Using Dialout/EZ with a Cisco Access Server
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
Tactical Software's DialOut/EZ product allows desktop LAN users to share network access server (NAS) ports as a modem pool for outbound asynchronous communications. Users of DialOut/EZ no longer need dedicated modems and phone lines at their desktops, but instead use the communication (COM:) port redirector software to allow dial ports on the access servers to appear as local modems to desktop communications applications. Windows users can dial through a central NAS/access server to access remote on-line services and even to send faxes from their PCs. The Cisco IOS® Software Release running on the NAS must support COM Port Control protocol (RFC 2217). You can find out more information about Tactical Software's DialOut/EZ from the company's website at: http://www.tacticalsoftware.com ![]() .
.
Note: DialOut/EZ is a replacement for the Cisco Dialout Utility.
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
Tactical Software requires that Cisco IOS Software Release 12.0(9) or later be installed on the NAS to interoperate with DialOut/EZ.
-
Due to Cisco bug ID CSCds28071, Cisco recommends that you run Cisco IOS Software Release 12.1(8) or later.
Conventions
Refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Installation and Configuration
Installing Appropriate Modem Drivers for Dialout/EZ the Virtual COM Port
-
Install DialOut/EZ.
For complete DialOut/EZ installation information on a client workstation, refer to the User Guide on Tactical Software's website: DialOut/EZ.
-
Download Modem Drivers.
The DialOut/EZ virtual COM ports do not have any modem devices attached to them. The DialOut/EZ user should use an appropriate .inf file for the modems (install a modem driver on the virtual COM ports). The MICA, NextPort and Microcom .inf files are available for download from the Cisco website. For the other platforms use the specified .inf files.
Modem Type Platform .inf file MICA 3600, AS5200,AS5300,AS5800 mdcsmica.inf NextPort AS5350,AS5400 AS5800, AS5850 Microcom AS5200 mnpv90.inf NM-xAM 2600, 3600 Microcom DeskPorte V.34 FAST WIC-xAM 2600, 3600 mdmrock5.inf (or the standard 28800 bps modem file) Note: For Windows XP, the Cisco provided .inf files may not work. Try using a Windows built-in .inf file instead.
-
Install Modem Drivers.
To install a modem driver on the Windows PC, use the following procedure:
-
Start > Settings > Control Panel > Phone and Modem Options.
-
Select Modem and Add to add a new modem.
-
Select Don't detect my modem; I will select it from a list, then click Next.
-
Select the Manufacturer and Model of your modem. Selecting Cisco on the left window displays Mica on the right window.
-
Select Have Disk and browse to the location where the .inf file is saved.
-
In the Selected ports option, use the COM port selected during EZ Dialout installation (for example, COM 5).
-
Configuring the Access Server
The IOS software configuration needed for character-mode modem dialout applications only (such as with DialOut/EZ) goes under the line configuration:
line starting_line_number ending_line_number
modem dtr-active
! -- If the router is for dialin and dialout use "modem inout" instead
transport input telnet
! -- Or transport input all could be used
escape-character NONE
! -- Due to Bug CSCdv12194 for the AS5350/AS5400.
rotary 1
! -- Specifies the use of TCP port 7001 in the Dialout/EZ manager ! -- window to dial out rotary 1
If external modems are used, then add the RS232 physical-layer and framing parameters under the line configuration as desired:
speed 115200
! -- Set to the highest speed supported by the modems
flowcontrol hardware
parity even
databits 7
! -- Or databits 8
stopbits 1
! -- Recommended for best throughput
If you want to control access to the dialout lines, add the following in line configuration mode:
password password
Alternatively, configure authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) and apply the list to the line with:
login authentication listname
If you wish to control which trunks are used for the dialout calls, use the modem dialout controller command introduced in Cisco IOS Software Release 12.1(T) (as of now, supported on the AS5300 only). For more information, refer to Configuring a T1 or E1 Interface for Outgoing Analog Calls Using the modem dialout controller Command.
Tip: Sometimes DialOut/EZ can get confused by the Password OK message from the IOS software. To avoid this issue, configure AAA (local or server-based) on the router. Refer to the AS5xxx with AAA section of this document for a sample configuration.
Optional: You can also configure a modemcap to reset the modem to the default configuration after each call. Use the command modem autoconfigure type mica under the line configuration. This modemcap (which sets factory default &F) can be applied to all routers regardless of the type of modem (MICA, NextPort, Microcom, etc.). For more information on modemcaps, refer to Recommended Modemcaps for Internal Digital and Analog Modems on Cisco Access Servers.
The same Access Server can be used for dialin as well as dialout (application). For comprehensive sample configurations refer to the section Sample NAS Configurations for the DialOut/EZ Utility.
Troubleshooting DialOut/EZ
Follow the method outlined below to troubleshoot DialOut/EZ related issues:
-
Reverse Telnet to the NAS modem from the NAS exec prompt. Ensure you can connect to the modem by issuing an AT command which should return an OK response. If you can connect to the modem, try to dial the number of the remote device using the atdt ######## command. If the connection is successful, then the router configuration is correct and the hardware is working correctly.
Note: Use the binary Telnet TCP port range: 6000+line to use a specific line, or 7000+ rotary_number for a dialout rotary.
The example below shows a successful call:
maui-nas-03#telnet 172.22.53.150 7001 ! -- Reverse Telnet to an up/up interface on the router ! -- and use port 7000+rotary Trying 172.22.53.150, 7001 ... Open User Access Verification ! Username: admin Password: at OK ! -- Modem is responding atdt 81560 ! -- Dial number 81560 to connect to remote device. ! -- This may take up to 30 seconds. CONNECT 33600 /V.42/V.42bis ! -- Call is connected to the remote device. User Access Verification ! -- Username prompt by remote device Username: cisco Password: maui-nas-01>
If the reverse Telnet does not reach the modem AT command mode, then the NAS is misconfigured. Check the following:
-
The interface whose IP address you're Telnetting to should be up/up and pingable from the PC host on the LAN. If you cannot ping the router interface troubleshoot your LAN for routing related issues.
-
The modem line should have modem inout (for dialin/dialout) or modem dtr-active (for dialout only).
-
The line should be configured with transport input telnet or transport input all.
If the reverse Telnet succeeds in reaching the modem AT command mode, but the manual call fails, then the problem could be a Telco or remote router issue. Troubleshoot the remote router, the line and retest the connection before proceeding further. Refer to Troubleshooting Dial Technology Connectivity - Non-DDR Callout for more information.
-
-
Try a reverse Telnet from a PC host on the LAN. Open Windows Hyper terminal (or Windows Telnet) and Telnet to the router's IP address and the port you are using for DialOut/EZ (for example 7001). If you can reach the modem and dialout, then there is nothing wrong with the LAN (we had previously verified that dialout from the NAS is working).
-
If the reverse Telnet does not reach the modem AT command mode, then the NAS is misconfigured or the IP network is not working. Check the following:
-
The interface whose IP address you're Telnetting to should be up/up and pingable from the PC host on the LAN. If you cannot ping the router interface troubleshoot your LAN for routing related issues.
-
There should be no access-class that is blocking the Telnet connection.
The following screen captures show a successful Hyperterminal session:
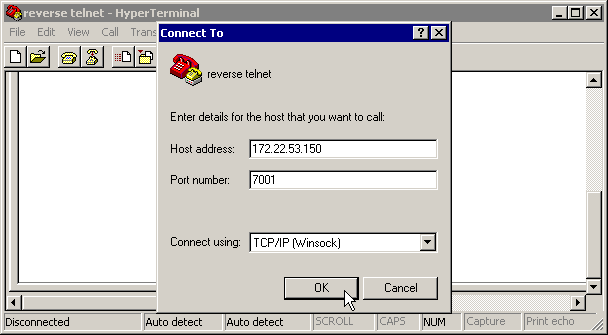
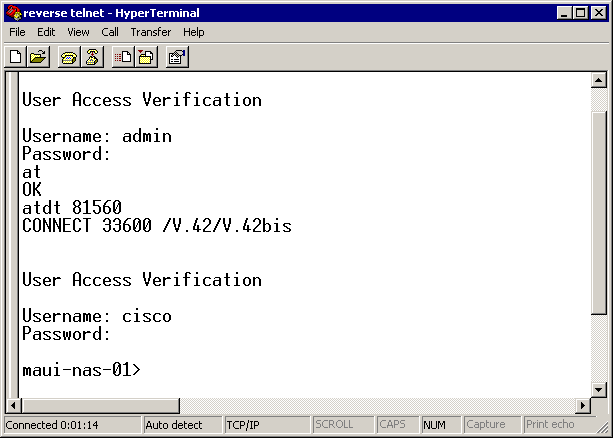
Note: If you are using the Microsoft Windows Telnet client and AAA is configured on the NAS, the windows Telnet login may fail. This failure is caused by application settings and is characterized by an inability to enter the password, thus login fails. To correct the Telnet application setting for this session, follow the procedure below on the host PC:
-
Start > Run > type telnet, click OK.
-
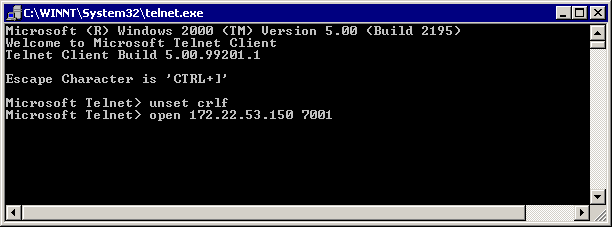
Type the unset crlf command. (This ensures that you send a carriage returns as Telnet <CR><NUL> rather than <CR><LF>.)
-
Use open <ip_address> <port> to Telnet to the modem.
-
You should now be connected to the modems and can now initiate the manual dial using atdt just as with the Hyperterminal example shows above. The following screen capture is an example:
-
-
Use Hyperterminal to directly connect to the NAS modems via DialOut/EZ's emulated COM port. Refer to the DialOut/EZ User Guide chapter on installation on http://www.tacticalsoftware.com
 for more information. This will verify that DialOut/EZ's emulated COM port is functioning.
for more information. This will verify that DialOut/EZ's emulated COM port is functioning. If Hyperterminal over DialOut/EZ's emulated COM port does NOT work, then the problem would seem to be peculiar to DialOut/EZ's communication with IOS. Gather the following information:
-
These debugs determines if the NAS is receiving the Telnet connection.
debug telnet debug modem
-
The DialOut/EZ Trace Log: Selecting the Trace Window menu option opens the DialOut/EZ Port Monitor 3.0 window, with the Trace Window tab enabled. To begin tracing, check the Enable Trace box at the bottom of this window. Make sure you save the log for further analysis. Refer to the Troubleshooting section of the User Guide on the Tactical Software's website for more information.
-
-
Since we have verified that DialOut/EZ can connect to the modems, next have the end application initiate a connection. If the end applications cannot talk to each other using the DialOut/EZ connection, then the problem could be peculiar to the end application. The DialOut/EZ Trace Log may be useful in troubleshooting this issue. Also turn on the Windows TAPI modem log, and also any logging available from the application. Refer to Microsoft's website
 for the following Microsoft article: How to Create and Use the Modemlog.txt File (Q142730) for more information.
for the following Microsoft article: How to Create and Use the Modemlog.txt File (Q142730) for more information. If the operation still does not work as desired, gather the IOS debugs, the DialOut/EZ Trace Log, and (if applicable) the Windows modem log, and analyze the results to determine where the application is failing.
Refer to Tactical Software: Frequently Asked Questions
 for additional information.
for additional information.
Sample NAS Configurations for the DialOut/EZ Utility
AS25xx, NM-xAM, WIC-xAM
Following is a sample configuration file for routers with external analog modems, such as Cisco AS2509, Cisco AS2510, Cisco AS2511, or Cisco AS2512 access server as well as routers with internal analog modems (NM-xAM and the WIC-xAM) such as the 26xx, and 36xx series routers.
The example below shows the router capable of incoming and outgoing calls. If the router is for outbound use only, then the line configuration is all that is needed.
interface Group-Async1
! -- Group-Async interface used for dialin calls ! -- This is not used for dialout
ip unnumbered Ethernet0
no ip mroute-cache
encapsulation ppp
no ip route-cache
async default routing
async dynamic address
async mode interactive
peer default ip address pool local
dialer in-band
no cdp enable
ppp authentication chap
group-range 1 8
! -- Range of lines include 1 through 8 ! -- Modems 1 through 8 can now be used for incoming or outgoing calls
!
line 1 8
! -- Line configuration used for Dialout/EZ
modem InOut
! -- Modem can be used for dialing and dialout ! -- If the line is used for dialout only use "modem dtr-active"
rotary 1
! -- The lines are placed in a rotary ! -- They are accessed by Dialout EZ using port (7000 + rotary)=7001
transport preferred telnet
transport input all
! -- You could also use transport input telnet instead
rxspeed 115200
txspeed 115200
! -- Speed for external modems ! -- This is not needed for internal analog modems (NM-xAM, WIC-xAM)
flowcontrol hardware
! -- Flowcontrol for external modems ! -- This is not needed for internal analog modems (NM-xAM, WIC-xAM
AS5xxx without AAA
Following is a sample configuration file for a Cisco AS5xxx series access server without AAA.
This example shows the router accepting incoming calls and making outbound calls:
controller T1 0
! -- T1 interface used for incoming and outgoing calls
framing esf
clock source line primary
linecode b8zs
pri-group timeslots 1-24
!
interface Serial0:23
! -- D-channel configuration for T1 0 ! -- This configuration is only needed for incoming calls
ip address 10.15.2.80 255.255.255.0
encapsulation ppp
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no keepalive
dialer idle-timeout 400
dialer map ip 10.15.2.60 6661210
dialer-group 1
isdn incoming-voice modem
! -- Incoming analog calls will be switched to the modems
peer default ip address pool setup_pool
no fair-queue
no cdp enable
ppp authentication chap
ppp multilink
!
interface Group-Async1
! -- Group-async configuration for incoming calls ! -- This configuration is not used for outgoing calls
ip unnumbered Ethernet0
encapsulation ppp
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
async dynamic address
async dynamic routing
async mode interactive
peer default ip address pool setup_pool
ppp authentication chap pap
group-range 1 48
! -- Range of lines include 1 through 48 ! -- Modems 1 through 48 can now be used for incoming or outgoing calls
!
line 1 48
! -- Line configuration for Dialout/EZ
exec-timeout 0 0
autoselect during-login
autoselect ppp
! -- The autoselect commands are used for protocol selection for incoming calls ! -- This is not needed if the router only makes outbound calls
modem InOut
! -- Modem can be used for dialing and dialout if the line is used for ! -- dialout only use, modem dtr-active transport preferred telnet
rotary 1
! -- The lines are placed in a rotary ! -- They are accessed by Dialout EZ using port (7000 + rotary)=7001
transport input all
transport input telnet
! -- Configure one or both of the above commands
AS5xxx with AAA
Following is a sample configuration file for Cisco AS5xxx series access servers with server-based AAA configured.
The following example, shows an access server configured for dialin and dialout calls:
aaa new-model
aaa authentication login default radius
! -- Use the radius server for login on the default list ! -- for local AAA replace "radius" with "local" ! -- (make sure to configure the username/password locally as well
aaa authentication ppp ppptac radius
! -- Use the radius server for ppp on the list named ppptac ! -- This is used for incoming ppp calls and is not used for outgoing ! -- Dialout/EZ calls !
controller T1 0
! -- T1 interface used for incoming and outgoing calls
framing esf
clock source line primary
linecode b8zs
pri-group timeslots 1-24
!
interface Serial0:23
! -- D-channel configuration for T1 0 ! -- This configuration is only needed for incoming calls
ip address 10.15.2.80 255.255.255.0
encapsulation ppp
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no keepalive
dialer idle-timeout 400
dialer map ip 10.15.2.60 name test 5551210
dialer-group 1
isdn incoming-voice modem
peer default ip address pool setup_pool
no fair-queue
no cdp enable
ppp authentication chap ppptac
ppp multilink
!
!
interface Group-Async1
! -- Group-async configuration for incoming calls ! -- This configuration is not used for outgoing calls
ip unnumbered Ethernet0
encapsulation ppp
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
async dynamic address
async dynamic routing
async mode interactive
peer default ip address pool setup_pool
ppp authentication chap pap ppptac
! -- Use list named ppptac for authentication
group-range 1 48
! -- Range of lines include 1 through 48 ! -- Modems 1 through 48 can now be used for incoming or outgoing calls
!
!
radius-server host 10.4.1.10
radius-server timeout 20
radius-server key nas1
! -- Radius server configuration
!
line 1 48
! -- Line configuration for Dialout/EZ as well as dialin calls
exec-timeout 0 0
autoselect during-login
autoselect ppp
! -- The autoselect commands are used for protocol selection for incoming calls ! -- This is not needed if the router only makes outbound calls
modem InOut
! -- Modem can be used for dialing and dialout ! -- If the line is used for dialout only, use modem dtr-active transport ! -- preferred telnet
rotary 1
! -- The lines are placed in a rotary ! -- They are accessed by Dialout EZ using port (7000 + rotary)=7001
transport preferred telnet
transport input all
! -- You could also use transport input telnet instead
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
29-Jan-2008 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)



 Feedback
Feedback