WiSM Troubleshooting FAQ
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document discusses some of the most frequently asked questions (FAQs) on how to troubleshoot the Wireless Services Module (WiSM).
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Q. What is the Cisco Wireless Services Module (WiSM)?
A. Cisco WiSM is a component of the Cisco Unified Wireless Network. WiSM is the most innovative, unified, scalable wireless solution in the industry. The Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series WiSM provides unparalleled security, mobility, redundancy, and ease of use for business-critical wireless LANs (WLANs). Cisco WiSM works in conjunction with Cisco Aironet® series lightweight access points, the Cisco Wireless Control System (WCS), and the Cisco Wireless Location Appliance to deliver a secure and unified wireless solution that supports mission-critical wireless data, voice, and video applications. The Cisco WiSM occupies one slot in a Catalyst 6500 series switch.
Q. Can I use the WiSM module with a Cisco Integrated Services Router (ISR)?
A. No. Cisco WiSM cannot be installed on Cisco ISRs. They are compatible only with the Cisco Catalyst 6500 series switch and a Cisco Catalyst 6500 Supervisor Engine 720 (all Supervisor Engine 720 versions are supported). .The WiSM is also supported on Cisco 7600 routers that run only Cisco IOS® Software Release 12.2(18)SXF5.
You can install the wireless LAN controller module (WLCM) on the Cisco ISRs. Refer to the Cisco WLAN Controller Network Module Feature Guide for more information on the WLCM.
Q. Which devices are compatible with the Cisco WiSM?
A. The Catalyst chassis on which the Cisco WiSM is installed needs a Supervisor 720 module. This table shows the supported slots for the Cisco WiSM:
Slot 6503-E 6504-E 6506 6509 6513 1-3 X X X X 4 X X X 5-6 X X 7-8 X 9 X X 10-13 X The WiSM is also supported on Cisco 7600 routers that run only Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(18)SXF5.
Q. Where can I find more information on the Cisco WiSM?
A. You can find more information on the Cisco WiSM in the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Wireless Services Module Q&A.
Q. Are mesh access points (APs) compatible with the WiSM cards?
A. Yes, since mesh APs run based on Lightweight Access Point Protocol (LWAPP), these APs are compatible with the WiSM cards. In general, all APs that are LWAPP capable are compatible with the Cisco WiSM card.
Q. Where can I find installation instructions on how to install Cisco WiSM?
A. The Installing the WiSM section of Catalyst 6500 Series Switch Wireless Services Module Installation and Configuration Note explains the step-by-step procedure that needs to be followed to install the Cisco WiSM.
Q. How can I reset the WiSM to factory default settings?
A. Complete these steps to reset the WiSM controller to factory defaults:
- Enter reset system at the WiSM controller CLI.
- At the prompt that asks whether you need to save changes to the configuration, enter Y or N. The unit reboots.
- When you are prompted for a username, enter recover-config to restore the factory default configuration. The Cisco WLAN controller reboots and displays this message:
Welcome to the Cisco WLAN Solution Wizard Configuration Tool- The WiSM is now reset to factory defaults. Use the configuration wizard to enter new configuration settings.
Q. Is it true that one Cisco WiSM module consists of two WLAN controllers?
A. Yes. The Cisco WiSM consists of two Cisco 4404 controllers. The first controller is considered the WiSM-A card, while the second controller is considered the WiSM-B card. Interfaces and IP addressing have to be considered on both cards independently. WiSM-A manages 150 access points, while WiSM-B manages a separate lot of 150 access points. These controllers can be grouped together in a mobility group, forming a cluster.
Q. I have a Cisco 6500 Series WiSM module with a firmware version of 4.0.155.5 configured for one Radio Frequency (RF) group name and to use auto-RF. A controller can see itself in the RF group as RF group leader but cannot see two controllers, what is wrong?
A. Each controller in a WiSM only sees the other group if access points are associated to them. One possible solution is to move one access point to each controller. Once both controllers have access points associated to them then each controller starts to show two controllers.
Q. I am currently creating a WLAN setup that contains two 6500 core switches (Layer 2 separated) and both have one WiSM blade per core. I use one core (WiSM) as the active side and the other WiSM as back-up. I plan to run up to 300 lightweight access points (LAPs) which are used for serving wireless clients. I have two questions: a) Can the AP Manager address be on a different subnet as the management interface or should they be on the same subnet? b) Is there a way to put multiple AP Manager interfaces in different subnets and still have the full roaming capabilities for wireless IP phones (without losing the active call)?
