Configure AireOS Wireless LAN Controller and Lightweight Access Point
Available Languages
Download Options
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Contents
Introduction
This document describes the configuration steps to register the Lightweight Access Point to the WLC and basic operation of the LWAPP wireless network.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
-
Basic knowledge of the configuration of lightweight APs and Cisco WLCs.
-
Basic knowledge of Lightweight AP Protocol (LWAPP).
-
Knowledge of the configuration of an external DHCP server and/or domain name server (DNS).
-
Basic configuration knowledge of Cisco switches.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
Cisco Aironet 1232AG Series Lightweight AP
-
Cisco 4402 Series WLC that runs firmware version 5.2.178.0
This configuration works with any other Cisco WLC and any lightweight AP.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Background Information
In order for the WLC to be able to manage the LAP, the LAP must discover the controller and register with the WLC. There are different methods that an LAP uses in order to discover the WLC. For detailed information on the different methods the LAPs use to register to the WLCs, refer to Lightweight AP (LAP) Registration to a Wireless LAN Controller (WLC).
This document describes the configuration steps needed to register the LAP to the WLC and for basic operation of the LWAPP wireless network.
Configure
In order to register the LAP to the WLC and for basic operation of the LWAPP wireless network, complete these steps:
1. Have a DHCP server present so that the APs can acquire a network address.
Note: Option 43 is used if the APs reside in a different subnet.
2. Configure the WLC for Basic Operation
3. Configure the Switch for the WLC
4. Configure the Switch for the APs
5. Register the lightweight APs to the WLCs.
Configure the WLC for Basic Operation
When the controller boots at factory defaults, the bootup script runs the configuration wizard, which prompts the installer for initial configuration settings. This procedure describes how to use the configuration wizard on the command-line interface (CLI) in order to enter initial configuration settings.
Note: Be sure that you understand how to configure an external DHCP server and/or DNS.
Complete these steps in order to configure the WLC for basic operation:
1. Connect your computer to the WLC with a DB-9 null modem serial cable.
2. Open a terminal emulator session with these settings:
- 9600 baud
- 8 data bits
- 1 stop bit
- No parity
- No hardware flow control
3. At the prompt, log in to the CLI.
The default username is admin , and the default password is admin .
4. If necessary, enter reset system in order to reboot the unit and start the wizard.
5. At the first wizard prompt, enter a system name. The system name can include up to 32 printable ASCII characters.
6. Enter an administrator user name and password. The user name and password can include up to 24 printable ASCII characters.
7. Enter the service-port interface IP configuration protocol, either none or DHCP .
Enter none if you do not want to use the service port or if you want to assign a static IP address to the service port.
8. If you entered none in step 7 and need to enter a static IP address for the service port, enter the service-port interface IP address and netmask for the next two prompts.
If you do not want to use the service port, enter 0.0.0.0 for the IP address and netmask.
9. Enter values for these options:
- Management interface IP address
- Netmask
- Default router IP address
- Optional VLAN identifier
You can use a valid VLAN identifier or 0 for untagged.
Note: When the management interface on the controller is configured as part of the 'native vlan' on the switchport to which it connects, the controller must NOT tag the frames. Therefore, you must set the VLAN to be zero (on the controller).
10. Enter the Network Interface (Distribution System) Physical Port number.
For the WLC, the possible ports are 1 through 4 for a front-panel gigabit Ethernet port.
11. Enter the IP address of the default DHCP server that supplies IP addresses to clients, the management interface, and the service-port interface, if you use one.
12. Enter the LWAPP Transport Mode, either LAYER2 or LAYER3 .
Note: If you configure the WLC 4402 via Wizard and select AP transport Mode LAYER2 , the Wizard does not ask the details of AP Manager
13. Enter the Virtual Gateway IP Address.
This address can be any fictitious, unassigned IP address, such as 10.1.1.1, for the Layer 3 Security and Mobility managers to use.
Note: Usually the Virtual Gateway IP Address that is used is a private address.
14. Enter the Cisco WLAN Solution Mobility Group/RF Group name.
15. Enter the WLAN 1 service set identifier (SSID) or network name.
This identifier is the default SSID that lightweight APs use in order to associate to a WLC.
