Extension that allows BGP to transport Layer 2 MAC and Layer 3 IP information is EVPN and uses Multi-Protocol Border Gateway Protocol (MP-BGP) as the protocol to distribute reachability information that pertains to the VXLAN overlay network.
Migrate EVPN VxLAN to IPv6 Underlay on Catalyst 9000 Switches
Available Languages
Download Options
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Contents
Introduction
This document describes how to migrate EVPN VxLAN to an IPv6 underlay on Catalyst 9000 series switches.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
- Unicast EVPN VxLAN feature, BGP and MVPN (Multicast Virtual Private Network).
- IPv4 and IPv6 Unicast
- Multicast concepts and how multicast operates
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
- Catalyst 9000 Series Switches

Note: The 9200, 9500X, and 9600X do not support VXLANv6
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Background Information
Migration to a EVPN VXLANv6 requires changes to certain configurations in the EVPN Fabric to enable IPv6 underlay. This document details the relevant configuration changes and verification procedures to migrate existing EVPN VXLANv4 deployments to Greenfield (VXLANv6 only) or Brownfield (Dual-Stack- VXLANv4 and VXLANv6) deployments.
Greenfield EVPN VXLANv6 deployments require:
- IPv6 core
- Migration of EVPN Fabrics to VXLANv6 Underlay support
- Migration BGP EVPN neighborships to IPv6 Neighbor Peering
Brownfield EVPN VXLAN deployments require:
- IPv4 + IPv6 core
- Seamless Migrating EVPN Fabrics to Dual Stack (VXLANv4 + VXLANV6) Underlay
- Seamless Migration of BGP EVPN Neighbor Peering from IPv4 to IPv6 Neighbor Address
Terminology
|
EVPN |
Ethernet Virtual Private Network |
|
|
VXLAN |
Virtual Extensible LAN (Local Area Network) |
VXLAN is designed to overcome the inherent limitations of VLANs and STP. It is a proposed IETF standard [RFC 7348] to provide the same Ethernet Layer 2 network services as VLANs do, but with greater flexibility. Functionally, it is a MAC-in- UDP encapsulation protocol that runs as a virtual overlay on a Layer 3 underlay network. |
|
VTEP |
Virtual Tunnel Endpoint |
This is the device that does the encapsulation and de-encapsulation |
|
EVI |
EVPN Instance |
The EVPN instance (EVI) is represented by the virtual network identifier (VNI). An EVI represents a VPN on a PE router. It serves the same role of an IP VPN Routing and Forwarding (VRF), and EVIs are assigned import/export Route Targets (RTs) |
|
NVE |
Network Virtual Interface |
Logical interface where the encapsulation and de-encapsulation occur |
|
VNI |
VXLAN network identifier |
Uniquely identifies each Layer 2 subnet or segment. There are two types of VNI: Symmetric (L2VNI): VTEPs have same VNI Asymmetric (L3VNI): VTEPs do not have same VNI and are routed via a single common VNI. |
|
BUM |
Broadcast, Unknown Unicast, Multicast |
BUM traffic is sent via the Mcast group tied to the VNI under the NVE configuration. |
|
TRM |
Tenant Routed Multicast |
BGP-EVPN based solution that enables multicast routing between sources and receivers connected on VTEPS in VxLAN fabric [RFC7432]. There are two types L2TRM (Layer 2 TRM) & L3TRM (Layer 3 TRM) |
|
MDT |
Multicast Distribution Tree |
The multicast tree built between VTEPs for encapsulation and tunnelling of Tenant Multicast Traffic. |
|
PVLAN |
Private VLAN |
Partitions the Ethernet broadcast domain of a VLAN into subdomains, which allows you to isolate the ports on the switch from each other. |
|
MIB |
Management Information Base |
A Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) monitor object |
|
PIM-BIDIR |
Protocol Independent Multicast Bi-Directional |
A type of PIM where traffic is only forwarded along a shared tree that is rooted at the rendezvous point (RP) for the group. |
|
VFI |
Virtual Forwarding Instance |
A virtual bridge port that is capable of performing native bridging functions, such as forwarding, based on the destination MAC address, source MAC address learning and aging, and so forth. |
|
IRB |
Integrated Routing and Bridging |
enables a Layer 2 VPN and an Layer 3 VPN overlay that allows end hosts across the overlay to communicate with each other within the same subnet and across different subnets within the VPN. |
|
IMET |
Inclusive Multicast Ethernet Tag |
also called BGP Route Type 3 (RT3), for the auto-discovery of remote peers in order to set up the BUM tunnels over VXLAN. IMET routes carry the remote (egress) VNIs advertised from the remote peers, which can be different from the local VNI. These remote VNIs are called Downstream Assigned VNIs. |
|
DAG |
Distributed Anycast Gateway |
Default gateway function on all VTEPs. The same gateway IP lives on all VTEPs and allows for mobility in the fabric. |
Limitations
- Seamless migration is only supported for Cat9k switches
- Only one NVE interface and global migration is considered
VXLANv6 Underlay is NOT supported for these EVPN functionalities
- Centralized Gateway
- Multi-Homing support
- L3Multicast (TRM)
- L2TRM with Ingress Replication
- L2TRM with Default MDT (Multicast Replication)
- L3TRM with Default MDT
- L3TRM with Data MDT
- Border Gateway (Multi-site)
- Access VFI
- PVLAN
- MIB
- PIM-BIDIR for Multicast Underlay
Seamless Migration Concept Overview
Brownfield EVPN VXLAN deployments require gradual migration of network from VXLANv4 to VXLANv6 underlay. To achieve this EVPN VXLAN networks need to migrate incrementally from IPv4 to IPv6 Underlays and allow part of EVPN Networks migrated to IPv6 underlay and other parts of network continue to work with IPv4 underlay but still all nodes in the network be connected.
To achieve this seamless migration for Unicast and BUM (Broadcast, Unknown-unicast and Multicast) Ingress Replication, EVPN nodes need to support Dual-stack VTEP. A Dual-Stack VTEP node has two VTEP address (IPv4 and IPv6) associated with same VNI (VXLAN Network Identifier). During underlay migration and both these VTEP IP addresses are advertised to peers in a single BGP EVPN update (BGP EVPN Dual-Next-hop update) and give option for receiving nodes to choose either of the underlay for traffic forwarding.
BGP EVPN Dual-Next-hop Update Advertisement
The BGP Dual Next-Hop Update carries two next hops:
- Primary next hop (Existing Underlay) in MP_REACH_NLRI (EVPN Routetype-2/Routetype-5)/PMSI-tunnel (EVPN Routetype-3) attribute
- Secondary next hop (Migrating Underlay) in a BGP Tunnel Encapsulation Attribute (23)
The VTEP IP carried as Primary and Secondary depends on the migration mode of the EVPN node.
This table details the Primary/Secondary VTEP IPs carried in Dual-Nexthop updates
|
Migration Mode |
Primary Nexthop |
Secondary Nexthop |
|
VXLANv4 to VXLANv6 |
IPv4 VTEP |
IPv6 VTEP |
|
VXLANv6 to VXLANv4 |
IPv6 VTEP |
IPv4 VTEP |
BGP Leaf/Edge EVPN Dual Next-hop Update Processing
The Leaf/Edge/Border node receiving this BGP EVPN Dual-Next-hop update uses one of the received nexthops as remote VTEP for forwarding. The nexthop used for underlay depends upon these migration polices configured on the device.
- Local VTEP Addresses
- Local Underlay Preference
This table details how the local configured policies decide which Underlay is used to forward packets
|
Received BGP Update |
Local VTEP Address |
Local Underlay Preference |
VXLAN Underlay for Unicast/BUM-IR |
|
Dual-Next-hop (IPv4 + IPv6) |
IPv4 VTEP only |
N/A |
VXLANv4 |
|
Dual-Next-hop (IPv4 + IPv6) |
IPv6 VTEP only |
N/A |
VXLANv6 |
|
Dual-Next-hop (IPv4 + IPv6) |
Dual Stack (IPv4 + IPv6 VTEP IP) |
IPv4 |
VXLANv4 |
|
Dual-Next-hop (IPv4 + IPv6) |
Dual Stack (IPv4 + IPv6 VTEP IP) |
IPv6 |
VXLANv6 |
|
Single IPv4 Next-hop |
IPV4 VTEP only |
N/A |
VXLANv4 |
|
Single IPv4 Next-hop |
IPV6 VTEP only |
N/A |
NO VXLAN Underlay |
|
Single IPv4 Next-hop |
Dual Stack (IPv4 + IPv6 VTEP IP) |
N/A |
VXLANv4 |
|
Single IPv6 Next-hop |
IPV4 VTEP only |
N/A |
NO VXLAN Underlay |
|
Single IPv6 Next-hop |
IPV6 VTEP only |
N/A |
VXLANv6 |
|
Single IPv6 Next-hop |
Dual Stack (IPv4 + IPv6 VTEP IP) |
N/A |
VXLANv6 |
Configure (VXLAN Underlay Migration Modes)
New cli commands under “interface nve” configuration are available to set the VXLAN underlay migration mode, and underlay preference for unicast and multicast.
Migration Mode CLI for Unicast and BUM-Ingress Replication
interface nve 1
vxlan encapsulation ?
dual-stack Encapsulation type dual-stack
ipv4 Encapsulation type IPv4
ipv6 Encapsulation type IPv6
vxlan encapsulation dual-stack ?
prefer-ipv4 Dual-stack underlay with ipv4 preference
prefer-ipv6 Dual-stack underlay with ipv6 preference
This table details the CLI configurations for Unicast and BUM-IR Migration modes
|
CLI Configuration |
Local VTEP IP and Unicast/BUM-IR Underlay |
|
int nve 1 vxlan encapsulation ipv4 (this is optional as default vxlan encapsulation is ipv4) |
IPv4 (VXLANv4 underlay) |
|
int nve 1 vxlan encapsulation ipv6 |
IPv6 (VXLANv6 underlay) |
|
int nve 1 vxlan encapsulation dual-stack prefer-ipv4 |
Dual-Stack (IPv4 + IPv6) (Prefer VXLANv4 Underlay) |
|
int nve 1 vxlan encapsulation dual-stack prefer-ipv6 |
Dual-Stack (IPv4 + IPv6) (Prefer VXLANv6 underlay) |
Migration Mode CLI for Static Multicast Replication
interface nve 1
vxlan encapsulation ?
dual-stack Encapsulation type dual-stack
ipv4 Encapsulation type IPv4
ipv6 Encapsulation type IPv6
vxlan encapsulation dual-stack ?
prefer-ipv4 Dual-stack underlay with ipv4 preference
prefer-ipv6 Dual-stack underlay with ipv6 preference
vxlan encapsulation dual-stack prefer-ipv4 underlay-mcast ?
ipv4 Select IPv4 multicast underlay
ipv6 Select IPv6 multicast underlay
vxlan encapsulation dual-stack prefer-ipv6 underlay-mcast ?
ipv4 Select IPv4 multicast underlay
ipv6 Select IPv6 multicast underlay
|
CLI configuration |
Static Multicast Underlay |
|
int nve 1 member vni <L2VNI> mcast-group <v4-mcast-group> vxlan encapsulation ipv4 (this is optional as default vxlan encapsulation is ipv4) |
Send and Receive multicast traffic on configured IPv4 underlay multicast groups for L2VNI
|
|
int nve 1 member vni <L2VNI> mcast-group <v6-mcast-group> vxlan encapsulation ipv6 |
Send and Receive multicast traffic on configured IPv6 underlay multicast groups for L2VNI |
|
int nve 1 member vni <L2VNI> mcast-group <v4-mcast-group> <v6-mcast-group> vxlan encapsulation dual-stack prefer-ipv6 |
Dual-Stack (IPv4 +IPv6) Receive Multicast traffic on both configured IPv4 and IPv6 underlay multicast groups for L2VNI Send Multicast traffic only on configured IPv4 underlay multicast groups for L2VNI |
|
int nve 1 member vni <L2VNI> mcast-group <v4-mcast-group> <v6-mcast-group> vxlan encapsulation dual-stack prefer-ipv4 |
Dual-Stack (IPv4 +IPv6) Receive Multicast traffic on both configured IPv4 and IPv6 underlay multicast groups for L2VNI Send Multicast traffic only on configured IPv6 underlay multicast groups for L2VNI |
|
int nve 1 member vni <L2VNI> mcast-group <v4-mcast-group> <v6-mcast-group> vxlan encapsulation dual-stack prefer-ipv6 underlay-mcast ipv4 |
Dual-Stack (IPv4 +IPv6) Receive Multicast traffic on both configured IPv4 and IPv6 underlay multicast groups for L2VNI Send Multicast traffic only on configured IPv4 underlay multicast groups for L2VNI |
|
int nve 1 member vni <L2VNI> mcast-group <v4-mcast-group> <v6-mcast-group> vxlan encapsulation dual-stack prefer-ipv4 underlay-mcast ipv6 |
Dual-Stack (IPv4 +IPv6) Receive Multicast traffic on both configured IPv4 and IPv6 underlay multicast groups for L2VNI Send Multicast traffic only on configured IPv6 underlay multicast groups for L2VNI |
|
int nve 1 member vni <L2VNI> mcast-group <v4-mcast-group> <v6-mcast-group> vxlan encapsulation dual-stack prefer-ipv6 underlay-mcast ipv6 |
Dual-Stack (IPv4 +IPv6) Receive Multicast traffic on both configured IPv4 and IPv6 underlay multicast groups for L2VNI Send Multicast traffic only on configured IPv6 underlay multicast groups for L2VNI |
|
int nve 1 member vni <L2VNI> mcast-group <v4-mcast-group> <v6-mcast-group> vxlan encapsulation dual-stack prefer-ipv4 underlay-mcast ipv4 |
Dual-Stack (IPv4 +IPv6) Receive Multicast traffic on both configured IPv4 and IPv6 underlay multicast groups for L2VNI Send Multicast traffic only on configured IPv4 underlay multicast groups for L2VNI |
Underlay Migration Procedures
Underlay Migration steps are same for both EVPN L2Gateway and EVPN IRB (Distributed Anycast Gateway) deployments
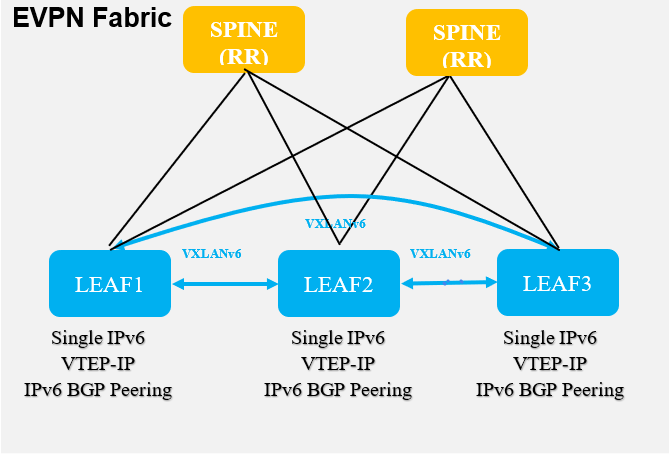
VXLANv4 to VXLANv6 Migration
The VXLANv6 deployment has a single IPv6 transport in the underlay. The VXLAN Tunnels and BGP neighborship are both IPv6 based.
Network Diagram
Unicast VxLANv4 to VxLANv6 Migration
This table details sample configuration changes required for VxLANv4 to VXLANv6 underlay migration for Unicast traffic.
|
Migration step |
VXLANv4 Underlay |
VXLANv6 underlay |
Description |
|
EVPN Router-ID Configuration |
|||
|
1 |
l2vpn router-id 10.1.1.1 |
Configure l2vpn router-id to be used as EVPN router-id |
|
|
VXLAN VTEP IP Configuration |
|||
|
2 |
interface Loopback1 ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 interface nve1 source-interface Loopback1 |
interface Loopback1 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:2::2/128 interface nve1 source-interface Loopback1 |
Loopback interface associated with VXLAN configured with IPv6 address. This IPV6 address is used local IPv6 VTEP for VXLAN. |
|
3 |
interface Loopback1 ip ospf 1 area 0 interface nve1 source-interface Loopback1 |
interface Loopback1 ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 interface nve1 source-interface Loopback1 |
IGP like OSPF is enabled for IPv6 addresses of the interface |
|
Underlay Migration Mode Configuration |
|||
|
4 |
interface nve1 vxlan encapsulation ipv6 |
VXLAN NVE interface must be configured with “vxlan encapsulation ipv6” configuration VXLANv6 underlay |
|
|
Unicast Routing Configuration |
|||
|
5 |
ipv6 unicast-routing |
Enables IPv6 routing |
|
|
IGP Configuration |
|||
|
6 |
router ospf 1 |
ipv6 router ospf 1 router-id 10.1.1.1 |
Enables OSPF for IPv6 |
|
BGP Configuration |
|||
|
7 |
router bgp 100 bgp router-id 10.2.2.1 |
Configure BGP router id |
|
|
8 |
router bgp 100 neighbor 10.99.99.99 remote-as 100 neighbor 10.99.99.99 update-source Loopback0 ! address-family l2vpn evpn neighbor 10.99.99.99 activate neighbor 10.99.99.99 send-community both exit-address-family ! exit-address-family |
router bgp 100 neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 remote-as 100 neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 update-source Loopback0 ! address-family l2vpn evpn neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 activate neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 send-community both exit-address-family |
BGP EVPN Peering moved to IPv6 neighbor address |
BUM Ingress Replication VxLANv4 to VxLANv6 Migration
This table details sample configuration changes required for VxLANv4 to VXLANv6 underlay migration for BUM-IR
|
Migration Step |
VXLANv4 Underlay |
VXLANv6 Underlay |
Description |
|
EVPN Router-ID Configuration |
|||
|
1 |
l2vpn router-id 10.1.1.1 |
Configure l2vpn router-id to used as EVPN router-id |
|
|
VXLAN VTEP IP Configuration |
|||
|
2 |
interface Loopback1 ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 interface nve1 source-interface Loopback1 |
interface Loopback1 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:2::2/128 interface nve1 source-interface Loopback1 |
Loopback interface associated with VXLAN configured with IPv6 address. This IPV6 address is used local IPv6 VTEP for VXLAN |
|
3 |
interface Loopback1 ip ospf 1 area 0 interface nve1 source-interface Loopback1 |
interface Loopback1 ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 interface nve1 source-interface Loopback1 |
IGP like OSPF is enabled for IPv6 addresses of the interface |
|
Underlay Migration Mode Configuration |
|||
|
4 |
interface nve1 vxlan encapsulation ipv6 |
VXLAN NVE interface must be configured with “vxlan encapsulation ipv6” configuration VXLANv6 underlay |
|
|
Unicast Routing Configuration |
|||
|
5 |
ipv6 unicast-routing |
Enables IPv6 routing |
|
|
IGP Configuration |
|||
|
6 |
router ospf 1 |
ipv6 router ospf 1 router-id 10.1.1.1 |
Enables OSPF for IPv6 |
|
BGP Configuration |
|||
|
7 |
router bgp 100 bgp router-id 10.2.2.1 |
Configure BGP router id |
|
|
8 |
router bgp 100 neighbor 10.9.9.9 remote-as 100 neighbor 10.9.9.9 update-source Loopback0 ! address-family l2vpn evpn neighbor 10.9.9.9 activate neighbor 10.9.9.9 send-community both exit-address-family ! exit-address-family |
router bgp 100 neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 remote-as 100 neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 update-source Loopback0 ! address-family l2vpn evpn neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 activate neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 send-community both exit-address-family |
BGP EVPN Peering moved to IPv6 neighbor address
|
Static Multicast Replication VxLANv4 to VxLANv6 Migration
This table details sample configuration changes required for VxLANv4 to VXLANv6 underlay migration for Static Multicast Replication
|
Migration Step |
VXLANv4 Underlay |
VXLANv6 Underlay |
Description |
|
Static Multicast Replication Configuration |
|||
|
1 |
interface nve1 member vni 20011 mcast-group 226.1.1.1 |
interface nve1 member vni 20011 mcast- group FF05::1 |
Configure the static IPv6 replication multicast address |
|
Underlay Migration Mode Configuration |
|||
|
2 |
interface nve1 vxlan encapsulation ipv6 |
VXLAN NVE interface must be configured with “vxlan encapsulation ipv6” configuration VXLANv6 underlay |
|
|
Unicast Routing Configuration |
|||
|
3 |
ipv6 unicast-routing |
Enables IPv6 routing |
|
|
Multicast Routing configuration |
|||
|
4 |
ip multicast-routing |
ipv6 multicast-routing |
Enables IPv6 multicast routing |
|
5 |
ip pim rp-address 10.9.9.9 |
ipv6 pim rp-address 2001:DB8::99:99 |
Migrate PIM RP address to IPv6 |
Brownfield – VXLANv4 and VXLANv6 Seamless Migration
Brownfield deployments have a transitive dual IPv4/IPv6 transport in the underlay for seamless migration. The VXLAN Tunnels and BGP neighborship are initially IPv4 based and are migrated to IPv6 based seamlessly (the IPv4 can be optionally removed from the underlay after the migration). In other words, individual VTEPs are able to be migrated to dual IPv4 and IPv6 while others continue to operate with IPv4. Once all the VTEPs inside the Fabric are dual IPv4 and IPv6 capable, individual VTEPs can now migrate to IPv6.
Network Diagram
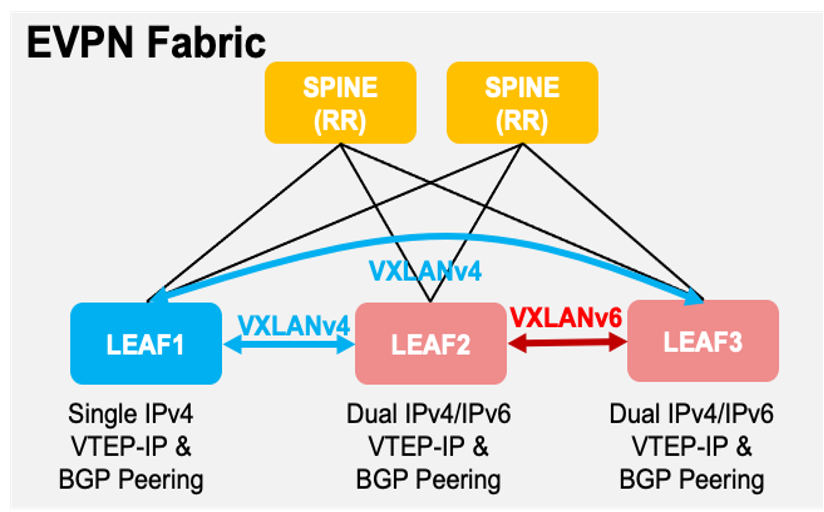
Brownfield Unicast VxLANv4 to Dual-Stack Migration
This table details sample configuration changes required for Brownfield VxLANv4 to Dual-Stack underlay migration for Unicast traffic
|
Migration Step |
VXLANv4 Underlay |
Dual-Stack (Prefer VxLANv6 Underlay) |
Description |
|
L2VPN Router-ID Configuration |
|||
|
1 |
l2vpn router-id 10.2.2.3 |
Configure l2vpn router-id to used as EVPN router-id |
|
|
VXLAN VTEP IP Configuration |
|||
|
2 |
interface Loopback1 ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 interface nve1 source-interface Loopback1 |
interface Loopback1 ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:2::2/128 interface nve1 source-interface Loopback1 |
Loopback interface associated with VXLAN configured with IPv4 and IPv4 addresses. |
|
3 |
interface Loopback1 ip ospf 1 area 0 interface nve1 source-interface Loopback1 |
interface Loopback1 ip ospf 1 area 0 ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 interface nve1 source-interface Loopback1 |
IGP like OSPF is enabled for IPv4 and IPv6 addresses of the interface |
|
Underlay Migration Mode Configuration |
|||
|
4 |
interface nve1 vxlan encapsulation dual-stack prefer-ipv6 |
VXLAN NVE interface must be configured with “vxlan encapsulation dual-stack prefer-ipv6” for dual-stack but prefer VXLANv6 underlay |
|
|
Unicast Routing Configuration |
|||
|
6 |
ipv6 unicast-routing |
Enables IPv6 routing |
|
|
IGP Configuration |
|||
|
7 |
router ospf 1 |
router ospf 1 ! ipv6 router ospf 1 router-id 10.1.1.1 |
Enable OSPF for IPv4 and IPv6 |
|
BGP Configuration |
|||
|
8 |
router bgp 100 bgp router-id 10.2.2.1 |
Configure BGP router id |
|
|
9 |
router bgp 100 neighbor 10.9.9.9 remote-as 100 neighbor 10.9.9.9 update-source Loopback0 ! address-family l2vpn evpn neighbor 10.9.9.9 activate neighbor 10.9.9.9 send-community both exit-address-family ! exit-address-family |
router bgp 100 neighbor 10.9.9.9 remote-as 100 neighbor 10.9.9.9 update-source Loopback0 neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 remote-as 100 neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 update-source Loopback0 ! address-family l2vpn evpn neighbor 10.9.9.9 activate neighbor 10.9.9.9 send-community both neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 activate neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 send-community both exit-address-family |
BGP EVPN Peering with both IPv4 and IPv6 neighbor addresses |
Brownfield BUM Ingress Replication VxLANv4 to Dual-Stack Migration
This table details sample configuration changes required for Brownfield VxLANv4 to Dual-Stack underlay migration for BUM-IR
|
Migration Step |
VXLANv4 Underlay |
Dual-Stack (Prefer VxLANv6 Underlay) |
Description |
|
L2VPN Router-ID Configuration |
|||
|
1 |
l2vpn router-id 10.2.2.3 |
Configure l2vpn router-id to used as EVPN router-id |
|
|
VXLAN VTEP IP Configuration |
|||
|
2 |
interface Loopback1 ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 interface nve1 source-interface Loopback1 |
interface Loopback1 ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:2::2/128 interface nve1 source-interface Loopback1 |
Loopback interface associated with VXLAN configured with both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses. |
|
3 |
interface Loopback1 ip ospf 1 area 0 interface nve1 source-interface Loopback1 |
interface Loopback1 ip ospf 1 area 0 ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 interface nve1 source-interface Loopback1 |
IGP like OSPF is enabled for both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses of the interface |
|
Underlay Migration Mode Configuration |
|||
|
4 |
interface nve1 vxlan encapsulation dual-stack prefer-ipv6 |
VXLAN NVE interface must be configured with “vxlan encapsulation dual-stack prefer-ipv6” for dual-stack but prefer VXLANV6 underlay |
|
|
Unicast Routing Configuration |
|||
|
5 |
ipv6 unicast-routing |
Enables IPv6 routing |
|
|
IGP Configuration |
|||
|
6 |
router ospf 1 |
router ospf 1 ipv6 router ospf 1 router-id 10.1.1.1 |
Enable OSPF for both IPv4 and IPv6 |
|
BGP Configuration |
|||
|
7 |
router bgp 100 bgp router-id 10.2.2.1 |
Configure BGP router id |
|
|
8 |
router bgp 100 neighbor 10.9.9.9 remote-as 100 neighbor 10.9.9.9 update-source Loopback0 ! address-family l2vpn evpn neighbor 10.9.9.9 activate neighbor 10.9.9.9 send-community both exit-address-family ! exit-address-family |
router bgp 100 neighbor 10.9.9.9 remote-as 100 neighbor 10.9.9.9 update-source Loopback0 neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 remote-as 100 neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 update-source Loopback0 ! address-family l2vpn evpn neighbor 10.9.9.9 activate neighbor 10.9.9.9 send-community both neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 activate neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 send-community both exit-address-family |
BGP EVPN Peering with both IPv4 and IPv6 neighbor addresses |
Brownfield Static Multicast Replication VxLANv4 to Dual-Stack Migration
This table details sample configuration changes required for Brownfield VxLANv4 to Dual-Stack underlay migration for Static Multicast Replication
|
Migration Step |
VXLANv4 Underlay |
Dual-Stack (VxLANv4 Multicast Underlay) |
Description |
|
Static Multicast Replication Configuration |
|||
|
1 |
interface nve1 member vni 20011 mcast-group 226.1.1.1 |
interface nve1 member vni 20011 mcast-group 226.1.1.1 FF05::1 |
Configure both static IPv4 and static IPv6 replication multicast address |
|
Underlay Migration Mode Configuration |
|||
|
2 |
interface nve1 vxlan encapsulation dual-stack prefer-ipv6 underlay-mcast ipv4 |
VXLAN NVE interface must be configured with “vxlan encapsulation dual-stack prefer-ipv6 underlay-mcast ipv4” |
|
|
Unicast Routing Configuration |
|||
|
3 |
ipv6 unicast-routing |
Enables IPv6 routing |
|
|
IPv6 Multicast Routing configuration |
|||
|
4 |
ip multicast-routing |
ip multicast-routing ! ipv6 multicast-routing |
Enables both IPV4 and IPv6 multicast routing |
|
5 |
ip pim rp-address 10.9.9.9 |
ip pim rp-address 10.9.9.9 ! ipv6 pim rp-address2001:DB8::99:99 |
Configure both IPV4 and IPv6 PIM RP |
Brownfield Dual-Stack to VXLANv6 Seamless Migration
The network can be migrated to VXLANv6 only underlay after all the network is migrated to dual stack. This configuration needs to be done on the devices to achieve this.
Unicast Dual-Stack to VXLANv6 migration
This table details sample configuration changes required for Brownfield Dual-Stack to VxLANv6 only underlay migration for Unicast traffic
|
Migration Step |
Dual-Stack (Prefer VxLANv6 Underlay) |
VXLANv6 Underlay |
Description |
|
VXLAN VTEP IP Configuration |
|||
|
1 |
interface Loopback1 ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:2::2/128 interface nve1 source-interface Loopback1 |
interface Loopback1 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:2::2/128 interface nve1 source-interface Loopback1 |
Loopback interface associated with VXLAN configured with IPv6 address only
|
|
2 |
interface Loopback1 ip ospf 1 area 0 ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 interface nve1 source-interface Loopback1 |
interface Loopback1 ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 interface nve1 source-interface Loopback1 |
IGP like OSPF is enabled only for IPv6 address of the interface |
|
Underlay Migration Mode Configuration |
|||
|
3 |
interface nve1 vxlan encapsulation dual-stack prefer-ipv6 |
interface nve1 vxlan encapsulation pv6 |
VXLAN NVE interface must be configured with “vxlan encapsulation ipv6” for VXLANv6 underlay |
|
IGP Configuration |
|||
|
4 |
router ospf 1 ! ipv6 router ospf 1 router-id 10.1.1.1 |
ipv6 router ospf 1 router-id 10.1.1.1 |
Enable OSPF for and IPv6 only |
|
BGP Configuration |
|||
|
5 |
router bgp 100 neighbor 10.9.9.9 remote-as 100 neighbor 10.9.9.9 update-source Loopback0 neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 remote-as 100 neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 update-source Loopback0 ! address-family l2vpn evpn neighbor 10.9.9.9 activate neighbor 10.9.9.9 send-community both neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 activate neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 send-community both exit-address-family |
router bgp 100 neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 remote-as 100 neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 update-source Loopback0 ! address-family l2vpn evpn neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 activate neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 send-community both exit-address-family |
BGP EVPN Peering with IPv6 neighbor addresses only |
BUM-Ingress Replication Dual-Stack to VXLANv6 Migration
This table details sample configuration changes required for Brownfield Dual-Stack to VxLANv6 only underlay migration for BUM-IR
|
Migration Step |
Dual-Stack (Prefer VxLANv6 Underlay) |
VXLANv6 Underlay |
Description |
|
1 |
interface Loopback1 ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:2::2/128 interface nve1 source-interface Loopback1 |
interface Loopback1 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:2::2/128 interface nve1 source-interface Loopback1 |
Loopback interface associated with VXLAN configured with IPv6 address only |
|
2 |
interface Loopback1 ip ospf 1 area 0 ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 interface nve1 source-interface Loopback1 |
interface Loopback1 ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 interface nve1 source-interface Loopback1 |
IGP like OSPF is enabled only for IPv6 address of the interface |
|
Underlay Migration Mode Configuration |
|||
|
3 |
interface nve1 vxlan encapsulation dual-stack prefer-ipv6 |
interface nve1 vxlan encapsulation pv6 |
VXLAN NVE interface must be configured with “vxlan encapsulation ipv6” for VXLANv6 underlay |
|
IGP Configuration |
|||
|
4 |
router ospf 1 ! ipv6 router ospf 1 router-id 10.1.1.1 |
ipv6 router ospf 1 router-id 10.1.1.1 |
Enable OSPF for IPv6 only |
|
BGP Configuration |
|||
|
5 |
router bgp 100 neighbor 10.9.9.9 remote-as 100 neighbor 10.9.9.9 update-source Loopback0 neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 remote-as 100 neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 update-source Loopback0 ! address-family l2vpn evpn neighbor 10.9.9.9 activate neighbor 10.9.9.9 send-community both neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 activate neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 send-community both exit-address-family |
router bgp 100 neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 remote-as 100 neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 update-source Loopback0 ! address-family l2vpn evpn neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 activate neighbor 2001:DB8:99::99 send-community both exit-address-family |
BGP EVPN Peering with IPv6 neighbor addresses only |
Static Multicast Replication Dual-Stack to VXLANv6 Migration
This table details sample configuration changes required for Brownfield Dual-Stack with multicast IPv4 Underlay to Brownfield Dual-Stack with multicast IPv6 Underlay for Static Multicast Replication
|
Migration Step |
Dual-Stack (Multicast VxLANv4 Underlay) |
Dual-Stack (Multicast VxLANv6 Underlay) |
Description |
|
Underlay Migration Mode Configuration |
|||
|
1 |
interface nve1 vxlan encapsulation dual-stack prefer-ipv6 underlay-mcast ipv4 |
interface nve1 vxlan encapsulation dual-stack prefer-ipv6 underlay-mcast ipv6 |
VXLAN NVE interface must be configured with “vxlan encapsulation dual-stack prefer-ipv6 underlay-mcast ipv6” to still receive multicast traffic on both V4 and V6 but only send on V6 underlay |
Static Multicast Replication Dual-Stack IPv6 Multicast to IPv6 Multicast Underlay Migration
This table details sample configuration changes required for Brownfield Dual-Stack with multicast IPv6 Underlay to VXLANv6 only Underlay for Static Multicast Replication
|
Migration Step |
Dual-Stack (with multicast VxLANv6 Underlay) |
VXLANv6 Underlay |
Description |
|
Static Multicast Replication Configuration |
|||
|
1 |
interface nve1 member vni 20011 mcast-group 226.1.1.1 FF05::1 |
interface nve1 member vni 20011 mcast- group FF05::1 |
Only static IPv6 replication multicast address is configured |
|
Underlay Migration Mode Configuration |
|||
|
2 |
interface nve1 vxlan encapsulation dual-stack prefer-ipv6 underlay-mcast ipv4 |
interface nve1 vxlan encapsulation ipv6 |
VXLAN NVE interface must be configured with “vxlan encapsulation ipv6” |
|
IPv6 Multicast Routing configuration |
|||
|
3 |
ip multicast-routing ! ipv6 multicast-routing |
ipv6 multicast-routing |
Only IPv6 multicast routing is enabled |
|
4 |
ip pim rp-address 10.9.9.9 ! ipv6 pim rp-address2001:DB8::99:99 |
ipv6 pim rp-address2001:DB8::99:99 |
Only IPv6 PIM RP is configured |
Spine / Route-Reflector Migration
Route-Reflectors can reflect the Dual-Nexthop updates even without upgrade to 17.9.2 release as the secondary next-hop address is encoded in the optional BGP transitive Tunnel Encapsulation attribute (existing BGP implementations already support receiving and reflecting the transitive Tunnel Encapsulation attribute).
Route-Reflectors/Spines NOT yet migrated to 17.9.2 are able to:
- Reflect the Dual Next-hop updates only if the Primary next-hop is reachable
- Have BGP Neighborship only over IPv4 Peering
Route-Reflectors/Spines migrated to 17.9.2 are able to:
- Reflect the Dual Next-hop updates if either Primary or Secondary next-hop or both are reachable
- Have BGP Neighborship over IPv4 & IPv6 Peering
Spine / Route-Reflector V4 to V6 EVPN Fabric Migration
This table details sample configuration changes required for Spine/RR migration from V4 core to V6 core
|
Migration Step |
V4 EVPN Fabric |
V6 EVPN Fabric |
Description |
|
Unicast Routing Configuration |
|||
|
1 |
ip routing |
ipv6 unicast-routing |
Enables IPv6 routing |
|
BGP Configuration |
|||
|
2 |
router bgp 100 bgp router-id 10.3.3.3 |
Configure BGP router id |
|
|
3 |
router bgp 100 neighbor 10.1.1.1 remote-as 100 neighbor 10.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0 ! address-family l2vpn evpn neighbor 10.1.1.1 activate neighbor 10.1.1.1 send-community both exit-address-family |
router bgp 100 neighbor 2001:DB8:1::1 remote-as 100 neighbor 2001:DB8:1::1 update-source Loopback0 ! address-family l2vpn evpn neighbor 2001:DB8:1::1 activate neighbor 2001:DB8:1::1 send-community both exit-address-family |
BGP EVPN Peering moved to IPv6 neighbor address.
|
Brownfield Spine / Route-Reflector V4 to V4+V6 EVPN Fabric Migration
This table details sample configuration changes required for Spine/RR migration from V4 core to V4+V6 core
|
Migration Step |
V4 EVPN Fabric |
V4+V6 EVPN Fabric |
Description |
|
Unicast Routing Configuration |
|||
|
1 |
ip routing |
ip routing ipv6 unicast-routing |
Enables IPv6 routing |
|
BGP Configuration |
|||
|
2 |
router bgp 100 bgp router-id 10.3.3.3 |
Configure BGP router id |
|
|
3 |
router bgp 100 neighbor 10.1.1.1 remote-as 100 neighbor 10.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0 ! address-family l2vpn evpn neighbor 10.1.1.1 activate neighbor 10.1.1.1 send-community both exit-address-family |
router bgp 100 neighbor 10.1.1.1 remote-as 100 neighbor 10.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0 neighbor 2001:DB8:1::1 remote-as 100 neighbor 2001:DB8:1::1 update-source Loopback0 ! address-family l2vpn evpn neighbor 10.1.1.1 activate neighbor 10.1.1.1 send-community both neighbor 2001:DB8:1::1 activate neighbor 2001:DB8:1::1 send-community both exit-address-family |
BGP EVPN Peering with both IPv6 and IPv6 neighbor address. |
Spine / Route-Reflector V4+V6 to V6 EVPN Fabric Migration
This table details sample configuration changes required for Spine/RR migration from V4+V6 core to V6 core
|
Migration Step |
V4+V6 EVPN Fabric |
V6 EVPN Fabric |
Description |
|
BGP Configuration |
|||
|
1 |
router bgp 100 neighbor 10.1.1.1 remote-as 100 neighbor 10.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0 neighbor 2001:DB8:1::1 remote-as 100 neighbor 2001:DB8:1::1 update-source Loopback0 ! address-family l2vpn evpn neighbor 10.1.1.1 activate neighbor 10.1.1.1 send-community both neighbor 2001:DB8:1::1 activate neighbor 2001:DB8:1::1 send-community both exit-address-family |
router bgp 100 neighbor 2001:DB8:1::1 remote-as 100 neighbor 2001:DB8:1::1 update-source Loopback0 ! address-family l2vpn evpn neighbor 2001:DB8:1::1 activate neighbor 2001:DB8:1::1 send-community both exit-address-family ! |
BGP EVPN Peering with IPv6 neighbor address. |
Verify
These sections detail show commands to verify the basic migration functionality.

Note: Refer to BGP VXLANv6 Migration Troubleshooting guide for detailed verification & troubleshooting procedures. (Coming Soon)
Local VTEP Configuration
Greenfield VXLANv6
#show nve interface nve1 detail
Interface: nve1, State: Admin Up, Oper Up
Encapsulation: Vxlan IPv6
Multicast BUM encapsulation: Vxlan IPv6
BGP host reachability: Enabled, VxLAN dport: 4789
VNI number: L3CP 1 L2CP 6 L2DP 0
source-interface: Loopback1 (primary: 2001:DB8:1::2 vrf: 0)
tunnel interface: Tunnel0
Pkts In Bytes In Pkts Out Bytes Out
0 0 0 0
Dual-Stack (Prefer IPv6)
#show nve interface nve1 detail
Interface: nve1, State: Admin Up, Oper Up
Encapsulation: Vxlan dual stack prefer IPv6
Multicast BUM encapsulation: Vxlan IPv4
BGP host reachability: Enabled, VxLAN dport: 4789
VNI number: L3CP 1 L2CP 6 L2DP 0
source-interface: Loopback1 (primary: 10.1.1.2 2001:DB8:1::2 vrf: 0)
tunnel interface: Tunnel0 Tunnel1
Pkts In Bytes In Pkts Out Bytes Out
0 0 0 0
L3 Functionality
L3 VRF VTEP
#show bgp l2vpn evpn local-vtep vrf red
Local VTEP vrf red:
Protocol: IPv4
RMAC Address: AABB.CC81.F500
VTEP-IP:10.1.1.2
SEC-VTEP-IP:2001:DB8:1::2
VNI: 30000
BDI:Vlan3
Protocol: IPv6
RMAC Address: AABB.CC81.F500
VTEP-IP:10.1.1.2
SEC-VTEP-IP:2001:DB8:1::2
VNI: 30000
BDI:Vlan3
BGP EVPN Route-Type 5 Route
Sourced Route
#show bgp l2vpn evpn route-type 5
BGP routing table entry for [5][100:101][0][24][192.168.11.0]/17, version 127
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table EVPN-BGP-Table)
Advertised to update-groups:
1
Refresh Epoch 1
Local, imported path from base
0.0.0.0 (via vrf red) from 0.0.0.0 (10.1.1.1)
Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 100, weight 32768, valid, external, best
EVPN ESI: 00000000000000000000, Gateway Address: 0.0.0.0, local vtep: 0.0.0.0, VNI Label 30000, MPLS VPN Label 18
Extended Community: RT:100:100 ENCAP:8 Router MAC:AABB.CC81.F500
Tunnel Encapsulation Attribute:
Encap type: 8
Secondary nexthop address 2001:DB8:1::2
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0x0
Updated on Apr 22 2022 09:28:45 PST
Remote Route
#show bgp l2vpn evpn route-type 5
BGP routing table entry for [5][100:102][0][24][192.168.11.0]/17, version 164
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table EVPN-BGP-Table)
Not advertised to any peer
Refresh Epoch 2
Local
10.2.2.2 (metric 21) (via default) from 10.9.9.9 (10.99.99.99) --> Primary Nexthop
Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, best
EVPN ESI: 00000000000000000000, Gateway Address: 0.0.0.0, VNI Label 30000, MPLS VPN Label 0
Extended Community: RT:100:100 ENCAP:8 Router MAC:AABB.CC81.F600
Originator: 10.2.2.1, Cluster list: 10.9.9.9
Tunnel Encapsulation Attribute:
Encap type: 8
Secondary nexthop address 2001:DB8:2::2(active) --> Secondary Nexthop
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0x0
Updated on Apr 22 2022 13:02:02 PST
BGP L3VPN Route
L3 VRF Sourced Route
#show bgp vpnv4 unicast all 192.168.11.0
Local
0.0.0.0 (via vrf red) from 0.0.0.0 (10.1.1.1)
Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 100, weight 32768, valid, sourced, best
Extended Community: RT:100:100
Local vxlan vtep:
vrf:red, vni:30000
local router mac:AABB.CC81.F500
encap:4
vtep-ip:10.2.1.2
sec-vtep-ip:2001:DB8:2::2
bdi:Vlan3
mpls labels in/out 18/nolabel(red)
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0x0
Updated on Apr 21 2022 07:43:07 PST
L3VRF Remote (Imported from EVPN) Route
#sh bgp vpnv4 uni all 192.168.11.0
BGP routing table entry for 100:101:192.168.11.0/24, version 24
Paths: (3 available, best #3, table red)
Not advertised to any peer
Refresh Epoch 2
Local, imported path from [5][100:102][0][24][192.168.11.0]/17 (global)
2001:DB8:2::2 (metric 20) (via default) from 10.9.9.9 (10.99.99.99)
Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal
Extended Community: RT:100:100 ENCAP:8 Router MAC:AABB.CC81.F600
Originator: 10.2.2.1, Cluster list: 10.9.9.9
Tunnel Encapsulation Attribute:
Encap type: 8
Secondary nexthop address 2001:DB8:2::2
Local vxlan vtep:
vrf:red, vni:30000
local router mac:AABB.CC81.F500
encap:4
vtep-ip:10.1.1.2
sec-vtep-ip:2001:DB8:1::2
bdi:Vlan3
Remote VxLAN:
Topoid 0x1(vrf red)
Remote Router MAC:AABB.CC81.F600
Encap 8
Egress VNI 30000
RTEP 2001:DB8:2::2
mpls labels in/out 18/nolabel
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0
Updated on Apr 22 2022 13:02:02 PST
L3RIB IP Route
#show ip route vrf red 192.168.2.0
Routing Table: red
Routing entry for 192.168.2.0/32, 1 known subnets
B 192.168.2.2 [200/0] via 2001:DB8:2::2 (red:ipv6), 01:08:20, Vlan3
#show ipv6 route vrf red2001:DB8:10::/128
Routing entry for2001:DB8:10::/128
Known via "bgp 100", distance 200, metric 0
Tag 10, type internal
Route count is 1/1, share count 0
Routing paths:
2001:DB8:3::2%default, Vlan3%default
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1
MPLS label: nolabel
From 2001:DB8:6363:6363::
opaque_ptr 0x7F6945444B78
Last updated 04:44:10 ago
L3FIB/CEF Route
#show ip cef vrf red 192.168.2.2
192.168.2.2/32
nexthop 2001:DB8:2::2 Vlan3
#show ipv6 cef vrf red2001:DB8:10::/128
2001:10::/128
nexthop 2001:DB8:3::2 Vlan3
VXLANv6 L3 Traffic Forwarding
#show ip cef vrf red 192.168.2.2
192.168.2.2/32
nexthop 2001:DB8:2::2 Vlan3
#show ipv6 cef vrf red2001:DB8:10::/128
2001:10::/128
nexthop 2001:DB8:3::2 Vlan3
#show ip interface Vlan3 stats
Vlan3
5 minutes input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packet/sec,
5 minutes output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packet/sec,
0 packets input, 0 bytes,
0 packets output, 0 bytes.
L2 Functionality
L2 EVI VTEP
#show l2vpn evpn evi 1 detail
EVPN instance: 1 (VLAN Based)
RD: 10.1.1.3:1 (auto)
Import-RTs: 100:1
Export-RTs: 100:1
Per-EVI Label: none
State: Established
Replication Type: Ingress
Encapsulation: vxlan
IP Local Learn: Enabled (global)
Adv. Def. Gateway: Enabled (global)
Re-originate RT5: Disabled
Adv. Multicast: Enabled (global)
Vlan: 11
Protected: False
Ethernet-Tag: 0
State: Established
Flood Suppress: Attached
Core If: Vlan3
Access If: Vlan11
NVE If: nve1
RMAC: aabb.cc81.f500
Core Vlan: 3
L2 VNI: 20011
L3 VNI: 30000
VTEP IP: 10.1.1.2
Sec. VTEP IP: 2001:DB8:1::2
VRF: red
IPv4 IRB: Enabled
IPv6 IRB: Enabled
Pseudoports:
Ethernet0/1 service instance 11
Routes: 1 MAC, 1 MAC/IP
Peers:
10.2.2.2
Routes: 2 MAC, 4 MAC/IP, 1 IMET, 0 EAD
2001:DB8:3::2
Routes: 1 MAC, 3 MAC/IP, 1 IMET, 0 EAD
BGP EVPN Route-Type 2 Routes
Sourced Route
#show bgp l2vpn evpn route-type 2
BGP routing table entry for [2][10.1.1.3:1][0][48][001100110011][32][192.168.11.254]/24, version 132
Paths: (3 available, best #1, table evi_1)
Advertised to update-groups:
1
Refresh Epoch 1
Local
:: (via default) from 0.0.0.0 (10.1.1.1)
Origin incomplete, localpref 100, weight 32768, valid, sourced, local, multipath, best
EVPN ESI: 00000000000000000000, Label1 20011
Extended Community: RT:100:1 RT:100:100 ENCAP:8 EVPN DEF GW:0:0
Router MAC:AABB.CC81.F500
Tunnel Encapsulation Attribute:
Encap type: 8
Secondary nexthop address 2001:DB8:1::2(active)
Local irb vxlan vtep:
vrf:red, l3-vni:30000
local router mac:AABB.CC81.F500
core-irb interface:Vlan3
vtep-ip:10.1.1.2
sec-vtep-ip:2001:DB8:1::2
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0x0
Updated on Apr 22 2022 09:28:34 PST
Refresh Epoch 2
Remote Route
#show bgp l2vpn evpn route-type 2
BGP routing table entry for [2][2.2.2.3:1][0][48][001100110011][32][192.168.11.254]/24, version 140
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table EVPN-BGP-Table)
Flag: 0x100
Not advertised to any peer
Refresh Epoch 2
Local
10.2.2.2 (metric 21) (via default) from 10.9.9.9 (10.99.99.99) <-- Primary Nexthop
Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, best
EVPN ESI: 00000000000000000000, Label1 20011
Extended Community: RT:100:1 RT:100:100 ENCAP:8 EVPN DEF GW:0:0
Router MAC:AABB.CC81.F600
Originator: 10.2.2.1, Cluster list: 10.9.9.9
Tunnel Encapsulation Attribute:
Encap type: 8
Secondary nexthop address 2001:DB8:2::2(active) <-- Secondary Nexthop
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0x0
Updated on Apr 22 2022 13:01:53 PST
L2RIB EVPN MAC Route
#show l2route evpn mac ip
EVI ETag Prod Mac Address Host IP Next Hop(s)
----- ---------- ----- -------------- --------------------------------------- --------------------------------------------------
1 0 BGP 0011.0011.0011 192.168.11.254 V:20011 2001:DB8:2::2
1 0 L2VPN 0011.0011.0011 192.168.11.254 Vl11:0
#show l2route evpn mac ip detail
EVPN Instance: 1
Ethernet Tag: 0
Producer Name: BGP
MAC Address: 0011.0011.0011
Host IP: 192.168.11.254
Sequence Number: 0
Label 2: 0
ESI: 0000.0000.0000.0000.0000
MAC Route Flags: BInt(Brm)Dgr
Next Hop(s): V:20011 2001:DB8:2::2
#show l2route evpn mac mac-address 0011.0011.0011 detail
EVPN Instance: 1
Ethernet Tag: 0
Producer Name: BGP
MAC Address: 0011.0011.0011
Num of MAC IP Route(s): 2
Sequence Number: 0
ESI: 0000.0000.0000.0000.0000
Flags: BInt(Brm)
Num of Default Gateways: 2
Next Hop(s): V:20011 10.1.1.2
L2FIB Unicast Route
#show l2fib bridge-domain 11 detail
Bridge Domain : 11
Reference Count : 12
Replication ports count : 3
Unicast Address table size : 2
IP Multicast Prefix table size : 1
Flood List Information :
Olist: 1035, Ports: 3
Port Information :
BD_PORT Gi1/0/1:11
VXLAN_REP PL:22(1) T:VXLAN_REP [IR]20011:2001:DB8:2::2
VXLAN_REP PL:18(1) T:VXLAN_REP [IR]20011:2001:DB8:3::2
Unicast Address table information :
aabb.0000.0021 VXLAN_UC PL:21(1) T:VXLAN_UC [MAC]20011:2001:DB8:2::2
aabb.0000.0031 VXLAN_UC PL:17(1) T:VXLAN_UC [MAC]20011:2001:DB8:3::2
IP Multicast Prefix table information :
Source: *, Group: 239.21.21.21, IIF: Null, Adjacency: Olist: 6160, Ports: 1
#show l2fib path-list 17 detail
VXLAN_UC Pathlist 17: topo 11, 1 paths, none
ESI: 0000.0000.0000.0000.0000
path 2001:DB8:3::2, type VXLAN, evni 20011, vni 20011, source MAC
oce type: vxlan_header, sw_handle 0x7FA98894B318
forwarding oce 0x7FA988AAE538 type adjacency, IPV6 midchain out of Tunnel0, addr 2001:DB8:3::2, cid: 1
output chain:
oce type: evpn_vxlan_encap, sw_handle 0x7FA988938728
oce type: vxlan_header, sw_handle 0x7FA98894B380
forwarding oce 0x7FA988AAE538 type adjacency, IPV6 midchain out of Tunnel0, addr 2001:DB8:3::2, cid: 1
VXLANv6 L2 Traffic Forwarding
#show interface Tunnel1
Tunnel1 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is Tunnel
MTU 9216 bytes, BW 100 Kbit/sec, DLY 50000 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation TUNNEL, loopback not set
Keepalive not set
Tunnel linestate evaluation up
Tunnel source 2001:DB8:1::2
Tunnel protocol/transport MUDP/IPV6 <-- VXLANv6 tunnel
TEID 0x0, sequencing disabled
Checksumming of packets disabled
source_port:4789, destination_port:0
Tunnel TTL 255
Tunnel transport MTU 9216 bytes
Tunnel transmit bandwidth 8000 (kbps)
Tunnel receive bandwidth 8000 (kbps)
Last input never, output never, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters 02:38:42
Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 8
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue: 0/0 (size/max)
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
0 packets input, 0 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 0 broadcasts (0 IP multicasts)
0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort
0 packets output, 0 bytes, 0 underruns
Output 0 broadcasts (0 IP multicasts)
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 unknown protocol drops
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
Multicast Functionality
BGP EVPN Route-Type 3 routes for BUM-IR
Sourced Route
#show bgp l2vpn evpn route-type 3
BGP routing table entry for [3][10.1.1.3:1][0][32][10.1.1.3]/17, version 116
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table evi_1)
Advertised to update-groups:
1
Refresh Epoch 1
Local
:: (via default) from 0.0.0.0 (10.1.1.1)
Origin incomplete, localpref 100, weight 32768, valid, sourced, local, best
Extended Community: RT:100:1 ENCAP:8 EVPN Mcast Flags:1
Tunnel Encapsulation Attribute:
Encap type: 8
Secondary nexthop address 2001:DB8:1::2(active)
PMSI Attribute: Flags:0x0, Tunnel type:IR, length 4, vni:20011 tunnel identifier: 0000 0000
Local irb vxlan vtep:
vrf:red, l3-vni:30000
local router mac:AABB.CC81.F500
core-irb interface:Vlan3
vtep-ip:10.1.1.2
sec-vtep-ip:2001:DB8:1::2
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0x0
Updated on Apr 22 2022 09:28:34 PST
Remote Route
#show bgp l2vpn evpn route-type 3
BGP routing table entry for [3][10.2.2.3:2][0][32][10.2.2.3]/17, version 151
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table EVPN-BGP-Table)
Flag: 0x100
Not advertised to any peer
Refresh Epoch 2
Local
10.2.2.2 (metric 21) (via default) from 10.9.9.9 (10.99.99.99)
Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, best
Extended Community: RT:100:2 ENCAP:8 EVPN Mcast Flags:1
Originator: 10.2.2.1, Cluster list: 10.9.9.9
Tunnel Encapsulation Attribute:
Encap type: 8
Secondary nexthop address 2001:DB8:2::2(active)
PMSI Attribute: Flags:0x0, Tunnel type:IR, length 4, vni:20012 tunnel identifier: < Tunnel Endpoint: 10.2.2.2 >
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0x0
Updated on Apr 22 2022 13:01:53 PST
L2RIB EVPN IMET route for BUM-IR
#sh l2route evpn imet detail
EVPN Instance: 1
Ethernet Tag: 0
Producer Name: BGP
Router IP Addr: 10.3.3.3
Route Ethernet Tag: 0
Tunnel Flags: 0
Tunnel Type: Ingress Replication
Tunnel Labels: 20011
Tunnel ID: 2001:DB8:3::2
Multicast Proxy: IGMP
Next Hop(s): V:0 2001:DB8:3::2
Static Multicast Replication Route
#show ipv6 mroute ff05::1
Multicast Routing Table
Flags: D - Dense, S - Sparse, B - Bidir Group, s - SSM Group,
C - Connected, L - Local, I - Received Source Specific Host Report,
P - Pruned, R - RP-bit set, F - Register flag, T - SPT-bit set,
J - Join SPT, Y - Joined MDT-data group,
y - Sending to MDT-data group
g - BGP signal originated, G - BGP Signal received,
N - BGP Shared-Tree Prune received, n - BGP C-Mroute suppressed,
q - BGP Src-Active originated, Q - BGP Src-Active received
E - Extranet
Timers: Uptime/Expires
Interface state: Interface, State
On All VTEPS
(*, FF05::1), 00:11:31/never, RP2001:DB8::99:99, flags: SCJ
Incoming interface: TenGigabitEthernet1/1/1
RPF nbr: FE80::822D:BFFF:FE7B:1DC8
Immediate Outgoing interface list:
Tunnel0, Forward, 00:11:31/never
On Sender VTEP
(2000::1:1, FF05::1), 00:10:59/00:00:41, flags: SFJT
Incoming interface: Loopback0
RPF nbr: FE80::822D:BFFF:FE9B:8480
Immediate Outgoing interface list:
TenGigabitEthernet1/1/1, Forward, 00:10:24/00:03:08
Inherited Outgoing interface list:
Tunnel0, Forward, 00:11:31/never
On Receiver VTEP
(2000::2:2, FF05::1), 00:10:34/00:00:49, flags: SJT
Incoming interface: TenGigabitEthernet1/1/1
RPF nbr: FE80::822D:BFFF:FE7B:1DC8
Inherited Outgoing interface list:
Tunnel0, Forward, 00:11:31/never
VXLANv6 Multicast Forwarding
#show ipv6 mfib ff05::1
Entry Flags: C - Directly Connected, S - Signal, IA - Inherit A flag,
ET - Data Rate Exceeds Threshold, K - Keepalive
DDE - Data Driven Event, HW - Hardware Installed
ME - MoFRR ECMP entry, MNE - MoFRR Non-ECMP entry, MP - MFIB
MoFRR Primary, RP - MRIB MoFRR Primary, P - MoFRR Primary
MS - MoFRR Entry in Sync, MC - MoFRR entry in MoFRR Client,
e - Encap helper tunnel flag.
I/O Item Flags: IC - Internal Copy, NP - Not platform switched,
NS - Negate Signalling, SP - Signal Present,
A - Accept, F - Forward, RA - MRIB Accept, RF - MRIB Forward,
MA - MFIB Accept, A2 - Accept backup,
RA2 - MRIB Accept backup, MA2 - MFIB Accept backup
Forwarding Counts: Pkt Count/Pkts per second/Avg Pkt Size/Kbits per second
Other counts: Total/RPF failed/Other drops
I/O Item Counts: HW Pkt Count/FS Pkt Count/PS Pkt Count Egress Rate in pps
Default
On All VTEPS
(*,FF05::1) Flags: C HW
SW Forwarding: 0/0/0/0, Other: 0/0/0
HW Forwarding: 1/0/277/0, Other: 0/0/0
TenGigabitEthernet1/1/1 Flags: A NS
Tunnel0, VXLAN v6 Decap Flags: F NS
Pkts: 0/0/0 Rate: 0 pps
On Sender VTEP
(2000::1:1,FF05::1) Flags: HW
SW Forwarding: 2/0/257/0, Other: 0/0/0
HW Forwarding: 698/1/174/1, Other: 0/0/0
Null0 Flags: A
TenGigabitEthernet1/1/1 Flags: F NS
Pkts: 0/0/0 Rate: 0 pps
On Receiver VTEP
(2000::2:2,FF05::1) Flags: HW
SW Forwarding: 1/0/259/0, Other: 0/0/0
HW Forwarding: 259/1/184/1, Other: 0/0/0
TenGigabitEthernet1/1/1 Flags: A
Tunnel0, VXLAN v6 Decap Flags: F NS
Pkts: 0/0/1 Rate: 0 pps
Sample Configurations
EVPN L2Gateway VXLANv4 Deployment
l2vpn evpn instance 1 vlan-based
encapsulation vxlan
replication-type ingress
!
l2vpn evpn instance 2 vlan-based
encapsulation vxlan
replication-type ingress
!
l2vpn
router-id 10.1.1.3
!
spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
spanning-tree extend system-id
!
vlan configuration 11
member evpn-instance 1 vni 20011
vlan configuration 12
member evpn-instance 2 vni 20012
vlan internal allocation policy ascending
!
vlan 3,11-12
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Loopback1
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.255
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Ethernet1/0
no switchport
ip address 10.0.1.2 255.255.255.252
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface nve1
no ip address
source-interface Loopback1
host-reachability protocol bgp
member vni 20011 ingress-replication
member vni 20012 ingress-replication
!
router ospf 1
redistribute connected
!
router bgp 100
bgp router-id 10.1.1.1
bgp log-neighbor-changes
bgp graceful-restart
neighbor 10.9.9.9 remote-as 100
neighbor 10.9.9.9 update-source Loopback0
!
address-family l2vpn evpn
neighbor 10.9.9.9 activate
neighbor 10.9.9.9 send-community both
exit-address-family
EVPN DAG (Distributed Anycast Gateway) IRB VXLANv4 Deployment
vrf definition red
rd 100:101
!
address-family ipv4
route-target export 100:100
route-target import 100:100
route-target export 100:100 stitching
route-target import 100:100 stitching
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv6
route-target export 100:200
route-target import 100:200
route-target export 100:200 stitching
route-target import 100:200 stitching
exit-address-family
!
l2vpn evpn
default-gateway advertise
!
l2vpn evpn instance 1 vlan-based
encapsulation vxlan
replication-type ingress
!
l2vpn evpn instance 2 vlan-based
encapsulation vxlan
replication-type ingress
!
l2vpn
router-id 10.1.1.3
!
spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
spanning-tree extend system-id
!
vlan configuration 3
member vni 30000
vlan configuration 11
member evpn-instance 1 vni 20011
vlan configuration 12
member evpn-instance 2 vni 20012
vlan internal allocation policy ascending
!
vlan 3,11-12
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Loopback1
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.255
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Loopback192
vrf forwarding red
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.255
ip pim sparse-mode
!
interface Ethernet1/0
no switchport
ip address 10.0.1.2 255.255.255.252
ip pim sparse-mode
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface nve1
no ip address
source-interface Loopback1
host-reachability protocol bgp
member vni 30000 vrf red
member vni 20011 ingress-replication
member vni 20012 ingress-replication
!
router ospf 1
redistribute connected
!
router bgp 100
bgp router-id 10.1.1.1
bgp log-neighbor-changes
bgp graceful-restart
neighbor 10.9.9.9 remote-as 100
neighbor 10.9.9.9 update-source Loopback0
!
address-family l2vpn evpn
neighbor 10.9.9.9 activate
neighbor 10.9.9.9 send-community both
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv4 vrf red
advertise l2vpn evpn
redistribute connected
redistribute static
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv6 vrf red
redistribute connected
advertise l2vpn evpn
exit-address-family
Related Information
- BGP EVPN VXLAN Configuration Guide
- BGP Tunnel Encapsulation Attribute (rfc9012)
- BGP VXLANv6 Migration Troubleshooting guide for detailed verification & troubleshooting procedures. (Coming Soon)
- Technical Support & Documentation - Cisco Systems
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
30-Nov-2022 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback