update the documentation after original publication. Therefore, you should always review the documentation on Cisco.com for any updates. |
|
Documentation Title |
What is Included |
|---|---|
|
Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine 6.0 Release Notes |
This document |
|
Shared installation guide for all the Cisco Crosswork applications and their common infrastructure. Covers:
|
|
|
Shared administration guide for all the Cisco Crosswork applications and their common infrastructure. Covers:
|
|
|
|
|
Open Source Software Used in Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine |
Lists of licenses and notices for open source software used in Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine. |
|
API Documentation |
Advanced users can extend the Cisco Crosswork functionality using the APIs. API documentation is available on Cisco Devnet. |
Related Product Documentation
You can access documentation for all Cisco Crosswork products at https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/cloud-systems-management/crosswork-network-automation/tsd-products-support-series-home.html
Known Issues and Limitations
The following section details the known issues and limitations for Cisco Crosswork Optimization.
TE Dashboard
-
Traffic Utilization is not supported on Tree-SID and SRv6 policies.
-
You cannot view the IGP path on the historical data when an event is selected.
-
The metric type for BWoD policies are not visible on the TE Dashboard.
-
Hop count metric and BWoD type are not shown in the TE Dashboard under metric/policy type.
-
State and Path change events are not visible in the Historic tab of a policy until you zoom in by 5 to 6 clicks.
IPv4 Unnumbered Interfaces
-
Bandwidth on Demand and SR Circuit Style Manager feature packs will not factor in IPv4 unnumbered interfaces.
-
Tree-SID policies are not supported.
-
RSVP-TE PCE-initiated tunnels are not supported.
Tree-SID
-
Only static Tree-SID policies can be created via the UI. Also, you can only update and delete static Tree-SID policies that have been created via the UI.
-
Tree-SID policies are only supported on devices running Cisco IOS XR software.
-
PCE HA is not supported if the static Tree-SID policy was configured manually on the device (not via the UI).
-
Tree-SID policies are not deleted from the UI when the SR-PCE in HA mode is down.
-
IPv4 Unnumbered interfaces are not supported.
-
Tree-SID policies are not supported in Label Switch Multicast (LSM) routing. In cases where LSM is enabled, IGP updates and traffic utilization data are not supported.
-
LCM will not operate in portions of the network carrying Tree-SID LSPs.
-
On Cisco 8000 Series Routers, only static Tree-SID policies with leaf role are supported.
-
The RestConf API is not supported.
-
Tree-SID policy details do not show IPv6 router ID or SRv6 core information.
SR-MPLS
-
In the SR-MPLS provisioning screen and while previewing an SR-MPLS policy with an IPv6 address, a parsing error is displayed instead of correct error message: "Request Failed. Endpoint address is IPv6, IPv6 provisioning is not supported yet."
-
Updating the SID constraint on an existing policy is not allowed by the SR-PCE. The modification screen gives a successful update message, instead of a warning message that it is not allowed.
APIs
-
The Topology API cannot discover and report IPv6 Link-Local style links.
-
The Dashboard Export API cannot export CSV files to an external location. It can only export to /mnt/cw_glusterfs/bricks/rscoean/export.
BWoD
-
BWoD gets disabled when SR Policy Traffic field has 'Measured' selected and Policy Violation field has 'Strict' selected.
PCE Initiated SR-TE Policy and RSVP-TE Tunnel Behavior After an High Availability Switchover
After a switchover in a High Availability setup, PCE initiated SR-TE policies and RSVP-TE tunnels created after the last cluster data synchronization will not be manageable and are considered orphan TE policies. Crosswork will display an alarm when it finds orphan TE policies (Administration > Alarms). You can use APIs to help clear these orphan policies so that they are manageable. For more information, see API documentation on Devnet.
Bugs
If you encounter problems while working with Cisco Crosswork, please check this list of open bugs (.xlsx file). Each bug ID in the list links to a more detailed description and workaround. You can use the Cisco Bug Search Tool to search for bugs.
-
Go to the Cisco Bug Search Tool.
-
Enter your registered Cisco.com username and password, and click Log In.
The Bug Search page opens.

Note
-
To search for all Cisco Crosswork bugs, from the Product list select and enter additional criteria (such as bug ID, problem description, a feature, or a product name) in the Search For field. Examples: "Optimization Engine" or "CSCwc62479".
-
When the search results are displayed, use the filter tools to narrow the results. You can filter the bugs by status, severity, and so on.
 Tip |
To export the results to a spreadsheet, click Export Results to Excel. |
Security
Cisco takes great strides to ensure that all our products conform to the latest industry recommendations. We firmly believe that security is an end-to-end commitment and are here to help secure your entire environment. Please work with your Cisco account team to review the security profile of your network.
For details on how we validate our products, see Cisco Secure Products and Solutions and Cisco Security Advisories.
If you have questions or concerns regarding the security of any Cisco products, please open a case with the Cisco Customer Experience team and include details about the tool being used and any vulnerabilities it reports.
Accessibility Features
For a list of accessibility features in Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine, visit https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/about/accessibility/voluntary-product-accessibility-templates.html (VPAT) website, or contact accessibility@cisco.com.
All product documents except for some images, graphics, and charts are accessible. If you would like to receive the product documentation in audio format, braille, or large print, contact accessibility@cisco.com.
Obtain Additional Information and Submit a Service Request
Information about Cisco products, services, technologies, and networking solutions is available from various online sources.
-
Sign up for Cisco email newsletters and other communications at:
-
Visit the Cisco Customer Experience website for the latest technical, advanced, and remote services to increase the operational reliability of your network. Go to:
-
Obtain general networking, training, and certification titles from Cisco Press publishers at:
-
To submit a service request, visit Cisco Support.
Support and Downloads
The Cisco Support and Downloads website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies.
Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Downloads website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password.
For more information:
 Feedback
Feedback