16. Allow or disallow Static IP Addresses for clients.
Enter yes in order to allow clients to supply their own IP addresses. Enter no in order to require clients to request an IP address from a DHCP server.
17. If you need to configure a RADIUS server on the WLC, enter yes and enter this information:
- RADIUS server IP address
- The communication port
- The shared secret
If you do not need to configure a RADIUS server or you want to configure the server later, enter no .
18. Enter a country code for the unit.
Enter help in order to see a list of the supported countries.
19. Enable and disable support for IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11a, and IEEE 802.11g.
20. Enable or disable radio resource management (RRM) (auto RF).
| WLC 4402—Configuration Wizard |
|---|
Welcome to the Cisco Wizard Configuration Tool Use the '-' character to backup System Name [Cisco_43:eb:22]: c4402 Enter Administrative User Name (24 characters max): admin Enter Administrative Password (24 characters max): ***** Service Interface IP Address Configuration [none][DHCP]: none Enable Link Aggregation (LAG) [yes][NO]: No Management Interface IP Address: 192.168.60.2 Management Interface Netmask: 255.255.255.0 Management Interface Default Router: 192.168.60.1 Management Interface VLAN Identifier (0 = untagged): 60 Management Interface Port Num [1 to 2]: 1 Management Interface DHCP Server IP Address: 192.168.60.25 AP Transport Mode [layer2][LAYER3]: LAYER3 AP Manager Interface IP Address: 192.168.60.3 AP-Manager is on Management subnet, uses same values AP Manager Interface DHCP Server (192.168.50.3): 192.168.60.25 Virtual Gateway IP Address: 10.1.1.1 Mobility/RF Group Name: RFgroupname Network Name (SSID): SSID Allow Static IP Addresses [YES][no]: yes Configure a RADIUS Server now? [YES][no]: no Enter Country Code (enter 'help' for a list of countries) [US]: US Enable 802.11b Network [YES][no]: yes Enable 802.11a Network [YES][no]: yes Enable 802.11g Network [YES][no]: yes Enable Auto-RF [YES][no]: yes |
Note: The WLC management interface is the only interface from outside of the WLC that consistently allows pinging. So it is an expected behavior if you are not able to ping the AP manager interface from outside of the WLC.
Note: You must configure the AP manager interface in order for the APs to associate with the WLC.
Configure the Switch for the WLC
This example uses a Catalyst 3750 switch that uses only one port. The example tags the AP-manager and management interfaces and places these interfaces on VLAN 60. The switch port is configured as an IEEE 802.1Q trunk and only the appropriate VLANs, which are VLANs 2 through 4 and 60 in this case, are allowed on the trunk. The management and AP-manager VLAN (VLAN 60) is tagged and is not configured as the native VLAN of the trunk. So when the example configures those interfaces on the WLC, the interfaces are assigned a VLAN identifier.
This is an example 802.1Q switch port configuration:
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1 description Trunk Port to Cisco WLC switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk allowed vlan 2-4,60 switchport mode trunk no shutdown
Note: When you connect the WLC gigabit port, make sure it is connected to the switch gigabit port only. If you connect the WLC gigabit Ethernet to the Switch FastEthernet port then it does not work.
Notice that this configuration example configures the neighbor switch port in a way that only allows relevant VLANs on the 802.1Q trunk. All other VLANs are pruned. This type of configuration is not necessary, but it is a deployment best practice. When you prune irrelevant VLANs, the WLC only processes relevant frames, which optimizes performance.
Configure the Switch for the APs
This is an example VLAN interface configuration from the Catalyst 3750:
interface VLAN5 description AP VLAN ip address 10.5.5.1 255.255.255.0
While the Cisco WLCs always connect to 802.1Q trunks, Cisco lightweight APs do not understand VLAN tagging and must only be connected to the access ports of the neighbor switch.
This is an example switch port configuration from the Catalyst 3750:
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/22 description Access Port Connection to Cisco Lightweight AP switchport access vlan 5 switchport mode access no shutdown
The infrastructure is now ready for connection to the APs. The LAPs use the different WLC discovery methods and select a WLC to join. The LAP then registers with the controller.
