Configure and Troubleshoot Cisco IOS Telephony Service (ITS)
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
Cisco IOS Telephony Service (ITS), formerly known as IP Keyswitch, is an IP Telephony call processing solution integrated into Cisco IOS® Software that fits in the Cisco Architecture for Voice, Video, and Integrated Data (AVVID). The basic concept is to provide minimal PBX/key-switch functionality to a small number of IP phones directly attached to the voice gateway. Cisco ITS can be deployed in instances where a branch office either does not have a WAN or has WAN connectivity through satellite links.
Cisco ITS makes sense in situations where a customer would like to add a telephony service at such a site without necessarily requiring all of the telephony features found in Cisco CallManager. This document describes a sample deployment of the ITS feature in a sample network.
Note: Cisco ITS is not the same, nor are the features the same, as the Survivable Remote Site Telephony (SRST) feature that is used in conjunction with Cisco CallManager.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Before attempting this configuration, please ensure that you meet the following prerequisites:
-
Familiarity with Cisco IOS Telephony Service Version 2.01.
-
A basic understanding of TCP/IP fundamentals, such as IP addressing, DHCP, Network Time Protocol (NTP), TFTP, and HTTP
-
A basic understanding of Cisco IOS Software fundamentals, such as command-line interface (CLI) configuration
-
A basic understanding of Voice over IP (VoIP) fundamentals, such as configuring dial-peers, voice ports, and quality of service (QoS)
Components Used
The information in this document is based on the following software and hardware versions:
-
Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(8)T or later, with a minimum of IP Plus (IP/VOX Plus on the 1700 series) feature set. This document assumes Cisco ITS 2.0 support in Cisco IOS Software.
-
Cisco 3660 Gateway with IOS Software Release 12.2(11)T with the IP PLUS feature set is used in the configuration example, although most IAD 2400, 1700, 2600, 3600, and 3700 series routers are currently applicable. Please check the Cisco IOS Software release notes for current version and software support information.
-
The Cisco ITS 2.0.3 software bundle was used in this example. You can download this bundle from Software Download: Cisco CallManager Express/ITS and SRST (registered customers only) .
-
To support Cisco ITS, it is recommended that you have the maximum amount of memory for each platform, especially if the maximum number of phones and the Distinguished Names (DNs) for the platform are to be configured.
-
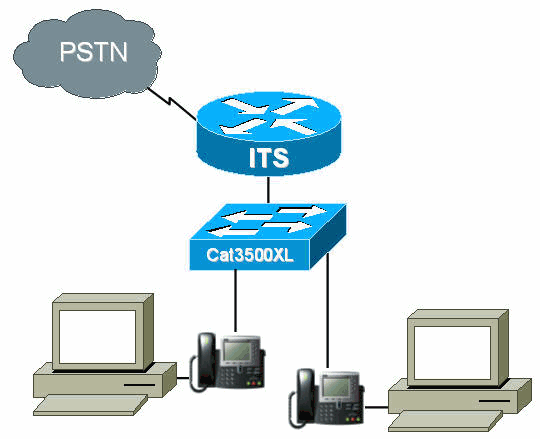
In this example, a Catalyst 3500 Series XL switch is used as the branch office switch. Configure separate VLANs for voice and data for quality and security reasons.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Network Diagram
This document uses the network setup shown in the diagram below.
Conventions
For more information on document conventions, refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions .
Background Information
The table below specifies information about voice and data transfer through the separate VLANs. It also specifies the network and interface addresses and ports.
| Purpose | VLAN | Network | Interface | Interface Address |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data | 50 | 10.1.50.0/24 | Fa0/0.50 | 10.1.50.1 / 24 |
| Voice | 150 | 10.1.150.0/24 | Fa0/0.150 | 10.1.150.1 / 24 |
The Cisco ITS router is a 3660 running Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(11)T with the IP Plus feature set. The Cisco ITS files should be downloaded in .tar or .zip format from Software Download: Cisco CallManager Express/ITS and SRST (registered customers only) .
Once extracted, each file must be transferred to the router's flash through TFTP. Do not erase the flash each time an individual file is copied. The following is a listing of the files found in Cisco ITS 2.0.3 (not all of these files are necessary).
| File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| P003G302.bin | The phone load to be used with Cisco ITS for the Cisco 7910 IP Phone. The phone load has a separate release note included that explains some of the fixes from previous versions. (Required) |
| P004G302.bin | The phone load to be used with Cisco ITS for the Cisco 7960 IP Phone. The phone load has a separate release note included that explains some of the fixes from previous versions. (Required) |
| admin_user.html | The administrator web page to configure the system |
| ephone_admin.html | The phone administration web page. |
| normal_user.html | The user (non-administrator) web page to administer phones for forwarding and other features. |
| telephony_service.html | The top-level web page that each user visits to configure phones or to configure the system as an administrator. (Optional) |
| logohome.gif | |
| en_dest_busy.au | A sample audio prompt for a busy extension. Used by the its_Cisco.2.0.0.tcl script. |
| en_dest_unreachable.au | A sample audio prompt for an unreachable extension. Used by the its_Cisco.2.0.0.tcl script. |
| en_disconnect.au | A sample audio prompt for a disconnected or unregistered extension. Used by the its_Cisco.2.0.0.tcl script. |
| en_enter_dest.au | A sample audio prompt for the user to enter a destination. Used by the its_Cisco.2.0.0.tcl script. |
| en_reenter_dest.au | A sample audio prompt for the user to reenter the destination. Used by the its_Cisco.2.0.0.tcl script. |
| en_welcome.au | A sample audio prompt for the user greeting. Used by the its_Cisco.2.0.0.tcl script. |
| its_Cisco.2.0.0.tcl | The TCL script for a sample Automated Attendant that can route calls to an extension. Uses the sample .au files to greet the user, prompt for a number, and route the call to the desired destination. |
| music-on-hold.au | A sample audio file used for music on hold. |
The following file is also part of the Cisco ITS-2.0.3.zip file, but does not need to be placed in the flash of the ITS router.