A. a) Both the AP Manager interface and the management interface can be on the same subnet. The important thing is that the management interface and the AP Manager interface have to be reachable from the LAPs. It is usually configured on the same VLAN or IP subnet as the management interface, but this is not a requirement.
b) No, when you have multiple AP Manager interfaces configured to support a maximum number of LAPs, all the AP Manager interfaces have to be on the same subnet. You need Layer 3 connectivity between LAPs and the AP Manager and management interfaces on the Wireless LAN Controller (WLC). The LAPs can still be configured to be on different subnets.
Q. I have two WiSMs to serve 60 lightweight access points (LAPs). I want 30 LAPs to register with WiSM 1 and the other 30 LAPs to join WiSM 2. For some reason this is not happening. All the LAPs register with the same WiSM. Both the WiSMs are in the same subnet. How do I troubleshoot this?
A. When there are multiple controllers that the LAP can reach, the LAP sends Lightweight Access Point Protocol (LWAPP) discovery requests to each of the controller IP addresses. In the Wireless LAN Controller (WLC) LWAPP discovery response, the WLCs embed this information:
Information on the current LAP load, which is defined as the number of LAPs that are joined to the WLC at the time
The LAP capacity
The number of wireless clients that are connected to the WLC
The LAP then attempts to join the least-loaded WLC, which is the WLC with the greatest available LAP capacity. Furthermore, after an LAP joins a WLC, the LAP learns the IP addresses of the other WLCs in the mobility group from its joined WLC. Subsequently, the AP sends LWAPP primary discovery requests to each of the WLCs in the mobility group. The WLCs respond with a primary discovery response to the AP. The primary discovery response includes information about the WLC type, total capacity, and current AP load. As long as the WLC has the AP Fallback parameter enabled, the AP can decide to change over to a less-loaded WLC.
Alternatively, if you want the LAP to connect to a specific WLC, you can configure the primary, secondary and tertiary controller names when the LAP is primed for the first time. This way when the LAP is deployed, the LAP searches for and registers with the WLC which is marked as primary. If the primary WLC is not available, it tries to register to the secondary WLC, and so on.
Q. Is the Link Aggregation (LAG) feature supported with the Cisco WiSM?
A. LAG bundles all of the distribution ports of a controller into a single EtherChannel. This reduces the number of AP Manager Interfaces required for full AP capacity. When LAG is enabled, the system dynamically manages port redundancy and load balances access points transparently to the user.
LAG is enabled automatically on the Cisco WiSM controllers. Without LAG, each distribution system port on the controller supports up to 48 access points. With LAG enabled, the logical port on each Cisco WiSM controller supports up to 150 access points. LAG simplifies the controller configuration because you no longer need to configure primary and secondary ports for each interface. If any of the controller ports fail, traffic is automatically migrated to one of the other ports. As long as one controller port functions, the system continues to operate, access points remain connected to the network, and wireless clients continue to send and receive data.
Q. How do the Cisco WiSM and the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Supervisor communicate with each other?
A. The Cisco WiSM uses the Wireless Control Protocol (WCP) to communicate with the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Supervisor. The WCP is a new UDP-based internal protocol for communication between the Supervisor and Cisco WiSM controllers. WCP is only communicated between the WiSM and Supervisor on the service interface of the controllers, which corresponds to ports 9 and 10 of the WiSM module. WCP runs on UDP/IP, port 10000 on a service interface.
Q. How do I check the status of the WiSM card? What commands can I use to troubleshoot my configuration?
A. These show commands can be used to learn the status of the WiSM module:
show wism status
show wism mod <slot no> controller <no> status
This is example output for the two commands.
Router#show wism status Service Vlan : 192, Service IP Subnet : 192.168.10.1/255.255.255.0 WLAN Slot Controller Service IP Management IP SW Version Status ----+-----------+----------------+----------------+-----------+--------------- 3 1 192.168.10.3 40.1.3.10 3.2.78.0 Oper-Up 3 2 192.168.10.4 40.1.3.15 3.2.78.0 Oper-Up Router#show wism mod 3 controller 1 status WISM Controller 1 in Slot 3 Operational Status of the Controller : Oper-Up Service VLAN : 192 Service Port : 9 Service Port Mac Address : 0011.92ff.8722 Service IP Address : 192.168.10.3 Management IP Address : 40.1.3.10 Software Version : 3.2.78.0 WCP Keep Alive Missed : 0
Q. What debug commands are useful to troubleshoot the configuration?
A. These debug commands are useful to troubleshoot the WiSM configuration.
These debug commands are issued from the router (Sup720) CLI.