Here is a link to a video on the Cisco Support Community that explains the initial configuration of Wireless LAN Controller that uses the CLI and GUI:Initial configuration of Wireless LAN Controller with the CLI and GUI .
Verify
Use this section in order to confirm that your configuration works properly.
After the LAPs register with the controller, you can view them under Wireless at the top of the user interface of the controller:
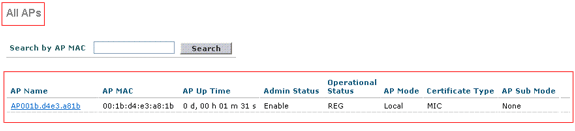 Top of the User Interface Controller
Top of the User Interface Controller
On the CLI, you can use the show ap summary command in order to verify that the LAPs registered with the WLC:
(Cisco Controller) >show ap summary Number of APs.................................... 1 Global AP User Name.............................. Not Configured Global AP Dot1x User Name........................ Not Configured AP Name Slots AP Model Ethernet MAC Location Port Country Priority ------------------ ----- ------------------- ----------------- ---------------- ---- ------- ------ AP001b.d4e3.a81b 2 AIR-LAP1232AG-A-K9 00:1b:d4:e3:a8:1b default location 2 IN 1
On the WLC CLI, you can also use the show client summary command in order to see the clients that are registered with the WLC:
(Cisco Controller) >show client summary Number of Clients................................ 1 MAC Address AP Name Status WLAN Auth Protocol Port ----------------- ------------- ------------- ---- ---- -------- ---- 00:40:96:a1:45:42 ap:64:a3:a0 Associated 4 Yes 802.11a 1 (Cisco Controller) >
Here is a video demonstration that explains how to perform the initial configuration of a Wireless LAN Controller that uses the GUI and CLI: Initial configuration of Wireless LAN Controller with the CLI and GUI .
Troubleshoot
Use this section in order to troubleshoot your configuration.
Commands
Use these commands in order to troubleshoot your configuration.
Note: Refer to Important Information on Debug Commands before you use debug commands.
This debug lwapp events enable WLC command output shows that the lightweight AP gets registered to the WLC:
(Cisco Controller) >debug lwapp events enable
Tue Apr 11 13:38:47 2006: Received LWAPP DISCOVERY REQUEST from AP
00:0b:85:64:a3:a0 to ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff on port '1'
Tue Apr 11 13:38:47 2006: Successful transmission of LWAPP Discovery-Response
to AP 00:0b:85:64:a3:a0 on Port 1
Tue Apr 11 13:38:58 2006: Received LWAPP JOIN REQUEST from AP
00:0b:85:64:a3:a0 to 00:0b:85:33:a8:a0 on port '1'
Tue Apr 11 13:38:58 2006: LWAPP Join-Request MTU path from AP 00:0b:85:64:a3:a0
is 1500, remote debug mode is 0
Tue Apr 11 13:38:58 2006: Successfully added NPU Entry for AP
00:0b:85:64:a3:a0 (index 48) Switch IP: 192.168.60.2, Switch Port: 12223,
intIfNum 1, vlanId 60 AP IP: 10.5.5.10, AP Port: 19002, next hop MAC:
00:0b:85:64:a3:a0
Tue Apr 11 13:38:58 2006: Successfully transmission of LWAPP Join-Reply to AP
00:0b:85:64:a3:a0
Tue Apr 11 13:38:58 2006: Register LWAPP event for AP
00:0b:85:64:a3:a0 slot 0
Tue Apr 11 13:38:58 2006: Register LWAPP event for AP 00:0b:85:64:a3:a0 slot 1
Tue Apr 11 13:39:00 2006: Received LWAPP CONFIGURE REQUEST from AP
00:0b:85:64:a3:a0 to 00:0b:85:33:a8:a0
Tue Apr 11 13:39:00 2006: Updating IP info for AP 00:0b:85:64:a3:a0 --
static 0, 10.5.5.10/255.255.255.0, gtw 192.168.60.1
Tue Apr 11 13:39:00 2006: Updating IP 10.5.5.10 ===> 10.5.5.10 for AP
00:0b:85:64:a3:a0
Tue Apr 11 13:39:00 2006: spamVerifyRegDomain RegDomain set for slot 0 code 0
regstring -A regDfromCb -A
Tue Apr 11 13:39:00 2006: spamVerifyRegDomain RegDomain set for slot 1 code 0
regstring -A regDfromCb -A
Tue Apr 11 13:39:00 2006: spamEncodeDomainSecretPayload:Send domain secret
Mobility Group<6f,39,74,cd,7e,a4,81,86,ca,32,8c,06,d3,ff,ec,6d,95,10,99,dd>
to AP 00:0b:85:64:a3:a0
Tue Apr 11 13:39:00 2006: Successfully transmission of LWAPP
Config-Message to AP 00:0b:85:64:a3:a0
Tue Apr 11 13:39:00 2006: Running spamEncodeCreateVapPayload for SSID 'SSID'
Tue Apr 11 13:39:00 2006: AP 00:0b:85:64:a3:a0 associated. Last AP failure was
due to Configuration changes, reason: operator changed 11g mode
Tue Apr 11 13:39:00 2006: Received LWAPP CHANGE_STATE_EVENT from AP
00:0b:85:64:a3:a0
Tue Apr 11 13:39:00 2006: Successfully transmission of LWAPP Change-State-Event
Response to AP 00:0b:85:64:a3:a0
Tue Apr 11 13:39:00 2006: Received LWAPP Up event for AP 00:0b:85:64:a3:a0 slot 0!
Tue Apr 11 13:39:00 2006: Received LWAPP CONFIGURE COMMAND RES from AP
00:0b:85:64:a3:a0
Tue Apr 11 13:39:00 2006: Received LWAPP CHANGE_STATE_EVENT from AP
00:0b:85:64:a3:a0
Tue Apr 11 13:39:00 2006: Successfully transmission of LWAPP Change-State-Event
Response to AP 00:0b:85:64:a3:a0
Tue Apr 11 13:39:00 2006: Received LWAPP Up event for AP
00:0b:85:64:a3:a0 slot 1!
This output shows these useful WLC debug commands:
-
debug pem state enable— Configures the access policy manager debug options
-
debug pem events enable
-
debug dhcp message enable— Shows the debug of DHCP messages that are exchanged to and from the DHCP server
-
debug dhcp packet enable— Shows the debug of DHCP packet details that are sent to and from the DHCP server
Tue Apr 11 14:30:49 2006: Applied policy for mobile 00:40:96:a1:45:42
Tue Apr 11 14:30:49 2006: STA [00:40:96:a1:45:42, 192.168.1.41] Replacing Fast
Path rule type = Airespace AP Client on AP 00:0B:85:64:A3:A0, slot 0
InHandle = 0x00000000, OutHandle = 0x00000000 ACL Id = 255, Jumbo Frames
= NO, interface = 1 802.1P = 0, DSCP = 0, T
Tue Apr 11 14:30:49 2006: Successfully plumbed mobile rule for mobile
00:40:96:a1:45:42 (ACL ID 255)
Tue Apr 11 14:30:49 2006: Plumbed mobile LWAPP rule on AP 00:0b:85:64:a3:a0
for mobile 00:40:96:a1:45:42
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: DHCP proxy received packet, src: 0.0.0.0,
len = 320
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: dhcpProxy: Received packet: Client 00:40:96:a1:45:42
DHCP Op: BOOTREQUEST(1), IP len: 320, switchport: 1, encap: 0xec03
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: dhcpProxy(): dhcp request, client:
00:40:96:a1:45:42: dhcp op: 1, port: 1, encap 0xec03, old mscb
port number: 1
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: dhcp option len, including the magic cookie = 84
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: dhcp option: received DHCP REQUEST msg
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: dhcp option: skipping option 61, len 7
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: dhcp option: requested ip = 192.168.1.41
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: dhcp option: skipping option 12, len 15
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: dhcp option: skipping option 81, len 19
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: dhcp option: vendor class id = MSFT 5.0 (len 8)
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: dhcp option: skipping option 55, len 11
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: dhcpParseOptions: options end, len 84, actual 84
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: mscb->dhcpServer: 192.168.60.2, mscb->dhcpNetmask:
255.255.255.0,mscb->dhcpGateway: 192.168.60.1, mscb->dhcpRelay:
192.168.60.2 VLAN: 60
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: Local Address: 192.168.60.2, DHCP Server:
192.168.60.2, Gateway Addr: 192.168.60.2, VLAN: 60, port: 1
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: DHCP Message Type received: DHCP REQUEST msg
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: op: BOOTREQUEST, htype: Ethernet, hlen: 6, hops: 1
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: xid: 3371152053, secs: 0, flags: 0
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: chaddr: 00:40:96:a1:45:42
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: ciaddr: 0.0.0.0, yiaddr: 0.0.0.0
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: siaddr: 0.0.0.0, giaddr: 192.168.60.2
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: Forwarding DHCP packet locally (348 octets) from
192.168.60.2 to 192.168.60.2
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: Received 348 byte dhcp packet from 0x0201a8c0
192.168.60.2:68
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: DHCP packet: 192.168.60.2 -> 192.168.60.2 uses
scope "InternalScope"
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: received REQUEST
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: Checking node 192.168.1.41 Allocated 1144765719,
Expires 1144852119 (now: 1144765853)
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: adding option 0x35
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: adding option 0x36
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: adding option 0x33
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: adding option 0x03
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: adding option 0x01
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: dhcpd: Sending DHCP packet (giaddr:192.168.60.2)to
192.168.60.2:67 from 192.168.60.2:1067
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: sendto (548 bytes) returned 548
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: DHCP proxy received packet, src: 192.168.60.2,
len = 548
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: dhcpProxy: Received packet: Client 00:40:96:a1:45:42
DHCP Op: BOOTREPLY(2), IP len: 548, switchport: 0, encap: 0x0
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: dhcp option len, including the magic cookie = 312
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: dhcp option: received DHCP ACK msg
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: dhcp option: server id = 192.168.60.2
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: dhcp option: lease time (seconds) = 86400
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: dhcp option: gateway = 192.168.60.1
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: dhcp option: netmask = 255.255.255.0
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: dhcpParseOptions: options end, len 312, actual 64
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: DHCP Reply to AP client: 00:40:96:a1:45:42,
frame len 412, switchport 1
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: DHCP Message Type received: DHCP ACK msg
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: op: BOOTREPLY, htype: Ethernet, hlen: 6, hops: 0
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: xid: 3371152053, secs: 0, flags: 0
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: chaddr: 00:40:96:a1:45:42
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: ciaddr: 0.0.0.0, yiaddr: 192.168.1.41
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: siaddr: 0.0.0.0, giaddr: 0.0.0.0
Tue Apr 11 14:30:53 2006: server id: 10.1.1.1 rcvd server id: 192.168.60.2
You can use these additional debug commands in order to troubleshoot your configuration:
-
debug lwapp errors enable — Shows output of the debug of LWAPP errors
-
debug pm pki enable — Shows the debug of certificate messages that are passed between the AP and the WLC
Troubleshoot a Lightweight Access Point that Does Not Join a Wireless LAN Controller
Refer to Troubleshoot a Lightweight Access Point that Does Not Join a Wireless LAN Controller for information on some of the issues why a Lightweight Access Point (LAP) fails to join a WLC and how to troubleshoot the issues.
Related Information
- Lightweight AP (LAP) Registration to a Wireless LAN Controller (WLC)
- Wireless LAN Controller (WLC) Software Upgrade
- Primary and Backup images on a Wireless LAN Controller(WLC)
- Troubleshoot a Lightweight Access Point that Does Not Join a Wireless LAN Controller
- Wireless LAN Controller (WLC) Configuration Best Practices
- Cisco Technical Support & Downloads
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
3.0 |
23-Jan-2024 |
Recertification |
2.0 |
22-Dec-2022 |
Updated formatting and usage. Recertification. |
1.0 |
03-Apr-2006 |
Initial Release |
Contributed by Cisco Engineers
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback