Configuring Hookflash Relay on FXS/FXO Voice Ports
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
When you integrate Voice over IP (VoIP) technologies to legacy private branch exchange (PBX) and public switched telephone networks (PSTNs), there is sometimes a need to pass a type of signaling known as 'hookflash'. A hookflash is a brief interruption in the loop current on loopstart trunks that the attached system does not interpret as a call disconnect.
Once the PBX or PSTN senses the hookflash, it generally puts the current call on hold and provides a secondary dial tone or access to other features such as transfer or call waiting access.
A hookflash is done by momentarily pressing down the cradle on a telephone. Some telephone handsets have a button called 'flash' or 'recall' that sends a 'timed loop break', or 'calibrated flash' which is a hookflash that has a precise timing.
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
Cisco 1750 routers
-
Cisco IOS® Software Release 12.2.5a
-
H.323 version 2 software support is a prerequisite. This has been available since Cisco IOS Software Release 12.05T and later. Hookflash detection/generation is supported on analog Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) and Foreign Exchange Office (FXO) voice ports. These are available on these Cisco hardware platforms:
-
1750/51/60
-
2600
-
3600
-
3700
-
MC3810
-
Catalyst 4000 with Access Gateway Module (AGM)
-
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
For more information on document conventions, refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions.
Background Information
Many customers use a combination of FXS and FXO ports to extend telephone handsets across IP networks. They want to preserve features of the existing PBX, such as call forward, no answer to voice mail, and transfer/hold on the remote extensions. Earlier Cisco VoIP software did not provide full control to allow transparent integration. However, with the release of H.323 version 2 support in Cisco IOS Software Release 12.0.5T and later, it is now possible to detect and pass hookflash signaling across IP networks.
When the FXS port is configured for a long 'hookflash in' timer value (greater than 500 msec), users may complain that when they hang up and immediately pick up the handset, the call has not cleared. If the value is set too low, the hookflash may be interpreted as a hang-up, but a higher value means the handset has to be left hung-up for a longer period to clear the call. In some cases, cradle bounce can cause problems as well. As the handset is hung-up, the spring tension on the hook button causes multiple short breaks on the line known as cradle bounce. Careful tuning of the hookflash in timing value may be needed for best results. One possibility in such cases is to use handsets with a flash button that sends a hookflash of a specific period. The FXO port can be set to match this value and the FXO port then generates the outgoing hookflash. Many PBXes have a Class of Service (CoS) option called 'calibrated flash' or 'timed loop break' which allows them to recognize hookflashes of specific duration and to ignore other shorter or longer loop breaks. Such settings are helpful in eliminating false disconnects and generation of invalid hookflash signals to the PBX.
Configure
In this section, you are presented with the information to configure the features described in this document.
Note: To find additional information on the commands used in this document, use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) .
Configure PLAR OPX and Hookflash Relay
Use this procedure to configure private line, automatic ringdown (PLAR) Off-Premises extension (OPX), and hookflash relay.
-
Configure the FXO port on the MainSite router as connection plar-opx.
The OPX mode allows remote users on FXS ports to appear to a central PBX as a directly connected extension. When the FXO port detects a ring signal from the PBX, the router sends a VoIP call setup to the remote FXS port but it does not take the FXO port off-hook. As a result, the PBX only sees the call answer signal when the RemoteSide router FXS port is picked up. After the PBX reaches the no answer timeout (call rings out), then it can end the call, transfer the call to voice mail, or ring another extension/ring group. Without OPX mode, the FXO port immediately goes off-hook after it senses the ringing and the PBX is then unable to perform a call forward, no answer, or roll over to voice mail.
-
The RemoteSite router must be configured to sense and then pass the hookflash signal on the FXS port.
Since the hookflash is a momentary break in the loop current on the FXS port and cannot be sent as an audio signal, the router passes the hookflash signal via dual tone multifrequency (DTMF) relay as the '!' character. The router with the FXO port then sends a short loop break which the external device sees as a hookflash. To properly pass the hookflash signal, the VoIP dial peers need to be configured for dtmf-relay h245-signal.
-
The physical port timers have to be adjusted to suit the characteristics of the handset on the FXS port and the duration of the hookflash loop break out of the FXO port as shown here:
-
The FXS voice port (RemoteSite router) uses the timing hookflash-in msec command where msec is the maximum value of a loop break (in milliseconds) from the telephone handset that is interpreted as a hookflash. A loop break greater than the configured value is regarded as a disconnect and the call is dropped. Any interval under this value causes the router to send the '!' character via the H.245-signal DTMF relay.
-
The FXO voice port (MainSite router) uses the timing hookflash-out msec command where msec is the duration of the outgoing loop break in milliseconds. When the router receives an H.245-signal DTMF relay signal, the FXO port generates a loop break for the configured interval.
-
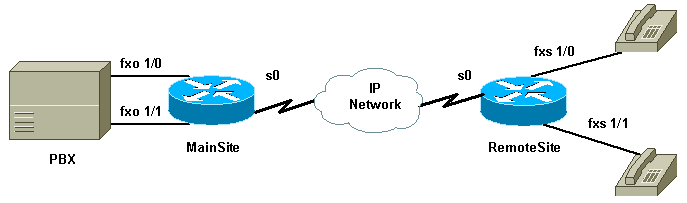
Network Diagram
This document uses the network setup shown in this diagram.
Configurations
This document uses the configurations shown here.
| MainSite |
|---|
MainSite#show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 1121 bytes ! version 12.2 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! hostname MainSite ! memory-size iomem 20 ip subnet-zero ! call rsvp-sync voice rtp send-recv ! interface Loopback1 ip address 205.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Serial0 bandwidth 1500 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.252 no fair-queue clockrate 1300000 ip rtp priority 16384 16383 100 ! router eigrp 1 network 192.168.1.0 network 205.1.1.0 no auto-summary no eigrp log-neighbor-changes ! ip classless no ip http server ip pim bidir-enable ! voice-port 1/0 timing hookflash-out 500 !--- Outgoing hookflash is 500 msec. connection plar opx 200 !--- Use PLAR OPX option on the FXO port. ! voice-port 1/1 timing hookflash-out 500 !--- Outgoing hookflash is 500 msec. connection plar opx 201 !--- Use PLAR OPX option on the FXO port. ! dial-peer voice 100 pots destination-pattern 100 port 1/0 ! dial-peer voice 101 pots destination-pattern 101 port 1/1 ! dial-peer voice 200 voip incoming called-number . destination-pattern 20. session target ipv4:200.1.1.1 dtmf-relay h245-signal !--- H.245-signal to pass hookflash. ip precedence 5 ! line con 0 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 ! no scheduler allocate end |
| Remote Site |
|---|
RemoteSite#show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 1096 bytes ! version 12.2 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! hostname RemoteSite ! memory-size iomem 25 ip subnet-zero ! call rsvp-sync voice rtp send-recv ! interface Loopback0 ip address 200.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Serial0 bandwidth 1500 ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.252 no fair-queue ip rtp priority 16384 16383 100 ! router eigrp 1 network 192.168.1.0 network 200.1.1.0 no auto-summary no eigrp log-neighbor-changes ! ip classless no ip http server ip pim bidir-enable ! ! voice-port 1/0 timing hookflash-in 1000 !--- Interpret loop breaks of up to 1 second. connection plar 100 !--- PLAR provides dial tone from remote PBX. ! voice-port 1/1 timing hookflash-in 1000 !--- Interpret loop breaks of up to 1 second. connection plar 101 !--- PLAR provides dial tone from the remote PBX. ! dial-peer voice 100 voip incoming called-number . destination-pattern 10. session target ipv4:205.1.1.1 dtmf-relay h245-signal !--- Use H.245-signal to pass hookflash. ip precedence 5 ! dial-peer voice 200 pots destination-pattern 200 port 1/0 ! dial-peer voice 201 pots destination-pattern 201 port 1/1 ! ! line con 0 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 ! no scheduler allocate end |
Verify and Troubleshoot
This section provides information you can use to verify and troubleshoot your configuration.
Certain show commands are supported by the Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) , which allows you to view an analysis of show command output.
Note: Before issuing debug commands, please see Important Information on Debug Commands.
-
debug h225 {asn1 | events} - Displays additional information about the actual contents of H.225 Registration, Admission, and Status (RAS) messages.
asn1 Indicates that only the ASN.1 contents of any H.225 message sent or received is displayed. events Indicates that key Q.931 events that occur when placing an H.323 call from one gateway to another are displayed.
The hookflash is passed as an H.245 message via TCP so it is possible to monitor the signaling by using debug h245 asn1 to display the H.245 packets.
These are two debug traces. The first shows the receipt of the digit '5' (the H.245 call signaling passes the digit and the duration). The second trace shows a hookflash (shown as '!'). There is no duration for a hookflash. The signal is sent out the FXO port based on the configured timing hookflash-out msec value.
MainSite#
MainSite#debug h245 asn1
H.245 ASN1 Messages debugging is on
MainSite#
00:52:17: H245 MSC INCOMING ENCODE BUFFER::= 6D 810B66A0 0F9F58AD AF684A00 00
00:52:17:
00:52:17: H245 MSC INCOMING PDU ::=
value MultimediaSystemControlMessage ::= indication : userInput : signal :
{
signalType "5"
!--- Digit relayed is 5.
duration 4000
rtp
{
timestamp 2913953866
logicalChannelNumber 1
}
}
00:52:18: H245 MSC INCOMING ENCODE BUFFER::= 6D 82064001 26000000
00:52:18:
00:52:18: H245 MSC INCOMING PDU ::=
value MultimediaSystemControlMessage ::= indication : userInput : signalUpdate :
{
duration 295
!--- Digit duration was 295 msec.
rtp
{
logicalChannelNumber 1
}
}
MainSite#
!--- This trace from the destination router shows !--- the hookflash passed as the character '!'.
MainSite#
00:52:36: H245 MSC INCOMING ENCODE BUFFER::= 6D 81020420
00:52:36:
00:52:36: H245 MSC INCOMING PDU ::=
value MultimediaSystemControlMessage ::= indication : userInput : signal :
{
signalType "!"
!--- Hookflash is passed as '!'.
}
MainSite#
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
02-Feb-2006 |
Initial Release |
 Feedback
Feedback