VG248 Port Configuration to Light the Caller ID MWI
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document provides a sample configuration for a VG248 port to deliver the proper signal to light the MWI on a Caller ID box connected to an analog phone.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Ensure that Cisco CallManager is integrated with your voice mail system before you attempt this configuration.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
Cisco VG248 Analog Phone Gateway
-
VG248 Software version 1.3
-
Analog phones
-
Caller ID box
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Background Information
The VG248 Gateway is a product enabled by Cisco AVVID (Architecture for Video, Voice, and Integrated Data) that permits organizations to continue using their analog devices with the current IP Telephony technology. The VG248 is a gateway for using analog phones, fax machines, modems, voice mail systems, and speakerphones within an organization voice system based on Cisco CallManager.
With a system of analog phones connected inline with Caller ID boxes that have Message Waiting Indicators (MWI), it has to be assured that the Caller ID boxes receive the proper signal from the telephone company to successfully light the MWI, which indicates that there is a voice mail waiting. The two types of signals that are propagated by telephone companies are Stutter Tones and Frequency-Shift Keying (FSK) Tones. Even though the purpose of these tones is to turn the MWI on when a message is recorded, they do not work for all the Caller ID box models that are provided by telephone companies.
Note: The power consumed by the VG248 ranges from 50W to 160W, which depends on the status of the phones connected to it.
The VG248 supports different methods for sending MWI messages to analog phones. Because you might have different types of analog phones connected to the VG248, you can modify the MWI type on a per-port basis. So, if you have analog phones that contain MWI lamps, then you can notify users of awaiting messages using the MWI lamp. Or, you can choose to play a tone when users pick up their phones.
These are the methods supported by the VG248:
-
Lamp (90-Volt Signal)—Illuminates the lamp on the phone.
-
Caller ID (FSK Tone)—Uses the caller ID mechanism to send MWI messages to the LCD screen on the phone.
-
Stutter (Stutter Tone)—Plays tones when the user picks up the phone.
-
Lamp + Stutter—Illuminates the lamp and plays a tone.
-
Caller ID + Stutter—Sends a message to the LCD screen and plays a tone.
-
None—Does not send MWI information.
Configure
Complete these steps in order to configure the VG248 port to support Caller ID (FSK Tone) on a Caller ID box inline with an analog phone.
-
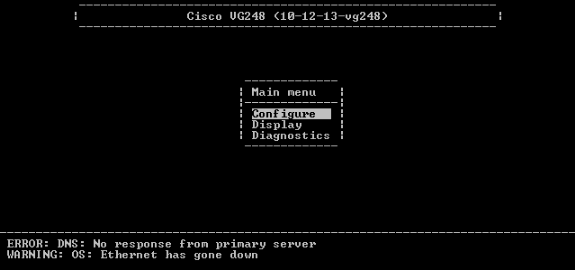
From the Main menu, choose Configure.
-
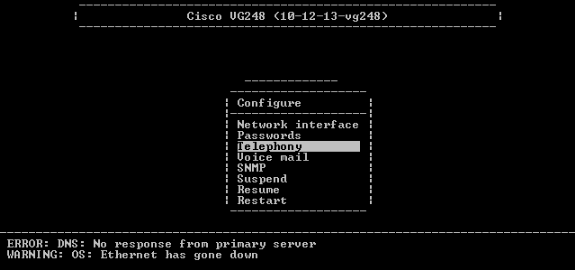
Choose Telephony.
-
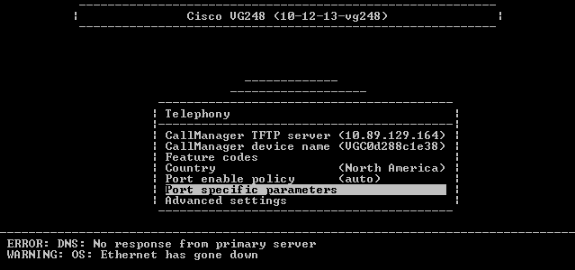
Choose Port specific parameters.
-
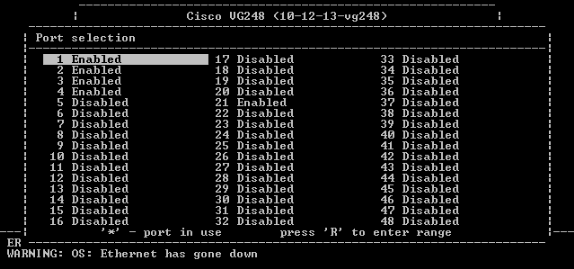
Use the arrow keys to select the port to configure and press Enter.
-
Choose MWI method.
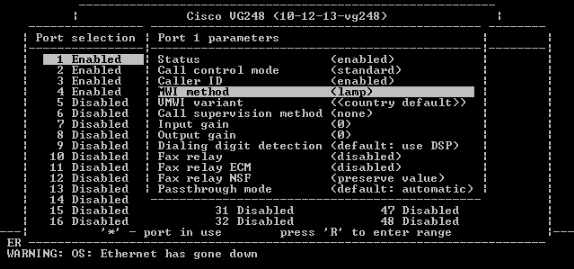
-
Choose the caller ID option.
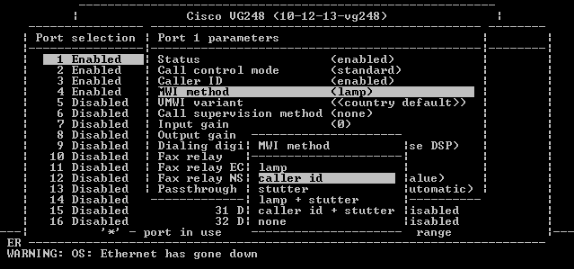
Verify
There is currently no verification procedure available for this configuration.
Troubleshoot
This section provides information you can use to troubleshoot your configuration.
You can set the VG248 to log much more detail (information, error, or warnings), and logging to specific ports. Complete these steps in order to set logging levels, and select ports:
-
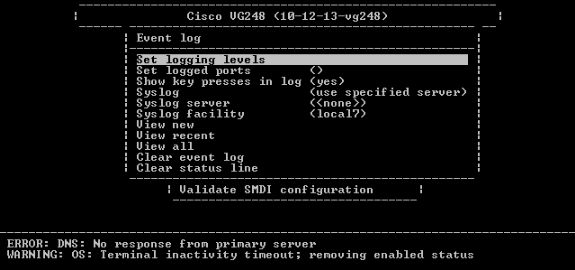
From the Main menu, choose Diagnostics.
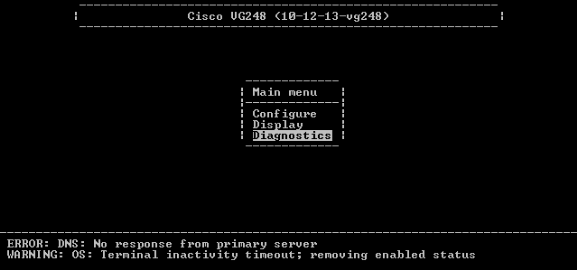
-
Choose Event log.
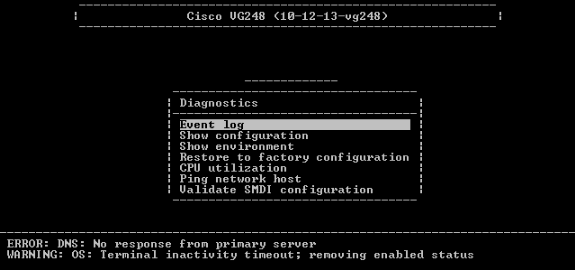
-
Choose Set logging levels.
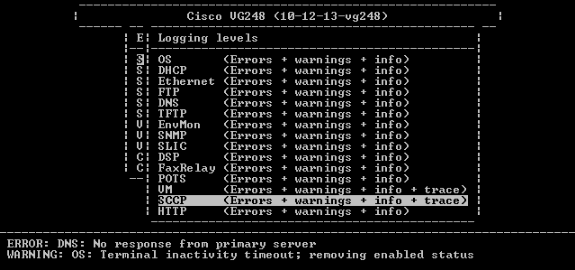
-
In the Set Logging Levels select Voice Mail (VM) and SCCP Errors + Warnings + Info + Trace.
-
In the Set Logged Port, select a port on which to test.
-
Select View New from the Diagnostics menu.
-
From the selected port, make a call to the analog phone inline with the Caller ID box and record a message. The events display in the VG248 Telnet session, and the MWI should light.
Related Information
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)










 Feedback
Feedback