Introduction
This document describes how to diagnose database replication issues and provides the steps necessary to troubleshoot and resolve those issues.
Steps to Diagnose the Database Replication
This section describes scenarios in which database replication is broken and provides the troubleshooting methodology in order to diagnose and isolate the problem.
Step 1. Verify Database Replication is Broken
In order to determine whether your database replication is broken, you must know the various states of the Real Time Monitoring Tool (RTMT) for the replication.
| Value |
Meaning |
Description |
|
0
|
Initialization State
|
Replication is in the process of setting up. A setup failure can occur if replication is in this state for more than an hour.
|
|
1
|
The Number of replicates is incorrect
|
Set up is still in progress. This state is rarely seen in versions 6.x and 7.x; in version 5.x, it indicates that the setup is still in progress.
|
|
2
|
Replication is good
|
Logical connections are established and the tables are matched with the other servers on the cluster.
|
|
3
|
Mismatched tables
|
Logical connections are established but there is an uncertainty whether the tables match.
In versions 6.x and 7.x, all servers could show state 3 even if one server is down in the cluster.
This issue can occur because the other servers are unsure whether there is an update to the User Facing Feature (UFF) that has not been passed from the subscriber to the other device in the cluster.
|
|
4
|
Setup Failed/Dropped
|
Server no longer has an active logical connection in order to receive any database table across the network. No replication occurs in this state.
|
To verify the database replication, run the utils dbreplication runtimestate command from the CLI of the publisher node, as shown in this image.
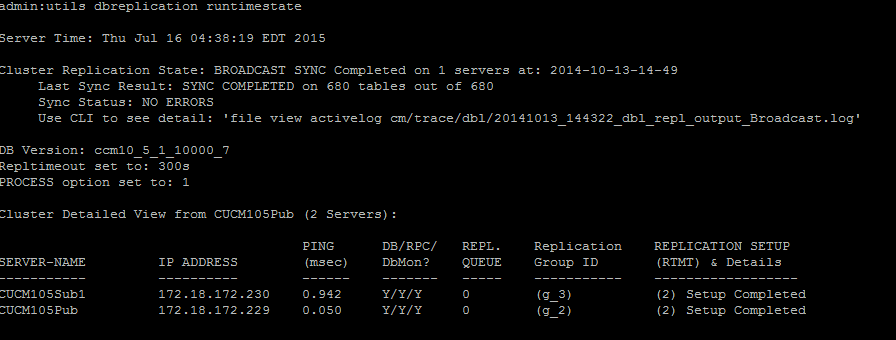
In the output, ensure that the Cluster Replication State does not contain the old sync information. Check the same and use the Timestamp.
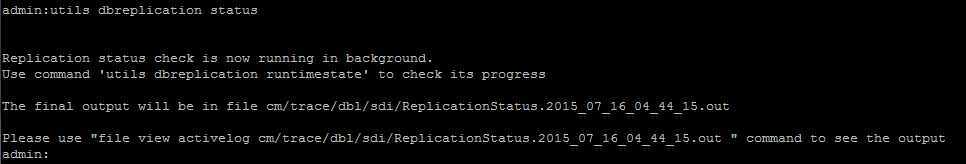
If the broadcast sync is not updated with a recent date, run the utils dbreplication status command to check all the tables and the replication. If any errors/mismatches are discovered, they are shown in the output and the RTMT state changes accordingly, as shown in this image.
o
After you run the command, all the tables are checked for consistency and an accurate replication status is displayed.
Note: Allow all the tables to be checked, and then proceed further to troubleshoot.
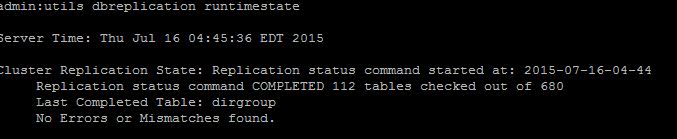
Once an accurate replication status is displayed, check the Replication Setup (RTMT) and details as shown in the first output. You must check the status for every node. If any node has a state other than 2, continue to troubleshoot.
Step 2. Collect the CM Database Status from the Cisco Unified Reporting Page on CUCM
- After you complete Step 1, choose the Cisco Unified Reporting option from the Navigation drop-down list in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (CUCM) publisher, as shown in this image.
2. Navigate to System Reports and click Unified CM Database Status as shown in this image.
3. Generate a new report, click on the Generate New Report icon as shown in this image.
4. Wait for the new report to be generated successfully.

5. Once it is generated, Click on the icon to Download the report and save it so that it can be provided to a TAC engineer in case a service request (SR) needs to be opened.

Step 3. Review the Unified CM Database Report of any Component Flagged as an Error
If there are any errors in the components, the errors are flagged with a red X icon, as shown in this image.
- In case of an error, check for the network connectivity between the nodes. Verify if the A Cisco DB service runs from the CLI of the node and uses the utils service list command.
- If the A Cisco DB service is down, run the utils service start A Cisco DB command to start the service. If this fails, contact Cisco TAC.