| File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| CiscoIOSTSP.zip | This Telephony Application Programming Interface (TAPI) Service Provider (TSP) was developed for Cisco ITS and acts as an interface between TAPI (part of the Windows 2000 Operating System) and the ITS. TSP allows TAPI-based applications such as Phone Dialer and ACT! software to provide call control to the IP phones on the Cisco ITS. The TAPI implementation on Cisco ITS is not a full TAPI stack, but a “TAPI Lite” implementation. It supports the following features:
Note: The TSP that ships with Cisco CallManager is not supported with ITS. |
Configurations
VLAN Configuration on the Catalyst 3500XL
Cisco ITS runs on the LAN where IP phones and Cisco CallManagers are connected to voice gateways through Catalyst switches. It is very important to configure these devices correctly with respect to the VLANS which carry the voice data. This section provides an overview of Catalyst 3500XL configuration and the corresponding LAN connection on the voice gateway 3660 router.
-
The voice and data VLAN should be set up with an unconfigured switch, as shown in the following example:
Cat3500BranchSwitch# vlan database Cat3500BranchSwitch(vlan)# vlan 50 name corporate-data-vlan VLAN 50 added: Name: corporate-data-vlan Cat3500BranchSwitch(vlan)# vlan 150 name corporate-voice-vlan VLAN 150 added: Name: corporate-voice-vlan Cat3500BranchSwitch(vlan)# Cat3500BranchSwitch(vlan)# exit APPLY completed. Exiting.... Cat3500BranchSwitch#
-
The following example is a sample configuration of the interface between the Catalyst 3500XL and the 3660 router:
interface FastEthernet0/1 description Port to 3660 (supports Dot1q) duplex full speed 100 switchport trunk native 50 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50,150,1002-1005 switchport mode trunk !
-
The following example is a port to be used for a phone connection:
interface FastEthernet0/2 description DOT1Q port to IP Phone switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk native vlan 50 switchport mode trunk switchport voice vlan 150 spanning-tree portfast !
For further information, refer to Catalyst 2900 Series XL and Catalyst 3500 Series XL Switches.
VLAN Configuration on the Cisco ITS Router
Follow the steps below to configure VLANs on the Cisco ITS router.
-
The first step is to configure QoS parameters and VLANs on the 3660 interface, as shown below.
! class-map match-all L3-to-L2_VoIP-Cntrl match ip dscp af31 class-map match-all L3-to-L2_VoIP-RTP match ip dscp ef ! ! policy-map output-L3-to-L2 class L3-to-L2_VoIP-RTP set cos 5 class L3-to-L2_VoIP-Cntrl set COs 3 !
-
Now apply these policies to the interface and create the VLANs.
interface FastEthernet0/0 description Catalyst 3500 Branch Office Switch no ip address no ip mroute-cache load-interval 30 speed 100 full-duplex ! interface FastEthernet0/0.50 encapsulation dot1Q 50 ip address 10.1.50.1 255.255.255.0 service-policy output output-L3-to-L2 ! interface FastEthernet0/0.150 description native subnet 10.1.150.0 voice encapsulation dot1Q 150 ip address 10.1.150.1 255.255.255.0 service-policy output output-L3-to-L2 !
For further information, refer to Catalyst 2900 Series XL and Catalyst 3500 Series XL Switches.
DHCP Server Configuration on the Cisco ITS Router
The following step is necessary to configure a DHCP server on the 3660 router. You need this step only if you have an external DHCP server, not if your IP addresses are statically configured. The example below shows a DHCP scope for the IP phones and for other devices on the other VLAN.
ip dhcp excluded-address 10.1.50.1 10.1.50.10 ip dhcp excluded-address 10.1.150.1 10.1.150.10 ! ip dhcp pool ip-phones network 10.1.150.0 255.255.255.0 !--- This defines the range of IP addresses to be assigned. default-router 10.1.150.1 option 150 ip 10.1.150.1 !--- This must be the IP address of the ITS router. ! ip dhcp pool Data-clients network 10.1.50.0 255.255.255.128 default-router 10.1.50.1 domain-name cisco.com dns-server 10.1.50.100 netbios-name-server 10.1.50.100 !
Note: If you want to enable DHCP only for specific devices, you can create a DHCP scope with the host command (instead of a network command, as shown above). You must also configure a client-identifier and a hardware address for the IP phone you wish to give an IP address to. For the client-identifier, you must specify 01 + MAC address of phone, and the hardware address must contain the MAC address of the phone as the parameter.
For further information, refer to Cisco IOS DHCP Server.
Time Configuration on the Cisco ITS Router
Since the IP phones receive their Date/Time settings from the Cisco ITS router, it is important to ensure that the clock is set correctly on the router. It is highly recommended that you configure the NTP, if possible. Specify the time zone and, if necessary, daylight savings time, and configure the NTP server. An example is shown below.
its-router(config)# clock time EST -5 its-router(config)# clock summer-time EST recurring its-router(config)# ntp server 172.18.106.15
For more information about NTP, refer to Performing Basic System Management.