Router#debug wism wcp {data/errors/headers}
Router#debug wism events
These debug commands can be issued directly from the WiSM CLI.
WiSM-A#debug wcp {packet/events}
WiSM-A#debug wps
Q. What do the LED patterns on the WiSM card indicate?
A. The LEDs on the WiSM front panel indicate the status of the module.

Q. What are the minimum software requirements to support the Cisco WiSM?
A. This table shows the minimum software required to support the Cisco WiSM:
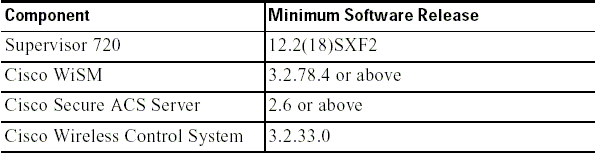
Q. How do I check if the Cisco WiSM module is installed correctly on the Catalyst 6500?
A. You can check if the WiSM module is installed on the Cisco Catalyst 6500 with the show module command.
Here is an example.
cat6506#show module Mod Ports Card Type Model Serial No. --- ----- -------------------------------------- ------------------ ----------- 3 10 Wireless Service Module WS-SVC-WISM-1-K9 SAD092504J8 4 48 48-port 10/100 mb RJ45 WS-X6148-45AF SAL08154UT3 5 2 Supervisor Engine 720 (Active) WS-SUP720-3BXL SAL0913827E <snip> Mod Online Diag Status ---- ------------------- 3 Pass <<Check that this entry has a state of PASS>> 4 Pass 5 Pass
Q. If I have a 6500 WiSM card to manage my access points that run Lightweight Access Point Protocol (LWAPP), what happens if the WiSM has a failure? I lose management capability but do I also lose functionality?
A. The WiSM has two controllers on the blade. This provides two points of management. In the event of a failure, you still have an additional controller to fail-over to.
Q. Is there any way to disable Link Aggregation (LAG) on the WiSM blade? I only have enable (no disable) from the drop-down menu.
A. The WiSM only operates in LAG mode. There is no way to disable it. The controller(s) are able to detect the physical connections and apply LAG accordingly.
Q. I understand that the WiSM card is supported on the Catalyst 6500 with Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(18)SXF2. Where can I find information on the upgrade procedure for the Catalyst 6500 switches?
A. Upgrading Software Images on Catalyst 6000/6500 Series Switches discusses in detail the procedure to upgrade software images on the Cisco Catalyst 6500 series switches.
Q. Where can I find troubleshooting information for the Cisco Catalyst 6500 series switches?
A. Troubleshooting Hardware and Common Issues on Catalyst 6500/6000 Series Switches Running Cisco IOS System Software discusses troubleshooting hardware and related common issues on Catalyst 6500/6000 switches that run Cisco IOS system software.
Q. What are the reasons for the WiSM module to fail to come online after being installed on the Catalyst 6500 switch?
A. The Troubleshoot a Module That Does Not Come On Line or Indicates faulty or other Status section of Troubleshooting Hardware and Common Issues on Catalyst 6500/6000 Series Switches Running Cisco IOS System Software discusses common reasons that one of the modules can fail to come online and how to solve the problem.
Q. When I use Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) between two 6500 chassis for a redundancy protocol and if I have one WiSM installed in each of the two chassis for failover purposes, how long of a convergence time is there for clients to fail to the other WiSM if there is a connectivity or chassis failure for one of the WiSMs?
A. The average Lightweight Access Point Protocol (LWAPP) access point failover process is approximately one minute and depends on the network design. The one minute delay is because the lightweight access point has to run the LWAPP join process in order to join the secondary controller.
Q. I forgot the password for my Cisco WiSM? Is there a password recovery procedure that I can use to reset the WiSM password?
A. You have to reset the WiSM to the default configuration in order to reset the password on the WiSM. Use the same procedure as standalone controllers. You have to have access through the console port, reboot the controller, and break into the bootloader as the system boots up.
The system then gives you five options. Select 5. Clear Configuration first. This is the only option that resets the password, which means you need to reconfigure the rest of the box again. Then, select 1. Run primary image (version 3.2.116.21) (active) to boot up the system again. Here is an example:
Booting Primary Image... Press <ESC> now for additional boot options... ***** External Console Active ***** Boot Options Please choose an option from below: 1. Run primary image (version 3.2.116.21) (active) 2. Run backup image (version 3.1.87.0) 3. Manually update images 4. Change active boot image 5. Clear Configuration Please enter your choice: 5 Please choose an option from below: 1. Run primary image (version 3.2.116.21) (active) 2. Run backup image (version 3.1.87.0) 3. Manually update images 4. Change active boot image 5. Clear Configuration Please enter your choice: 1
Q. I have a few autonomous access points that are converted to Lightweight Access Point Protocol (LWAPP) mode. Can these access points communicate with the WiSM card?
A. Yes, all the LWAPP converted access points can connect to the WiSM card.
Q. Can I use a Firewall Services Module (FWSM) and the WiSM module together in my network?
A. Yes. This configuration is supported. Refer to Integrating Cisco WiSM and Firewall Service Module for information on how to integrate the Cisco WiSM and FWSM.
.
Q. How do I integrate the VPN Services Module (VPNSM) with the Cisco WiSM configuration?
A. The VPNSM was introduced as a high-performance VPN option to further extend the existing VPN portfolio of products from Cisco. The VPNSM is part of the Catalyst 6500 service module family, which comprises the Firewall Services Module (FWSM), Content Switching Module (CSM), Intrusion Detection System Module (IDSM), Network Analysis Module (NAM), and the Secure Socket Layer Module (SSL).
Refer to Integrating Cisco WiSM and VPN Service Module for information on how to integrate the VPNSM with the Cisco WiSM configuration.
Q. The mobility group configured between my WiSM controllers does not function as expected. The access points (APs) registered with the first controller do not failover to the second controller as expected if my primary controller fails. What could be the possible reason and how do I rectify this problem?
A. An incorrect or incomplete mobility group configuration should be the most common reason for your problem. In order to overcome this, you need to ensure that your WiSM mobility group is configured correctly as follows:
The mobility group name configured must be the same on all the controllers that belong to a particular mobility group. This mobility group name is case sensitive.
The mobility group members list configured on each controller needs to contain all the controllers of that particular mobility group.
These configurations ensure that the failover occurs seamlessly and also that when the primary controller comes back on, the previously registered APs fall back to it.
Refer to the Mobility Group configuration document for more information on mobility groups.
Q. Are the Wireless Services Modules (WiSMs) in Catalyst 6500 Switches hot-swappable?
A. Yes, the WiSMs are hot-swappable blades, which means they can be inserted/removed without powering off the switch. The Cisco Catalyst chassis can hold one or more WiSMs, Supervisor Engine 720 modules, redundant power supplies, and cooling resources, in addition to the other integrated services modules. Modules communicate across a fully redundant backplane. This enables hot-swappable capabilities and easy serviceability.
Q. What are the best practices for when you configure the service VLAN in the WiSM?
A. The service VLAN is used to communicate only between the Supervisor Engine and the WiSM.
Refer to Configure Communication Between the Supervisor 720 and Cisco WiSM for more information on the best practices to use when you configure the service VLAN.
In addition, these are some of the best practices to you when you configure the service VLAN in the WiSM:
If VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) is configured on the switch in which the WiSM is installed, filter the service VLAN from the VTP configuration. This is because since the service VLAN is only for communication between the Supervisor Engine and the WiSM module installed in the same switch, you might not want the service VLAN traffic to be forwarded anywhere outside the switch(es) that contain the WiSM blades. If the service VLAN is not filtered from VTP, you actually trunk the service VLAN and hence the traffic is forwarded outside its local switch.
It is recommended that the service VLAN only exist on the chassis that the WiSM is in. If you have multiple WiSM in the same chassis, then these WiSM modules can share the same VLAN. But if they are in different chassis, then each chassis needs its own service VLAN configured.
Q. The "Lost Heartbeat with supervisor" error message is received on the WiSM controller at regular intervals. Why is this error message received? How do I get rid of this message?
A. There are several possible reasons that this error message is generated. From the WiSM's perspective, the most common reason is an incorrect configuration of the service port on the Supervisor Engine.
In the case of a WiSM, the service port is used solely for communication between the Supervisor 720 and the WiSM.
Complete these steps in order to get rid of this error message:
Create a new VLAN for the WiSM service ports on the Supervisor Engine that does not exist anywhere on the network.
Create a DHCP scope setup on your Supervisor 720 to assign IP addresses to the service ports of the controllers.
Note: It is recommended that you create a DHCP scope for the service port of the Catalyst WiSM. Alternatively, you can also session (session slot X process 1 or 2 ) or console directly into the WiSM and set the static IP addresses with the configure interface address service-port command.
Assign the WiSM service ports to this newly created VLAN with the command wism service-vlan new VLAN ID on the Supervisor Engine.
This VLAN is used for the Supervisor Engine to communicate with the service port of the WiSM. Refer to Configure Communication Between the Supervisor 720 and Cisco WiSM for more information on how to configure the procedure mentioned here.
Cisco bug ID CSCsg59144 ( registered customers only) is also associated with this error message.
Other possible reasons might be with the backplane connection of the module to the chassis This can be verified by first moving the WiSM to another slot and see if it continues. Sometimes, this might be an issue with the module itself. But these are rare circumstances.
Q. The WiSM does not send RADIUS accounting records for Hybrid Remote Edge Access Point (H-REAP) clients. The RADIUS accounting statistics do not increment when a wireless client logs onto an H-REAP enabled WLAN. RADIUS accounting does work on a wireless client that connects to a non- H-REAP WLAN (same access point). Why?
A. This might be due to Cisco bug ID CSCsh64994 ( registered customers only) in which RADIUS account records are not generated when an access point is configured as H-REAP with locally switched service-side identifiers (SSIDs). This bug is being resolved and fixed in controller version 4.0.217.0.
Q. The WiSM log shows many messages similar to "Unable to delete username anonymous for mobile xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx" while some wireless clients (especially those authenticated by Extensible Authentication Protocol-Flexible Authentication via Secure Tunneling [EAP-FAST]) fail in their authentication. Why?
A. Authentication methods like EAP-FAST undergo two phases of authentication.
In phase 1, the client and authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) server use Protected Access Credential (PAC) to authenticate each other and establish a mutually authenticated tunnel. This PAC is provisioned and managed dynamically by EAP-FAST through the AAA server. In other words, the first phase of authentication uses generic anonymous external identity in order to establish the tunnel.
In phase 2, client authentication is done in the established tunnel. The client sends the original username and password to authenticate and establish a client authorization policy.
As this authentication method hides the original user name at the first phase of authentication, the controller does not have a way to add the correct username to the authenticated user list. So the controller uses the anonymous username.
The reason you see this error message might be due to Cisco bug ID CSCse53024 ( registered customers only) .
Refer to EAP-FAST for more information about the EAP-FAST authentication type.
Q. Clients do not receive IP addresses from the DHCP server when the AP Group VLAN feature is enabled on the WiSM. The "dhcpd: DHCPDISCOVER from xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx via network x.x.x.x: no free leases" error message is seen on the DHCP server. What can be the reason for this?
A. This might be due to Cisco bug ID CSCse00268 in which wireless clients are unable to receive DHCP assigned IP addresses with AP Group VLANs enabled on WiSMs. According to this bug, the currently available workaround is to actually not use the AP Group feature.
Q. I have configured the WiSM as an internal DHCP server. What is the command to clear DHCP bindings on a WISM, if the WISM acts as the DHCP server?
A. With Wireless LAN Controller version 7.0.98, you can now clear the dhcp leases on the internal dhcp server of the WLC. In order to do this, use this command:
config dhcp clear-lease <all/IP Address>Here is an example.
config dhcp clear-lease all
Q. I plan to upgrade my WiSM to the latest software version. Is there any recommended procedure to upgrade the WiSM?
A. A WiSM upgrade follows the same procedure involved in the upgrade of a 4400 Series Controller. Since a single WiSM module contains two 4400 controllers in it, you need to individually upgrade both WiSM controllers. Also, if you plan to upgrade to version 4 or later, it is recommended to upgrade to the latest version which is version 4.0.217.
Q. What is the default syslog facility on the WiSM? What are the logging options available in the WiSM? Is it possible to configure for facility local5 or local7 syslog messages in the WiSM?
A. The setting on the WiSM for system logging is disabled by default. You can enter show syslog to view the current syslog status. If you enter config syslog, you can then send a log to a remote IP address or hostname. The logging options for the WiSM are totally dependant on which setting you choose. The only logging options you have are:
Message Log Level:
Critical Failure
Software Error
Authentication or Security Errors
Unexpected Software Events
Significant System Events
The Local5 facility on the WiSM is the Significant System Events log level. Local7, which are debugging messages, do not have an option with the WiSM logging facility.
Q. Does the WiSM blade support Hybrid mode on a 6509 or is Native mode the only way to run a WiSM?
A. The WiSM blade is not supported in Hybrid mode and Native mode is the only way to make it work in a 6509 chassis. It requires at least Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(18)SXF2 and later.
Related Information
- Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Wireless Services Module
- Catalyst 6500 Series Switch Wireless Services Module Installation and Configuration Note
- Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Wireless Services Module Q&A
- Configuring a Cisco Wireless Services Module and Wireless Control System
- Wireless Support Page
- Technical Support & Documentation - Cisco Systems
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)


 Feedback
Feedback