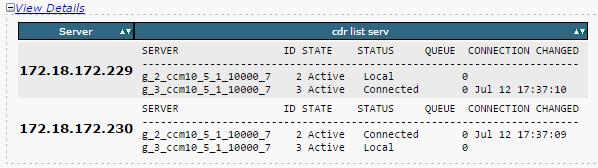
- Ensure Replication Server List (cdr list serv) is populated for all the nodes.
This image illustrates an ideal output.
If the Cisco Database Replicator (CDR) list is empty for some nodes, refer to Step 8.
- Ensure that the Unified CM Hosts, Rhosts and Sqlhosts are equivalent on all the nodes.
This is an important step. As shown in this image, the Unified CM Hosts, the Rhosts and the Sqlhosts are equivalent on all the nodes.
The Hosts files are mismatched:
There is a possibility of an incorrect activity when an IP address changes or updates to the Hostname on the server.
Refer to this link in order to change IP address to the Hostname for the CUCM.
IP Address and Hostname Changes
Restart these services from the CLI of the publisher server and check if the mismatch is cleared. If yes, go to Step 8. If no, contact Cisco TAC. Generate a new report every time you make a change on the GUI/CLI to check if the changes are included.
Cluster Manager ( utils service restart Cluster Manager)
A Cisco DB ( utils service restart A Cisco DB)
The Rhosts files are mismatched:
If the Rhosts files are mismatched along with the host files, follow the steps mentioned under The Hosts files are mismatched. If only the Rhosts files are mismatched, run the commands from the CLI:
A Cisco DB ( utils service restart A Cisco DB )
Cluster Manager ( utils service restart Cluster Manager)
Generate a new report and check if the Rhost files are equivalent on all the servers. If yes, go to Step 8. If no, contact Cisco TAC.
The Sqlhosts are mismatched:
If the Sqlhosts are mismatched along with the host files, follow the steps mentioned under The Hosts files are mismatched. If only the Sqlhosts files are mismatched, run the command from the CLI:
utils service restart A Cisco DB
Generate a new report and check if the Sqlhost files are equivalent on all the servers. If yes, go to Step 8. If no, contact Cisco TAC
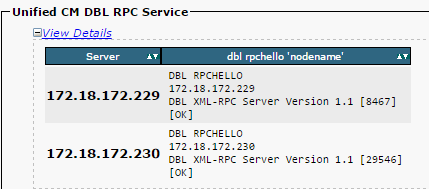
If the RPC hello does not work for a particular node:
- Ensure the network connectivity between the particular node and the publisher.
- Ensure that the port number 1515 is allowed on the network.
Refer to this link for details on TCP/UDP port usage:
Cisco Unified Communications Manager TCP and UDP port usage
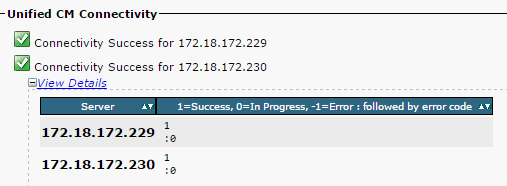
- Ensure that the network connectivity is successful between the nodes, as shown in this image:

If the network connectivity fails for the nodes:
- Ensure that the network reachability is present between the nodes.
- Ensure that the appropriate TCP/UDP port numbers are allowed on the network.
Generate a new report, and check for a successful connection. In case of an unsuccessful connection, go to Step 8.
Step 4. Check the Individual Components that Use the Utils Diagnose Test Command
The utils diagnose test command checks all the components and returns a passed/failed value. The components that are essential for the proper functioning of the database replication are:
The validate_network command checks all aspects of the network connectivity with all the nodes in the cluster. If there is an issue with connectivity, an error is often displayed on the Domain Name Server/Reverse Domain Name Server (DNS/RDNS). The validate_network command completes the operation in 300 seconds. The common error messages as seen in the network connectivity tests:
1. Error "Intra-cluster communication is broken", as shown in this image.
This error is caused when one or more nodes in the cluster have a network connectivity problem. Ensure that all the nodes have ping reachability.
If the intra-cluster communication is broken, database replication issues occur.
2. Reverse DNS lookup failed.
This error is caused when the reverse DNS lookup fails on a node. However, you can verify whether the DNS is configured and functions properly when you use these commands:
utils network eth0 all - Shows the DNS configuration (if present)
utils network host <ip address/Hostname> - Checks for resolution of ip address/Hostname
If the DNS does not function correctly, it can cause database replication issues when the servers are defined and use the hostnames.
The NTP is responsible to keep the server's time in sync with the reference clock. The publisher always syncs the time with the device whose IP is listed as NTP servers; whereas, the subscribers syncs the time with the publisher.
It is extremely important for the NTP to be fully functional in order to avoid any database replication issues.
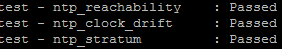
It is essential that the NTP stratum (Number of hops to the parent reference clock) must be less than 5 or else it is deemed unreliable.
Complete these steps in order to check NTP status:
- Use the utils diagnose test command to check the output, as shown in this image.
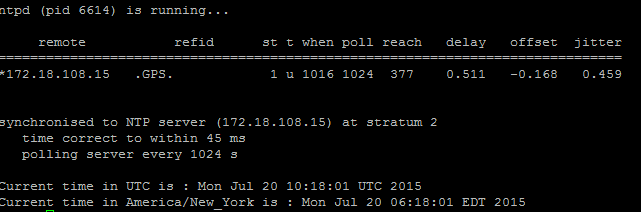
2. Additionally, you can run this command:
utils ntp status
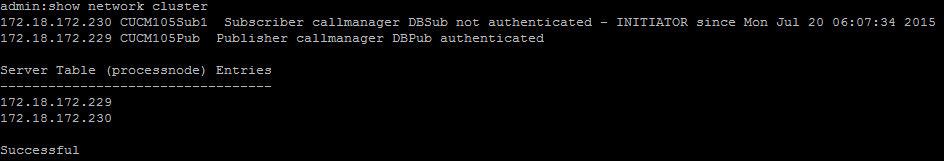
Step 5. Check the Connectivity Status from all the Nodes and Ensure They are Authenticated
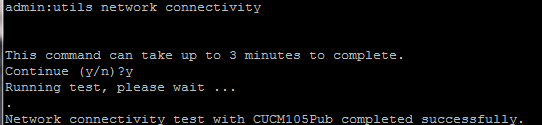
- After you complete Step 4, if there are no issues reported, run the utils network connectivity command on all the nodes to check the connectivity to the databases is successful, as shown in this image.
2. If you receive "Cannot send TCP/UDP packets" as an error message, check your network for any retransmissions or block the TCP/UDP ports. The show network cluster command checks for authentication of all nodes.
3. If the status of the node is unauthenticated, ensure that the network connectivity and the security password is the same on all the nodes, as shown in this image.
Refer to the links to change/recover the security passwords:
How to Reset Passwords on CUCM
CUCM Operating System Administrator Password Recovery
Step 6. The Utils Dbreplication Runtimestate Command Shows out of Sync or not Requested Statuses
It is important to understand that the database replication is a network intensive task as it pushes the actual tables to all the nodes in the cluster. Ensure that:
utils dbreplication setprocess <1-40>
Note: When you change this parameter, it improves the replication setup performance, but consumes additional system resources.
Server 1-5 = 1 Minute Per Server Servers 6-10 = 2 Minutes Per Server Servers >10 = 3 Minutes Per Server.
Example: 12 Servers in Cluster : Server 1-5 * 1 min = 5 min, + 6-10 * 2 min = 10 min, + 11-12 * 3 min = 6 min,
Repltimeout should be set to 21 Minutes.
Commands to check/set the replication timeout:
show tech repltimeout ( To check the current replication timeout value )
utils dbreplication setrepltimeout ( To set the replication timeout )
Steps 7 and 8 must be performed after the checklist is fulfilled:
Checklist:
- All the nodes have the connectivity to each other. Refer to Step 5.
- RPC is reachable. Refer to Step 3.
- Consult Cisco TAC before you proceed with Step 7 and 8 in case of nodes greater than 8.
- Perform the procedure in the off business hours.
Step 7. Repair All/Selective Tables for Database Replication
If the utils dbreplication runtimestate command shows that there are error/mismatched tables, run the command:
Utils dbreplication repair all
Run the utils dbreplication runtimestate command to check the status again.
Proceed to Step 8, if the status does not change.
Step 8. Reset the Database Replication from Scratch
Refer to the sequence to reset the database replication and start the process from scratch.
utils dbreplication stop all (Only on the publisher)
utils dbreplication dropadmindb (First on all the subscribers one by one then the publisher)
utils dbreplication reset all ( Only on the publisher )
To monitor the process, run the RTMT/utils dbreplication runtimestate command.
Refer to the sequence to reset the database replication for a particular node:
utils dbreplication stop <sub name/IP> (Only on the publisher)
utils dbreplcation dropadmindb (Only on the affected subscriber)
utils dbreplication reset <sub name/IP> (Only on the publisher )
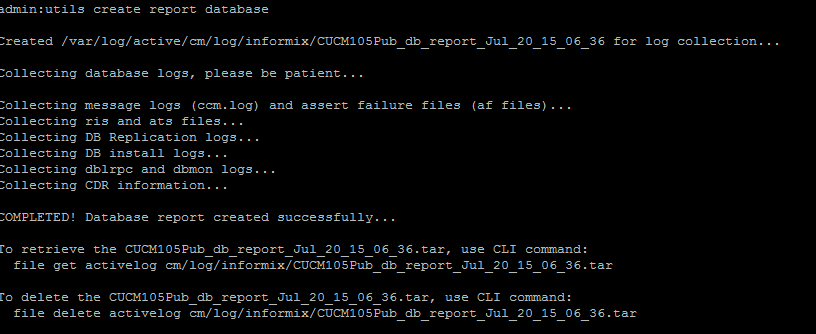
In case you reach Cisco TAC for further assistance, ensure that these outputs and the reports are provided:
utils dbreplication runtimestate
utils diagnose test
utils network connectivity
Reports:
- The Cisco Unified Reporting CM Database Report (Refer to Step 2).
- The utils create report database command from CLI. Download the .tar file and use a SFTP server.
Related Information



















 Feedback
Feedback