Cisco ITS Configuration on the 3660
Basic Configuration
The following configuration should be entered to configure Cisco ITS on the 3660:
telephony-service load 7910 P004G302 !--- This is the load file minus the .bin extension. !--- Only the 7910, 7940/7960, and 7935 IP Phones are supported. load 7960-7940 P003G302 !--- This is the load file minus the .bin extension. ip source-address 10.1.150.1 port 2000 !--- This is the ip address of the Cisco ITS router on the voice subnet. max-ephones 48 !--- This is the total number of phones that will be allowed to register. !--- The maximum varies by platform and sometimes by software level. max-dn 192 !--- This is the maximum number of directory numbers that can be configured !--- on this gateway (maximum varies by platform and sometimes by software level). voicemail 52222 !--- This is the number that will be dialed when the "Messages" !--- button is pressed on the phone (optional). !
Most of the remaining commands are optional. The only mandatory ones are the "load" statements (not all of which are necessary for all phones), which are the ip source-address, max-ephones, and max-dn commands.
Note: The Cisco ITS router is designed to work with load files from versions of Cisco CallManager earlier than 3.1; for example, load files that get their configuration from the SEPDEFAULT.cnf file, rather than from an XML file. Make sure this command is in the configuration:
tftp-server flash:XMLDefault.cnf.xml
Other telephony-service options are shown in the following example:
Its-router(config-telephony)# telephony-service
its-router(config-telephony)# ?
Cisco IOS Telephony Service configuration commands:
admin-password define password for admin user
admin-username define username for admin user
date-format Set date format for IP Phone display
default Set a command to its defaults
dialplan-pattern Define E.164 telephone number prefix
directory Define directory naming order
dn-webedit enable Edit DN through Web
exit Exit from telephony-service configuration mode
ip Define IP address and port for Telephony-Service/Fallback
keepalive Define keepalive timeout period to unregister IP phones
load Select the IP phone firmware load file
max-conferences Define max number of 3 party G.711 conferences
max-dn Maximum directory numbers supported
max-ephones Define max number of IP phones
moh Define music-on-hold filename
mwi Define IP address and port for MWI Server
no Negate a command or set its defaults
reset reset ethernet phone
time-format Set time format for IP Phone display
time-webedit enable Edit Time through Web
timeouts Define timeout value for IP phone
transfer-pattern Define valid call transfer destinations
url Define Ephone URL's
voicemail Set the voicemail access number called when the MESSAGES IP
phone button is pressed
its-router(config-telephony)#
 Caution: Many of the changes to the telephony service, such as changing the date or time format, require the phones to reset. Some options, such as changing the max-ephones or max-dn settings, require a full router reload. To reset all phones, enter the following:
Caution: Many of the changes to the telephony service, such as changing the date or time format, require the phones to reset. Some options, such as changing the max-ephones or max-dn settings, require a full router reload. To reset all phones, enter the following:
its-router(config-telephony)# telephony-service its-router(config-telephony)# reset all
Some of these options will be discussed in the following sections; others can be found by referring to Cisco IOS Telephony Service Version 2.01.
TFTP Configuration on the ITS Router
Follow the steps below to configure TFTP on the ITS router.
-
Make sure that all files have been properly transferred to the flash of the router. At the least, the load files P003G302.bin and P004G302.bin must be loaded. Once loaded, the flash should resemble the following example:
Its-router# show flash System flash directory: File Length Name/status 1 16084816 c3660-is-mz.122-11.T 2 229542 admin_user.html 3 42484 en_dest_busy.au 4 26376 en_dest_unreachable.au 5 14352 en_disconnect.au 6 19512 en_enter_dest.au 7 17167 en_reenter_dest.au 8 17486 en_welcome.au 9 4152 ephone_admin.html 10 5968 its_Cisco.2.0.0.0.tcl 11 29092 logohome.gif 12 496521 music-on-hold.au 13 35138 normal_user.html 14 268008 P003G302.bin 15 258360 P004G302.bin 16 522 telephony_service.html 17 54 SEPDEFAULT.cnf !--- This file will not show up until telephony-service is configured. 18 249 XMLDefault.cnf.xml !--- This file will not show up until telephony-service is configured. [17551227 bytes used, 49033349 available, 66584576 total] 65536K bytes of processor board System flash (Read/Write) its-router#
-
In the configuration, you must allow the IP phones to download the load files by TFTP from the Cisco ITS router. Note that these file names are case sensitive.
tftp-server flash:P003G302.bin tftp-server flash:P004G302.bin tftp-server flash:SEPDEFAULT.cnf tftp-server flash:XMLDefault.cnf.xml
-
The SEPDEFAULT.cnf and XMLDefault.cnf.xml files are created automatically once the telephony-service and ip source-address commands are issued.
-
The XMLDefault.cnf.xml file contains the IP address of one of the Ethernet ports of the router to which the ATA adapter should register. These files are specific to the router and cannot be shared by multiple routers.
IP Phone Configuration on the ITS Router
Follow the steps below to configure IP phones on the ITS router.
-
At this point, if the IP phones are plugged in and have received a DHCP address, they can register with the Cisco ITS router. They will not have any lines configured. You can verify that the phones are registered by issuing the show ephone command and looking at the output, which should resemble the following:
its-router# show ephone ephone-1 Mac:0006.D74B.0F46 TCP socket:[1] activeLine:0 REGISTERED mediaActive:0 offhook:0 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 paging 0 debug:0 IP:10.1.150.10 50568 Telecaster 7960 keepalive 889 max_line 6 ephone-2 Mac:0006.D74B.1361 TCP socket:[2] activeLine:0 REGISTERED mediaActive:0 offhook:0 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 paging 0 debug:0 IP:10.1.150.11 52397 Telecaster 7960 keepalive 872 max_line 6 ephone-3 Mac:0006.D74B.107C TCP socket:[3] activeLine:0 REGISTERED mediaActive:0 offhook:0 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 paging 0 debug:0 IP:10.1.150.12 51116 Telecaster 7960 keepalive 871 max_line 6 ephone-4 Mac:0008.E31B.7A8A TCP socket:[5] activeLine:0 REGISTERED mediaActive:0 offhook:0 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 paging 0 debug:0 IP:10.1.150.13 50321 Telecaster 7960 keepalive 867 max_line 6 its-router#
-
You can now configure these phones through the CLI or through web administration. (Refer to the Configuring Web Administration of the Cisco ITS Router section of this document.) Some special configuration information is available for the Cisco 7910 IP Phone in the Cisco ITS Configuration for the 7910 IP Phone section.
! ephone-dn 1 number 1000 name George P Burdell call-forward noan 52222 timeout 10 no huntstop ! ! ephone-dn 2 number 1000 name George P Burdell preference 1 call-forward busy 52222 call-forward noan 52222 timeout 10 ! ! ephone-dn 10 number 1111 name Helpdesk no huntstop ! ! ephone-dn 11 number 1111 name Helpdesk preference 1 ! ! ephone-dn 12 number 1111 name Helpdesk preference 2 ! ! ephone-dn 13 number 1111 name Helpdesk preference 3 !
-
Each ephone-dn represents one line. You can assign the lines to multiple phones, if desired. In this example, a user has been configured who has extension 1000 on two lines. A helpdesk line, which is a hunt group of four lines, has been added as well. Now configure the ephones, which assign the lines to the actual phone devices.
! ephone 1 username "gpburdell" password letmein mac-address 0006.D74B.0F46 button 1:10 2:11 3:12 4:13 5:1 6:2 ! ! ! ephone 2 Mac-address 0006.D74B.1361 button 1:15 2:10 3:11 4:12 5:13 speed-dial 1 1000 !
-
The button tags refer back to the ephone-dn tags. The show ephone command output should resemble the output below.
its-router# show ephone ephone-1 Mac:0006.D74B.0F46 TCP socket:[3] activeLine:0 REGISTERED mediaActive:0 offhook:0 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 paging 0 debug:0 IP:10.1.150.14 52311 Telecaster 7960 keepalive 6 max_line 6 button 1: dn 10 number 1111 IDLE button 2: dn 11 number 1111 IDLE button 3: dn 12 number 1111 IDLE button 4: dn 13 number 1111 IDLE button 5: dn 1 number 1000 IDLE button 6: dn 2 number 1000 IDLE Username: gpburdell Password: letmein ephone-2 Mac:0006.D74B.1361 TCP socket:[2] activeLine:0 REGISTERED mediaActive:0 offhook:0 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 paging 0 debug:0 IP:10.1.150.11 50512 Telecaster 7960 keepalive 7 max_line 6 button 1: dn 15 number 1001 IDLE button 2: dn 10 number 1111 IDLE button 3: dn 11 number 1111 IDLE button 4: dn 12 number 1111 IDLE button 5: dn 13 number 1111 IDLE speed dial 1:1000 its-router#
Ephone 1 Ephone 2 Line 1 1111 Line 1 1001 Line 2 1111 Line 2 1111 Line 3 1111 Line 3 1111 Line 4 1111 Line 4 1111 Line 5 1000 Line 5 1111 Line 6 1000 Line 6 George P Burdell -
When a call comes in to 1111, it rings until someone picks it up (no call-forwarding configured). If ephone-dn 10 (line 1 on ephone 1 or line 2 on ephone 2) is in use, then the next call to 1111 automatically goes to ephone-dn 10, because no huntstop is configured and the preference is higher (default preference is 0). If the preferences were the same, then both lines would ring.
-
If a call is placed to 1000 and no one picks up, it will roll to voicemail (extension 5222 in this call forwarding setup). If ephone-dn 1 is in use, the next call gets routed to ephone-dn 2. This is because of regular dial-peer routing and the fact that no huntstop is configured. It is not necessary to have a forward-busy setting in this case, unless you wanted the call to forward to a different DN altogether when busy (for example, if 1000 is busy, then forward to 1001). On the ephone-dn 2, you must configure the call forwarding for busy and no answer, because there is no other extension 1000 with a higher preference to route to (even if there were, you have huntstop implicitly configured, so the call would end there).
For more information on normal dial-peer routing, refer to Voice Technology Support.
Ephone 1 also has a username and password for "gpburdell." This will allow the user to access and log in to the same telephony_service.html web page and change his forwarding (busy, no answer, all) and speed dials, as well as perform local directory searches.
Ephone 2 has a speed dial on line 6. If that button is pressed, 1001 will dial 1000. The speed-dial command itself does not specify the button location. It says, in this case, that the first free line will be a speed dial to number 1000. The fact that it happens to be line 6 is not directly configured. If another speed dial were configured ("speed dial 2 1004," for example), it would not generate an error, but it would not display, either.
Some other configuration commands for ephone-dns listed below.
its-router(config-ephone-dn)# ? Ephone DN configuration commands: application The selected application call-forward Define E.164 telephone number for call forwarding caller-id Configure port caller id parameters cor Class of Restriction on dial-peer for this dn default Set a command to its defaults description dn desc, for DN Qualified Display Name exit Exit from ephone-dn configuration mode hold-alert Set Call On-Hold timeout alert parameters huntstop Stop hunting on Dial-Peers intercom Define intercom/auto-call extension number loopback-dn Define dn-tag to create loopback dn pair with this ephone-dn mwi set message waiting indicator options (mwi) name Define dn user name no Negate a command or set its defaults number Define E.164 telephone number paging set audio paging mode preference Preference for the attached dial-peer for the primary dn number translate Translation rule its-router(config-ephone-dn)#
Shown below are other configuration commands for ephones.
Its-router(config-ephone-dn)# ephone 1 its-router(config-ephone)# ? Ethernet phone configuration commands: button define button to dn map default Set a command to its defaults exit Exit from ephone configuration mode Mac-address define ethernet phone MAC address no Negate a command or set its defaults paging-dn set audio paging dn group for phone reset reset ethernet phone speed-dial Define ip-phone speed-dial number username define username to access ethernet phone from Web vm-device-id define voice-mail id string its-router(config-ephone)#
 Caution: After any change to the ephone or ephone-dn, the phones to which the changes apply must be reset. This can be done under the ephone itself with the reset command, or globally under the telephony-service configuration menu as described earlier.
Caution: After any change to the ephone or ephone-dn, the phones to which the changes apply must be reset. This can be done under the ephone itself with the reset command, or globally under the telephony-service configuration menu as described earlier.
Cisco ITS Configuration for the 7910 IP Phone
Unlike the 7960 IP Phone, the 7910 has only one line button. To support call waiting and transfer on this phone, two lines are required. So for this phone, you may configure two lines with the same DN as follows:
ephone-dn 20 number 1020 no huntstop ! ! ephone-dn 21 number 1020 preference 1 ! ... ephone 10 button 1:20 2:21 !
Even though these are two line appearances, it is not possible to place both of these lines on hold at the same time. When the primary line is on hold, pressing the line button selects the second line and a second call can be placed (or answered). Once the second call is connected, pressing the hold button will place the second call on hold and reconnect the primary line. Pressing the hold button again will toggle between the primary and secondary lines. Pressing the line button again will disconnect the currently connected party.
Configuring Web Administration of the Cisco ITS Router
To properly administer the Cisco ITS server through the web, as well as allow end users to administer their phones through the web, the following files must be present in flash:
-
admin_user.html
-
ephone_admin.html
-
logohome.gif
-
normal_user.html
-
telephony_service.html
To allow administration of the web pages through the web, the following global configuration commands must be entered:
ip http server ip http path flash
Other commands must be entered under the telephony-service configuration section.
telephony-service admin-username administrator !--- This sets up the administrator account used to access the web page. admin-password cisco !--- This sets up the password for the admin account. dn-webedit !--- (optional) This permits the editing of DNs through the web interface. time-webedit !--- (optional) This permits editing of the system time through the web interface. !
To access the Cisco ITS router through the web, point your browser to the following URL:
http://ITSrouter_ipaddr/telephony_service.html
The URL is the same for everyone. Other .html files are considered internal files called by the telephony-service.html web page. Calling other files directly can lead to JavaScript errors. Users who are to use the web page must be configured first on ephone, as shown below.
ephone 1 username "gpburdell" password letmein
The user (in this example, "gpburdell") can log in and change their forwarding information, perform directory searches, and even configure their own speed dial settings. There is online help available, as well.
Administrators can perform phone or DN adds, deletes, and changes, as well as some system changes. Note that there may be problems if you configure through the web as well as by the command line, because the web page does not poll the Cisco IOS Software configuration periodically, nor does the Refresh button on the browser update this information. In fact, when trying to refresh in that way, you will be logged out of the GUI page and see the “Configuration Change Failed, Configuration Change is not allowed” error message box. Only the Update button on the main menu retrieves the latest changes from the Cisco ITS router.
From the web page, the Write System Configuration button causes changes to be written immediately to NVRAM. However, for regular users, the changes are written every 10 minutes as long as there is no active session on vty, console, and aux lines.
Note: For Update to work, please make sure that at least four free vty lines are available in Cisco ITS, even though one free vty line is enough for normal configuration changes.
Call History information is also available to administrators. First it must be enabled by configuring as follows:
call-history-mib retain-timer 500 call-history-mib max-size 500
At most, 500 entries and 500 minutes of call history are retained in the MIB table.
You can view the call records by choosing View System Configuration from the GUI after logging in, and then choosing View Call History Information.
Configuring the PSTN Connection on the Cisco ITS Router
Assuming that the ITS router has voice interface cards, you will now want to configure those cards so that calls can be placed to and from the IP phones. This is not significantly different than other voice connections on a router. You can think of the ephones with the numbers that were assigned to each ephone-dn as Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) ports on the routers.
Configuring Other ITS Features
Hold Feature Configuration
One additional feature for outside callers is Music on Hold (MoH)/Tone on Hold (ToH). ToH is always on by default and cannot be disabled. MoH can be provided to public switched telephone network (PSTN) or G.711 on-net calls that are placed on hold. Calls from IP phone to IP phone on the same ITS router that are placed on hold always hear only the ToH beep. For MoH, after making sure that the audio file exists in flash, configure as follows:
telephony-service moh music-on-hold.au
The .au or .wav file played for MoH needs to be in the G.711 u-law or a-law format. In order to distinguish the call waiting from the ToH, the call waiting tone is heard as periodic beeps, with an interval of 10 seconds between beeps. If there are multiple lines of call waiting, only one tone is sent every 10 seconds. The ToH, however, is heard at periodic intervals of every 8 seconds and consists of three beeps (a single tone repeated three times). ToH takes higher precedence than the call waiting tone. If both tones should be played at exactly the same time, a user will hear the ToH first, then in 8 seconds, another ToH, and finally in two more seconds, a call waiting tone.
Once calls are placed on hold, there are several options, shown below, to send audible notifications to users that a call is still on hold.
Its-router(config-ephone-dn)# hold-alert 15 ? idle alert on-hold originator only if idle originator alert on-hold originator always shared alert all phones that share the line
A one-second ring alert at the configured interval (every 15 to 300 seconds) can be configured to always be sent to the party that placed the call on hold, or to be sent only if that party is idle. Another option is to configure the alert to be sent to all phones that share the same line. The default setting is for no alert, no matter how long a call has been on hold.
Conferencing Configuration
Three-way conferencing is supported as long as the parties are all G.711 users and conference resources are available. Conference resources are configured as follows:
telephony-service max-conferences 10
If one of the parties in a conference presses Hold, the other two parties will hear the MoH or ToH. However, they will also be able to talk to each other, with the music or tone playing in the background.
Transfer Configuration
The ability to transfer inbound calls often requires additional configuration. By default, Cisco ITS-registered IP phones can transfer to other IP phones registered to the same ITS router. Other transfers, to PSTN or VoIP destinations, are denied. To enable these types of transfers, transfer-patterns must be configured under the telephony-service as follows:
Telephony-service transfer-pattern 9.......
Now, assuming that there is a pots dial-peer to route the calls to the PSTN, an IP phone can now transfer calls to any seven-digit number by dialing 9 first. There is no option for secondary dial-tone with ITS.
 Caution: Be especially cautious when transferring calls that came in by a Foreign Exchange Office (FXO) port on the ITS router and went out by another FXO port, because this may cause both ports to remain in use even after both parties have hung up. Refer to Understanding FXO Disconnect Problem. If your provider cannot support a form of disconnect supervision with FXO, then do not allow transfers back to the PSTN.
Caution: Be especially cautious when transferring calls that came in by a Foreign Exchange Office (FXO) port on the ITS router and went out by another FXO port, because this may cause both ports to remain in use even after both parties have hung up. Refer to Understanding FXO Disconnect Problem. If your provider cannot support a form of disconnect supervision with FXO, then do not allow transfers back to the PSTN.
To transfer/forward calls that arrive from another VoIP destination (such as another ITS router), a loopback-dn is required. This is an advanced topic outside the scope of this document.
Intercom Configuration
The intercom feature allows a press-to-talk feature between two IP phones. It is not supported on shared lines, meaning that an ephone-dn that is configured for intercom operation must only be associated with one IP phone.
! ephone-dn 30 number A1234 name "Intercom" intercom A4321 label "Office A" ! ! ephone-dn 31 number A4321 name "Intercom" intercom A1234 label "Office B" ! ... ! ephone 3 Mac-address 0006.D74B.107C button 1:16 6:30 ! ! ! ephone 4 Mac-address 0008.E31B.7A8A button 1:17 6:31 !
Now, when ephone 4 presses line 6, a call is placed to line 6 of ephone 3 (for example, it calls A1234 automatically). By default, if the destination phone is on-hook, then it goes off-hook, goes to speaker mode, and mutes its microphone. Other options in the intercom command are barge-in and no-auto-answer. The barge-in option allows the inbound intercom call to force an existing call into the hold state. The phone then answers the intercom call immediately. The no-auto-answer option causes the intercom call to simply ring, instead of being automatically picked up.
With all intercom calls, the label configured with the intercom statement appears on the right side of the display, much like a speed dial would. Without the label option, the name (if configured on the ephone-dn) appears on the left side of the line display, while the intercom number is displayed on the right.
Note: Cisco does not recommend use of the Cisco 7910 for intercom functionality, because the phone does not have a microphone and the speaker cannot be unmuted, so the handset must be picked up to answer.
Paging Configuration
The paging feature works much like the intercom feature previously described, except that it provides only a one-way voice stream with no press-to-answer option. Only idle phones are reached by paging; phones in use will not receive the page. Paging supports audio distribution using unicast, multicast (up to ten devices), or both (so that the audio can reach phones that cannot be reached through multicast). Multicast paging is recommended. Each paging extension requires a unique IP multicast address.
For example, say that three paging groups are created: "Cool People," "Uncool People," and "All People," which is simply the sum of the first two groups. Multicast is the audio delivery method, so you would configure the following:
! ephone-dn 40 number 4001 name "Cool People" paging ip 239.0.1.20 port 2000 ! ! ephone-dn 41 number 4002 name "Uncool People" paging ip 239.0.1.21 port 2000 ! ! ephone-dn 42 number 4000 name "All People" paging ip 239.0.1.22 port 2000 paging group 40,41 !
Note: IP phones do not support multicast at 224.x.x.x addresses.
Now configure and assign each ephone to a paging DN as shown below (additional configuration on each ephone omitted). Remember that each IP phone can belong to only one paging group. Also, the ephone-dn configured for paging must not be assigned to a phone button.
! ephone 1 paging-dn 40 ! ephone 2 paging-dn 40 ! ephone 3 paging-dn 41 ! ephone 4 paging-dn 41 ! ephone 5 paging-dn 42 !
With this configuration, you have assigned the paging number 4001 ("Cool People") to ephones 1 and 2, paging number 4002 ("Uncool People") to ephones 3 and 4, and paging number 4000 ("All People") to ephones 1 to 5.
Any call to 4001 connects to ephones 1 and 2 (if they are not busy) for example.
Note: Paging is supported a maximum of one router hop away from the ITS router.
Verify
This section provides information you can use to confirm your configuration is working properly.
Certain show commands are supported by the Output Interpreter Tool ![]() (registered customers only) , which allows you to view an analysis of show command output.
(registered customers only) , which allows you to view an analysis of show command output.
The show telephony-service commands listed below (especially all) will give you a snapshot of the configuration.
its-router# show telephony-service ? admin Show telephony-service admin username and password all Show telephony-service details dial-peer Show telephony-service dialpeers ephone Show ephone configuration ephone-dn Show ephone-dn configuration voice-port Show telephony-service voice ports | Output modifiers <cr>
The show ephone commands listed below give you the current state of the IP phones. Most of the time, show ephone by itself is all that is necessary.
Its-router# show ephone ? 7910 7910 phone status 7940 7940 phone status 7960 7960 phone status H.H.H mac address dn Dn with tag assigned offhook Offhook phone status registered Registered ephone status remote non-local phones (with no arp entry) ringing Ringing phone status summary Summary of all ephone tapiclients Ephone status of tapi client telephone-number Telephone number assigned unregistered Unregistered ephone status | Output modifiers <cr>
The show ephone-dn command output will look very similar to show voice port command output. For most common problems, this command is not as useful as some of the other tools.
Its-router# show ephone-dn ? <1-960> dn tag loopback Show ephone-dn in loopback mode summary Summary of all ephone-dn | Output modifiers <cr>
Troubleshoot
This section provides information you can use to troubleshoot your configuration.
Troubleshooting Commands
Certain show commands are supported by the Output Interpreter Tool ![]() (registered customers only) , which allows you to view an analysis of show command output.
(registered customers only) , which allows you to view an analysis of show command output.
Note: Before issuing debug commands, please see Important Information on Debug Commands.
Cisco ITS has some additional troubleshooting commands and debugs that can make collecting information much easier.
There are a few debugs that may be useful when troubleshooting problems. The debug ephone command is the only Cisco ITS-specific command in that regard.
Its-router# debug ephone ? alarm Enable ephone alarm message debugging detail Enable ephone detail debugging error Enable ephone error debugging keepalive Enable ephone keepalive debugging loopback Enable ephone loopback debugging moh Enable ephone music-on-hold debugging mwi Enable ephone mwi debugging pak Enable ephone packet debugging raw Enable ephone raw protocol debugging register Enable ephone registration debugging state Enable ephone state debugging statistics Enable ephone statistics debugging
For most situations, when troubleshooting a problem between one or two phones, it is useful to issue the debug ephone error and debug ephone state commands, unless the problem specifically involves registration, Message Waiting Indicator (MWI), or MoH. If there are a lot of phones, then it is a good idea to limit the output to only the relevant MAC addresses. For example:
its-router# debug ephone state Mac-address 0009.433C.E5EC EPHONE state debugging is enabled for phone 0009.433C.E5EC
Problems such as calling remote VoIP destinations may require additional debug commands that are more general to VoIP on Cisco routers, such as the debug voip ccapi inout and debug vtsp all commands. Specifics for troubleshooting PSTN signaling and other implementation-specific items are not covered in this document. For more information, refer to the following documents:
Here is a sample debug ephone state command output for a call from 1004 to 1002. The relevant portion of the show ephone command output is shown below.
ephone-3 Mac:0006.D74B.107C TCP socket:[5] activeLine:0 REGISTERED mediaActive:0 offhook:0 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 paging 0 debug:1 IP:10.1.150.12 51718 Telecaster 7960 keepalive 92 max_line 6 button 1: dn 16 number 1002 IDLE ephone-4 Mac:0008.E31B.7A8A TCP socket:[2] activeLine:0 REGISTERED mediaActive:0 offhook:0 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 paging 0 debug:1 IP:10.1.150.13 50396 Telecaster 7960 keepalive 96 max_line 6 button 1: dn 17 number 1004 IDLE
Now you can examine the debug. The OFFHOOK message is seen, the call is placed (you do not see individual digits captured in this trace), and it is answered. The OpenReceive channel messages are sent to each phone and are later acknowledged; a StartMedia message tells each phone what IP address and port to send the audio to. In the end, the ONHOOK message is seen.
Its-router# debug ephone state EPHONE state debugging is enabled its-router# Sep 26 18:39:40.837: ephone-4[2]:OFFHOOK Sep 26 18:39:40.837: ephone-4[2]:SIEZE on activeline 0 Sep 26 18:39:40.837: ephone-4[2]:SetCallState line 1 DN 17 ref 52 TsOffHook Sep 26 18:39:40.837: DN 17 Voice_Mode Sep 26 18:39:40.837: dn_tone_control DN=17 tonetype=0:DtSilence onoff=0 pid=113 Sep 26 18:39:40.841: dn_tone_control DN=17 tonetype=33:DtInsideDialTone onoff=1 pid=113 Sep 26 18:39:40.841: dn_tone_control DN=17 tonetype=0:DtSilence onoff=0 pid=113 Sep 26 18:39:40.841: dn_tone_control DN=17 tonetype=33:DtInsideDialTone onoff=1 pid=113 Sep 26 18:39:42.349: dn_tone_control DN=17 tonetype=0:DtSilence onoff=0 pid=113 Sep 26 18:39:42.853: dn_tone_control DN=17 tonetype=0:DtSilence onoff=0 pid=113 Sep 26 18:39:43.105: dn_tone_control DN=17 tonetype=0:DtSilence onoff=0 pid=113 Sep 26 18:39:43.609: ephone-4[2]:Skinny-to-Skinny call DN 17 to DN 16 instance 1 Sep 26 18:39:43.609: ephone-4[2]:SetCallState line 1 DN 17 ref 52 TsRingOut Sep 26 18:39:43.609: ephone-4[2]:Call Info DN 17 line 1 ref 52 called 1002 calling 1004 origcalled calltype 2 Sep 26 18:39:43.609: ephone-4[2]: John Doe calling Sep 26 18:39:43.609: ephone-4[2]: Jane Doe Sep 26 18:39:43.609: dn_tone_control DN=17 tonetype=0:DtSilence onoff=0 pid=113 Sep 26 18:39:43.609: ephone-3[5]:SetCallState line 1 DN 16 ref 53 TsRingIn Sep 26 18:39:43.613: ephone-3[5]:Call Info DN 16 line 1 ref 53 called 1002 calling 1004 origcalled calltype 1 Sep 26 18:39:43.613: ephone-3[5]: John Doe calling Sep 26 18:39:43.613: ephone-3[5]: Jane Doe Sep 26 18:39:43.613: ephone-3[5]:Ringer Inside Ring On Sep 26 18:39:43.613: dn_tone_control DN=17 tonetype=36:DtAlertingTone onoff=1 pid=113 Sep 26 18:39:51.926: ephone-3[5]:OFFHOOK Sep 26 18:39:51.926: ephone-3[5]:Ringer Off Sep 26 18:39:51.926: ephone-3[5]:ANSWER call Sep 26 18:39:51.926: ephone-3[5]:Answer Incoming call from ephone-(4) DN 17 Sep 26 18:39:51.926: ephone-3[5]:SetCallState line 1 DN 16 ref 53 TsConnected Sep 26 18:39:51.926: ephone-4[2]:SetCallState line 1 DN 17 ref 52 TsConnected Sep 26 18:39:51.926: ephone-4[2]:OpenReceive DN 17 codec 4:G711Ulaw64k duration 20 ms bytes 160 Sep 26 18:39:51.926: ephone-3[5]:OpenReceive DN 16 codec 4:G711Ulaw64k duration 20 ms bytes 160 Sep 26 18:39:51.926: dn_tone_control DN=16 tonetype=0:DtSilence onoff=0 pid=113 Sep 26 18:39:51.930: DN 17 End Voice_Mode Sep 26 18:39:51.930: DN 17 Voice_Mode Sep 26 18:39:51.930: DN 16 Voice_Mode Sep 26 18:39:51.930: dn_tone_control DN=17 tonetype=0:DtSilence onoff=0 pid=113 Sep 26 18:39:52.182: ephone-4[2]:OpenReceiveChannelAck:IP 10.1.150.13, port=23094, dn_index=17, dn=17 Sep 26 18:39:52.182: ephone-3[5]:StartMedia 10.1.150.13 port=23094 Sep 26 18:39:52.182: DN 17 codec 4:G711Ulaw64k duration 20 ms bytes 160 Sep 26 18:39:52.182: ephone-3[5]:OpenReceiveChannelAck:IP 10.1.150.12, port=22778, dn_index=16, dn=16 Sep 26 18:39:52.182: ephone-4[2]:StartMedia 10.1.150.12 port=22778 Sep 26 18:39:52.182: DN 17 codec 4:G711Ulaw64k duration 20 ms bytes 160 Sep 26 18:40:01.254: ephone-3[5]:ONHOOK Sep 26 18:40:01.254: ephone-4[2]:CloseReceive Sep 26 18:40:01.254: ephone-4[2]:StopMedia Sep 26 18:40:01.254: ephone-3[5]:call clean up this DN 16 was called by other DN 17 Sep 26 18:40:01.254: this ephone-3 other ephone-(4) other DN state CONNECTED Sep 26 18:40:01.254: ephone-3[5]:CloseReceive Sep 26 18:40:01.254: ephone-3[5]:StopMedia Sep 26 18:40:01.254: DN 16 End Voice_Mode Sep 26 18:40:01.254: ephone-3[5]:SetCallState line 1 DN 16 ref 53 TsOnHook Sep 26 18:40:01.254: ephone-3[5]:SpeakerPhoneOnHook Sep 26 18:40:01.254: DN 17 End Voice_Mode Sep 26 18:40:01.254: ephone-4[2]:SetCallState line 1 DN 17 ref 52 TsOnHook Sep 26 18:40:01.254: ephone-4[2]:SpeakerPhoneOnHook Sep 26 18:40:01.258: ephone-3[5]:SpeakerPhoneOnHook Sep 26 18:40:01.354: DN 16 Voice_Mode Sep 26 18:40:01.354: DN 16 End Voice_Mode Sep 26 18:40:01.354: dn_tone_control DN=16 tonetype=0:DtSilence onoff=0 pid=113 Sep 26 18:40:01.366: SkinnyReportDnState DN 17 ONHOOK Sep 26 18:40:01.366: dn_tone_control DN=17 tonetype=0:DtSilence onoff=0 pid=113
Related Information
- Software Download: Cisco CallManager Express/ITS and SRST ( registered customers only)
- Troubleshooting and Debugging VoIP Call Basics
- Understanding How Digital T1 CAS (Robbed Bit Signaling) Works in IOS Gateways
- Troubleshooting Codec and Voice Card Complexity Mismatch
- Voice and Unified Communications Product Support
- Troubleshooting Cisco IP Telephony

- Technical Support - Cisco Systems
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
21-Oct-2009 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback